1.理论快速回顾
1.1 模型
当y>0.5时,z为TRUE,else 为False
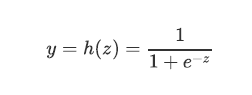
模型输出时,根据以上:1--TRUE,0--FALSE
1.2 损失函数

1.3 优化:梯度下降法
求导:

向量化

2.实战
2.1 实现逻辑回归类
import numpy as np
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score
class LogisticRegression(object):
def __init__(self):
""" 初始化Logistic Regression模型"""
self.coef=None
self.intercept=None
self._theta=None
def sigmoid(self,t):
return 1./(1.+np.exp(-t))
def fit(self,X_train,y_train,eta=0.01,n_iters=1e4):
'''使用梯度下降法训练logistic Regression模型 '''
assert X_train.shape[0]==y_train.shape[0]
''' 定义损失函数'''
def J(theta,X_b,y):
y_hat=self.sigmoid(X_b.dot(theta))
try:
return -np.sum(y*np.log(y_hat)+(1-y)*np.log(1-y_hat))/len(y)
except:
return float('inf')
''' 损失函数求导'''
def dJ(theta,X_b,y):
'''向量化后的公式 '''
return X_b.T.dot(self.sigmoid(X_b.dot(theta))-y)/len(y)
'''梯度下降函数'''
def gradient_descent(X_b,y,initial_theta,eta,n_iters=1e4,epsilon=1e-8):
theta=initial_theta
cur_iter=0
while cur_iter < n_iters:
gradient=dJ(theta,X_b,y)
last_theta=theta
theta=theta-eta*gradient
if abs(J(theta,X_b,y)-J(last_theta,X_b,y))<epsilon:
break
cur_iter+=1
return theta
X_b=np.hstack([np.ones((len(X_train),1)),X_train])
initial_theta=np.zeros(X_b.shape[1])
self._theta=gradient_descent(X_b,y_train,initial_theta,eta,n_iters)
#截距
self.intercept=self._theta[0]
# x_i前的参数
self.coef=self._theta[1:]
return self
''' 预测'''
def predict_proba(self,X_predict):
'''给定待预测数据集X_predict,返回表示X_predict的结果概率向量 '''
assert self.intercept is not None and self.coef is not None
'''must fit before predict '''
assert X_predict.shape[1]==len(self.coef)
'''the feature number of X_predict must be equal to X_train '''
X_b=np.hstack([np.ones((len(X_predict),1)),X_predict])
return self.sigmoid(X_b.dot(self._theta))
def predict(self,X_predict):
'''给定待预测数据集X_predict,返回表示X_predict的结果向量 '''
assert self.intercept is not None and self.coef is not None
assert X_predict.shape[1]==len(self.coef)
prob=self.predict_proba(X_predict)
return np.array(prob>=0.5,dtype='int')
def score(self,X_test,y_test):
"""根据测试数据集X_test和y_test确定当前模型的准确度"""
y_predict=self.predict(X_test)
return accuracy_score(y_test,y_predict)
def __repr__(self):
return "LogisticRegression()"
2.2用小数据集进行测试
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn import datasets
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
#取鸢尾花数据集
iris=datasets.load_iris()
X=iris.data
y=iris.target
# 筛选特征
X=X[y<2,:2]
y=y[y<2]
#绘制出图像
plt.scatter(X[y==0,0],X[y==0,1],color='red')
plt.scatter(X[y==1,0],X[y==1,1],color='blue')
plt.show()
# 切分数据集
X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test=train_test_split(X,y,random_state=666)
# 调用我们自己的逻辑回归函数
log_reg=LogisticRegression()
log_reg.fit(X_train,y_train)
print('final score is :%s'% log_reg.score(X_test,y_test))
print('actual prob is:')
print(log_reg.predict_proba(X_test))





















 690
690











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








