深度学习绘图
The applications of deep learning has been explored in various components throughout the autonomous driving stack, for example, in perception, prediction, and planning. Deep learning can also be used in mapping, a critical component for higher-level autonomous driving.
深度学习的应用已在整个自动驾驶堆栈的各个组件中进行了探索,例如在感知,预测和计划中。 深度学习也可以用于制图 ,这是高级自动驾驶的关键组成部分。
Having accurate maps is essential to the success of autonomous driving for routing, localization as well as to ease perception. Maps with varying degrees of information can be obtained through subscribing to the commercially available map service. However, in areas where maps are not available, self-driving vehicles need to rely on their own map building capability to ensure the functionality and safety of autonomous driving.
拥有精确的地图对于自动驾驶成功进行路由,本地化以及简化感知至关重要。 可以通过订阅市售地图服务来获取具有不同程度信息的地图。 但是,在没有地图的地区,自动驾驶汽车需要依靠自己的地图构建能力来确保自动驾驶的功能和安全性。
离线映射与在线映射 (Offline Mapping vs Online Mapping)
In an offline mapping scenario, sensor data are aggregated in a centralized location. The data could either be satellite imagery or data collected by onboard sensors such as cameras or lidars. It could be from multiple passes of the same vehicle through the same location or crowd-sourced to a fleet of cars. A rendering of the map is built offline, and human annotators are required to annotate semantic structures on the map and review the final results. Traditional mapping service works in this offline fashion, then the annotated and curated maps are then served to vehicles on the road.
在离线映射方案中,传感器数据被聚集在一个集中的位置。 数据可以是卫星图像,也可以是机载传感器(例如相机或激光雷达)收集的数据。 它可能来自同一辆车经过同一地点的多次通行,也可能来自众包车辆。 地图的呈现是离线构建的,并且需要人工注释者来注释地图上的语义结构并查看最终结果。 传统的地图服务以这种离线方式工作,然后将带注释和精选的地图提供给道路上的车辆。
Online mapping happens onboard the vehicle and are thus cannot afford to have the human in the loop. Typical examples are SLAM systems for simultaneous localization and mapping. Recently, semantic SLAM focusing on the geometry and semantic meanings of the surface markings on the road are explored as a lightweight solution to mapping. In addition, monocular semantic online mapping (monoSOM) is one trending topic where a neural network is used to fuse temporal sequences of monocular images from multiple camera into a semantic birds-eye-view map. These topics are beyond the scope of this post and will be reviewed elsewhere.
在线地图是在车辆上进行的,因此无法让人类陷入困境。 典型示例是用于同时定位和映射的SLAM系统 。 最近,重点研究道路上表面标记的几何和语义含义的语义SLAM作为一种轻量级的制图解决方案。 另外, 单眼语义在线映射(monoSOM)是一个趋势话题,其中使用神经网络将来自多个摄像机的单眼图像的时间序列融合到语义鸟瞰图中。 这些主题超出了本文的范围,将在其他地方进行讨论。
SD地图与HD地图 (SD Maps vs HD Maps)
Depending on the input resolution, there are roughly two types of applications of deep learning in mapping. The first line of work focuses on the discovery of the topology of maps, such as road network, and do not usually contain lane level information. They only require a relatively low-resolution image with roughly meter-level accuracy. The other type of application focuses on extracting lane level information such as lane lines, road surface arrows, and other semantic markings. This requires a higher resolution image with centimeter-level accuracy. Correspondingly, these two types of maps will be loosely referred to as SD maps and HD maps for the rest of this post.
根据输入分辨率,大约有两种类型的深度学习在地图中的应用。 第一行工作重点是地图拓扑的发现,例如道路网络,通常不包含车道级别信息。 他们只需要相对低分辨率的图像, 精度大约为米级 。 另一种类型的应用程序侧重于提取车道级别信息,例如车道线,路面箭头和其他语义标记。 这需要具有厘米级精度的高分辨率图像。 相应地,在本文的其余部分中,这两类地图将被简称为SD地图和HD地图。
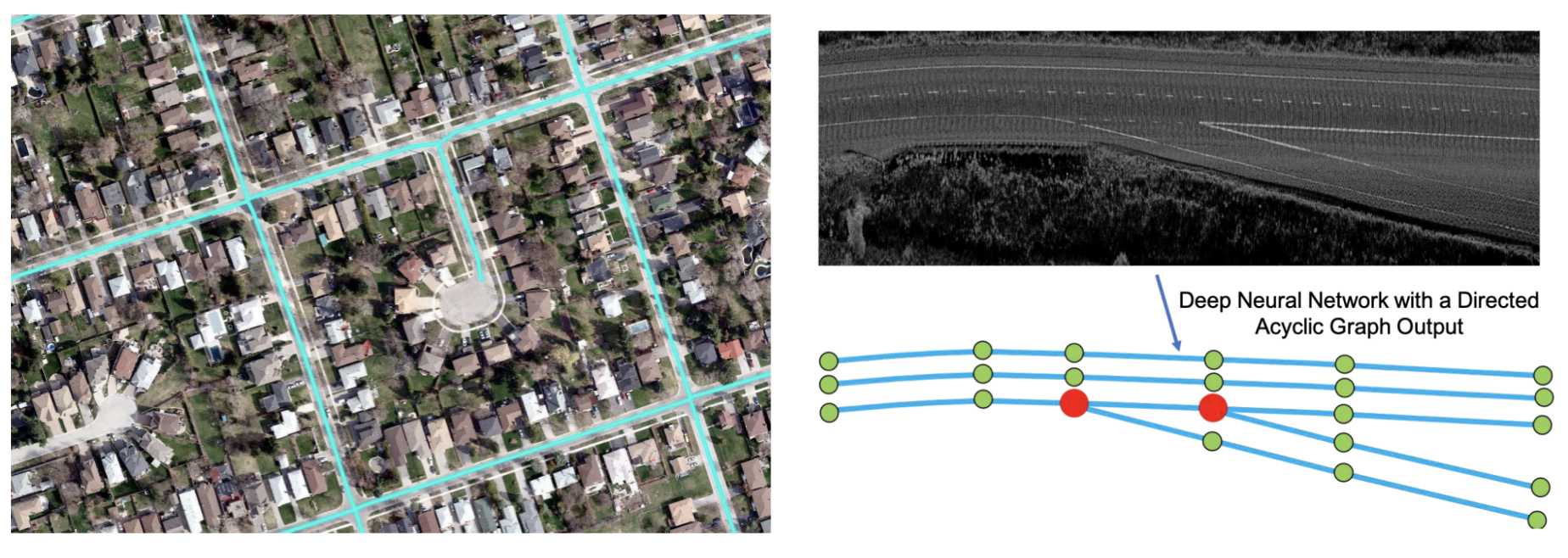
This post focuses on the offline generation of HD maps. Note that some of the methods can be applied to online mapping as well, and a short review session is dedicated to some related works of SD mapping.
这篇文章重点介绍了高清地图的离线生成。 注意,有些方法也可以应用于在线映射,简短的回顾会专门讨论SD映射的一些相关工作。
注释者友好的映射 (Annotator-friendly Mapping)
In offline mapping, it is affordable and essential to have a human reviewer to review the results of deep learning. Thus not only does the overall accuracy matter but also the presentation of the results in the sense that the results should be easy to be modified by a human annotator.
在离线地图中,让人工审阅者审阅深度学习的结果是负担得起且必不可少的。 因此,总的准确性不仅很重要,而且结果的表示也很重要,因为结果应该易于被人工注释者修改。
As most motion planners can only handle lane graphs that are structured and represent the right topology, the output of the mapping algorithm is usually a structured representation (polylines for lane lines, etc). This representation luckily lends itself to efficient modification of the human annotator.
由于大多数运动计划者只能处理结构化并代表正确拓扑的车道图,因此映射算法的输出通常是 结构化表示 (车道线的折线等)。 幸运的是,这种表示形式有助于对人类注释者进行有效的修改。
SD映射(道路拓扑发现) (SD Mapping (Road Topology Discovery))
Early application of deep learning on mapping focuses on extracting road level topology from relatively low-resolution aerial images. Deep learning creates an affordable solution with large coverage for SD mapping. The primary purpose of the generated road topology in SD maps is relatively limited in the context of autonomous driving— for routing and navigation. Yet the methodologies proposed in some of these studies are highly relevant to later works on HD maps and are thus reviewed here.
深度学习在地图上的早期应用着重于从相对低分辨率的航空图像中提取道路拓扑。 深度学习创建了一种负担得起的解决方案,涵盖了SD映射的大量内容。 SD地图中生成的道路拓扑的主要目的在自动驾驶(用于路线选择和导航)的环境中相对受限。 然而,其中一些研究提出的方法与高清地图的后续工作高度相关,因此在此进行了综述。
DeepRoadMapper (ICCV 2017) takes in aerial images obtained from satellites and creates a structured road network. It first performs semantic segmentation and runs a thinning and pruning algorithm on the generated road graph. Due to the inaccuracies in the semantic segmentation (occlusions by trees, buildings, etc), many roads are left disconnected. To address this, DeepRoadMapper uses A* search algorithm to generate connection hypotheses to close the gaps.
DeepRoadMapper (ICCV 2017)吸收从卫星获得的航拍图像并创建结构化的道路网络。 它首先执行语义分割,然后对生成的路线图运行细化和修剪算法。 由于语义分割的不准确(树木,建筑物等遮挡),许多道路保持断开状态。 为了解决这个问题,DeepRoadMapper使用A *搜索算法来生成连接假设以弥合差距。
RoadTracer (CVPR 2018) also noted the unreliable semantic segmentation results and eliminated it as the intermediate representation. It uses an iterative graph construction to get the topology of the road directly. The algorithm needs to make a decision to step a certain distance toward a certain direction, resembling an agent in a reinforcement learning setting.
RoadTracer (CVPR 2018)也注意到了不可靠的语义分割结果,并将其作为中间表示消除了。 它使用迭代图构造直接获取道路拓扑。 该算法需要做出决定,朝特定方向迈进一定距离,类似于增强学习环境中的主体。

PolyMapper (ICCV 2019) may have been inspired by RoadTracer and it also eliminates the intermediate representation. It explicitly unifies the shape representation for different types of objects, including both roads and street blocks of buildings, and formulates them as closed polygons. The formulation is extremely clever and clean, following the Maze wall follower algorithm.
PolyMapper (ICCV 2019)可能受到RoadTracer的启发,并且也消除了中间表示形式。 它明确统一了不同类型对象的形状表示,包括建筑物的道路和街区,并将其表示为封闭的多边形。 遵循迷宫墙追随者算法,配方极其巧妙和清洁。
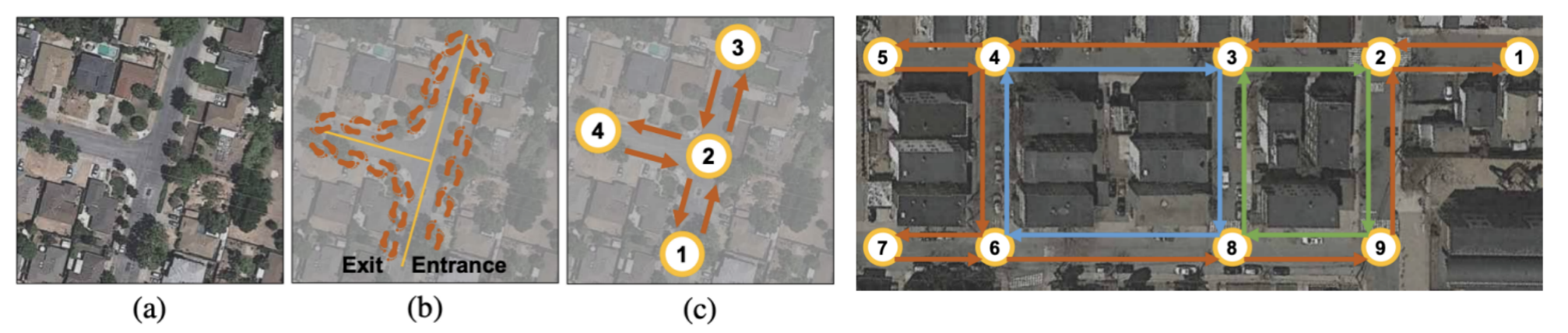
PolyMapper uses Mask RCNN architecture for extracting boundary masks for buildings and roads. Based on the mask, it extracts vertices, finds the starting vertex, and autoregressively iterate all of them with an RNN to form the closed polygon.
PolyMapper使用遮罩RCNN架构提取建筑物和道路的边界遮罩。 基于蒙版,它提取顶点,找到起始顶点,然后使用RNN对所有顶点进行自回归迭代以形成闭合多边形。

The autoregressive generation of a structured presentation of the map in RoadTracer and PolyMapper closely resembles that used in HD mapping.
在RoadTracer和Google中自动生成地图的结构化表示形式 PolyMapper 与高清映射中使用的非常相似。
高清映射(车道信息提取) (HD Mapping (Lane Level Information Extraction))
SD maps lack the fine detail and accuracy needed for a safe localization and motion planning of an autonomous car. HD Maps with lane level information are necessary for autonomous driving. HD map generation usually takes on a higher resolution birds-eye-view (BEV) image, generated by stitching onboard camera images, and/or lidar sweeps.
SD地图缺乏自动驾驶汽车的安全定位和运动计划所需的精细细节和准确性。 带有车道高度信息的高清地图对于自动驾驶至关重要。 HD地图的生成通常采用高分辨率的鸟瞰图(BEV)图像,该图像是通过拼接车载摄像机图像和/或激光雷达扫描生成的。
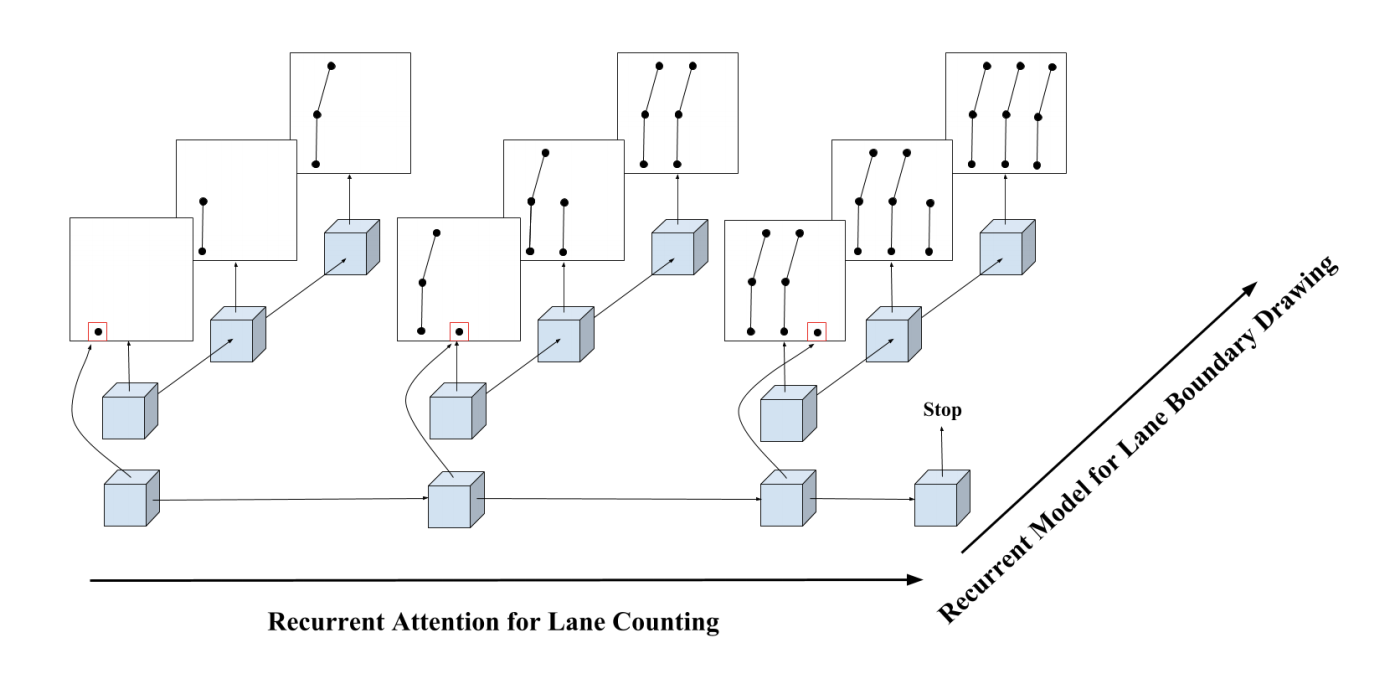
HRAN (Hierarchical Recurrent Attention Networks for Structured Online Maps, CVPR 2018) takes in a sparse point cloud sweep of the road and outputs a structured representation of the road network containing lane boundary instance. It first iteratively finds the starting point of each lane line, then for each lane line, iteratively draws the next vertex along the line. The two RNNs are organized in a hierarchical fashion, thus the name HRAN — hierarchical recurrent attention networks.
汉兰 (用于结构化在线地图的分层递归注意网络,CVPR 2018)获取道路的稀疏点云扫描并输出包含车道边界实例的道路网络的结构化表示。 它首先迭代找到每条车道线的起点,然后对于每条车道线,迭代地绘制沿该线的下一个顶点。 这两个RNN以分层方式进行组织,因此名称为HRAN-分层递归注意网络。
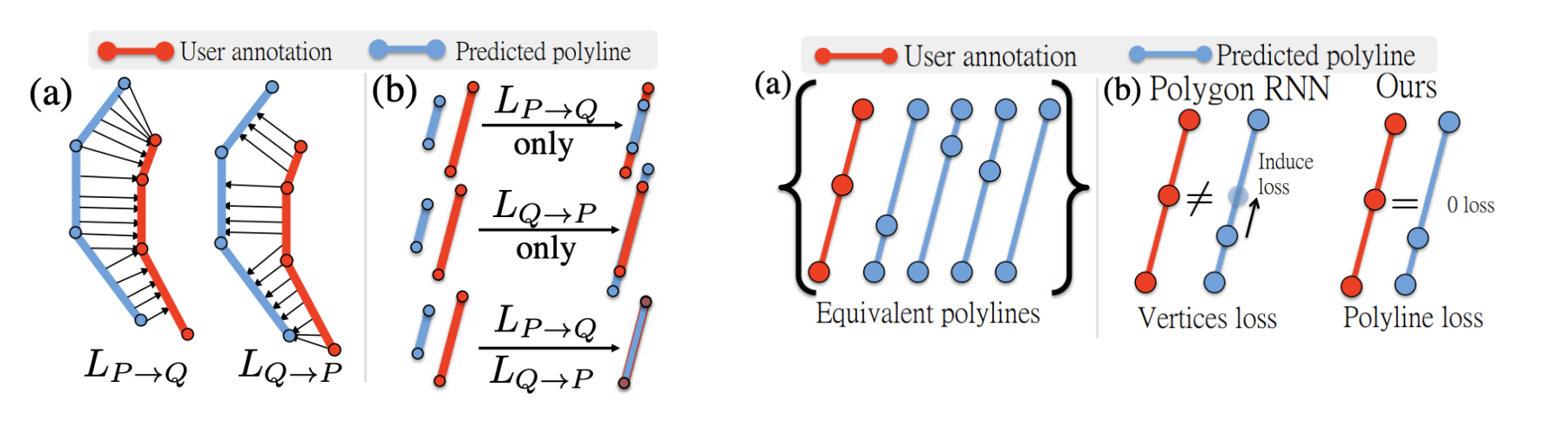
It proposed the idea of polyline loss to encourage the neural network to output structured polylines. The polyline loss measures the deviation of the edges of the ground truth polylines and their predictions. This is more suitable than distance on vertices, as there exist many ways to draw equivalent polylines.
它提出了折线损失的想法,以鼓励神经网络输出结构化折线。 折线损失可衡量地面真线折线及其预测的边缘的偏差。 这比在顶点上的距离更合适,因为存在许多绘制等效折线的方法。
HRAN uses 5 cm per pixel resolution and achieves 0.91 recall within 20 cm accuracy. The main failure mode is from missed or extra lane lines. Note that 100% accuracy is not necessarily the ultimate goal as an annotator still needs to manually review these images and fix them. These failure cases can be fixed relatively easily. The height gradient map used in a later work Deep Boundary Extractor may be able to fix the FP case where the guardrail is mistaken for lane lines.
HRAN使用每像素5厘米的分辨率,并在20厘米的精度内实现0.91的召回率。 主要故障模式来自错过或多余的车道线。 请注意,100%的准确性不一定是最终目标,因为注释者仍然需要手动查看并修复这些图像。 这些故障案例可以相对容易地解决。 在以后的工作“ 深边界提取器”中使用的高度梯度图可能能够修复FP护栏误认为车道线的情况。
Deep Structured Crosswalk (End-to-End Deep Structured Models for Drawing Crosswalks, ECCV 2018) extract structured crosswalk from BEV images produced by Lidar points and camera images (lidar + RGB = 4 channels). The network generates three distinctive feature maps — semantic segmentation, contour detection as well as angles defining the crosswalk direction from direct supervision.
深层结构人行横道 (用于绘制人行横道的端到端深度结构化模型,ECCV 2018)从激光雷达点产生的BEV图像和相机图像(激光雷达+ RGB = 4通道)中提取结构化人行横道。 该网络生成三个独特的特征图-语义分割,轮廓检测以及在直接监督下定义人行横道方向的角度。
Naively, the contour map and angle/alignment map only has non-zero values at the crosswalk boundary. This is similar to a one-hot encoding and provides too sparses supervision. To fix this, the contour map takes on the form of Inverse Distance Transform (DT), and the angle map also extends non-zero regions to a dilated contour band. An alternative is to use Gaussian blur to the almost one-hot groundtruth, as in CenterNet.
天真地,轮廓图和角度/对齐图在人行横道边界处只有非零值。 这类似于单热编码,并且提供了过于稀疏的监视。 为了解决这个问题,轮廓图采用逆距离变换(DT)的形式,并且角度图还将非零区域扩展到膨胀的轮廓带。 一个替代方案是使用高斯模糊到几乎独热真实状况,如在CenterNet 。
This work is in a sense not exactly end-to-end, as the ultimate goal of the pipeline is to generate two structured, oriented boundaries of the crosswalk. To get the structured boundaries, the three intermediate feature maps, along with a coarse map (OpenStreetMaps, which provides the road centrelines and intersection polygons) are fed into an energy maximization pipeline to find the best boundaries and orientation angle of the crosswalks.
从某种意义上说,这项工作并不是端到端的,因为管道的最终目标是生成人行横道的两个结构化,定向的边界。 为了获得结构化的边界,将三个中间特征地图以及一个粗略的地图(OpenStreetMaps,提供道路中心线和交叉点多边形)馈入能量最大化管道,以找到人行横道的最佳边界和方向角。
The BEV input resolution is 4 cm/pixel, and an overall 0.96 accuracy is achieved. The main failure mode is poor paint quality, leading to incorrect distance transformation and segmentation prediction.
BEV输入分辨率为4厘米/像素,整体精度为0.96。 主要的故障模式是油漆质量差,导致不正确的距离转换和分段预测。
The above results are obainted offline by input generated by several passes of driving. The model can also run online with a single pass through the same location and can achieve similar performance, with additional failure mode of poor image quality generated online.
上述结果是通过多次驾驶产生的输入离线显示的。 该模型还可以一次通过同一位置在线运行,并且可以实现类似的性能,并具有在线生成的不良图像质量的其他故障模式。

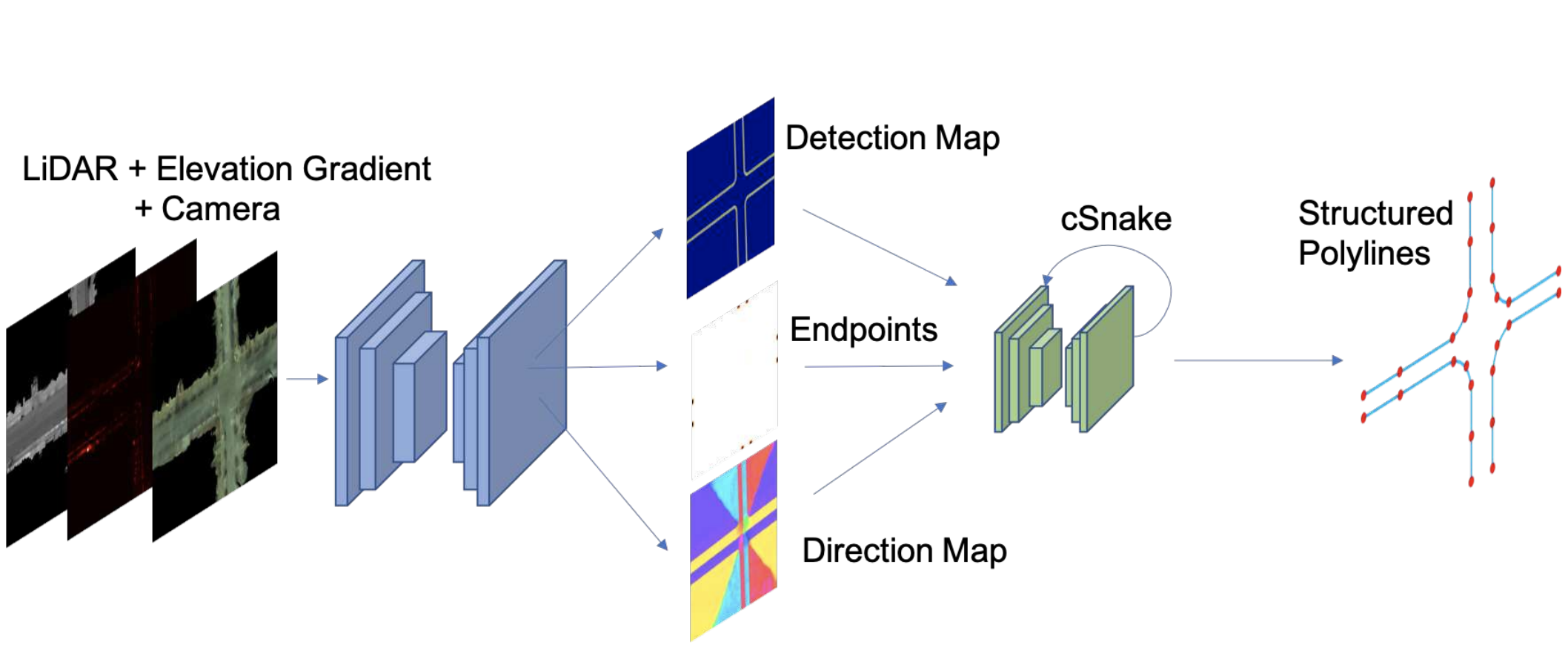
Deep Boundary Extractor (Convolutional Recurrent Network for Road Boundary Extraction, CVPR 2019) extracts road boundary with polylines. It is inspired by Deep Structured Crosswalk and uses a convolutional RNN (convolutional Snake, or cSnake) to predict in an autoregressive fashion. The input extends that of Deep Structured Crosswalk by adding one additional channel of lidar height gradient, generated by taking the magnitude of Sobel filtered lidar BEV map.
深边界提取器 (用于道路边界提取的卷积循环网络,CVPR 2019)使用折线提取道路边界。 它受到“ 深层结构人行横道”的启发,并使用卷积RNN(卷积Snake或cSnake)以自回归方式进行预测。 输入通过添加一个额外的激光雷达高度梯度通道扩展了深度结构人行横道的输入范围,该通道是通过获取Sobel滤波的激光雷达BEV图的大小而生成的。
The cSnake network iteratively attends to rotated ROIs and outputs the vertices of a polyline corresponding to a road boundary. It predicts endpoint first. Based on each endpoint, it crops and rotates patch of feature maps centered on the endpoint and locates the next point is located. The above process runs autoregressively.
cSnake网络迭代处理旋转的ROI,并输出对应于道路边界的折线的顶点。 它首先预测端点。 基于每个端点,它会裁剪并旋转以端点为中心的特征图的面片,并找到下一个点的位置。 上面的过程是自动回归的。
Deep Boundary Extractor runs with an input resolution of 4 cm/pixel, and achieves ~0.90 point-wise F1 score and 0.993 topology accuracy.
深度边界提取器的输入分辨率为4 cm /像素,可达到〜0.90的逐点F1分数和0.993的拓扑精度。
DAGMapper (Learning to Map by Discovering Lane Topology, ICCV 2019) takes the structured lane line extraction work of HRAN one step further and focuses on harder cases like forks and merges. It takes in lidar intensity maps and outputs a DAG (directed acyclic graph), instead of a simple polyline in HRAN.
DAGMapper (学习到地图通过发现巷拓扑,ICCV 2019)采用的结构化车道线提取工作HRAN一步,着眼于困难情况下,像叉子和合并。 它接受激光雷达强度图并输出DAG(有向无环图),而不是HRAN中的简单折线。
At the heart of DAGMapper is also one recurrent convolutional head that iteratively attends to a cropped feature map patch centered around the last predicted points, and predicts the location of the next point. The change is that it also predicts the point status to be merge, fork, or continue.
DAGMapper的核心还有一个循环卷积头,它迭代地关注以最后一个预测点为中心的裁剪特征图补丁,并预测下一个点的位置。 变化之处在于它还预测了点的状态为合并,派生或继续。

The input resolution is 5 cm/pixel. The precision/recall/F1 is about 0.76 at 2 pixel (10 cm) threshold and about 0.96 at 10 pixel (50 cm). The topology accuracy is about 0.89.
输入分辨率为5厘米/像素。 精度/召回率/ F1在2像素(10厘米)阈值处约为0.76,在10像素(50厘米)处约为0.96。 拓扑精度约为0.89。

外卖 (Takeaways)
- Deep learning for offline mapping has a human in the loop. The results of deep learning need to be structured to be readily consumable by an autonomous driving stack and easily modifiable by the human annotator. 离线地图的深度学习有一个人在循环。 深度学习的结果需要构造成易于由自动驾驶堆栈使用,并易于由人工注释者修改。
- Current HD mapping applications focus on extraction of road boundaries, lane lines (including merge and fork topologies), and cross walk boundaries. 当前的高清制图应用程序专注于提取道路边界,车道线(包括合并和岔路拓扑)和人行横道边界。
- The core building block of all the HD mapping studies is a recurrent convolutional network which iteratively takes in a cropped feature map centered at the current annotation point, and predict the next annotation point. 所有高清映射研究的核心组成部分都是循环卷积网络,该网络以迭代方式获取以当前注释点为中心的裁剪特征图,并预测下一个注释点。
翻译自: https://towardsdatascience.com/deep-learning-in-mapping-for-autonomous-driving-9e33ee951a44
深度学习绘图







 本文探讨了深度学习如何在自动驾驶的制图中发挥作用,介绍了如何利用深度学习技术进行高精度地图绘制和更新。
本文探讨了深度学习如何在自动驾驶的制图中发挥作用,介绍了如何利用深度学习技术进行高精度地图绘制和更新。

















 2万+
2万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








