onnx 的导出和分析
一、PyTorch 导出 ONNX 的方法
1.1、一个简单的例子 – 将线性模型转成 onnx
首先我们用 pytorch 定义一个线性模型,nn.Linear : 线性层执行的操作是 y = x * W^T + b,其中 x 是输入,W 是权重,b 是偏置。(实际上就是一个矩阵乘法)
class Model(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_features, out_features, weights, bias=False):
super().__init__()
self.linear = nn.Linear(in_features, out_features, bias)
with torch.no_grad():
self.linear.weight.copy_(weights)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.linear(x)
return x
然后我们再定义一个函数,用于导出 onnx
def export_onnx():
input = torch.zeros(1, 1, 1, 4)
weights = torch.tensor([
[1, 2, 3, 4],
[2, 3, 4, 5],
[3, 4, 5, 6]
],dtype=torch.float32)
model = Model(4, 3, weights)
model.eval() #添加eval防止权重继续更新
torch.onnx.export(
model = model,
args = (input,),
f = "model.onnx",
input_names = ["input0"],
output_names = ["output0"],
opset_version = 12)
print("Finished onnx export")
可以看到,这里面的关键在函数 torch.onnx.export(),这是 pytorch 导出 onnx 的基本方式,这个函数的参数有很多,但只要一些基本的参数即可导出模型,下面是一些基本参数的定义:
- model (torch.nn.Module): 需要导出的PyTorch模型
- args (tuple or Tensor): 一个元组,其中包含传递给模型的输入张量
- f (str): 要保存导出模型的文件路径。
- input_names (list of str): 输入节点的名字的列表
- output_names (list of str): 输出节点的名字的列表
- opset_version (int): 用于导出模型的 ONNX 操作集版本
最后我们完整的运行一下代码:
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.onnx
class Model(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_features, out_features, weights, bias=False):
super().__init__()
self.linear = nn.Linear(in_features, out_features, bias)
with torch.no_grad():
self.linear.weight.copy_(weights)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.linear(x)
return x
def export_onnx():
input = torch.zeros(1, 1, 1, 4)
weights = torch.tensor([
[1, 2, 3, 4],
[2, 3, 4, 5],
[3, 4, 5, 6]
],dtype=torch.float32)
model = Model(4, 3, weights)
model.eval() #添加eval防止权重继续更新
torch.onnx.export(
model = model,
args = (input,),
f = "model.onnx",
input_names = ["input0"],
output_names = ["output0"],
opset_version = 12)
print("Finished onnx export")
if __name__ == "__main__":
export_onnx()
导出模型后,我们用 netron 查看模型,在终端输入
netron model.onnx

1.2、导出多个输出头的模型
第一步:定义一个多输出的模型:
class Model(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_features, out_features, weights1, weights2, bias=False):
super().__init__()
self.linear1 = nn.Linear(in_features, out_features, bias)
self.linear2 = nn.Linear(in_features, out_features, bias)
with torch.no_grad():
self.linear1.weight.copy_(weights1)
self.linear2.weight.copy_(weights2)
def forward(self, x):
x1 = self.linear1(x)
x2 = self.linear2(x)
return x1, x2
第二步:编写导出 onnx 的函数
def export_onnx():
input = torch.zeros(1, 1, 1, 4)
weights1 = torch.tensor([
[1, 2, 3, 4],
[2, 3, 4, 5],
[3, 4, 5, 6]
],dtype=torch.float32)
weights2 = torch.tensor([
[2, 3, 4, 5],
[3, 4, 5, 6],
[4, 5, 6, 7]
],dtype=torch.float32)
model = Model(4, 3, weights1, weights2)
model.eval() #添加eval防止权重继续更新
torch.onnx.export(
model = model,
args = (input,),
f = "model.onnx",
input_names = ["input0"],
output_names = ["output0", "output1"],
opset_version = 12)
print("Finished onnx export")
可以看到,和例 1.1 不一样的地方是 torch.onnx.export 的 output_names
例1.1:output_names = [“output0”]
例1.2:output_names = [“output0”, “output1”]
运行一下完整代码:
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.onnx
class Model(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_features, out_features, weights1, weights2, bias=False):
super().__init__()
self.linear1 = nn.Linear(in_features, out_features, bias)
self.linear2 = nn.Linear(in_features, out_features, bias)
with torch.no_grad():
self.linear1.weight.copy_(weights1)
self.linear2.weight.copy_(weights2)
def forward(self, x):
x1 = self.linear1(x)
x2 = self.linear2(x)
return x1, x2
def export_onnx():
input = torch.zeros(1, 1, 1, 4)
weights1 = torch.tensor([
[1, 2, 3, 4],
[2, 3, 4, 5],
[3, 4, 5, 6]
],dtype=torch.float32)
weights2 = torch.tensor([
[2, 3, 4, 5],
[3, 4, 5, 6],
[4, 5, 6, 7]
],dtype=torch.float32)
model = Model(4, 3, weights1, weights2)
model.eval() #添加eval防止权重继续更新
torch.onnx.export(
model = model,
args = (input,),
f = "model.onnx",
input_names = ["input0"],
output_names = ["output0", "output1"],
opset_version = 12)
print("Finished onnx export")
if __name__ == "__main__":
export_onnx()
用 netron 查看模型,结果如下,模型多出了一个输出结果

1.3、导出含有动态维度的模型
完整运行代码如下:
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.onnx
class Model(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_features, out_features, weights, bias=False):
super().__init__()
self.linear = nn.Linear(in_features, out_features, bias)
with torch.no_grad():
self.linear.weight.copy_(weights)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.linear(x)
return x
def export_onnx():
input = torch.zeros(1, 1, 1, 4)
weights = torch.tensor([
[1, 2, 3, 4],
[2, 3, 4, 5],
[3, 4, 5, 6]
],dtype=torch.float32)
model = Model(4, 3, weights)
model.eval() #添加eval防止权重继续更新
torch.onnx.export(
model = model,
args = (input,),
f = "model.onnx",
input_names = ["input0"],
output_names = ["output0"],
dynamic_axes = {
'input0': {0: 'batch'},
'output0': {0: 'batch'}
},
opset_version = 12)
print("Finished onnx export")
if __name__ == "__main__":
export_onnx()
可以看到,比例 1.1 多了一行 torch.onnx.export 的 dynamic_axes 。我们可以用 dynamic_axes 来指定动态维度,其中 'input0': {0: 'batch'} 中的 0 表示在第 0 维度上的元素是动态的,这里取名为 ‘batch’
用 netron 查看模型:

可以看到相对于例1.1,他的维度 0 变成了动态的,并且名为 ‘batch’
二、pytorch 导出 onnx 不成功的时候如何解决
上面是 onnx 可以直接被导出的情况,是因为对应的 pytorch 和 onnx 版本都有相应支持的算子在里面。但是有些时候,我们不能顺利的导出 onnx,下面记录一下常见的解决思路 。
2.1、修改 opset 的版本
这是首先应该考虑的思路,因为有可能只是版本过低然后有些算子还不支持,所以考虑提高 opset 的版本。
比如下面的这个报错,提示当前 onnx 的 opset 版本不支持这个算子,那我们可以去官方手册搜索一下是否在高的版本支持了这个算子
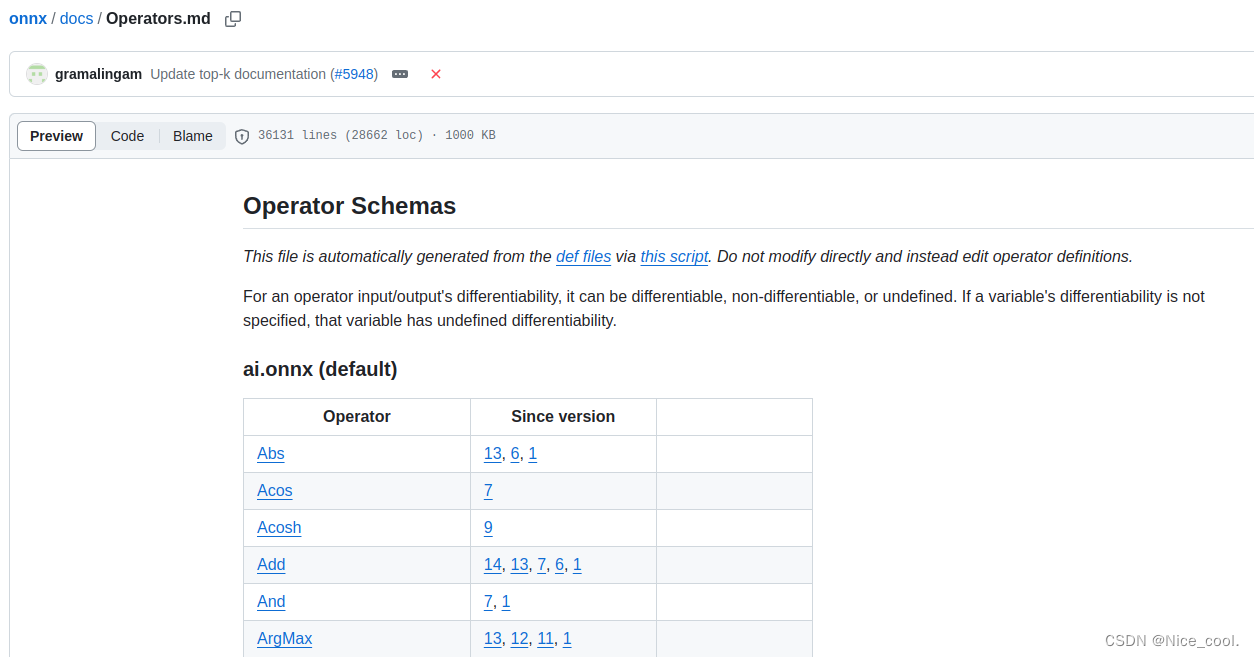
官方手册地址:https://github.com/onnx/onnx/blob/main/docs/Operators.md
又比如说 Acosh 这个算子,在 since version 9 才开始支持,那我们用 7 的时候就是不合适的,升级 opset 版本即可
2.2、替换 pytorch 中的算子组合
有些时候 pytorch 中的一些算子操作在 onnx 中并没有,那我们可以把这些算子替换成 onnx 支持的算子
2.3、在 pytorch 登记( 注册 ) onnx 中某些算子
案例一:
有些算子在 onnx 中是有的,但是在 pytorch 中没被登记,则需要注册一下
比如下面这个案例,我们想要导出 asinh 这个算子的模型
import torch
import torch.onnx
class Model(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
def forward(self, x):
x = torch.asinh(x)
return x
def export_norm_onnx():
input = torch.rand(1, 5)
model = Model()
model.eval()
file = "asinh.onnx"
torch.onnx.export(
model = model,
args = (input,),
f = file,
input_names = ["input0"],
output_names = ["output0"],
opset_version = 9)
print("Finished normal onnx export")
if __name__ == "__main__":
export_norm_onnx()
但是报错,提示 opset_version = 9 不支持这个算子

但是我们打开官方手册去搜索发现 asinh 在 version 9 又是支持的
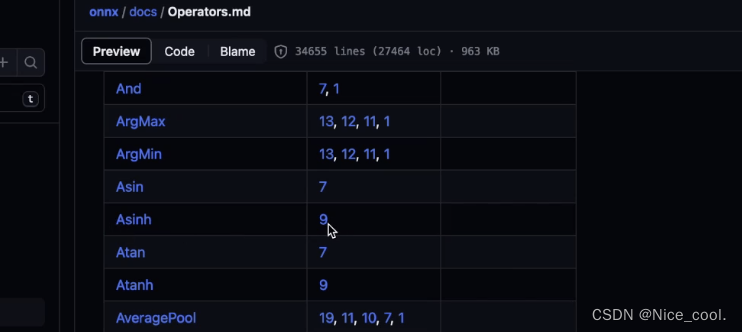
这里的问题是 PyTorch 与 onnx 之间没有建立 asinh 的映射 (没有搭建桥梁),所以我们编写一个注册代码,来手动注册一下这个算子
2.3.1、注册方法一
完整代码如下:
import torch
import torch.onnx
import onnxruntime
from torch.onnx import register_custom_op_symbolic
def asinh_symbolic(g, input, *, out=None):
return g.op("Asinh", input)
register_custom_op_symbolic('aten::asinh', asinh_symbolic, 12)
class Model(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
def forward(self, x):
x = torch.asinh(x)
return x
def validate_onnx():
input = torch.rand(1, 5)
# PyTorch的推理
model = Model()
x = model(input)
print("result from Pytorch is :", x)
# onnxruntime的推理
sess = onnxruntime.InferenceSession('asinh.onnx')
x = sess.run(None, {'input0': input.numpy()})
print("result from onnx is: ", x)
def export_norm_onnx():
input = torch.rand(1, 5)
model = Model()
model.eval()
file = "asinh.onnx"
torch.onnx.export(
model = model,
args = (input,),
f = file,
input_names = ["input0"],
output_names = ["output0"],
opset_version = 12)
print("Finished normal onnx export")
if __name__ == "__main__":
export_norm_onnx()
# 自定义完onnx以后必须要进行一下验证
validate_onnx()
这段代码的关键在于 算子的注册:
1、定义 asinh_symbolic 函数
def asinh_symbolic(g, input, *, out=None):
return g.op("Asinh", input)
- 函数必须是 asinh_symbolic 这个名字
- g: 就是 graph,计算图 (在计算图中添加onnx算子)
- input :symblic的参数需要与Pytorch的asinh接口函数的参数对齐
(def asinh( input: Tensor, *, out: Optional[Tensor]=None) -> Tensor: … )- 符号函数内部调用 g.op, 为 onnx 计算图添加 Asinh 算子
- g.op中的第一个参数是onnx中的算子名字: Asinh
2、使用 register_custom_op_symbolic 函数
register_custom_op_symbolic('aten::asinh', asinh_symbolic, 12)
- aten 是"a Tensor Library"的缩写,是一个实现张量运算的C++库
- asinh 是在名为 aten 的一个c++命名空间下进行实现的
- 将 asinh_symbolic 这个符号函数,与PyTorch的 asinh 算子绑定
- register_op 中的第一个参数是PyTorch中的算子名字: aten::asinh
- 最后一个参数表示从第几个 opset 开始支持(可自己设置)
3、自定义完 onnx 以后必须要进行一下验证,可使用 onnxruntime
2.3.2、注册方法二
import torch
import torch.onnx
import onnxruntime
import functools
from torch.onnx import register_custom_op_symbolic
from torch.onnx._internal import registration
_onnx_symbolic = functools.partial(registration.onnx_symbolic, opset=9)
@_onnx_symbolic('aten::asinh')
def asinh_symbolic(g, input, *, out=None):
return g.op("Asinh", input)
class Model(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
def forward(self, x):
x = torch.asinh(x)
return x
def validate_onnx():
input = torch.rand(1, 5)
# PyTorch的推理
model = Model()
x = model(input)
print("result from Pytorch is :", x)
# onnxruntime的推理
sess = onnxruntime.InferenceSession('asinh2.onnx')
x = sess.run(None, {'input0': input.numpy()})
print("result from onnx is: ", x)
def export_norm_onnx():
input = torch.rand(1, 5)
model = Model()
model.eval()
file = "asinh2.onnx"
torch.onnx.export(
model = model,
args = (input,),
f = file,
input_names = ["input0"],
output_names = ["output0"],
opset_version = 12)
print("Finished normal onnx export")
if __name__ == "__main__":
export_norm_onnx()
# 自定义完onnx以后必须要进行一下验证
validate_onnx()
与上面例子不同的是,这个注册方式跟底层文件的写法是一样的(文件在虚拟环境中的 torch/onnx/symbolic_opset*.py )
通过torch._internal 中的 registration 来注册这个算子,让这个算子可以与底层C++实现的 aten::asinh 绑定
_onnx_symbolic = functools.partial(registration.onnx_symbolic, opset=9)
@_onnx_symbolic('aten::asinh')
def asinh_symbolic(g, input, *, out=None):
return g.op("Asinh", input)
案例二:
对于下面这个案例,我们想导出这个算子,这个算子在pytorch 中是存在的,并且可以运行 ,但是直接导出会报错
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torchvision
import torch.onnx
class Model(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(3, 18, 3)
self.conv2 = torchvision.ops.DeformConv2d(3, 3, 3)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.conv2(x, self.conv1(x))
return x
def infer():
input = torch.rand(1, 3, 5, 5)
model = Model()
x = model(input)
print("input is: ", input.data)
print("result is: ", x.data)
def export_norm_onnx():
input = torch.rand(1, 3, 5, 5)
model = Model()
model.eval()
file = "../models/sample-deformable-conv.onnx"
torch.onnx.export(
model = model,
args = (input,),
f = file,
input_names = ["input0"],
output_names = ["output0"],
opset_version = 12)
print("Finished normal onnx export")
if __name__ == "__main__":
infer()
export_norm_onnx()
运行报错如下:torchvision.ops.DeformConv2d 这个算子无法被识别

所以我们需要注册一下,写一个注册函数:
@parse_args("v", "v", "v", "v", "v", "i", "i", "i", "i", "i","i", "i", "i", "none")
def dcn_symbolic(
g,
input,
weight,
offset,
mask,
bias,
stride_h, stride_w,
pad_h, pad_w,
dil_h, dil_w,
n_weight_grps,
n_offset_grps,
use_mask):
return g.op("custom::deform_conv2d", input, offset)
register_custom_op_symbolic("torchvision::deform_conv2d", dcn_symbolic, 12)
注意:
- 这里需要把args的各个参数的类型都指定
- 注册的时候指定
"torchvision::deform_conv2d"和dcn_symbolic绑定 dcn_symbolic的每个参数要跟"torchvision::deform_conv2d"一一对应
2.4、直接修改 onnx,创建 plugin
直接手动创建一个 onnx (这是一个思路,会在后续博客进行总结记录)






















 3823
3823











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








