Mean shift 算法是一种半自动跟踪方法在起始跟踪帧通过手工确定搜索窗口来选择运动目标计算核函数加权下的搜索窗口的直方图分布用同样的方法计算当前帧对应窗口的直方图分布以两个分布的相似性最大为原则使搜索窗口沿密度增加最大的方向移动目标的真实位置。
加权直方图
传统直方图仅仅统计落入直方图区间的像素的个数,而加权直方图进一步考虑了像素与目标中心的距离,远离目标中心的像素对直方图的贡献较小。
带空间位置信息的加权直方图的思想就是:在计算直方图时,给每个点赋予一定的权值,权值的大小根据它离中心点的远近,可以用高斯核函数或Epanechnikov Kernal来调节。常用的核密度函数有EpanechnikovKernal:
在统计颜色级的分布情况时,对每一个像素,根据它离窗口中心点的距离大小,赋予它一定的权值。当它离中心点越近时,它的权值越大,反之越小。这也增加了对象描述的鲁棒性,因为在有遮挡或复杂背景的影响时,越靠近对象外围的点越不靠。
//t_w和t_h分别为检测窗口的宽度和高度
h = pow(((double)t_w)/2,2) + pow(((double)t_h)/2,2); //带宽
//初始化权值矩阵和目标直方图
for (i = 0;i < t_w*t_h;i++)
{
m_wei[i] = 0.0;
}
for (i=0;i<4096;i++)
{
hist1[i] = 0.0;
}
//生成权值矩阵
for (i = 0;i < t_h; i++)
{
for (j = 0;j < t_w; j++)
{
dist = pow(i - (double)t_h/2,2) + pow(j - (double)t_w/2,2);
m_wei[i * t_w + j] = 1 - dist / h;
C += m_wei[i * t_w + j] ;
}
}
//计算目标权值直方
for (i = t_y;i < t_y + t_h; i++)
{
for (j = t_x;j < t_x + t_w; j++)
{
//rgb颜色空间量化为16*16*16 bins
q_r = ((u_char)current->imageData[i * current->widthStep + j * 3 + 2]) / 16;
q_g = ((u_char)current->imageData[i * current->widthStep + j * 3 + 1]) / 16;
q_b = ((u_char)current->imageData[i * current->widthStep + j * 3 + 0]) / 16;
q_temp = q_r * 256 + q_g * 16 + q_b;
hist1[q_temp] = hist1[q_temp] + m_wei[(i - t_y) * t_w + (j - t_x)] ;
}
}
//归一化直方图
for (i=0;i<4096;i++)
{
hist1[i] = hist1[i] / C;
} 颜色模型相似性度量
初始帧的目标模型
以一定间隔的颜色值为单位将取值为像素颜色值的特征空间分为多个特征值那么在初始帧包含目标的搜索窗口中第u 个特征值的概率为
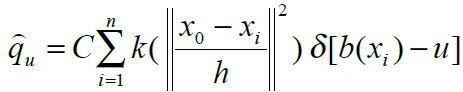
式中x0是搜索窗口(n个像素)的中心像素坐标;xi是第i个像素的坐标;k( ||x||2 ) 是核函数,用来对颜色分布的概率密度进行加权,为什么要加权呢?
采用核函数估计法,在采样充分的情况下,能够渐进地收敛于任意的密度函数,即可以对服从任何分布的数据进行密度估计。
这样可以保证meanshift算法的收敛,才能用meanshift向量进行迭代。h表示核函数的带宽,一般等于窗口宽度的一半;函数b和δ 的作用是判断xi处的颜色值是否属于特征值u ,如果xi属于特征值u,
δ 的值取1,否则δ 的值取0;
C 是一个标准化的常量系数使得所有特征值的概率和为1。
C=1/
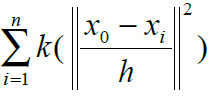
权值的计算是通过核函数k调节的,也正是核函数k的引入,使得直方图匹配能和均值漂移算法结合起来。
当前帧的模型
计算当前帧(第N 帧)中搜索窗口的特征值u 的概率为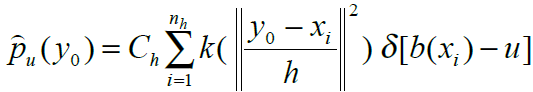
式中y0是当前帧搜索窗口的中心像素坐标,xi是第i个像素的坐标,Ch对应上式中的C。
相似性函数Bhattacharrya 距离
用巴氏系数度量目标直方图和候选直方图的相似性,巴氏系数越大,越相似。
相似性函数描述初始帧目标模型和当前帧模型的相似性度量定义为
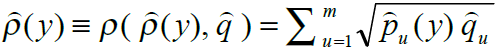

所以为在领域中找到下一帧目标的位置,即是要在下一帧图像中找到一个候选窗口,使得候选直方图于目标直方图相似性最大,即最大化巴氏系数。
在领域内怎样搜索才能用最少的迭代次数使巴氏系数最大化呢?这就要用到meanshift向量。
meanshift向量
为使 最大在当前帧中以前一帧搜索窗口的位置作为当前帧搜索窗口的位置设窗口中心为y0,在y0邻域内寻找局部最优目标位置 y1 对上式在
最大在当前帧中以前一帧搜索窗口的位置作为当前帧搜索窗口的位置设窗口中心为y0,在y0邻域内寻找局部最优目标位置 y1 对上式在 处进行泰勒展开相似性函数可近似为
处进行泰勒展开相似性函数可近似为
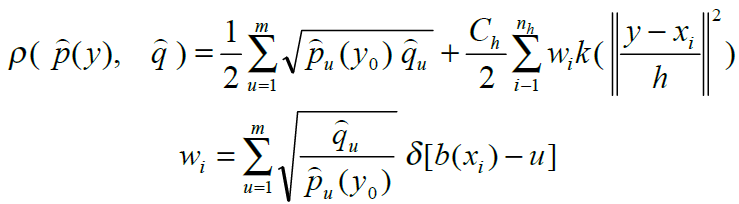
因为p中第一项与y无关,只需最大化第二项。而第二项恰好是用核函数加权的概率密度估计,这样,根据均值漂移理论,就可以用meanshift进行迭代找到概率密度的峰值,即第二项的最大值。
通过对相似性函数求最大值,即对y求偏导并令偏导数为0,可以推导出Mean shift向量
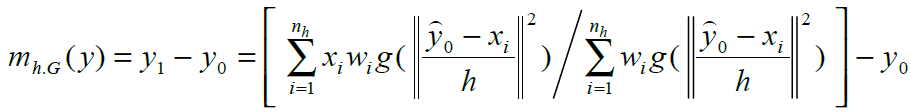
所以

其中g() 是加权函数k() 的导数
令y0 = y1, 用上式进行迭代计算, 直到||y1-y0||小于某一阈值或达到了最大迭代次数。Mean shift算法反复迭代最后得到在当前帧目标的最优位置y。
function [] = select()
close all;
clear all;
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%根据一幅目标全可见的图像圈定跟踪目标%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
I=imread('result72.jpg');
figure(1);
imshow(I);
[temp,rect]=imcrop(I);
[a,b,c]=size(temp); %a:row,b:col
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%计算目标图像的权值矩阵%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
y(1)=a/2;
y(2)=b/2;
tic_x=rect(1)+rect(3)/2;
tic_y=rect(2)+rect(4)/2;
m_wei=zeros(a,b);%权值矩阵
h=y(1)^2+y(2)^2 ;%带宽
for i=1:a
for j=1:b
dist=(i-y(1))^2+(j-y(2))^2;
m_wei(i,j)=1-dist/h; %epanechnikov profile
end
end
C=1/sum(sum(m_wei));%归一化系数
%计算目标权值直方图qu
%hist1=C*wei_hist(temp,m_wei,a,b);%target model
hist1=zeros(1,4096);
for i=1:a
for j=1:b
%rgb颜色空间量化为16*16*16 bins
q_r=fix(double(temp(i,j,1))/16); %fix为趋近0取整函数
q_g=fix(double(temp(i,j,2))/16);
q_b=fix(double(temp(i,j,3))/16);
q_temp=q_r*256+q_g*16+q_b; %设置每个像素点红色、绿色、蓝色分量所占比重
hist1(q_temp+1)= hist1(q_temp+1)+m_wei(i,j); %计算直方图统计中每个像素点占的权重
end
end
hist1=hist1*C;
rect(3)=ceil(rect(3));
rect(4)=ceil(rect(4));
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%读取序列图像
myfile=dir('D:\matlab7\work\mean shift\image\*.jpg');
lengthfile=length(myfile);
for l=1:lengthfile
Im=imread(myfile(l).name);
num=0;
Y=[2,2];
%%%%%%%mean shift迭代
while((Y(1)^2+Y(2)^2>0.5)&num<20) %迭代条件
num=num+1;
temp1=imcrop(Im,rect);
%计算侯选区域直方图
%hist2=C*wei_hist(temp1,m_wei,a,b);%target candidates pu
hist2=zeros(1,4096);
for i=1:a
for j=1:b
q_r=fix(double(temp1(i,j,1))/16);
q_g=fix(double(temp1(i,j,2))/16);
q_b=fix(double(temp1(i,j,3))/16);
q_temp1(i,j)=q_r*256+q_g*16+q_b;
hist2(q_temp1(i,j)+1)= hist2(q_temp1(i,j)+1)+m_wei(i,j);
end
end
hist2=hist2*C;
figure(2);
subplot(1,2,1);
plot(hist2);
hold on;
w=zeros(1,4096);
for i=1:4096
if(hist2(i)~=0) %不等于
w(i)=sqrt(hist1(i)/hist2(i));
else
w(i)=0;
end
end
%变量初始化
sum_w=0;
xw=[0,0];
for i=1:a;
for j=1:b
sum_w=sum_w+w(uint32(q_temp1(i,j))+1);
xw=xw+w(uint32(q_temp1(i,j))+1)*[i-y(1)-0.5,j-y(2)-0.5];
end
end
Y=xw/sum_w;
%中心点位置更新
rect(1)=rect(1)+Y(2);
rect(2)=rect(2)+Y(1);
end
%%%跟踪轨迹矩阵%%%
tic_x=[tic_x;rect(1)+rect(3)/2];
tic_y=[tic_y;rect(2)+rect(4)/2];
v1=rect(1);
v2=rect(2);
v3=rect(3);
v4=rect(4);
%%%显示跟踪结果%%%
subplot(1,2,2);
imshow(uint8(Im));
title('目标跟踪结果及其运动轨迹');
hold on;
plot([v1,v1+v3],[v2,v2],[v1,v1],[v2,v2+v4],[v1,v1+v3],[v2+v4,v2+v4],[v1+v3,v1+v3],[v2,v2+v4],'LineWidth',2,'Color','r');
plot(tic_x,tic_y,'LineWidth',2,'Color','b');
end #ifndef CTrackH
#define CTrackH
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
#include <string.h>
#include <math.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include<vector>
#define M_PI 3.14159
enum KERNEL_TYPE { MODEL, CANDIDATE };
struct PIXEL
{
float x;
float y;
};
struct KERNEL
{
float radius;
float radius_sqr; //this just for getting rid of square computation for making program faster
float area;
KERNEL_TYPE type;
PIXEL center;
};
struct SEQUENCE
{
char input_dir[200];
char output_dir[200];
char frame_name[100];
char image_type[5];
int start;
int end;
int bins;
};
#ifdef CALCULATE_DISTANCE_FROM_GROUND_TRUTH
struct GROUND_TRUTH
{
PIXEL center; //of the target
float x_diameter; //of the target
float y_diameter; //of the target
float x_x; //square of x diameter
float y_y; //square of y diameter
};
#endif
class CCPixel
{
public:
float y;
float x;
public:
CCPixel();
CCPixel(int _y, int _x);
float length();
float distance(CCPixel a);
float distance(int _y, int _x);
CCPixel& operator = (const CCPixel &a);
CCPixel operator - (const CCPixel &a);
CCPixel operator + (const CCPixel &a);
CCPixel operator / (const float a);
};
//enum IMAGE_TYPE { VARIANCE_IMAGE, FLIR_IMAGE };
class CTrack
{
#define LINEWIDTH(bits) (((bits) + 31) / 32 * 4)
// Declaration of the variables
private:
//CMyImage FLIR_image;
BYTE*img;
CCPixel target_center;
CCPixel candidate_center;
int imgH, imgW;
int model_window_radius;
int candidate_window_radius;
int number_of_bins;
float **FLIR_model_color_probabilities;
float **FLIR_candidate_color_probabilities;
float **FLIR_weights;
std::vector<std::pair<int,int>>trail;
double alpha;//control the update ratio,0-1;alpha increase means update slower
double resize_ratio;
// Declaration of the functions
public:
CTrack();
~CTrack();
void track_target(char*, char*, char*, char*, int, int);
void setimgdata(BYTE*src, int w, int h){
img = src;
imgH = h; imgW = w;
}
void set_targetcenter(std::pair<int, int>center){
target_center.x = center.first;
target_center.y = center.second; }
std::pair<int, int>get_target_center()
{
return std::pair<int, int>(target_center.x, target_center.y);
}
void init(std::pair<int,int>center,int window_radius,int histbin,double alpha,double resizeratio);
float track_target_in_consecutive_frames();
std::vector<std::pair<int, int>>gettrail(){ return trail; }
private:
float kronecker_delta_function(float, float);
float eponechnikov_profile(float);
float derivative_of_eponechnikov_profile(float);
float constant_C(); //for model
float constant_Ch(); //for candidate
void model_density_function_q();//for model
void candidate_density_function_p();//for candidate
float bhattacharyya_coefficient();
void calculate_weights();
void determine_new_candidate_location();
void update_model();
};
#endif#include "stdafx.h"
#include "meanshiftTracker.h"
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
#define TRACKING_OUTPUT 1
CCPixel::CCPixel()
{
}
CCPixel::CCPixel(int _y, int _x)
{
x = _x;
y = _y;
}
float CCPixel::length()
{
return sqrt(x*x + y*y);
}
float CCPixel::distance(CCPixel a)
{
return sqrt(float((x - a.x)*(x - a.x) + (y - a.y)*(y - a.y)));
}
float CCPixel::distance(int _y, int _x)
{
return sqrt(float((x - _x)*(x - _x) + (y - _y)*(y - _y)));
}
CCPixel& CCPixel::operator = (const CCPixel &a)
{
(*this).x = a.x;
(*this).y = a.y;
return (*this);
}
CCPixel CCPixel::operator - (const CCPixel &a)
{
CCPixel c;
c.x = x - a.x;
c.y = y - a.y;
return c;
}
CCPixel CCPixel::operator + (const CCPixel &a)
{
CCPixel c;
c.x = x + a.x;
c.y = y + a.y;
return c;
}
CCPixel CCPixel::operator / (const float a)
{
CCPixel c;
c.x = x / a;
c.y = y / a;
return c;
}
CTrack::CTrack()
{
}
CTrack::~CTrack()
{
}
//%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
// Kronecker delta function's implementation
//%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
float CTrack::kronecker_delta_function(float color1, float color2)
{
return color1 == color2;
}
//%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
// Eponechnikov profile's implementation for 2D (x>=0)
//%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
float CTrack::eponechnikov_profile(float x)
{
float volume_of_unit_d_dimensional_sphere = M_PI; //since d=2
if (x<1) return 2.0*(1 - x) / (volume_of_unit_d_dimensional_sphere);
else return 0.0;
}
//%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
// Uniform profile's implementation for 2D (x>=0)
// derivative of eponechnikov profile (don't put minus)
//%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
float CTrack::derivative_of_eponechnikov_profile(float x)
{
float volume_of_unit_d_dimensional_sphere = M_PI; //since d=2
if (x<1) return 2.0 / (volume_of_unit_d_dimensional_sphere);
else return 0.0;
}
//%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
// Calculate constant c used in model density function
//%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
float CTrack::constant_C()
{
int x, y;
CCPixel pixel;
float sum = 0.0;
for (y = -model_window_radius; y <= model_window_radius; y++)
for (x = -model_window_radius; x <= model_window_radius; x++)
{
pixel.x = (float)x / (float)model_window_radius;
pixel.y = (float)y / (float)model_window_radius;
sum += eponechnikov_profile(pow(pixel.length(), 2));
}
return 1 / (3 * sum);
}
//%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
// Calculate constant ch used in candidate density function
//%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
float CTrack::constant_Ch()
{
int x, y;
CCPixel pixel;
float sum = 0.0;
for (y = -candidate_window_radius; y <= candidate_window_radius; y++)
for (x = -candidate_window_radius; x <= candidate_window_radius; x++)
{
pixel.x = (float)x / (float)candidate_window_radius;
pixel.y = (float)y / (float)candidate_window_radius;
sum += eponechnikov_profile(pow(pixel.length(), 2));
}
return 1 / (3 * sum);
}
//%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
// Calculate model's density estimation q
//%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
void CTrack::model_density_function_q()
{
int x, y, u;
CCPixel pixel;
int r_color, g_color, b_color;
float color_dividor = 256 / number_of_bins;
float epanechnikov_number;
float constant_c = constant_C(); //normalization constant
int rows =imgH, cols = imgW;
int nSrcLine = LINEWIDTH(imgW*24);
for (u = 0; u<number_of_bins; u++)
FLIR_model_color_probabilities[u][0] =
FLIR_model_color_probabilities[u][1] =
FLIR_model_color_probabilities[u][2] = 0.0;
for (y = -model_window_radius; y <= model_window_radius&&y + target_center.y<rows; y++)
for (x = -model_window_radius; x <= model_window_radius&&x + target_center.x<cols; x++)
{
pixel.x = (float)x / (float)model_window_radius;
pixel.y = (float)y / (float)model_window_radius;
r_color = (int)(img[(y + (int)target_center.y)*nSrcLine+3*( x + (int)target_center.x)] / color_dividor);
g_color = (int)(img[(y + (int)target_center.y)*nSrcLine + 3 * (x + (int)target_center.x)+1] / color_dividor);
b_color = (int)(img[(y + (int)target_center.y)*nSrcLine + 3 * (x + (int)target_center.x)+2] / color_dividor);
epanechnikov_number = eponechnikov_profile(pow(pixel.length(), 2));
FLIR_model_color_probabilities[r_color][0] += epanechnikov_number*constant_c;
FLIR_model_color_probabilities[g_color][1] += epanechnikov_number*constant_c;
FLIR_model_color_probabilities[b_color][2] += epanechnikov_number*constant_c;
}
}
//%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
// Calculate candidate's density estimation q
//%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
void CTrack::candidate_density_function_p()
{
int x, y, u;
CCPixel pixel;
int r_color, g_color, b_color;
float color_dividor = 256 / number_of_bins;
float epanechnikov_number;
float constant_ch = constant_Ch(); //normalization constant
int rows = imgH, cols = imgW;
int nSrcLine = LINEWIDTH(imgW * 24);
for (u = 0; u<number_of_bins; u++)
FLIR_candidate_color_probabilities[u][0] =
FLIR_candidate_color_probabilities[u][1] =
FLIR_candidate_color_probabilities[u][2] = 0.0;
for (y = -candidate_window_radius; y <= candidate_window_radius; y++)
for (x = -candidate_window_radius; x <= candidate_window_radius; x++)
{
if (y + floor(candidate_center.y + 0.5)<rows&&y + floor(candidate_center.y + 0.5) >= 0 && x + floor(candidate_center.x + 0.5)<cols&&x + floor(candidate_center.x + 0.5) >= 0)
{
pixel.x = (float)x / (float)candidate_window_radius;
pixel.y = (float)y / (float)candidate_window_radius;
r_color = (int)(img[(y + (int)floor(candidate_center.y + 0.5))*nSrcLine+3*( x + (int)floor(candidate_center.x + 0.5))] / color_dividor);
g_color = (int)(img[(y + (int)floor(candidate_center.y + 0.5))*nSrcLine + 3 * (x + (int)floor(candidate_center.x + 0.5))+1] / color_dividor);
b_color = (int)(img[(y + (int)floor(candidate_center.y + 0.5))*nSrcLine + 3 * (x + (int)floor(candidate_center.x + 0.5))+2] / color_dividor);
epanechnikov_number = eponechnikov_profile(pow(pixel.length(), 2))*constant_ch;
FLIR_candidate_color_probabilities[r_color][0] += epanechnikov_number;
FLIR_candidate_color_probabilities[g_color][1] += epanechnikov_number;
FLIR_candidate_color_probabilities[b_color][2] += epanechnikov_number;
}
}
}
//%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
// calculate the bhattacharyya coefficient
//%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
float CTrack::bhattacharyya_coefficient()
{
int u;
float flir_sum = 0.0;
for (u = 0; u<number_of_bins; u++)
flir_sum += sqrt(FLIR_model_color_probabilities[u][0] *
FLIR_candidate_color_probabilities[u][0]) +
sqrt(FLIR_model_color_probabilities[u][1] *
FLIR_candidate_color_probabilities[u][1]) +
sqrt(FLIR_model_color_probabilities[u][2] *
FLIR_candidate_color_probabilities[u][2]);
return (flir_sum);
}
//%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
// determine the weights for calculating the mean shift
//%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
void CTrack::calculate_weights
()
{
int x, y;
float flir_weight;
CCPixel pixel;
float r_color, g_color, b_color;
float color_dividor = 256 / number_of_bins;
int rows = imgH, cols = imgW;
int nSrcLine = LINEWIDTH(imgW * 24);
for (y = -candidate_window_radius; y <= candidate_window_radius; y++)
for (x = -candidate_window_radius; x <= candidate_window_radius; x++)
{
pixel.x = (float)x / (float)candidate_window_radius;
pixel.y = (float)y / (float)candidate_window_radius;
flir_weight = 0.0;
if (pixel.length()<1 &&
y + floor(candidate_center.y + 0.5)<rows&&y + floor(candidate_center.y + 0.5) >= 0 &&
x + floor(candidate_center.x + 0.5)<cols&&x + floor(candidate_center.x + 0.5) >= 0)
{
r_color = (int)(img[nSrcLine*(y + (int)floor(candidate_center.y + 0.5))+3*( x + (int)floor(candidate_center.x + 0.5))] / color_dividor);
g_color = (int)(img[nSrcLine*(y + (int)floor(candidate_center.y + 0.5)) + 3 * (x + (int)floor(candidate_center.x + 0.5))+1] / color_dividor);
b_color = (int)(img[nSrcLine*(y + (int)floor(candidate_center.y + 0.5)) + 3 * (x + (int)floor(candidate_center.x + 0.5))+2] / color_dividor);
flir_weight = (sqrt(FLIR_model_color_probabilities[(int)r_color][0] / (FLIR_candidate_color_probabilities[(int)r_color][0] + 1e-4)) +
sqrt(FLIR_model_color_probabilities[(int)g_color][1] / (FLIR_candidate_color_probabilities[(int)g_color][1] + 1e-4)) +
sqrt(FLIR_model_color_probabilities[(int)b_color][2] / (FLIR_candidate_color_probabilities[(int)b_color][2] + 1e-4))) / 3.0;
}
FLIR_weights[y + candidate_window_radius][x + candidate_window_radius] = flir_weight;
}
}
//%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
// calculate the new location of the target
//%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
void CTrack::determine_new_candidate_location
()
{
int x, y;
CCPixel pixel;
float denominator = 0.0, numarator_x = 0.0, numarator_y = 0.0;
float weighted;
for (y = -candidate_window_radius; y <= candidate_window_radius; y++)
for (x = -candidate_window_radius; x <= candidate_window_radius; x++)
{
pixel.x = (float)x / (float)candidate_window_radius;
pixel.y = (float)y / (float)candidate_window_radius;
weighted =
FLIR_weights[y + candidate_window_radius][x + candidate_window_radius] *
derivative_of_eponechnikov_profile(pow(pixel.length(), 2));
denominator += weighted;
numarator_x += weighted*(x + floor(candidate_center.x + 0.5));
numarator_y += weighted*(y + floor(candidate_center.y + 0.5));
}
if (numarator_x != 0 || numarator_y != 0)
{
candidate_center.x = numarator_x / denominator;
candidate_center.y = numarator_y / denominator;
}
}
//%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
// algorithm for the estimated location of the target in two frames
//%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
float CTrack::track_target_in_consecutive_frames
()
{
trail.clear();
int i, iter_cnt = 0, inner_iter_cnt;
float distance;
float bhattacharyya_coefficient_1;
float bhattacharyya_coefficient_2;
//initialize the location of the target in the current frame
candidate_center = target_center;
//candidate_center.x = target_center.x+20;
//candidate_center.y = target_center.y + 20;
//target_center.x = target_center.x + 20;
//target_center.y = target_center.y + 20;
do
{ //calculate the distrubution for the target at candidate location
candidate_density_function_p();
//evaluate the bhattacharyya coefficient
bhattacharyya_coefficient_1 = bhattacharyya_coefficient();
//--------------------------------------------------------------------
FLIR_weights = new float*[2 * candidate_window_radius + 1];
for (i = 0; i<2 * candidate_window_radius + 1; i++)
FLIR_weights[i] = new float[2 * candidate_window_radius + 1];
//derive the weigths
calculate_weights();
//Calculate the new location of the target
determine_new_candidate_location();
for (i = 0; i<2 * candidate_window_radius + 1; i++)
delete FLIR_weights[i];
delete FLIR_weights;
//--------------------------------------------------------------------
//update the distrubution for the target at the new location
candidate_density_function_p();
//evaluate the updated bhattacharyya coefficient
bhattacharyya_coefficient_2 = bhattacharyya_coefficient();
inner_iter_cnt = 0;
while (bhattacharyya_coefficient_2 - bhattacharyya_coefficient_1 < -0.01 && inner_iter_cnt<30)
{
candidate_center = (candidate_center + target_center) / 2;
//update the distrubution for the target at the new candidate location
candidate_density_function_p();
//evaluate the updated bhattacharyya coefficient
bhattacharyya_coefficient_2 = bhattacharyya_coefficient();
inner_iter_cnt++;
}
//Calculate the distance between two vectors
distance = candidate_center.distance(target_center);
trail.push_back(std::pair<int, int>(candidate_center.x, candidate_center.y));
target_center = candidate_center;
iter_cnt++;
} while (distance >= 0.0001 && iter_cnt<30);
update_model();
return bhattacharyya_coefficient_2;
}
int frameNumber = 0;
int code = 0;
bool pause = false;
int window_radiusDynamic;
int centerXMouse, centerYMouse;
bool changeCenter;
//this module allows mouse input
//if left button clicked then if number typed the left mouse
//coordinates are used as new center location
//if after left mouse button the r key is pressed then you can type a new radius
//size in the command prompt
//the right mouse button toggles between pause and unpause
//while paused you may press the - or = key to move backwards or forwards manually
void CTrack::init(std::pair<int, int>targetcenter, int window_radius,
int histbin, double alpha, double resizeratio)
{
candidate_window_radius = model_window_radius = window_radius;
this->alpha = alpha;
resize_ratio = resizeratio;
number_of_bins = histbin;
window_radiusDynamic = window_radius;
FLIR_model_color_probabilities = new float*[number_of_bins];
for (int i = 0; i<number_of_bins; i++)
FLIR_model_color_probabilities[i] = new float[3];
FLIR_candidate_color_probabilities = new float*[number_of_bins];
for (int i = 0; i<number_of_bins; i++)
FLIR_candidate_color_probabilities[i] = new float[3];
target_center.x = targetcenter.first;
target_center.y = targetcenter.second;
trail.push_back(targetcenter);
model_density_function_q();
}
//%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
// algorithm for the estimated location of the target in video
//%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
void CTrack::track_target
(char *input_file,
char *output_directory,
char *frame_name,
char *frame_type,
int file_start_index,
int file_end_index
)
{
//create open cv window
changeCenter = false;
char filename[1000];
int frame, i;
int min_scale, scale;
float min_bhattacharyya;
float bhattacharyya_distastance;
float temp_candidate_window_radius;
CCPixel temp_center, correct_center;
//initialize the variables
//Generate the target model from the first frame
int frameCount;// = cvGetCaptureProperty(capture, CV_CAP_PROP_FRAME_COUNT);
//calculate the distrubution for the model ahead of time
model_density_function_q();
#if (TRACKING_OUTPUT)
//cvCircle(image, cvPoint((int)target_center.x, (int)target_center.y), model_window_radius, 255);
sprintf(filename, "%s%s%05d.%s", output_directory, frame_name, file_start_index, frame_type);
//cvFlip(image, NULL, 0);
//cvSaveImage(filename, image);
FILE *cmd_out;
cmd_out = fopen("cmd_output.txt", "w");
#endif
//track the target in the other frames
for (frameNumber = file_start_index; frameNumber<file_end_index;)
{
model_window_radius = window_radiusDynamic;
candidate_window_radius = model_window_radius;
//track the target for 3 scales
temp_candidate_window_radius = candidate_window_radius;
min_scale = 0;
min_bhattacharyya = 1e+10;
temp_center = target_center;
int size = resize_ratio*model_window_radius;
for (scale = -size; scale <= size; scale++)
{
target_center = temp_center;
if (temp_candidate_window_radius + scale>2 &&
temp_candidate_window_radius + scale<120)
{
candidate_window_radius = (int)temp_candidate_window_radius + scale;
bhattacharyya_distastance = exp(-.3*abs(scale))*sqrt(1 - track_target_in_consecutive_frames());
if (bhattacharyya_distastance<min_bhattacharyya)
{
min_scale = scale;
min_bhattacharyya = bhattacharyya_distastance;
correct_center = target_center;
}
}
}
target_center = correct_center;
model_window_radius = (int)(temp_candidate_window_radius + min_scale);
update_model();
#if (TRACKING_OUTPUT)
//cvCircle(image, cvPoint((int)target_center.x, (int)target_center.y), model_window_radius, 255);
//cvCircle(image, cvPoint((int)target_center.x, (int)target_center.y), 3, CV_RGB(255, 0, 0));
sprintf(filename, "%s%s%05d.%s", output_directory, frame_name, frameNumber, frame_type);
//cvFlip(image, NULL, 0);
//cvShowImage(m_windowName, image);
//cvWaitKey(1);
//cvSaveImage(filename, image);
fprintf(cmd_out, "%05d %f %f %d\n", frameNumber, target_center.x, target_center.y, model_window_radius);
#endif
}
delete FLIR_model_color_probabilities;
delete FLIR_candidate_color_probabilities;
#if (TRACKING_OUTPUT)
fclose(cmd_out);
#endif
}
void CTrack::update_model()
{
for (int i = 0; i < number_of_bins; i++)
{
FLIR_model_color_probabilities[i][0] =alpha* FLIR_model_color_probabilities[i][0]+
(1-alpha)* FLIR_candidate_color_probabilities[i][0];
FLIR_model_color_probabilities[i][1] = alpha* FLIR_model_color_probabilities[i][1] +
(1 - alpha)* FLIR_candidate_color_probabilities[i][1];
FLIR_model_color_probabilities[i][2] = alpha* FLIR_model_color_probabilities[i][2] +
(1 - alpha)* FLIR_candidate_color_probabilities[i][2];
}
}
下图是我在一张图上面实现的迭代shift,首先选中一块目标区域,计算好目标直方图,然后将候选区域从目标区域的位置平移一段距离,执行meanshift算法,结果候选区域慢慢收敛到了目标区域,图上绿十字代表整个shift的轨迹。这就是跟踪的基础了,把在同一张图上执行meanshift改为在连续两帧图像上执行就可以实现跟踪了。

多目标跟踪
同时进行多目标跟踪也很容易实现,存储多个目标直方图及其对应的目标位置就行了,简单的for循环就行了。
目标特征的更新
实际中目标可能会发生变化,比如人转头,所以需要更新直方图。
跟踪丢失的处理
当前帧如果出现遮挡等情况造成跟踪丢失,应保存之前的模板,从当前帧开始启动搜索,搜索到后恢复跟踪。























 6502
6502

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








