Sumo安装
注意事项:需要工具的使用需要环境变量的设置。需要包含文件Sumo安装路径下的bin和tools。
Sumo配置文件
Sumo中项目的配置文件的组成如下所示
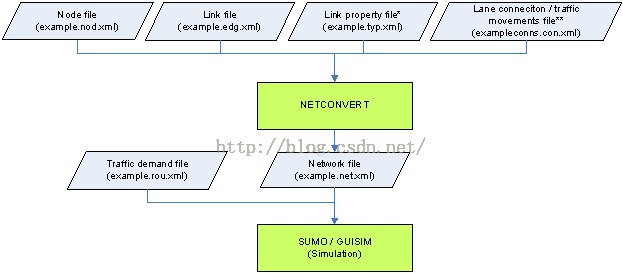
节点文件

图 1 节点及边的拓扑图
Node的属性主要有id,x,y,type。
id 表示节点编号
x,y分别表示节点的x,y坐标
type有两种类型为priority和traffic_light,分别对应于无信号灯和有信号的路口。
上述图中节点对应的节点文件如下所示
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<nodes xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:noNamespaceSchemaLocation="http://sumo.dlr.de/xsd/nodes_file.xsd">
<node id="91" x="-1000.0" y="1000.0" />
<node id="92" x="-1000.0" y="0.0" />
<node id="93" x="3000.0" y="0.0" />
<node id="94" x="+3000.0" y="+1000.0" />
<node id="911" x="-500.0" y="+1000.0" />
<node id="912" x="-500.0" y="0.0" />
<node id="913" x="+2500.0" y="0.0" />
<node id="914" x="2500.0" y="+1000.0" />
<node id="1" x="0.0" y="+1000.0" />
<node id="2" x="0.0" y="0.0" />
<node id="3" x="+1000.0" y="0.0" />
<node id="4" x="+2000.0" y="0.0" />
<node id="5" x="+2000.0" y="+1000.0" />
<node id="6" x="+1000.0" y="+1000.0" />
</nodes>
上述路口都是没有信号灯的路口。
边文件
图1中对应的边文件如下所示
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<edges xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:noNamespaceSchemaLocation="http://sumo.dlr.de/xsd/edges_file.xsd">
<edge id="D1" from="911" to="91" type="a"/>
<edge id="D2" from="91" to="911" type="b"/>
<edge id="D3" from="912" to="92" type="a"/>
<edge id="D4" from="92" to="912" type="b"/>
<edge id="D5" from="913" to="93" type="a"/>
<edge id="D6" from="93" to="913" type="b"/>
<edge id="D7" from="914" to="94" type="a"/>
<edge id="D8" from="94" to="914" type="b"/>
<edge id="L1" from="1" to="911" type="a"/>
<edge id="L2" from="911" to="1" type="b"/>
<edge id="L3" from="2" to="912" type="a"/>
<edge id="L4" from="912" to="2" type="b"/>
<edge id="L5" from="4" to="913" type="a"/>
<edge id="L6" from="913" to="4" type="b"/>
<edge id="L7" from="5" to="914" type="a"/>
<edge id="L8" from="914" to="5" type="b"/>
<edge id="L9" from="5" to="6" type="a"/>
<edge id="L10" from="6" to="5" type="a"/>
<edge id="L11" from="6" to="1" type="a"/>
<edge id="L12" from="1" to="6" type="a"/>
<edge id="L13" from="3" to="2" type="a"/>
<edge id="L14" from="2" to="3" type="a"/>
<edge id="L15" from="6" to="3" type="c"/>
<edge id="L16" from="3" to="6" type="c"/>
<edge id="L17" from="4" to="3" type="a"/>
<edge id="L18" from="3" to="4" type="a"/>
</edges>
Link文件
每个link类型的信息也可以定义在后缀为.typ.xml中。列表1.2展示了在实例中用到的link type文件还有其四个参数:id, priority, numLanes, speed。其中的id的值与.edg.xml文件中的type属性值对应。numLanes对应于车道的数量。Priority对应于车道的优先级。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<types>
<type id="a" priority="3" numLanes="3" speed="13.889"/>
<type id="b" priority="3" numLanes="2" speed="13.889"/>
<type id="c" priority="2" numLanes="3" speed="13.889"/>
</types>
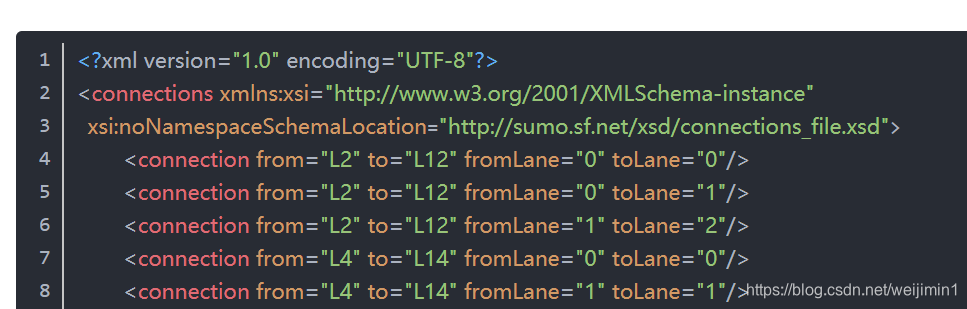
车道连接文件
交通状况和道路连接,一个后缀为.con.xml的文件是必须的。列表1.4展示了实例网络的响应的设置。该文件确定了车从起点道路第几个车道至终点道路的第几个车道。 每个参数的意义如下
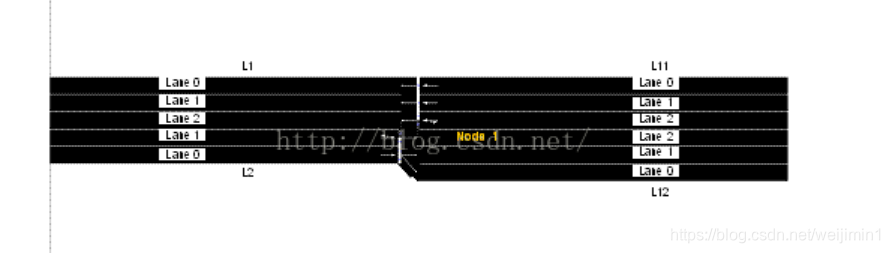
第一行<connection from="L2" to="L12"fromLane="0" toLane="0"/>和第二行<connection from="L2" to="L12"fromLane="0" toLane="1"/>意味着Link L2的Lane 0只使用Link L12的Lane 0和1。
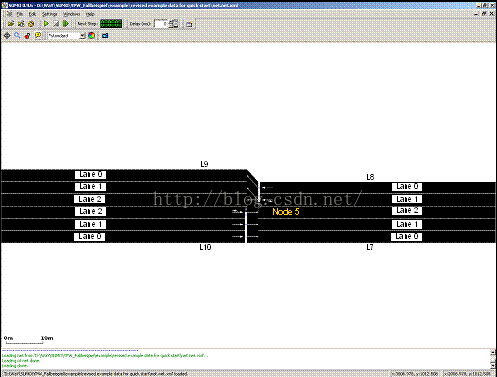
路网生成
SUMO的网路文件后缀为.net.xml。根据前面生成的文件quiclkstart.nod.xml,quickstart.edg.xml,quickstart.con.xml和quickstart.typ.xml,可以通过SUMO的NETCONVERT程序生成网络文件。为了有效执行,包含输入文件名、输出文件名和其他需要动作的的配置文件应该被创建。
由于生成路网需要的文件较多,也可建立一个路网的配置文件 *.netccfg,例如下,通过命令netconvert –c quickstart.netccfg生成路网*.net.xml文件。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!-- generated on Thu Sep 6 09:32:11 2018 by Eclipse SUMO netconvert Version v1_0_0+0032-77a1026
-->
<configuration xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:noNamespaceSchemaLocation="http://sumo.dlr.de/xsd/netconvertConfiguration.xsd">
<input>
<node-files value="quickstart.nod.xml"/>
<edge-files value="quickstart.edg.xml"/>
<connection-files value="quickstart.con.xml"/>
<type-files value="quickstart.typ.xml"/>
</input>
<output>
<output-file value="quickstart.net.xml"/>
</output>
<junctions>
<no-turnarounds value="true"/>
</junctions>
<report>
<verbose value="true"/>
</report>
</configuration>
车辆参数定义文件
交通需求、路由数据及车辆类型数据都定义在后缀为.rou.xml的文件中。
其中定义了车辆的Id,车辆的加速、减速等信息,车辆的路径。
车辆路径包含的参数如下
(a) id: ID of a certain routeand defined by users with numbers, word strings or both.
(b) edges: The sequence of thenames of the links, composing the defined route.

车辆的总参数
(a) depart: departure time of a certain vehicle. (该车出来的时刻)
(b) id: ID of a certain vehicle and defined by users with numbers, word strings or both.
(c) route: the route used by the defined vehicle;
(d) type: ID of the defined vehicle type.

交通信号灯相位配置文件
该文件里主要包含红绿灯持续时间和每个路口对应的红绿状态
<tlLogics version="0.13" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:noNamespaceSchemaLocation="http://sumo.dlr.de/xsd/tllogic_file.xsd">
<tlLogic id="C" type="static" programID="custom" offset="0">
<phase duration="100000" state="GGGGr"/> <!-- do not switch vehicle phase automatically -->
<phase duration="4" state="yyyyr"/>
<phase duration="10" state="rrrrG"/>
<phase duration="10" state="rrrrr"/> <!-- give pedestrians time to clear the intersection -->
</tlLogic>
</tlLogics>
项目的配置文件
直接使用命令来运行会导致命令后面的选型列表会很长,因此需要设置一个配置文件,包含运行应用程序所有参数。
配置文件是一个XML文件,有一个名为“configuration”的根元素。选项被写为元素名称,在属性value中存储值。
举例说明,配置文件(让我们保存为“test.sumocfg”)样式如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<configuration xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:noNamespaceSchemaLocation="http://sumo.dlr.de/xsd/sumoConfiguration.xsd">
<input>
<net-file value="cross.net.xml"/>
<route-files value="cross.rou.xml"/>
<additional-files value="cross.det.xml"/>
</input>
<time>
<begin value="0"/>
</time>
<report>
<verbose value="true"/>
<no-step-log value="true"/>
</report>
</configuration>在命令行中直接运行
sumo.exe test.sumocfg
交通信号灯
信号灯的颜色的定义
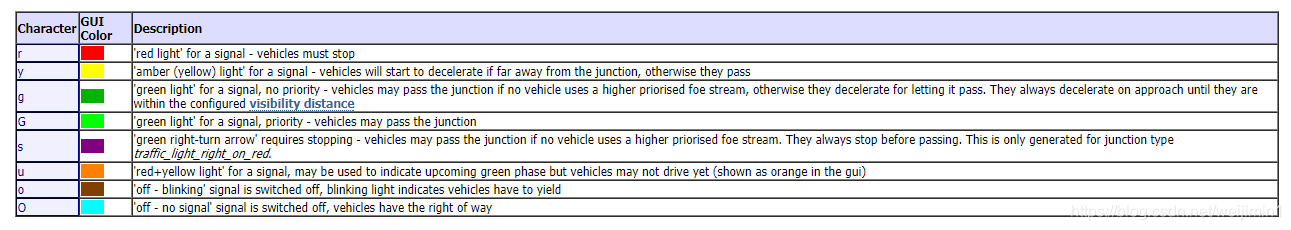
信号灯与道路的对应
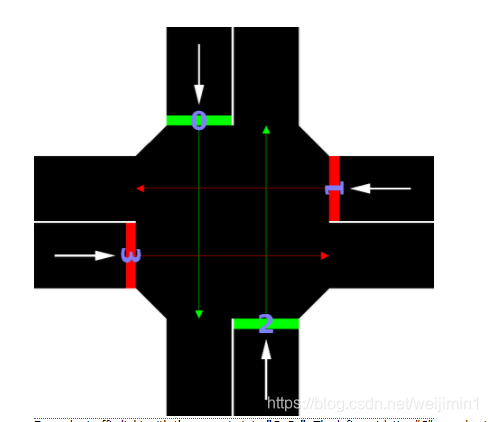
上述图中交通信号灯的状态为“GrGr”,第一个“G”表示link 0为绿第一“r”表示link 1为红灯,link2 为绿灯,link 3为红灯。
Link的编号默认有NETCONVERT通过顺时针的方式产生,其中link 0在12点钟的方位。右转、直行、左转依次进行。
一般的十字路口的会有4个绿色的相位。加上黄灯相位则有8个相位。相位的编号是从0-7。
| 相位编号 traci.trafficlights.getPhase | 对应红绿灯的颜色 traci.trafficlights.getRedYellowGreenState |
| 0 | GrrrGrrr |
| 1 | yrrryrrr |
| 2 | rGrrrGrr |
| 3 | ryrrryrr |
| 4 | rrGrrrGr |
| 5 | rryrrryr |
| 6 | rrrGrrrG |
| 7 | rrryrrry |
相位的属性如下所示

Matlab定义sumo中红绿灯的相位程序如下所示
//定义八个相位的持续时间,红绿灯的状态,最小持续时间,最大持续时间。
myRYGDefinition = traci.trafficlights.Logic('0',0,0,...
{traci.trafficlights.Phase(15,'GrrrGrrr',15,15),...
traci.trafficlights.Phase(3,'yrrryrrr',3,3),...
traci.trafficlights.Phase(15,'rGrrrGrr',15,15),...
traci.trafficlights.Phase(3,'ryrrryrr',3,3),...
traci.trafficlights.Phase(15,'rrGrrrGr',15,15),...
traci.trafficlights.Phase(3,'rryrrryr',3,3),...
traci.trafficlights.Phase(15,'rrrGrrrG',15,15),...
traci.trafficlights.Phase(3,'rrryrrry',3,3)});
//将定义的相位逻辑发送给Sumo
traci.trafficlights.setCompleteRedYellowGreenDefinition('0',myRYGDefinition);
注:红绿灯的相位持续时间需设置为大于0的整数。
SUMO支持基于间隙的驱动交通控制。这种控制方案在德国很常见,并且只要检测到连续的交通流,就可以延长交通相位。在检测到车辆之间有足够的时间间隔后,它会切换到下一相位。这允许在相位之间更好地分配绿灯时间,并且根据动态交通状况而影响周期持续时间。
Sumo 仿真过程

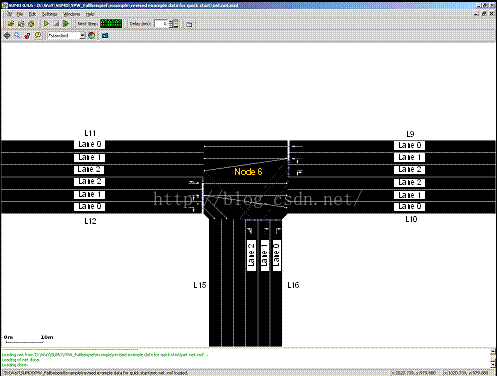
通过命令行sumo-gui –c *.sumocfg来启动运行sumo gui界面
Sumo-gui界面
Sumo-gui的界面如下图所示。

1、在运行过程中,将delay设置为1000,单位为ms,那么仿真就是和真实时间是同步的,即每秒更新一次。
2、可以通过setProgram来切换预先在.net.xml中定义好的红绿灯配时。
问题及解决方法
Sumo是服务器,Matlab是客户端,通过TCP/IP进行信息交互。
1、运行trai4matlab软件的traci_test2案例时需要在window的命令提示符窗口运行如下命令:
![]()
如果没有运行该指令直接运行traci_test2 则会爆出缺少cross.rou.xml 的错误。
2、如果显示port 8813被占用的错误,
Error: tcpip::Socket::accept() Unable to create listening socket: Address already in use
Quitting (on error).
则在window的命令提示符窗口输入如下命令查看8813端口的使用情况,如果显示8813端口显示被占用,则关闭已经打开的Sumo-gui窗口,再次输入netstat命令查看端口占用情况。
注意事项
- traci4matlab并未完全实现sumo与外部交互交互的接口,仅支持部分TraCI命令。
- sumo与python的接口已经完全实现,建议采用python实现与sumo的交互,支持全部TraCI命令。
- sumo中没有排队长度(queue length)的参数。用等待时间替代(waiting time)?
- sumo中没有车辆的平均延误(average delay)的参数。
参数解释
车辆的等待时间(waitingtime) :车辆速度低于0.1m/s开始至车辆车速大于0.1m/s之间的时间。
参考文献
1、trai4matlab软件的user_manual
























 1375
1375

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








