javascript递归
What is recursion?
什么是递归?
A process in which a function/method calls itself.
函数/方法调用自身的过程。
Why do we use it?
我们为什么用它?
Solutions can be written with shorter lines of code.
解决方案可以用较短的代码行编写。
Some examples:
一些例子:
Fibonacci sequence, AJAX calls such as json.stringify, DOM traversal algorithms, etc.
斐波那契序列,AJAX调用(例如json.stringify),DOM遍历算法等。
Important parts of recursion:
递归的重要部分 :
A base case. Creating a condition to exit out of the self-recursive loop.
基本情况 。 创建一个退出自递归循环的条件。
A recursive step. Any logic along with different parameters on the self-recursive loop, usually reduced in size or complexity.
递归步骤 。 自递归循环上的任何逻辑以及不同的参数通常会减小大小或复杂性。
//simple recursion
const newYearCount = num => {
//base case
if(num === 0){
console.log("Happy New Year!");
return
}
console.log(num)
num--
//recursive step newYearCount(num)
}
//invoke the function
newYearCount(10)As shown above, the function will continue to call itself until the parameter num = 0. When the base case is met, an exit is created out of the recursive step.
如上所示,该函数将继续调用自身,直到参数num =0。遇到基本情况时,将在递归步骤之外创建一个出口。
The console will log: 10, 9, 8, 7, 6, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1, “Happy New Year!”.
控制台将记录:10、9、8、7、6、5、4、3、2、1,“新年快乐!”。
Another example:
另一个例子:
Write a function that takes two inputs, a base number and an exponent. Return the expected value of base ^ exponent. (Note: num⁰ = 1)
编写一个接受两个输入的函数,即基数和指数。 返回基数^指数的期望值。 (注意:num⁰= 1)
If base is 2 and exp is 3
如果base为2且exp为3
2³ = 2 * 2 * 2 = 8
2³= 2 * 2 * 2 = 8
First, try to find the base case when exp = 0.
首先,尝试找到exp = 0时的基本情况。
2⁰ = 1
2⁰= 1
if (exp === 0) return 1Afterwards, think of the self-recursive loop using different values for the function: pow(base, exp)
然后,考虑对函数使用不同值的自递归循环:pow(base,exp)
Visualize a upside-down tree:
可视化颠倒的树:
pow(2,3)
/ \
2 * pow(2,2)
/ \
2 * pow(2,1)
/ \
2 * pow(2,0)
\
1 //base case Work up from the base case:
从基本情况开始工作:
pow(2,0) = 1
pow(2,0)= 1
pow(2,1) = 2 * pow(2,0)
pow(2,1)= 2 * pow(2,0)
pow(2,2 ) = 2 * pow(2,1)
pow(2,2)= 2 * pow(2,1)
pow(2,3) = 2 * pow(2,2)
pow(2,3)= 2 * pow(2,2)
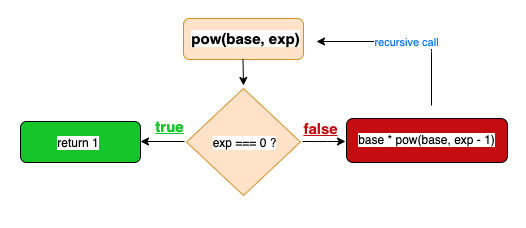
//possible solution
function pow(base, exp){
if(exp === 0) return 1;
return base * pow(base,exp-1);
}Under the hood:
在引擎盖下:
Let’s discuss the call stack. JavaScript uses the call stack to manage function invocations.
让我们讨论一下调用堆栈。 JavaScript使用调用堆栈来管理函数调用。
Think of stacking plates. New plates are stacked on top (push). When grabbing a plate from the stack, grab from the top (pop).
想想堆叠板。 新板堆叠在顶部(推动)。 从堆栈中拿起盘子时,从顶部抓起(弹出)。
Within the global memory, we have the execution context which is continuously adding onto the call stack for each recursive call. Meanwhile, the nested functions is paused on the call stack as the recursion continuously adds on more recursive functions.
在全局内存中,我们具有执行上下文,该上下文将针对每个递归调用不断添加到调用堆栈中。 同时,随着递归不断添加更多的递归函数,嵌套函数将在调用堆栈上暂停。
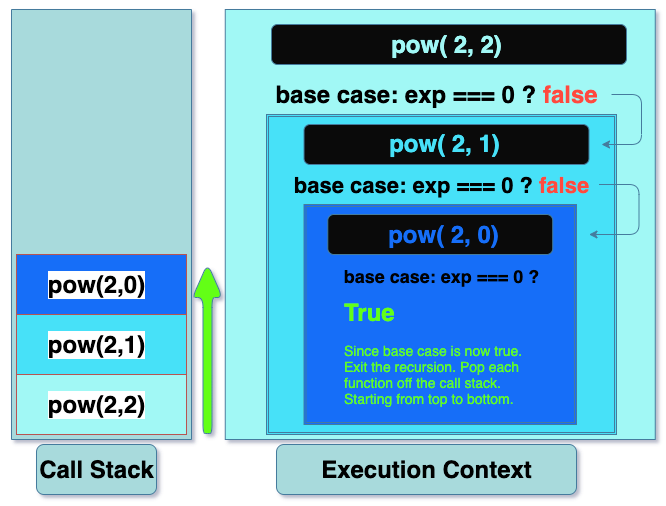
When the base case returns true, each recursive call is popped off the call stack starting from the top. Refers to the green arrow popping off from top-down.
当基本情况返回true时,将从顶部开始从调用堆栈中弹出每个递归调用。 指从上到下弹出的绿色箭头。
Importance of base case:
基本案例的重要性:
Without base case what would happen?
没有基本情况,会发生什么?
An infinite loop?
无限循环?
Luckily, this will cause the call stack to overflow (stack overflow).
幸运的是,这将导致调用堆栈溢出(堆栈溢出)。
A defined limit will be hit based on the browser. Each browser has its own limit before throwing an error ‘Maximum call size exceeded’.
将根据浏览器达到定义的限制。 每个浏览器在抛出错误“超出最大通话大小”之前都有自己的限制。
Environments such as Node.js also has its own limit before throwing an error.
在抛出错误之前,Node.js之类的环境也有其自身的限制。
The Fibonacci numbers, commonly denoted F(n) form a sequence, called the Fibonacci sequence, such that each number is the sum of the two preceding ones, starting from 0 and 1. That is,
斐波那契数 ,通常表示为 F(n) 形成的序列,称为 Fibonacci序列 ,使得每个数字是两个前述者的总和,从开始 0 和 1 。 那是,
F(0) = 0, F(1) = 1
F(N) = F(N - 2) + F(N - 1), for N > 1.Given N, calculate F(N).
给定 N ,计算 F(N) 。
For the problem above, think of the the sequence and the possible base case.
对于上述问题,请考虑顺序和可能的基本情况 。
sequence: 0,1,1,2,3,5,8,13,21…
顺序:0,1,1,2,3,5,8,13,21…
The example provides details on a base case:
该示例提供了有关基本情况的详细信息:
F(0) = 0 , F(1) = 1
F(0)= 0,F(1)= 1
Thus, a possible base case:
因此,可能的基本情况是:
if (n==0 || n==1) return n
//or
if (n < 2) return nNext, think of the recursive step (self-recursive logic)
接下来,考虑一下递归步骤 (自递归逻辑)
Additional hints:
其他提示:
F(N) = F(N — 2) + F(N — 1)
F(N)= F(N_2)+ F(N_1)
Visualize the tree structure:
可视化树结构:
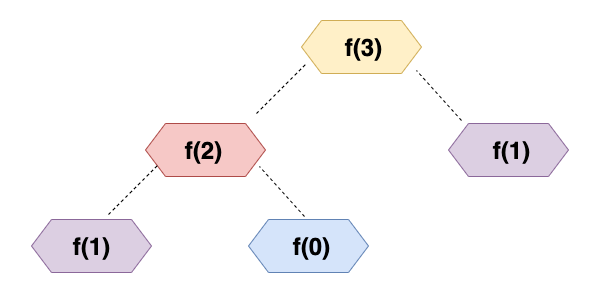
f(3) = f(2) + f(1) = f(1) + f(0) + f(1)The tree diagram: when fib(3) is invoked, will return 2.
树形图:调用fib(3)时,将返回2。
Putting it all together:
放在一起:
//possible solution
const fib = N => {
if (N < 2) return N; //base case
return fib(N - 2) + fib(N - 1);
};
Recursion logic too slow?
递归逻辑太慢了吗?
The solution can be improved using dynamic programming.
使用动态编程可以改善该解决方案。
Dive into memoization & dynamic programming!
潜入备忘录和动态编程!
Additional resource: https://web.mit.edu/6.005/www/fa15/classes/10-recursion/#reading_10_recursion
附加资源: https : //web.mit.edu/6.005/www/fa15/classes/10-recursion/#reading_10_recursion
感谢您的阅读! (Thank you for reading!)
翻译自: https://medium.com/@dhahm01/native-recursion-using-javascript-c0e9a16da8e0
javascript递归





















 1313
1313











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








