We describe an ordinal Probit model for post-secondary education choice and estiamted a simple model with the dependant variable of interest is PSECHOICE and the explanatory variable is GRADES(Lower numberical value of GRADES indicate better performance). We rank the college possibilities as follows:
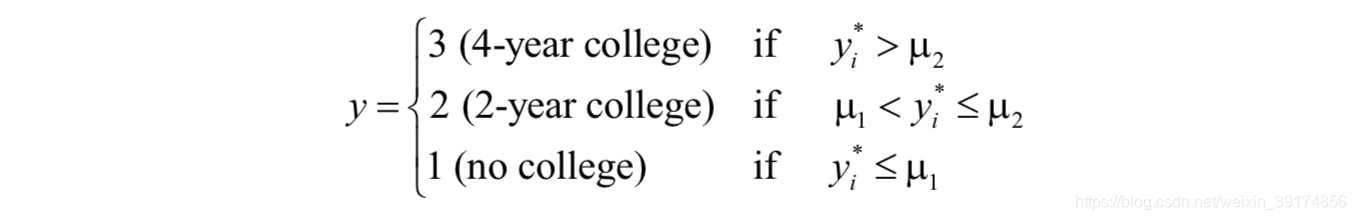 The following table shows the ordered Probit estimation results:
The following table shows the ordered Probit estimation results:

- Based on the estimated results in the above table, comment on the changes for probabilities of “2-year college” group and “no college” group when GRADES increases. Explain if they are consistent with your expectations.
Answer: when grades increases, the pr of the highest ranked choice (4-year) goes down, and the lowest ranked choice (no college)goes up, but difficult to say about 2 year college according to the formula of group 2. (According to marginal effect formula for group 1, we find that only sign of beta matter since the pdf is alwyas positive. These are consistent with the expectation.) - Compute the marginal effect of GRADES on the probability that a student with GRADES = 6 attends 2- year college.
For Ordered Probit model,
∂ P [ y = 2 ] ∂ x = [ ϕ ( μ 1 − β x ) − ϕ ( μ 2 − β x ) ] ∗ β ] = 0.0522 \frac{\partial P[y=2]}{\partial x}=[\phi(\mu_1-\beta x)-\phi(\mu_2-\beta x)]*\beta]=0.0522 ∂x∂P








 本文探讨了一个用于高等教育选择的有序Probit模型,其中依变量为PSECHOICE,自变量为成绩(成绩数值越小表示表现越好)。模型结果显示,随着成绩的提高,四年制大学的概率下降,不读大学的概率上升,但两年制大学的变化难以确定。进一步计算了成绩对两年制大学概率的边际效应,并通过似然比检验验证了家庭收入、家庭规模、种族和父母教育程度等变量的显著性。最终,根据给定条件计算了黑人学生进入四年制大学的概率。
本文探讨了一个用于高等教育选择的有序Probit模型,其中依变量为PSECHOICE,自变量为成绩(成绩数值越小表示表现越好)。模型结果显示,随着成绩的提高,四年制大学的概率下降,不读大学的概率上升,但两年制大学的变化难以确定。进一步计算了成绩对两年制大学概率的边际效应,并通过似然比检验验证了家庭收入、家庭规模、种族和父母教育程度等变量的显著性。最终,根据给定条件计算了黑人学生进入四年制大学的概率。
 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章

















 8649
8649

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








