b站刘二大人《PyTorch深度学习实践》课程第十一讲循环神经网络(基础篇 + 高级篇)笔记与代码:
https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1Y7411d7Ys?p=12&vd_source=b17f113d28933824d753a0915d5e3a90
https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1Y7411d7Ys?p=13&spm_id_from=pageDriver&vd_source=b17f113d28933824d753a0915d5e3a90
markdown笔记:https://github.com/Jian-wei-peng/StudyNotes/tree/main/DRL/%E5%88%98%E4%BA%8Cpytorch%E6%B7%B1%E5%BA%A6%E5%AD%A6%E4%B9%A0
一、循环神经网络基础篇
回顾
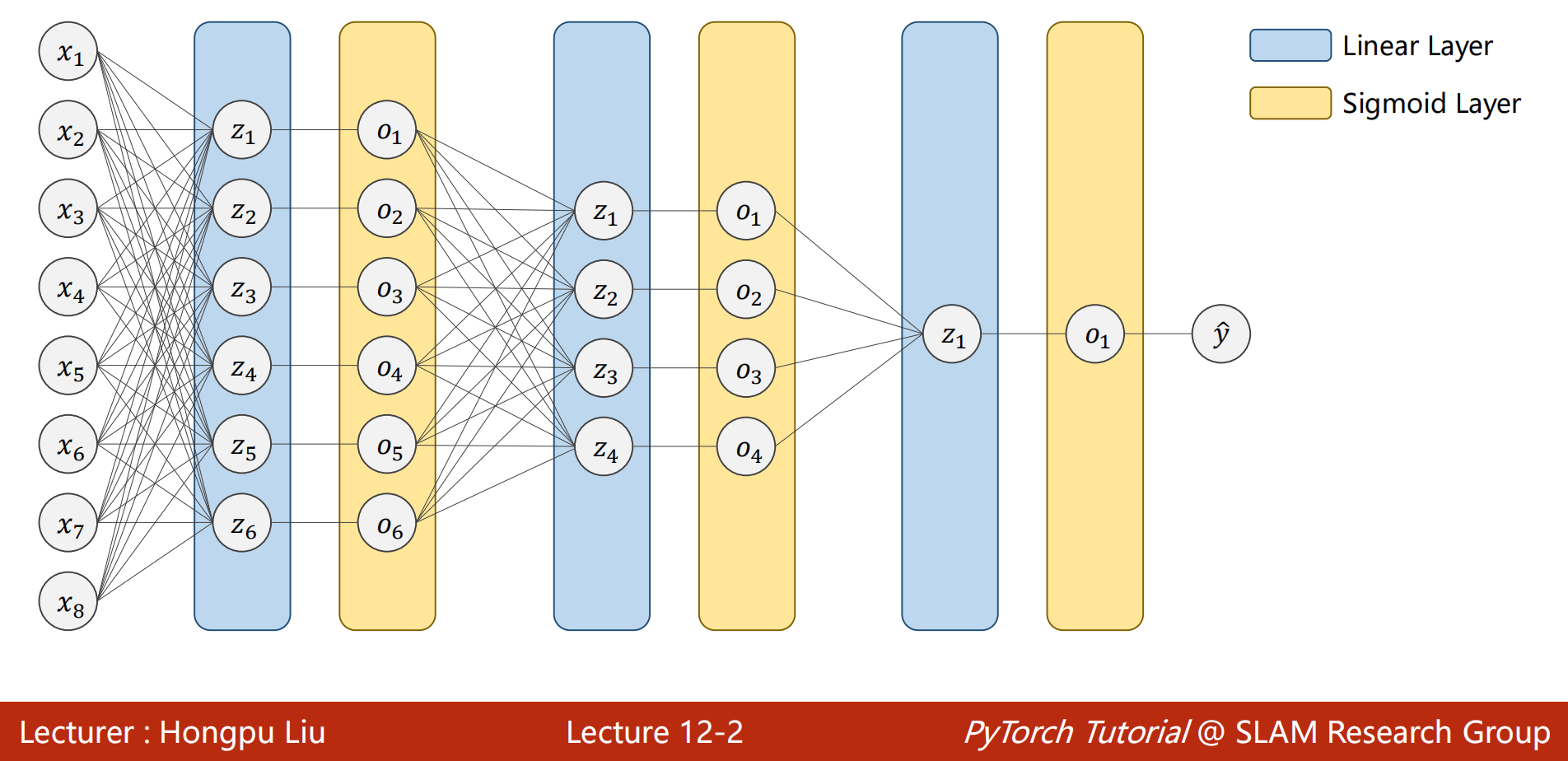
- 之前构建使用的神经网络都是稠密神经网络(Dense Neural Network)或者称为深度神经网络(Deep Neural Network)
- 有很多的线性层,对输入的数据进行空间上的变换
- $x_1 到 到 到 x_8$是样本的8个特征
-
另一种场景:
-
假设有一个关于是否下雨的数据集,包含每一天的温度、气压和天气情况的数据,是否下雨与温度和气压有关。需要根据这些数据来预测是否下雨
-
如果要预测今天是否下雨,那么就需要根据历史天气情况数据进行预测,而不是今天的温度和气压数据
- 用过去三天的数据预测今天的,那么输入的数据就是 X = [ x 1 , x 2 , x 3 ] X = [x_1, x_2, x_3] X=[x1,x2,x3],每个 x x x又包含了温度、气压和是否下雨三个数据

-
如果采用全连接神经网络,那就把 [ x 1 , x 2 , x 3 ] [x_1, x_2, x_3] [x1,x2,x3]拼成一个有9个维度的长向量来进行训练
- 如果输入序列很长,而且每个序列的维度很高,对稠密的神经网络而言(例如全连接网络)非常难训练,计算量很大
-
RNN就是专门用于处理带有序列模式的数据,其中也采用了权重共享的概念来减少需要训练的权重数量
- 将 x 1 x_1 x1, x 2 x_2 x2, x 3 x_3 x3看成一个序列,在使用的时候不仅要考虑 x 1 x_1 x1和 x 2 x_2 x2之间的连接关系,还要考虑到这些数据之间存在先后的时间顺序,即 x 2 x_2 x2依赖于 x 1 x_1 x1, x 3 x_3 x3依赖于 x 2 x_2 x2
- RNN主要用于处理具有序列关系的数据,如天气、股市、自然语言等等

-
-
RNN Cell
-
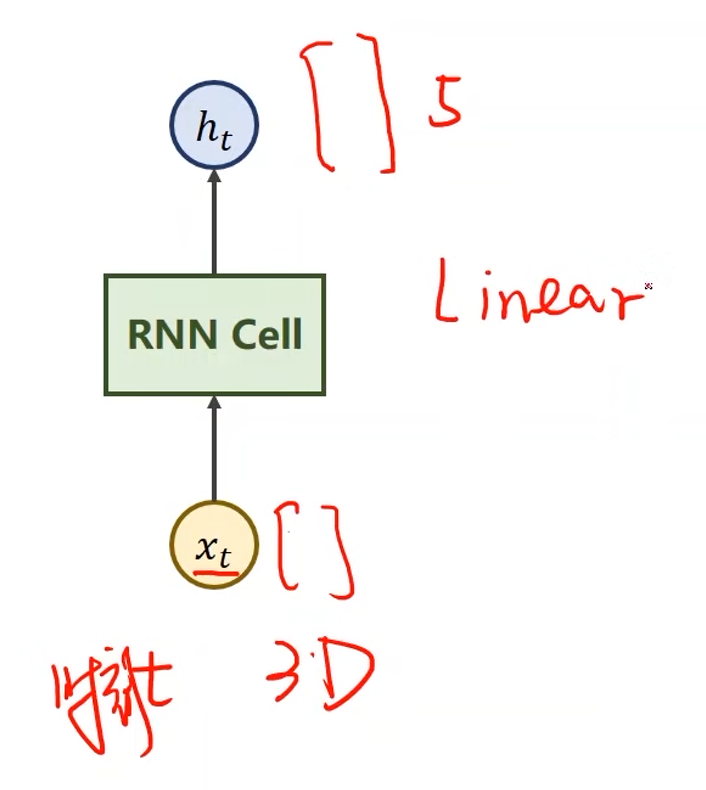
x t x_t xt表示序列当中时刻 t t t的数据,经过RNN Cell之后得到另外一个维度的向量 h t h_t ht,例如从三维变五维,那么这也说明RNN Cell的本质是一个线性层
- 与一般的线性层的区别是RNN Cell是共享的
-
假设 x 1 x_1 x1, x 2 x_2 x2, x 3 x_3 x3, x 4 x_4 x4是输入序列,输入到RNN Cell中进行一个线性变换得到输出 h h h,输出也称为 h i d d e n hidden hidden,隐藏层

- 序列之间存在关联,那么在输入 x 2 x_2 x2求 h 2 h_2 h2的时候不仅要包含 x 2 x_2 x2的信息,还要包含 x 1 x_1 x1的信息,需要进行信息融合(图中红色箭头)
- 对于 x 1 x_1 x1也需要一个输入的 h 0 h_0 h0(表示先验知识),如果没有先验知识,则输入一个与 h 1 h_1 h1, h 2 h_2 h2等的维度相等的全零向量
-
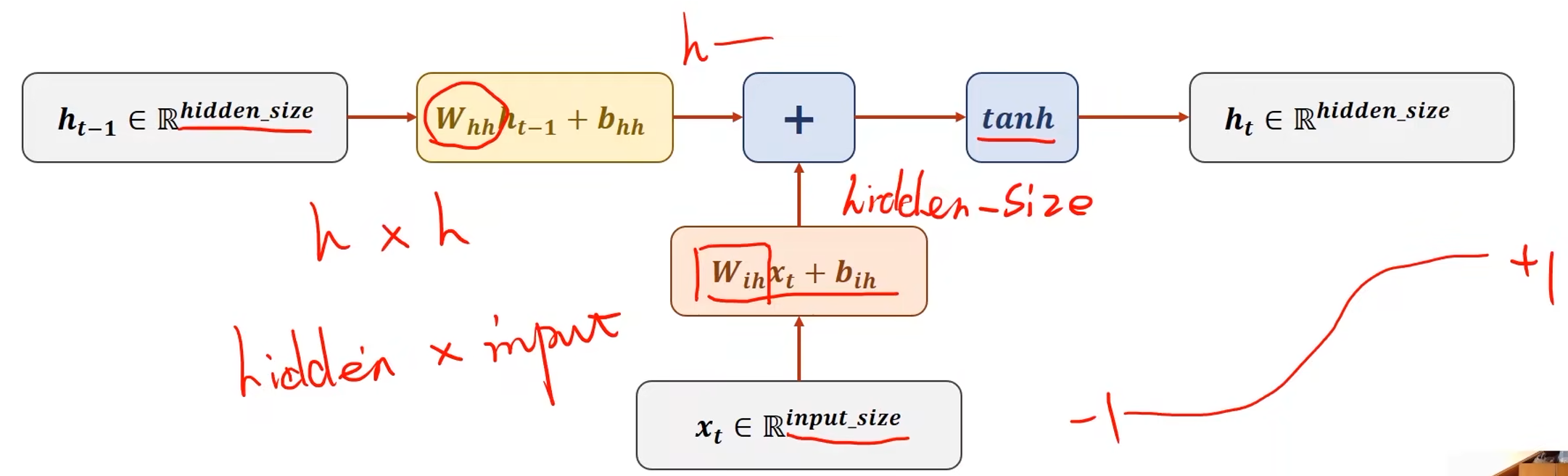
input_size:输入维度
-
hidden_size:隐藏层维度
-
权重 w i h w_{ih} wih的维度是hidden_size*input_size,这样与输入序列 x t x_t xt相乘后才能得到维度为hidden_size*1的向量
-
权重 w h h w_{hh} whh的维度是hidden_size*hidden_size,与 h t − 1 h_{t-1} ht−1相乘后得到维度为hidden_size*1的向量
-
RNN Cell中将两个维度为hidden_size*1的向量相加即可融合 h h h和 x x x的信息,然后再用 t a n h tanh tanh做激活,最终计算得到 h t h_t ht
-
注意:
-
w h h h t − 1 + b h h w_{hh}h_{t-1} + b_{hh} whhht−1+bhh和 w i h x t + b i h w_{ih}x_{t} + b_{ih} wihxt+bih可以整合到一起

-
在构建RNN Cell的时候,实际上是将 x t x_t xt和 h t − 1 h_{t-1} ht−1拼接起来,组成一个维度为(hidden_size+input_size)*1的向量,那么权重就是一个维度为hidden_size * (hidden_size + input_size)的矩阵,因此RNN Cell本质上就是一个线性层

-
RNN Cell的实现
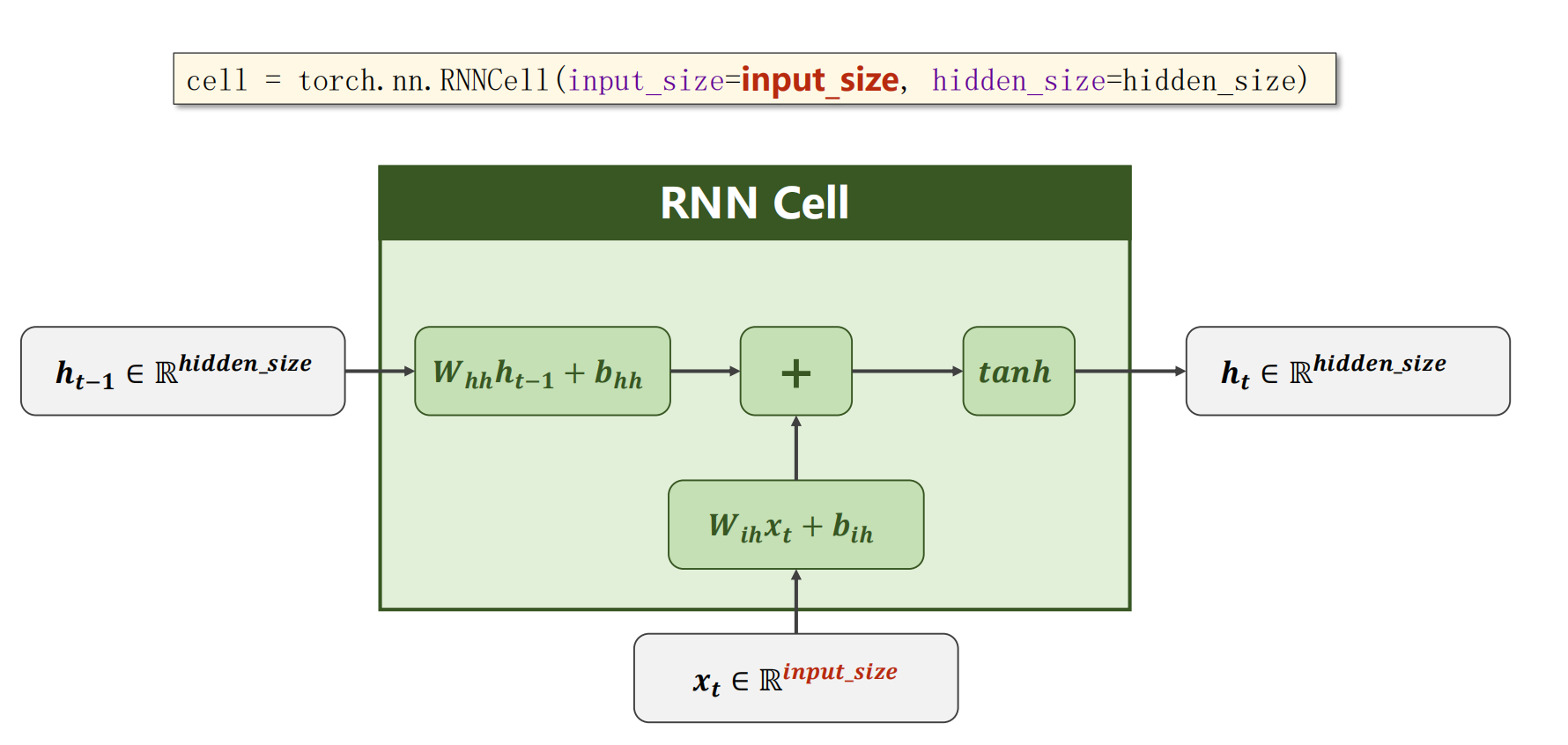
cell = torch.nn.RNNCell(input_size=input_size, hidden_size=hidden_size) # 两个参数都是输入维度
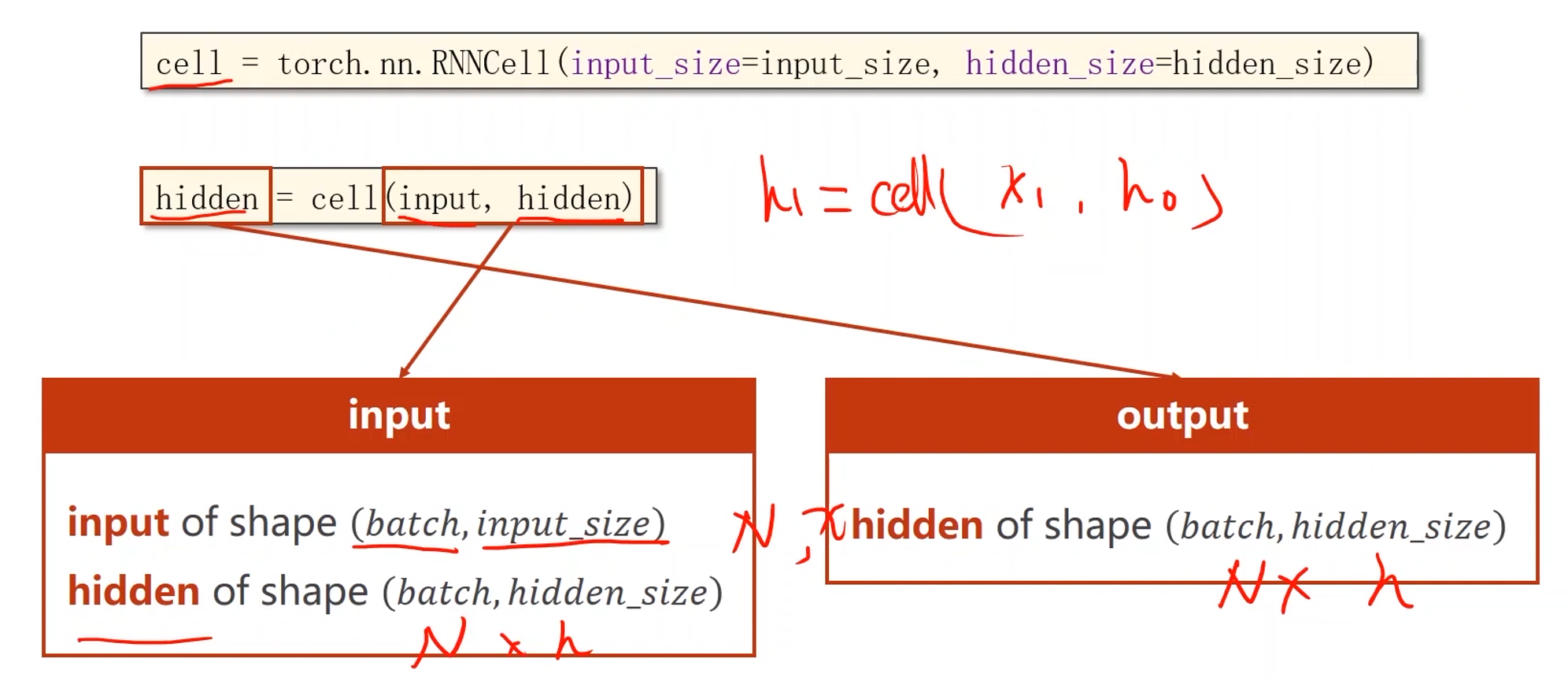
例子:
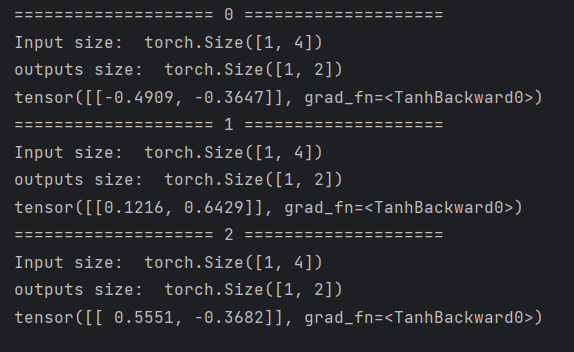
- 假设有一个序列,batchSize = 1,序列长度为3,输入维度为4,输出维度为2
import torch
batch_size = 1
seq_len = 3
input_size = 4
hidden_size = 2
# 构造RNNCell
cell = torch.nn.RNNCell(input_size=input_size, hidden_size=hidden_size)
# (seq, batch, features)
dataset = torch.randn(seq_len, batch_size, input_size)
# 将隐层初始化为0
hidden = torch.zeros(batch_size, hidden_size)
for idx, input in enumerate(dataset):
print('=' * 20, idx, '=' * 20)
print('Input size: ', input.shape)
hidden = cell(input, hidden)
print('outputs size: ', hidden.shape)
print(hidden)
RNN的实现
# input_size输入序列维度,hidden_size是隐层维度
# num_layers是RNN的层数(需要注意的是RNN的运算是很耗时的)
cell = torch.nn.RNN(input_size=input_size, hidden_size=hidden_size, num_layers=num_layers)
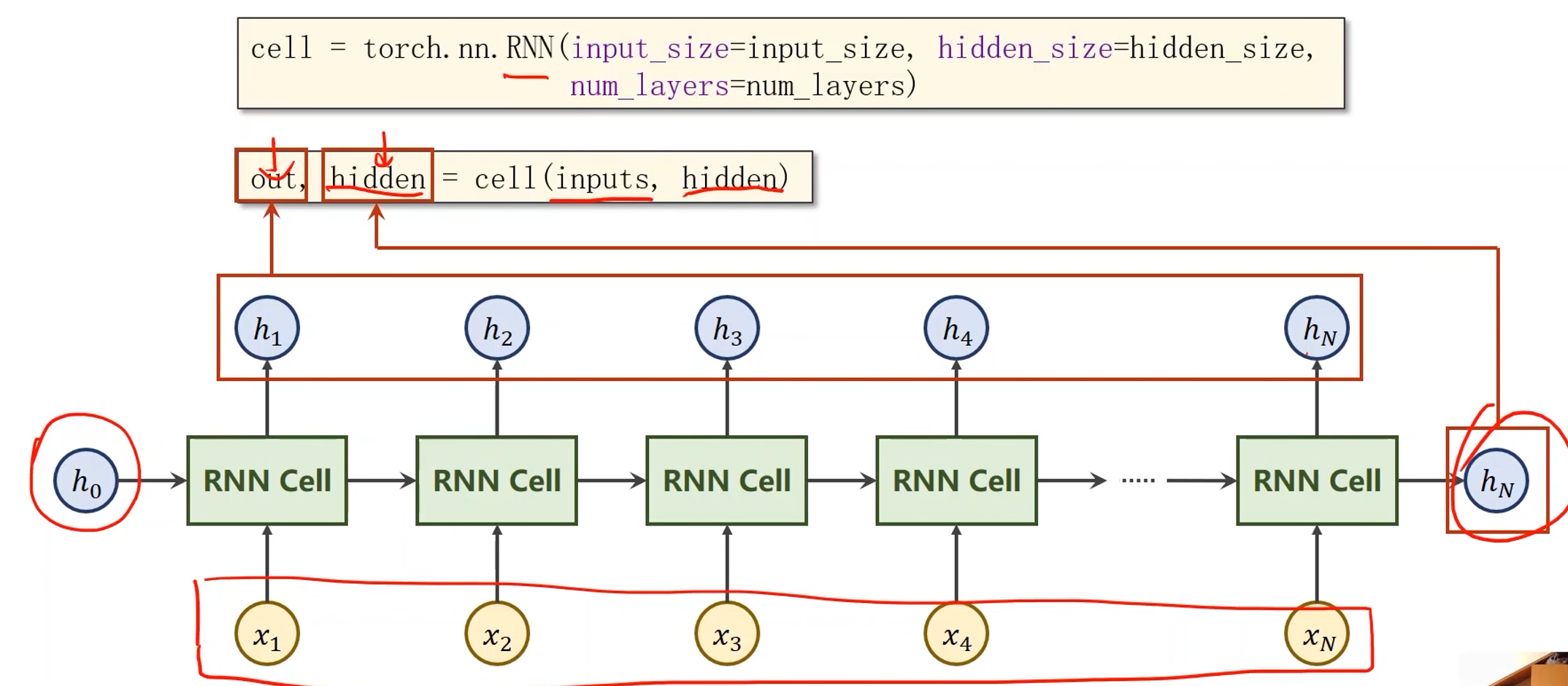
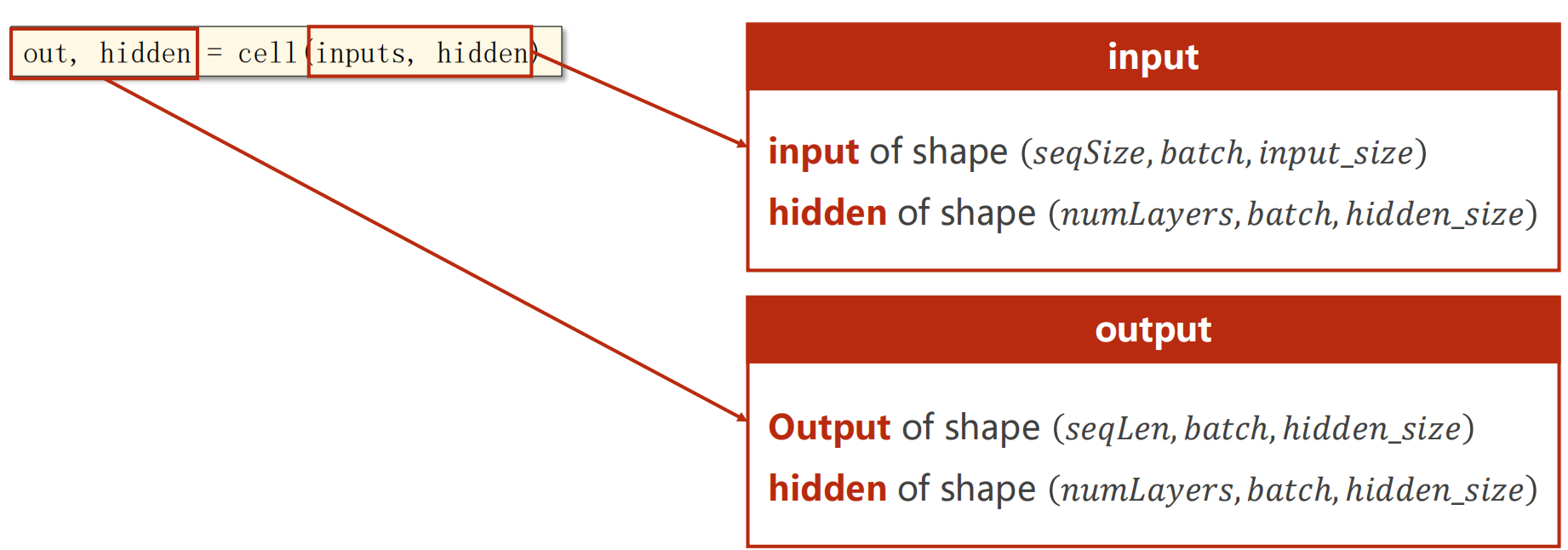
- cell的输入inputs是所有的序列( x 1 x_1 x1, x 2 x_2 x2, x 3 x_3 x3,…, x N x_N xN),hidden是 h 0 h_0 h0
- cell的输出out是所有的隐层输出( h 1 h_1 h1, h 2 h_2 h2, h 3 h_3 h3,…, h N h_N hN),hidden是 h N h_N hN
numLayers:
- 同样颜色的RNN Cell是相同的,因此下图中只有三个线性层
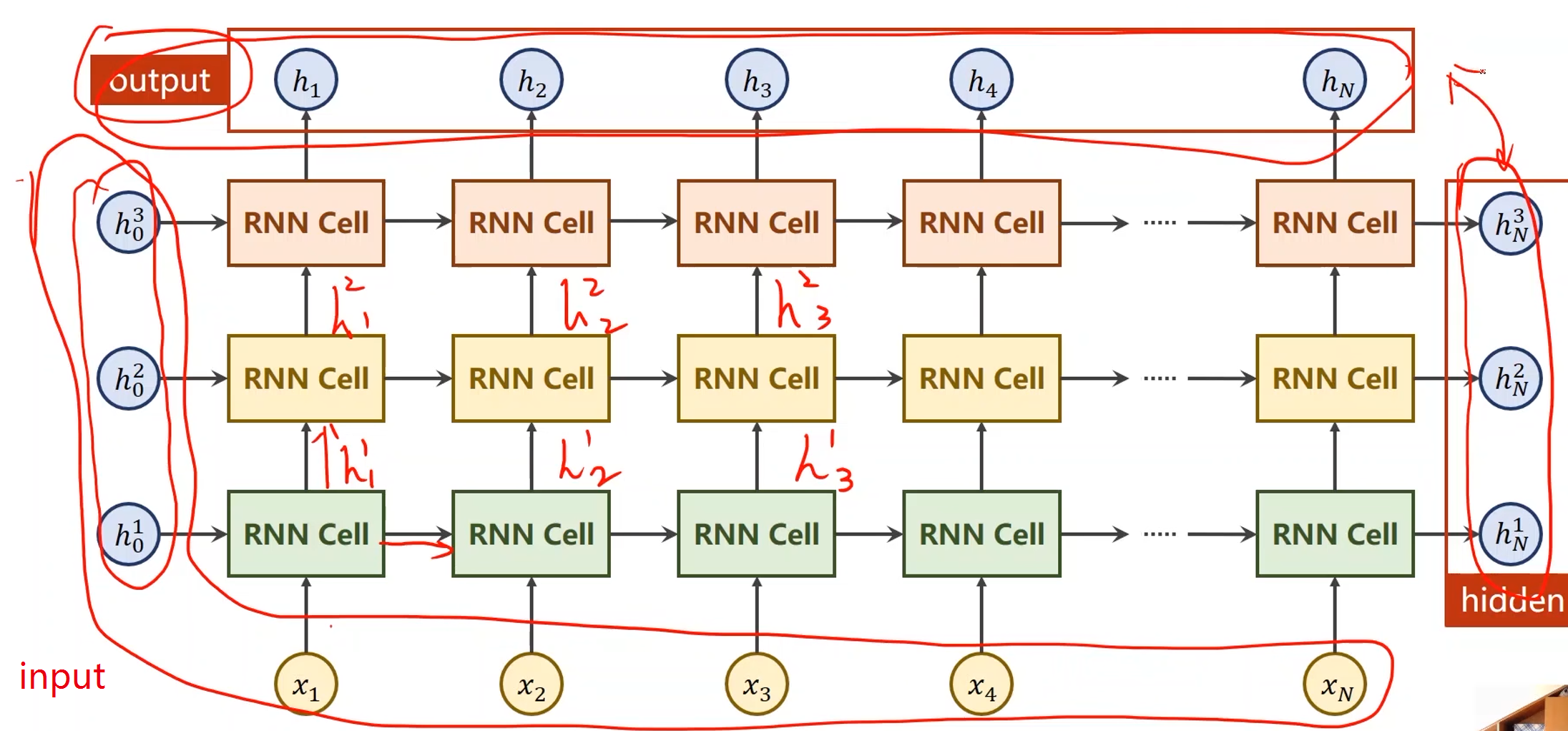
import torch
# 参数
batch_size = 1
seq_len = 3
input_size = 4
hidden_size = 2
num_layers = 1
# 构造RNN
cell = torch.nn.RNN(input_size=input_size, hidden_size=hidden_size,
num_layers=num_layers)
# (seqLen, batchSize, inputSize)
inputs = torch.randn(seq_len, batch_size, input_size)
# 将隐层初始化为0
hidden = torch.zeros(num_layers, batch_size, hidden_size)
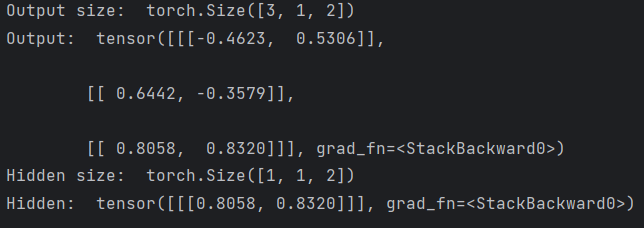
out, hidden = cell(inputs, hidden)
print('Output size: ', out.shape)
print('Output: ', out)
print('Hidden size: ', hidden.shape)
print('Hidden: ', hidden)
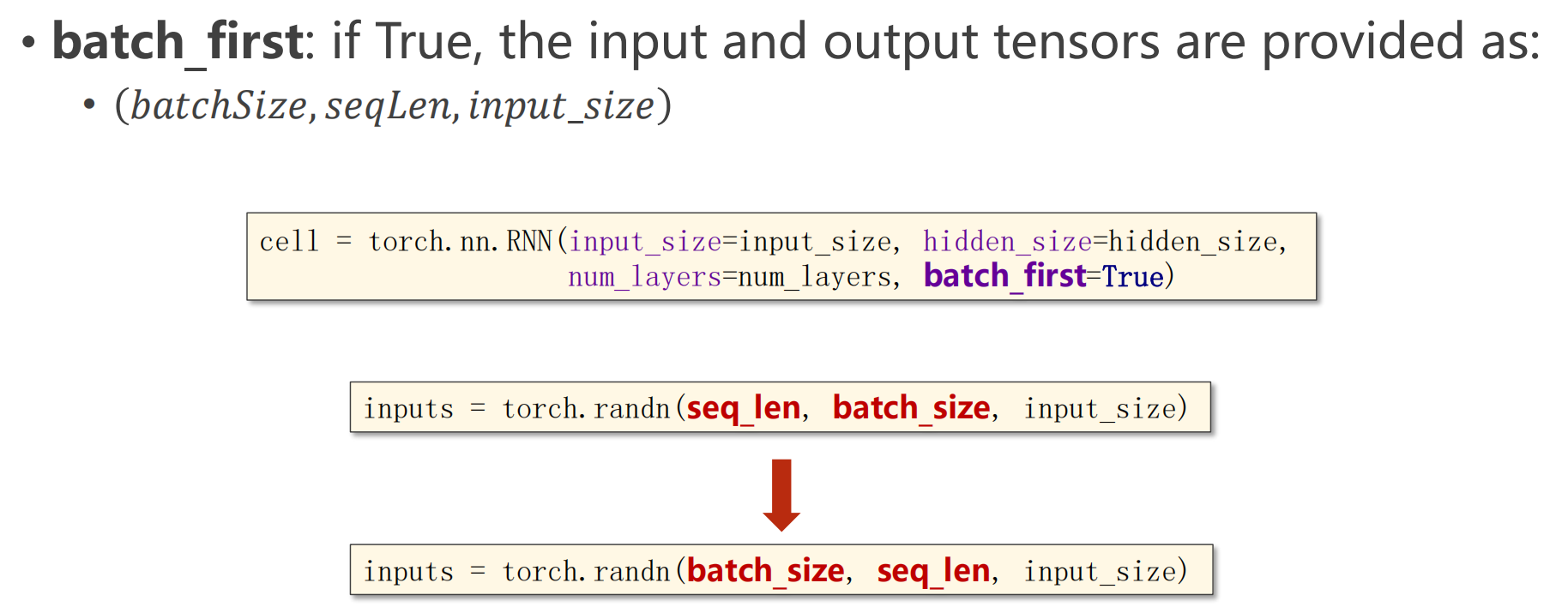
- batch_first设置为True,那么要把参数batch_size放在第一位

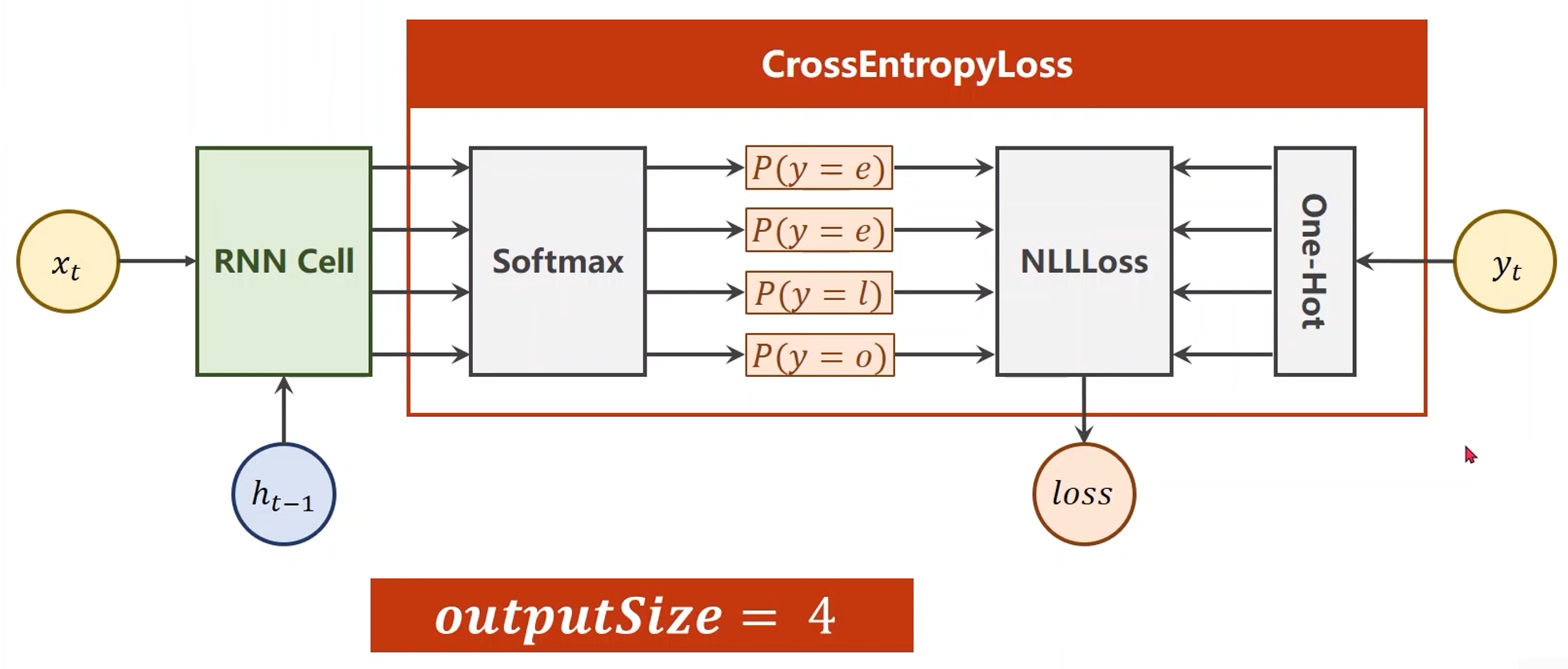
例子 —— 使用RNNCell:
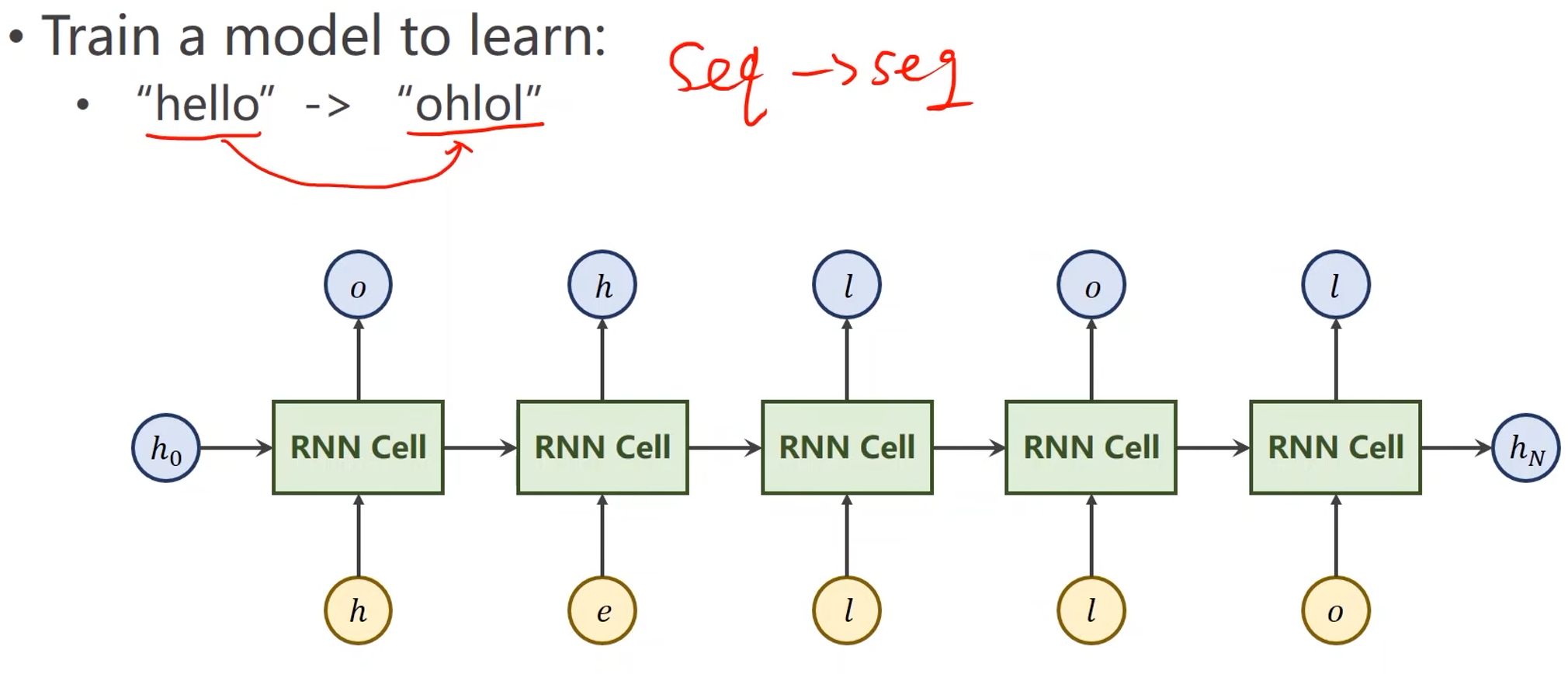
-
例子中的字符并不是向量,直接输入的话无法计算,因此第一步要先将这些字符向量化
- 先根据字符构造一个词典,给每个词分配一个索引
- 再根据词典将输入字符变成相应的索引
- 最后将索引转成向量(宽度等于词典的元素数量,高度等于输入字符数量)
- 如果索引值为1,那么除了1以外其他的值都为0,即0100
- 向量化处理得到的结果称为独热向量One-Hot Vectors
- inputSize=4,输入维度是向量的宽度(列数)

代码实现:
-
定义参数
import torch input_size = 4 hidden_size =4 batch_size = 1 -
准备数据集
# 数据集 idx2char = ['e', 'h', 'l', 'o'] # 词典 x_data = [1, 0, 2, 2, 3] # 输入序列hello y_data = [3, 1, 2, 3, 2] # 输出序列ohlol # 将输入字符的索引转成独热向量 one_hot_lookup = [[1, 0, 0, 0], [0, 1, 0, 0], [0, 0, 1, 0], [0, 0, 0, 1]] x_one_hot = [one_hot_lookup[x] for x in x_data] # reshape the inputs to (seqLen, batchSize, inputSize),-1的意思是自动计算 inputs = torch.Tensor(x_one_hot).view(-1, batch_size, input_size) # reshape the labels to (seqLen, 1) labels = torch.LongTensor(y_data).view(-1, 1) -
构造模型
class Model(torch.nn.Module): def __init__(self, input_size, hidden_size, batch_size): super(Model, self).__init__() # 初始化参数 self.batch_size = batch_size self.input_size = input_size self.hidden_size = hidden_size # 构造RNN Cell self.rnncell = torch.nn.RNNCell(input_size=self.input_size, hidden_size=self.hidden_size) def forward(self, input, hidden): hidden = self.rnncell(input, hidden) return hidden def init_hidden(self): # 将隐层初始化为零。仅在构造h_0的时候会用上 return torch.zeros(self.batch_size, self.hidden_size) net = Model(input_size, hidden_size, batch_size) -
构造损失和优化器
# Loss and Optimizer criterion = torch.nn.CrossEntropyLoss() optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(net.parameters(), lr=0.1) -
训练
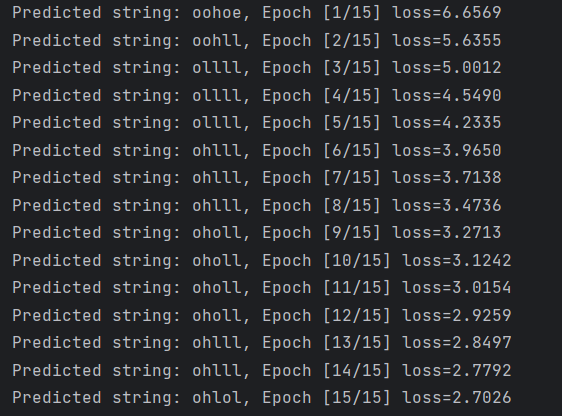
# Trainning steps for epoch in range(15): loss = 0 optimizer.zero_grad() hidden = net.init_hidden() print('Predicted string: ', end='') for input, label in zip(inputs, labels): hidden = net(input, hidden) loss += criterion(hidden, label) _, idx = hidden.max(dim=1) print(idx2char[idx.item()], end='') loss.backward() optimizer.step() print(', Epoch [%d/15] loss=%.4f' % (epoch+1, loss.item()))
完整代码:
import torch
# 参数
input_size = 4
hidden_size =4
batch_size = 1
# 数据集
idx2char = ['e', 'h', 'l', 'o'] # 词典
x_data = [1, 0, 2, 2, 3] # 输入序列hello
y_data = [3, 1, 2, 3, 2] # 输出序列ohlol
# 将输入字符的索引转成独热向量
one_hot_lookup = [[1, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 1, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 1, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 1]]
x_one_hot = [one_hot_lookup[x] for x in x_data]
# reshape the inputs to (seqLen, batchSize, inputSize),-1的意思是自动计算
inputs = torch.Tensor(x_one_hot).view(-1, batch_size, input_size)
# reshape the labels to (seqLen, 1)
labels = torch.LongTensor(y_data).view(-1, 1)
# 模型
class Model(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self, input_size, hidden_size, batch_size):
super(Model, self).__init__()
# 初始化参数
self.batch_size = batch_size
self.input_size = input_size
self.hidden_size = hidden_size
# 构造RNN Cell
self.rnncell = torch.nn.RNNCell(input_size=self.input_size,
hidden_size=self.hidden_size)
def forward(self, input, hidden):
hidden = self.rnncell(input, hidden)
return hidden
def init_hidden(self):
return torch.zeros(self.batch_size, self.hidden_size) # 将隐层初始化为零。仅在构造h_0的时候会用上
net = Model(input_size, hidden_size, batch_size)
# Loss and Optimizer
criterion = torch.nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(net.parameters(), lr=0.1)
# Trainning steps
for epoch in range(15):
loss = 0
optimizer.zero_grad()
hidden = net.init_hidden()
print('Predicted string: ', end='')
for input, label in zip(inputs, labels):
hidden = net(input, hidden)
loss += criterion(hidden, label)
_, idx = hidden.max(dim=1)
print(idx2char[idx.item()], end='')
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
print(', Epoch [%d/15] loss=%.4f' % (epoch+1, loss.item()))
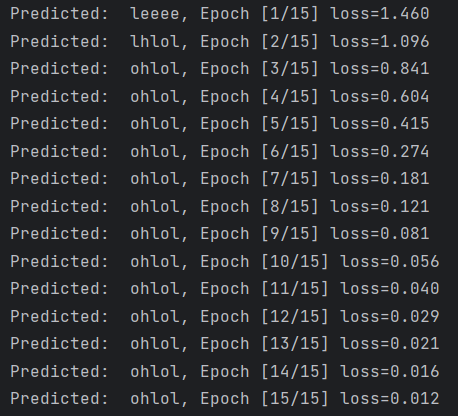
例子 —— 使用RNN:
import torch
# 参数
input_size = 4
hidden_size =4
num_layers = 1
batch_size = 1
seq_len = 5
# 数据集
idx2char = ['e', 'h', 'l', 'o'] # 词典
x_data = [1, 0, 2, 2, 3] # 输入序列hello
y_data = [3, 1, 2, 3, 2] # 输出序列ohlol
# 将输入字符的索引转成独热向量
one_hot_lookup = [[1, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 1, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 1, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 1]]
x_one_hot = [one_hot_lookup[x] for x in x_data]
# reshape the inputs to (seqLen, batchSize, inputSize)
inputs = torch.Tensor(x_one_hot).view(seq_len, batch_size, input_size)
# reshape the labels to (seqLen*batchSize, 1)
labels = torch.LongTensor(y_data)
# 模型
class Model(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self, input_size, hidden_size, batch_size, num_layers=1):
super(Model, self).__init__()
# 初始化参数
self.batch_size = batch_size
self.input_size = input_size
self.hidden_size = hidden_size
self.num_layers = num_layers
# 构造RNN
self.rnn = torch.nn.RNN(input_size=self.input_size,
hidden_size=self.hidden_size,
num_layers=num_layers)
def forward(self, input):
# shape of hidden: (numLayers, batchSize, hiddenSize)
hidden = torch.zeros(self.num_layers,
self.batch_size,
self.hidden_size)
out, _ = self.rnn(input, hidden)
return out.view(-1, self.hidden_size) # reshape out to: (seqLen*batchSize, hiddenSize)
net = Model(input_size, hidden_size, batch_size, num_layers)
# Loss and Optimizer
criterion = torch.nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(net.parameters(), lr=0.05)
# Trainning steps
for epoch in range(15):
optimizer.zero_grad()
outputs = net(inputs)
loss = criterion(outputs, labels)
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
_, idx = outputs.max(dim=1)
idx = idx.data.numpy()
print('Predicted: ', ''.join([idx2char[x] for x in idx]), end='')
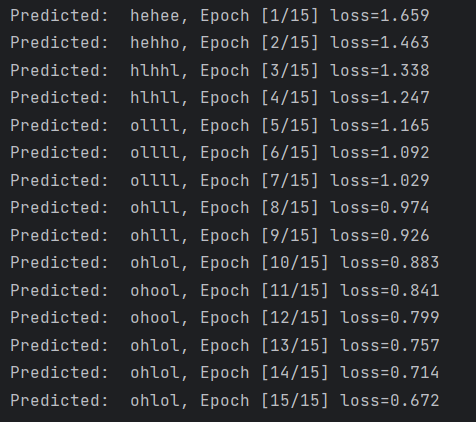
print(', Epoch [%d/15] loss=%.3f' % (epoch+1, loss.item()))
独热向量的缺陷:
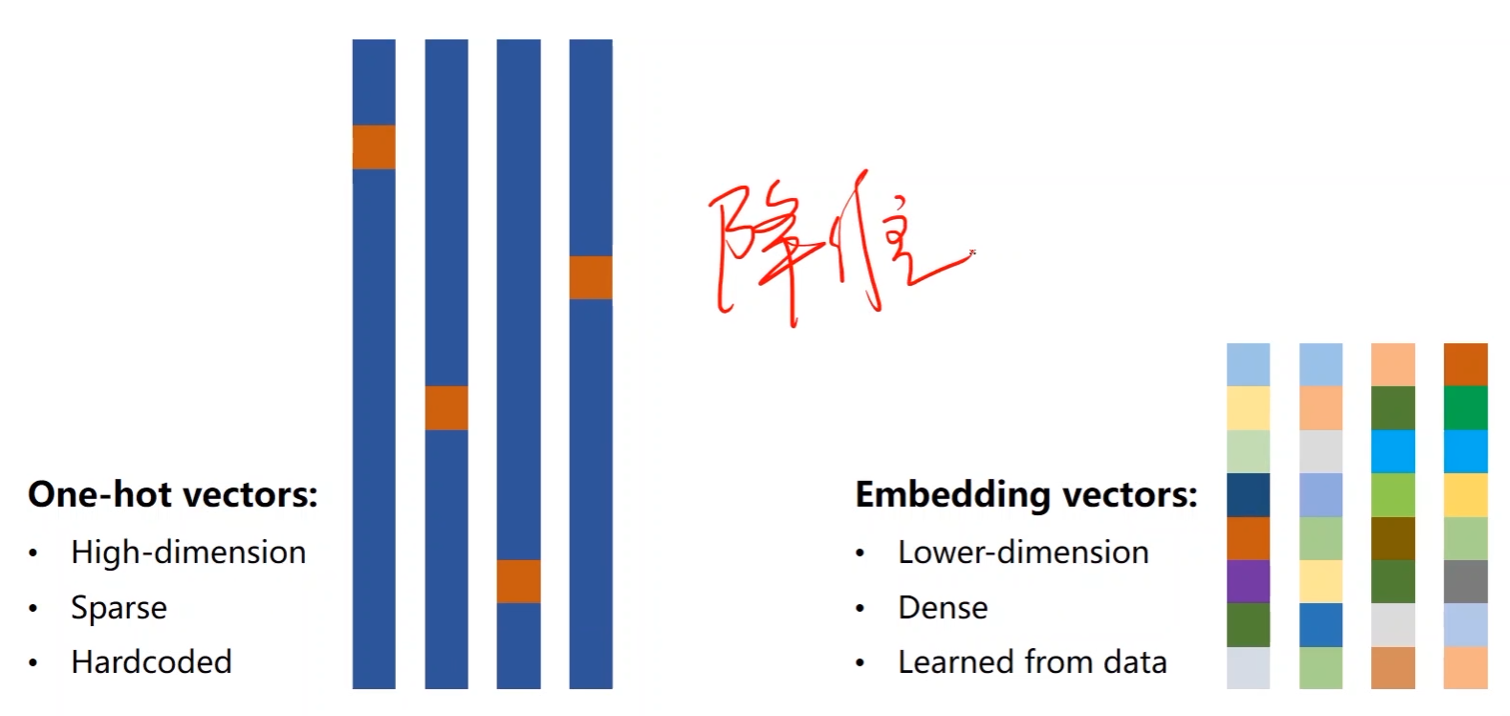
- 维度太高(维度诅咒)
- one-hot vectors是稀疏的(很多零)
- 硬编码(每个字符或者词对应哪个向量都是定好的)
是否有方法能够解决上述问题:
- 低维
- 稠密
- 从数据中学习
嵌入层Embedding:
- 将高维的稀疏的样本映射到一个低维的稠密的空间中(数据降维)
-
降维方式;


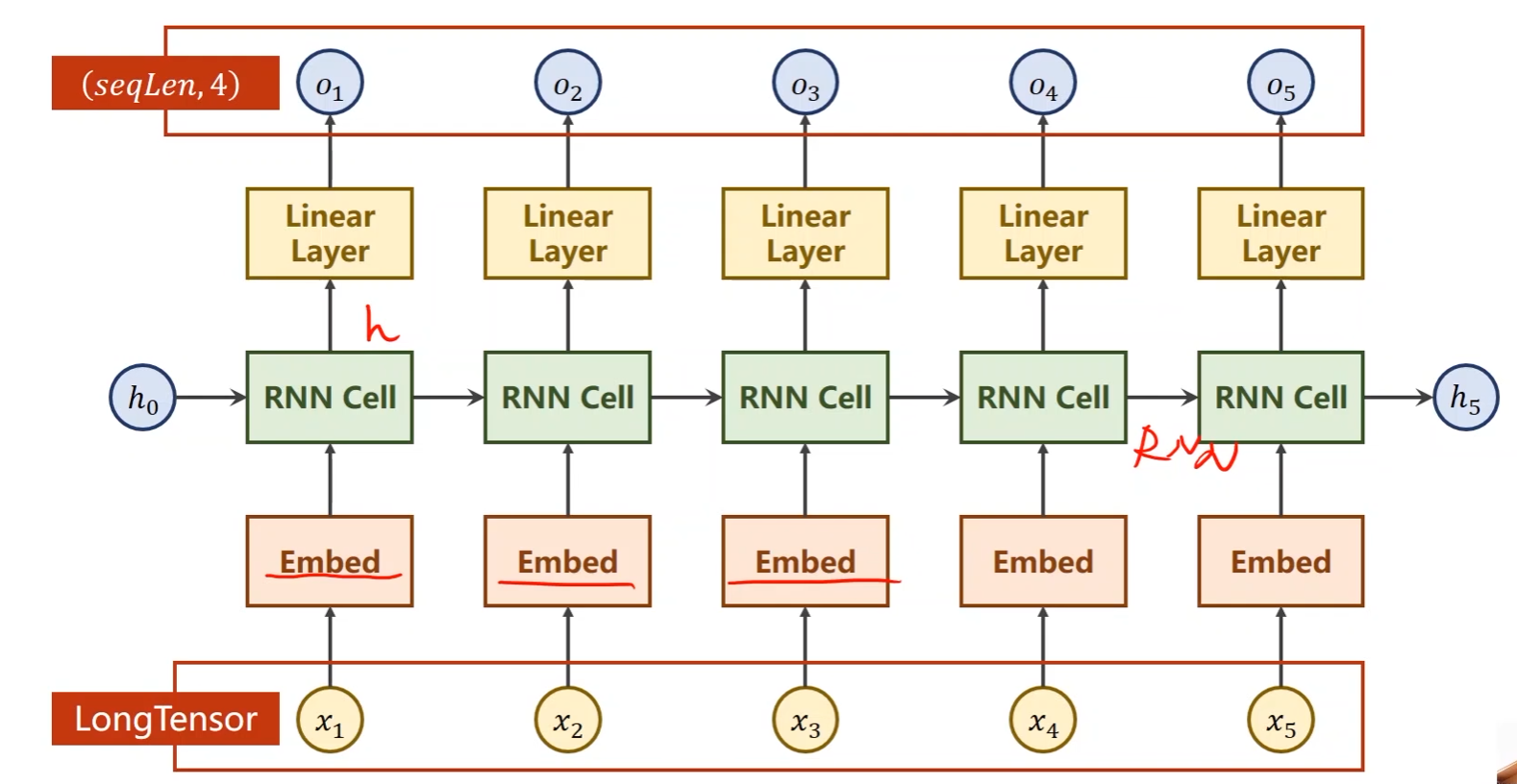
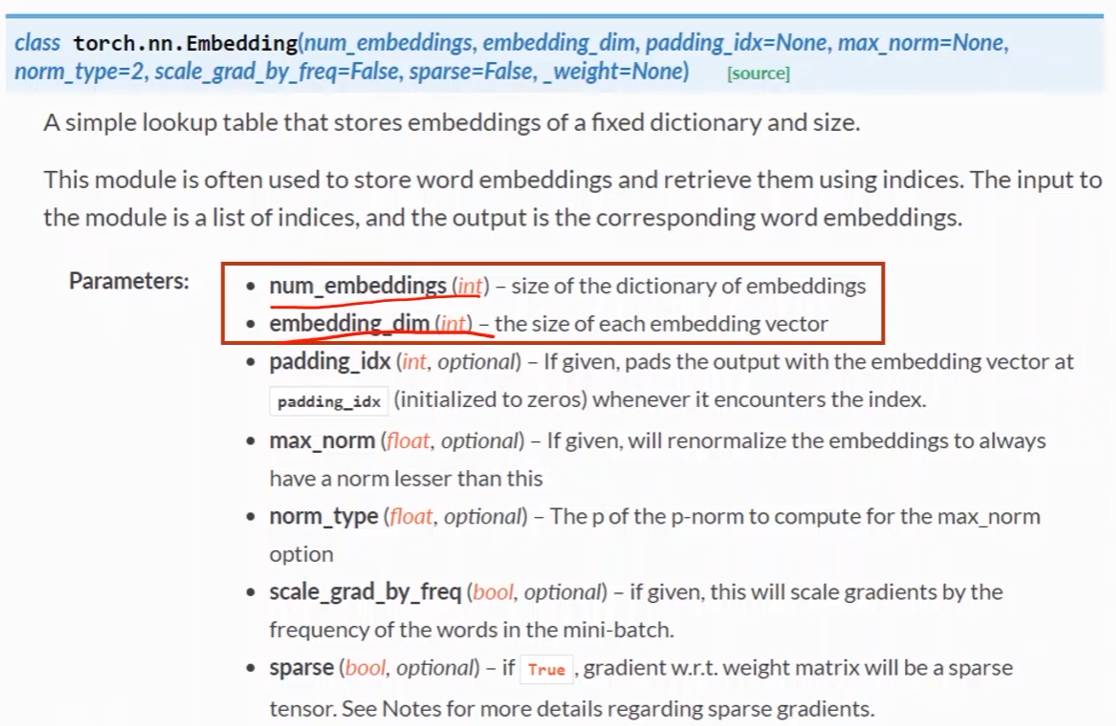
- num_embedding就是one_shot的维度
- emdedding_dim就是所需要的降维后的维度

代码实现:
import torch
# 参数
num_class = 4
input_size = 4
hidden_size = 8
embedding_size = 10
num_layers = 2
batch_size = 1
seq_len = 5
# 数据集
idx2char = ['e', 'h', 'l', 'o'] # 词典
x_data = [[1, 0, 2, 2, 3]] # 输入序列hello, (batch, seq_len)
y_data = [3, 1, 2, 3, 2] # 输出序列ohlol, (batch * seq_len)
# reshape the inputs to (seqLen, batchSize, inputSize)
inputs = torch.LongTensor(x_data)
# reshape the labels to (seqLen*batchSize, 1)
labels = torch.LongTensor(y_data)
# 模型
class Model(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(Model, self).__init__()
self.emb = torch.nn.Embedding(input_size, embedding_size)
# 构造RNN
self.rnn = torch.nn.RNN(input_size=embedding_size,
hidden_size=hidden_size,
num_layers=num_layers,
batch_first=True)
self.fc = torch.nn.Linear(hidden_size, num_class)
def forward(self, x):
hidden = torch.zeros(num_layers,
x.size(0),
hidden_size)
x = self.emb(x) # (batch, seqLen, embeddingSize)
x, _ = self.rnn(x, hidden)
x = self.fc(x)
return x.view(-1, num_class)
net = Model()
# Loss and Optimizer
criterion = torch.nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(net.parameters(), lr=0.05)
# Trainning steps
for epoch in range(15):
optimizer.zero_grad()
outputs = net(inputs)
loss = criterion(outputs, labels)
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
_, idx = outputs.max(dim=1)
idx = idx.data.numpy()
print('Predicted: ', ''.join([idx2char[x] for x in idx]), end='')
print(', Epoch [%d/15] loss=%.3f' % (epoch+1, loss.item()))
LSTM
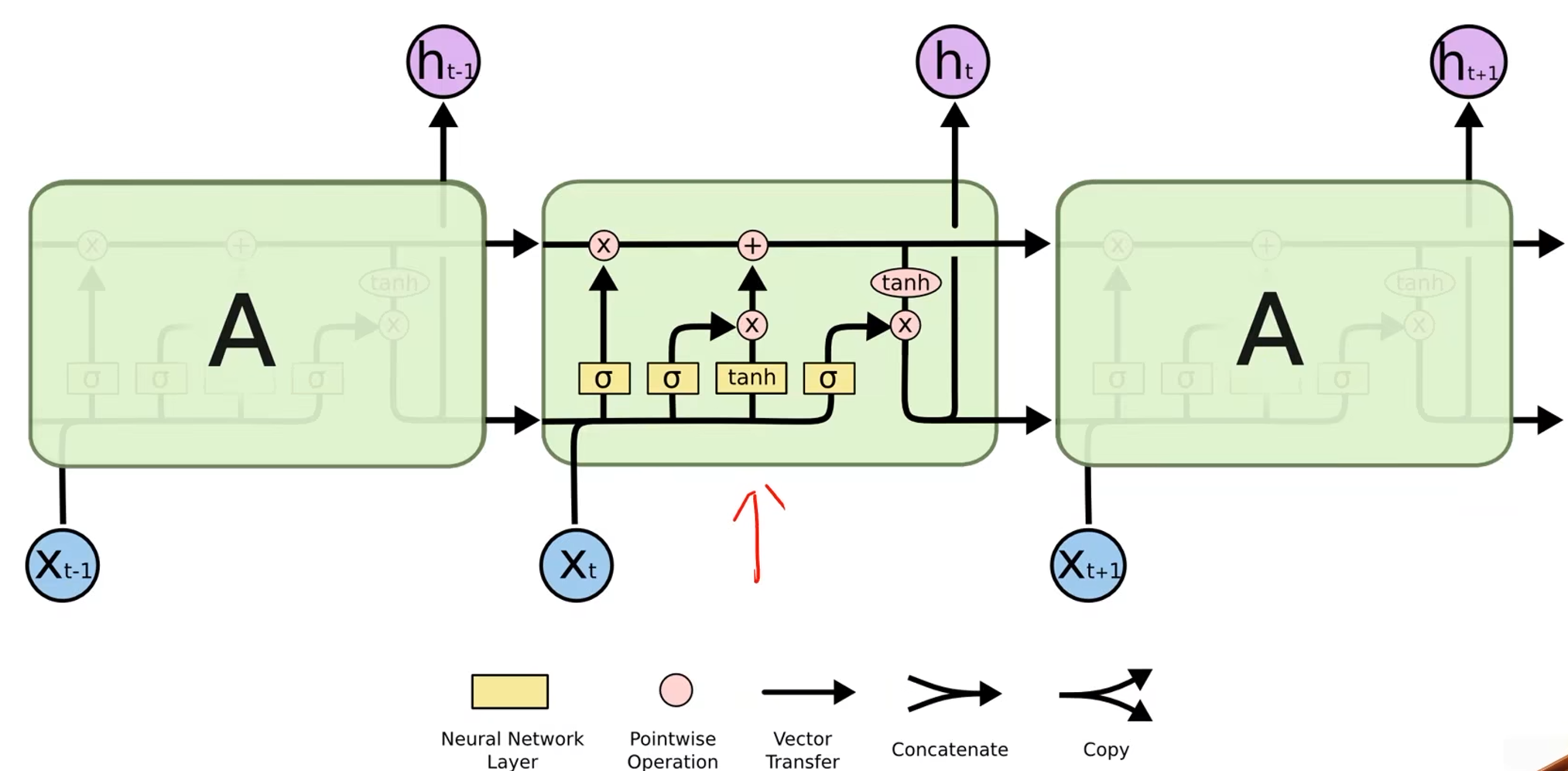

- LSTM的效果一般会比RNN好得多,但是LSTM的计算更复杂,它的运算性能比较低,时间复杂度比较高
- 因此产生了一个LSTM和RNN的折中方法:GRU
- 比RNN性能更好,准确率更高,学习能力更强
- 比LSTM运算性能更高,时间复杂度更低
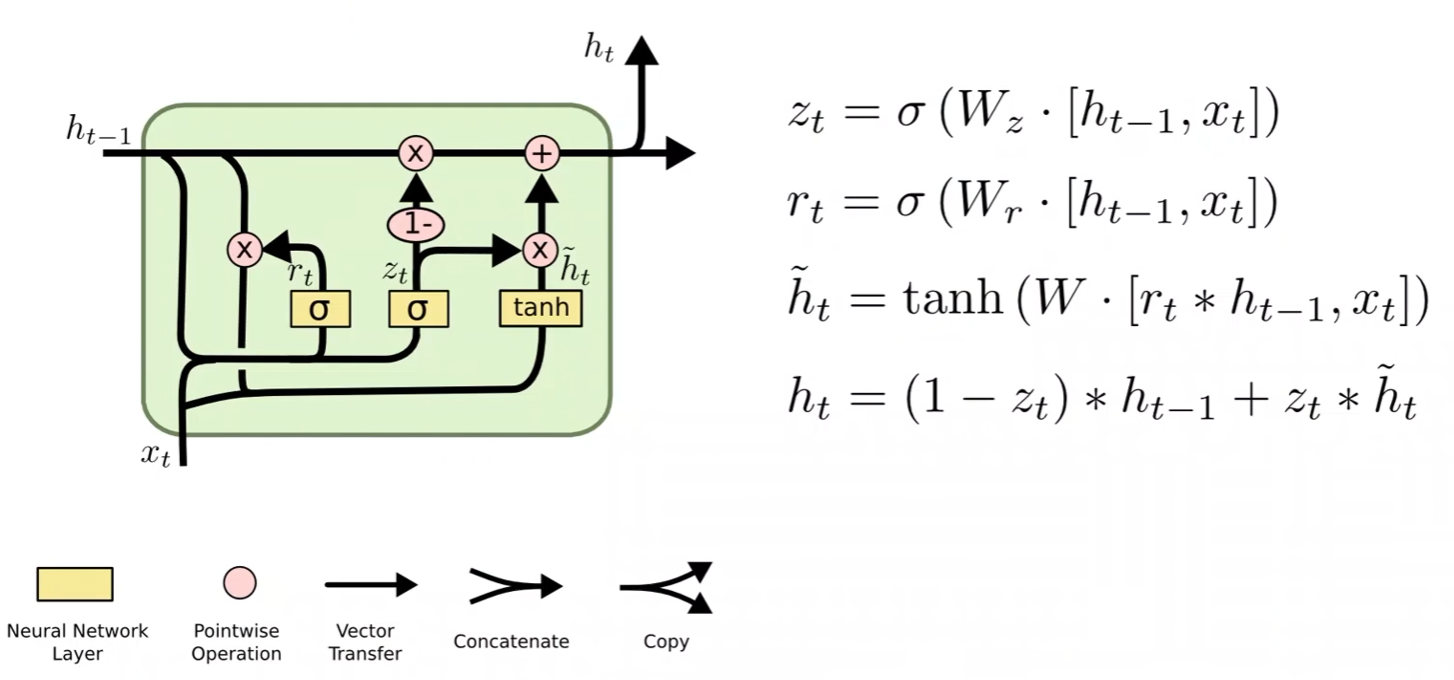
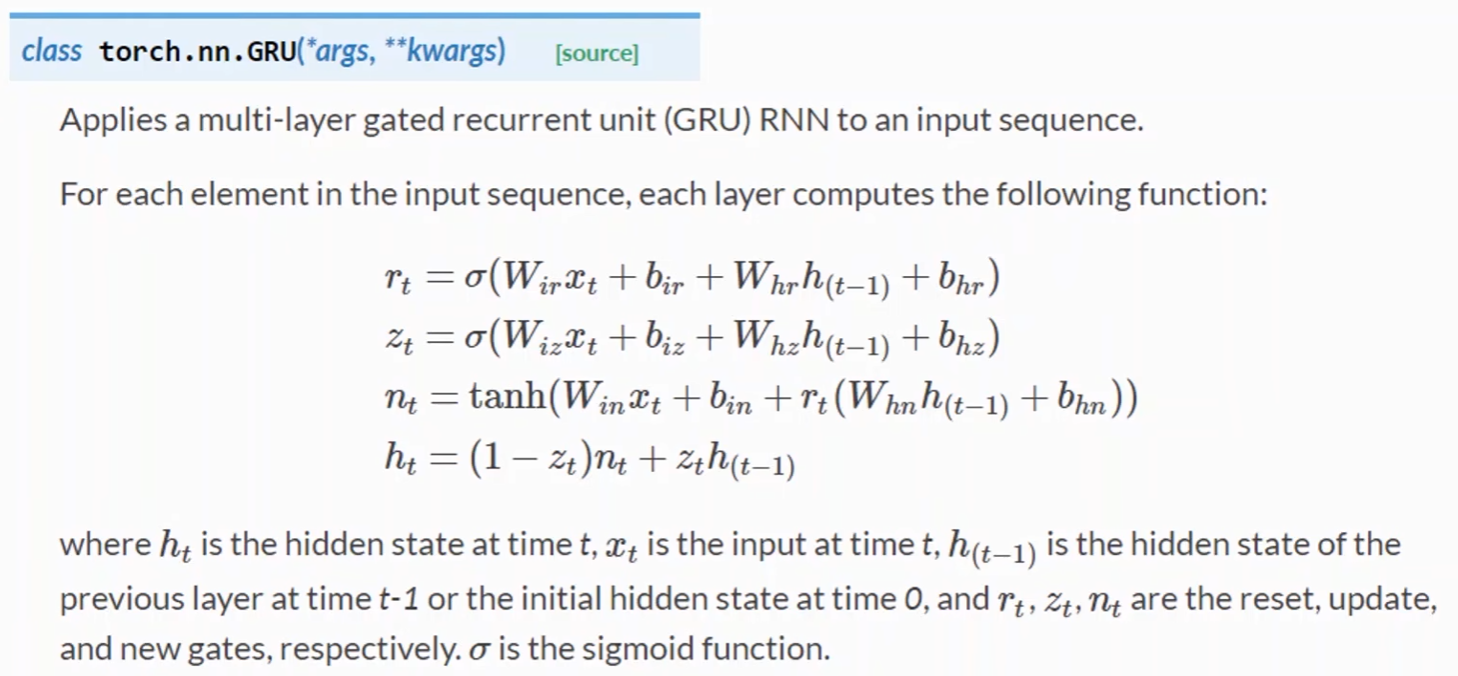
二、循环神经网络高级篇(实现一个分类器)
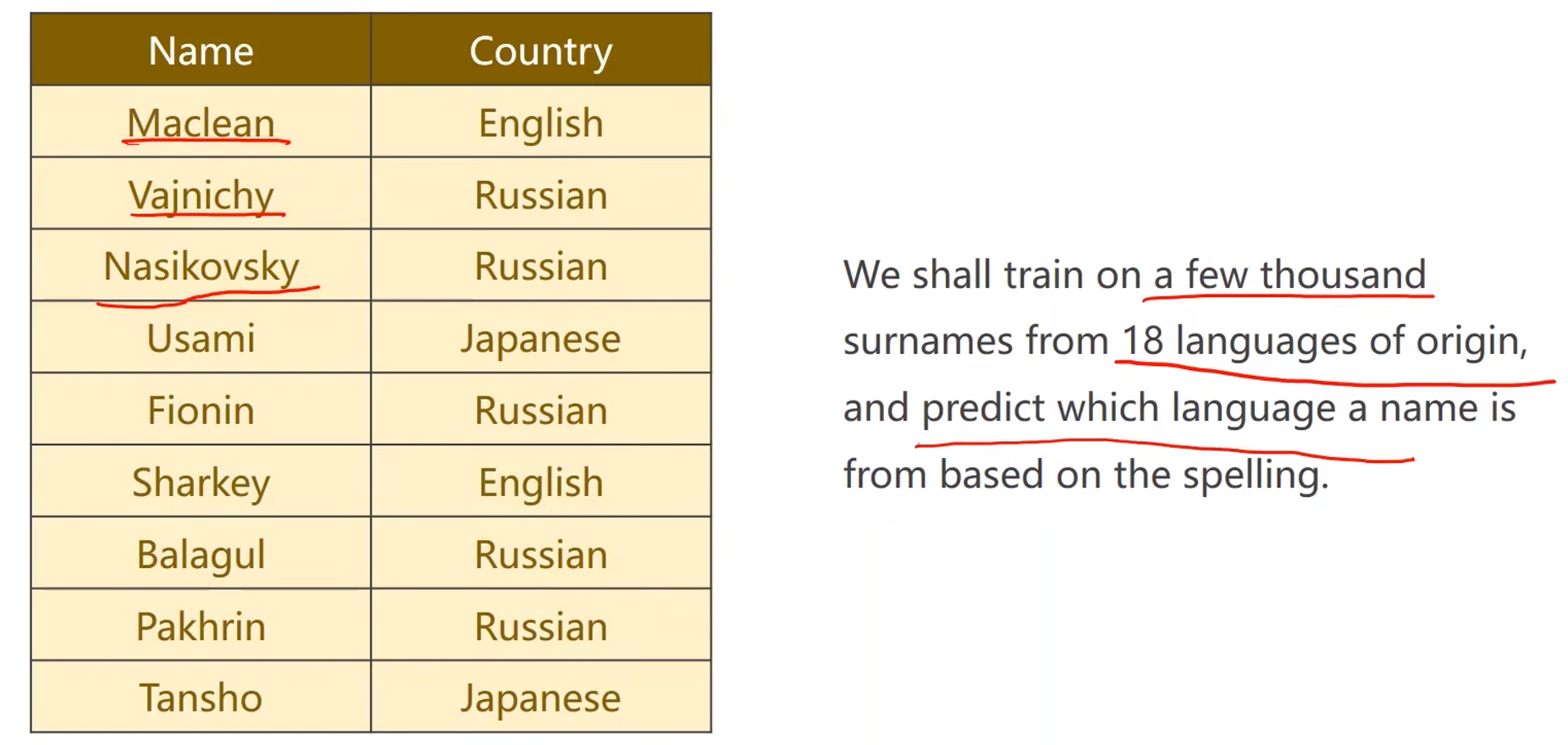
问题:名字分类
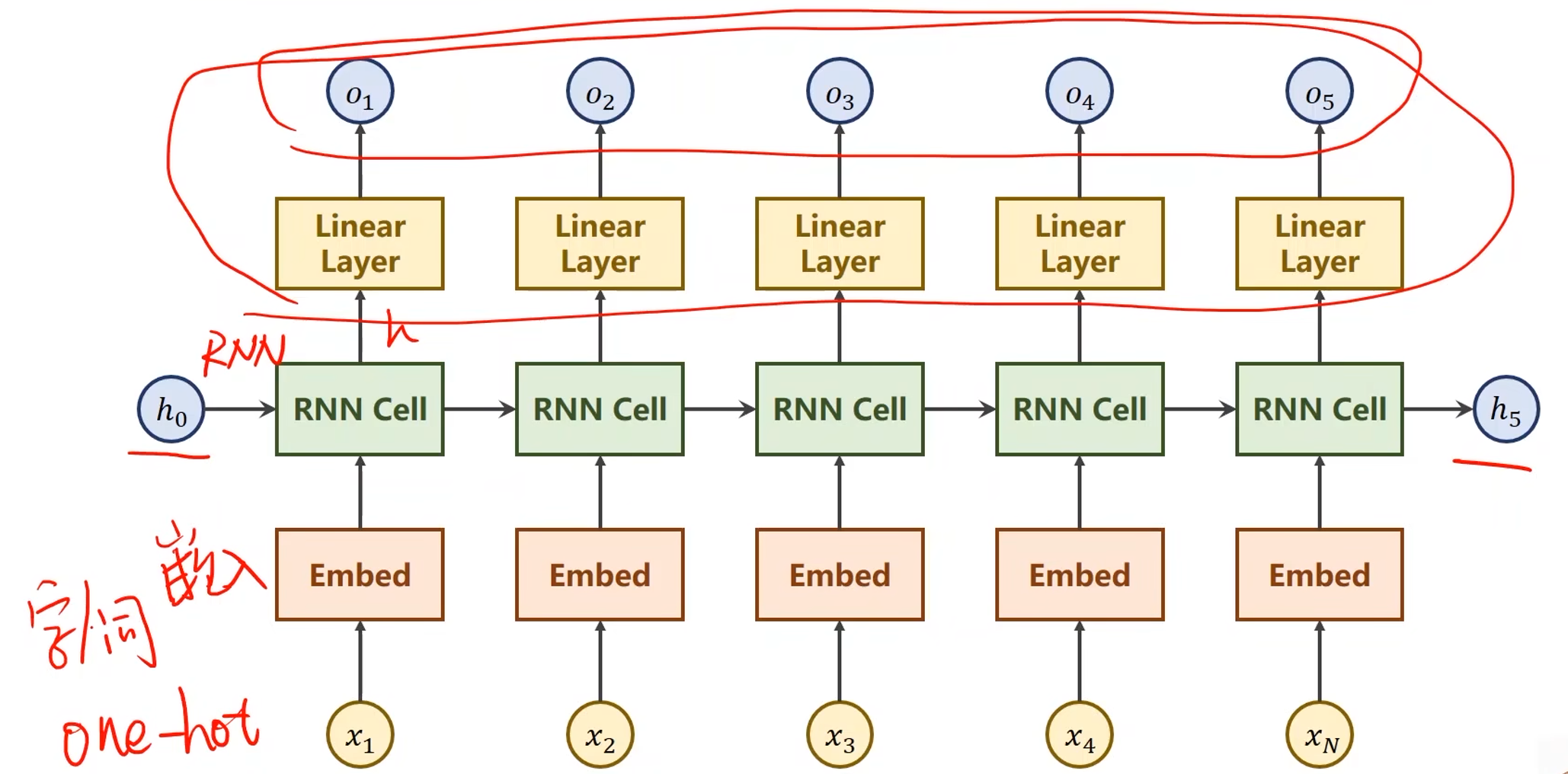
上一讲中的循环神经网络结构:
- 在本问题中要求最后输出一个大的分类,即名字对应的国家,不需要对所有隐层的输出都做线性变换
本问题的网络结构:
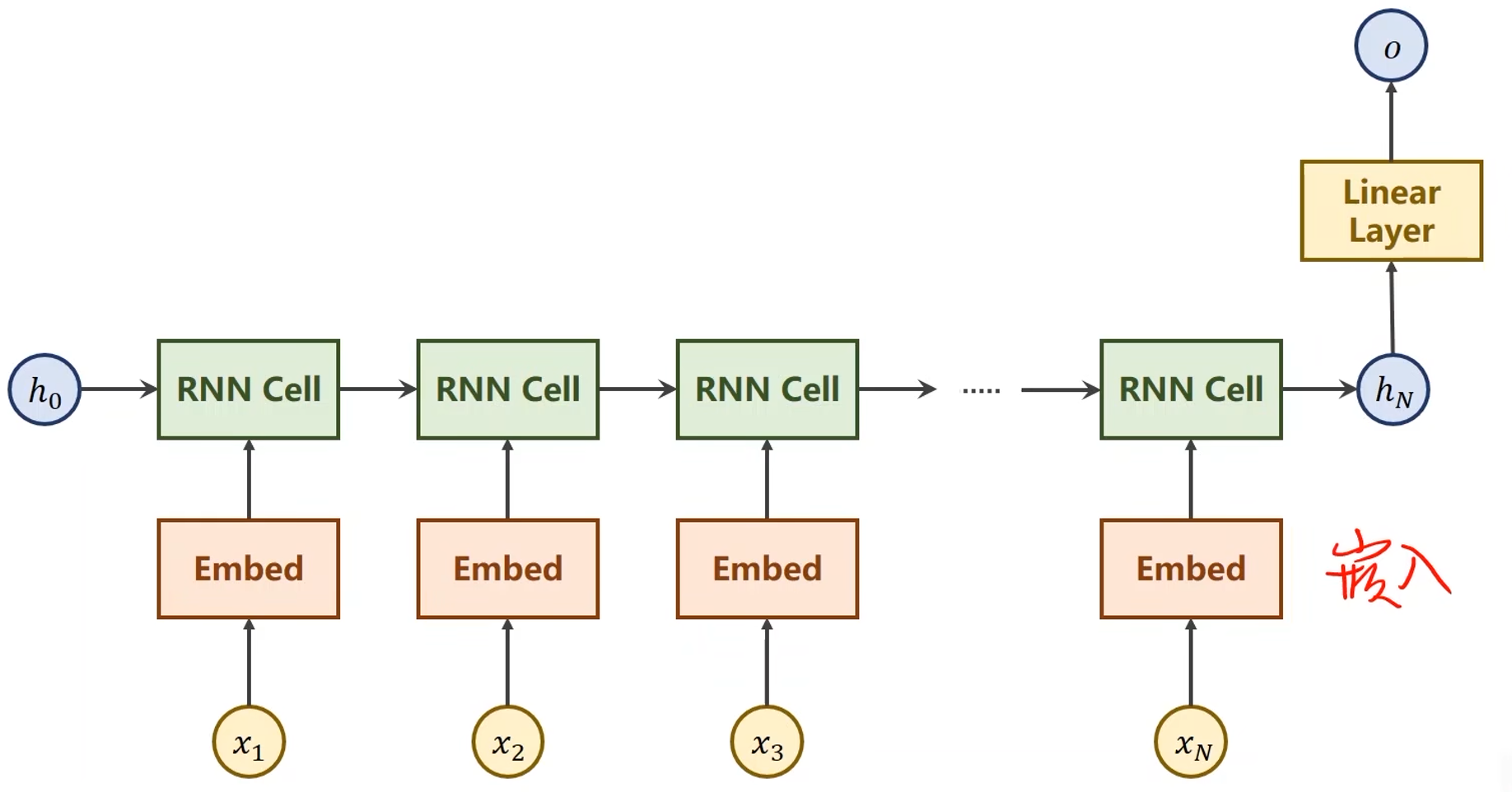
- 使用了GRU模型
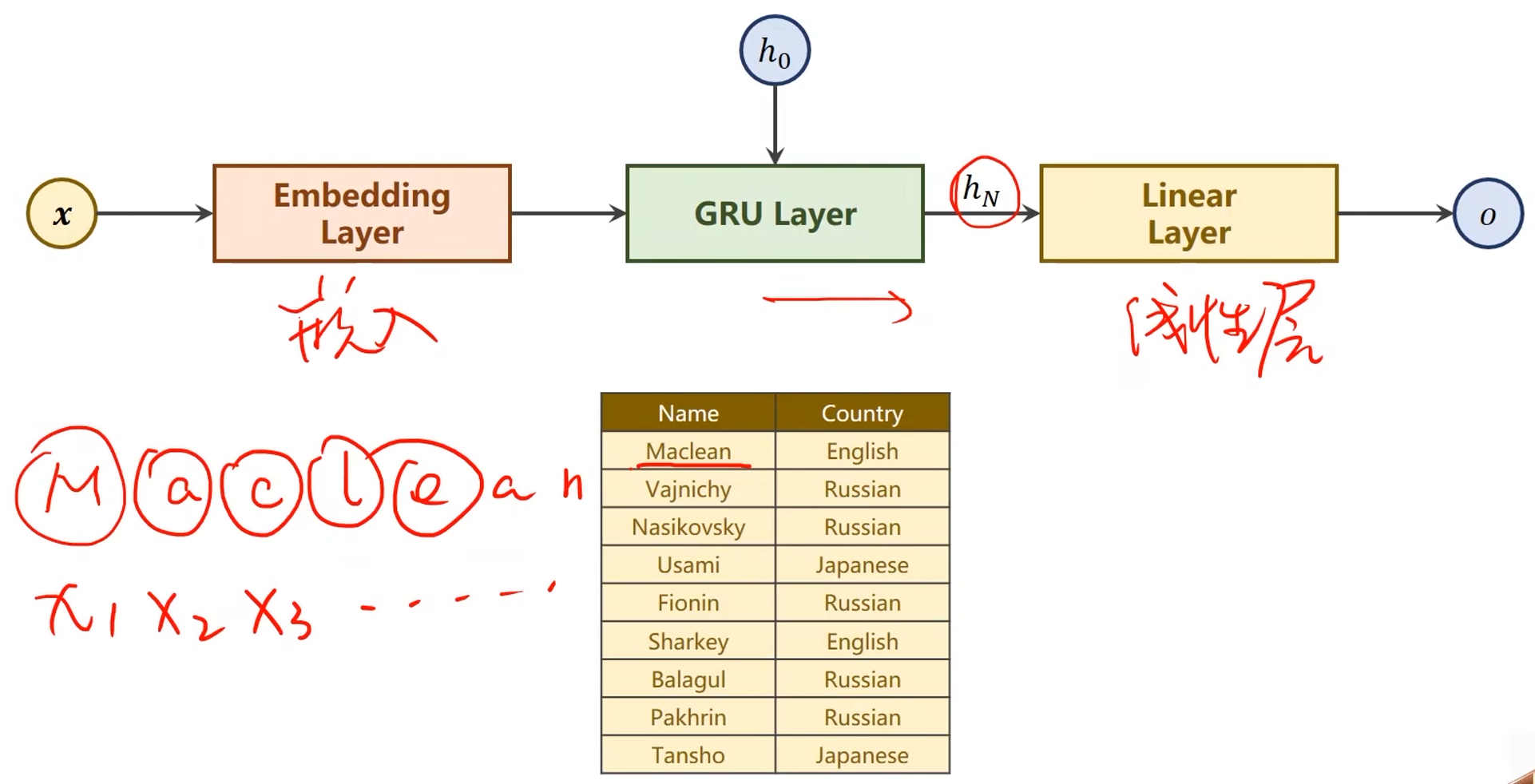
代码实现:
Main Cycle:
if __name__ == '__main__':
# 初始化分类模型
# N_CHARS是字母表的大小,HIDDEN_SIZE是GRU输出隐层的维度,N_COUNTRY分类数量,N_LAYER是GRU层数
classifier = RNNClassifier(N_CHARS, HIDDEN_SIZE, N_COUNTRY, N_LAYER)
# 是否要使用GPU
if USE_GRU:
device = torch.device("cuda:0")
classifier.to(device)
# Loss(交叉熵) and Optimizer
criterion = torch.nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(classifier.parameters(), lr=0.001)
# 记录训练开始时间
start = time.time()
print("Training for %d epochs..." % N_EPOCHS)
acc_list = []
for epoch in range(1, N_EPOCHS + 1):
# Train cycle
trainModel() # 模型训练
acc = testModel() # 模型测试
acc_list.append(acc) # 存储测试准确率
# 绘制测试准确率曲线
epoch = np.arange(1, len(acc_list) + 1, 1)
acc_list = np.array(acc_list)
plt.plot(epoch, acc_list)
plt.xlabel('Epoch')
plt.ylabel('Accuracy')
plt.grid()
plt.show()
具体实现步骤:
-
Preparing Data and DataLoader
-
用ASCII表来做词典

-
序列长短不一,无法构成张量(做padding处理)

-
处理输出分类(国家)
- 将国家转成分类索引,从0开始

class NameDataset(Dataset): def __init__(self, is_train_set=True): # 读取数据集数据 filename = 'D:/pycharm_workspace/Liuer_lecturer/dataset/names_train.csv.gz' if is_train_set else 'D:/pycharm_workspace/Liuer_lecturer/dataset/names_test.csv.gz' with gzip.open(filename, 'rt') as f: reader = csv.reader(f) rows = list(reader) # (name, countries)元组 self.names = [row[0] for row in rows] # 将名字(数据)提取出来 self.len = len(self.names) # 计算字符长度 self.countries = [row[1] for row in rows] # 将名字(数据)对应的标签(国家)提取出来 # 获取国家的索引 # set将列表转成集合,即去除重复元素;sorted进行排序;list转成列表 self.country_list = list(sorted(set(self.countries))) self.country_dict = self.getCountryDict() # 将country_list这个列表转成字典 self.country_num = len(self.country_list) # 得到国家数量 def __getitem__(self, index): # 为数据集提供索引访问 return self.names[index], self.country_dict[self.countries[index]] def __len__(self): # 返回数据集长度 return self.len def getCountryDict(self): # 将列表转成字典 country_dict = dict() for idx, country_name in enumerate(self.country_list, 0): # 对country_list进行遍历,然后构造键值对 country_dict[country_name] = idx return country_dict def idx2country(self, index): # 根据索引index返回国家的字符串 return self.country_list[index] def getCountriesNum(self): # 获取国家数量 return self.country_num trainset = NameDataset(is_train_set=True) trainLoader = DataLoader(trainset, batch_size=BATCH_SIZE, shuffle=True) testset = NameDataset(is_train_set=False) testloader = DataLoader(testset, batch_size=BATCH_SIZE, shuffle=False) # 模型输出的维度 N_COUNTRY = trainset.getCountriesNum() -
-
Model Design
-
双向(Bi-direction)RNN / LSTM / GRU


-
沿着序列的正方向计算,利用了历史信息

-
沿着序列的反方向计算一次,输出的隐层再和正向计算输出的隐层进行拼接

- 调用GRU的时候有两个输出,一个是out,另一个是hidden
- out就是各个隐层的输出
- hidden = [ h N f , h N b ] [h_N^f, h_N^b] [hNf,hNb]
- 调用GRU的时候有两个输出,一个是out,另一个是hidden
class RNNClassifier(torch.nn.Module): def __init__(self, input_size, hidden_size, output_size, n_layers=1, bidirectional=True): super(RNNClassifier, self).__init__() # GRU参数 self.hidden_size = hidden_size self.n_layers = n_layers # 如果GRU是双向即为2,单向的则为1 self.n_directions = 2 if bidirectional else 1 # 构造嵌入层。input是(seqLen, batchSize) ; output是(seqLen, batchSize, hiddenSize) self.embedding = torch.nn.Embedding(input_size, hidden_size) # 构造GRU。 # input:(seqLen, batchSize, hiddenSize); hidden:(nLayers * nDirections, batchSize, hiddenSize) # output:(seqLen, batchSize, hiddenSize * nDirections); hidden:(nLayers * nDirections, batchSize, hiddenSize) # 第一个hidden_size是输入维度,第二个是输出维度,n_layers是层数,bidirectional用于说明是单向还是双向 self.gru = torch.nn.GRU(hidden_size, hidden_size, n_layers, bidirectional=bidirectional) # 如果是双向的则要乘上self.n_directions self.fc = torch.nn.Linear(hidden_size * self.n_directions, output_size) def _init_hidden(self, batch_size): # 根据batch_size构成一个全零的张量hidden hidden = torch.zeros(self.n_layers * self.n_directions, batch_size, self.hidden_size) return create_tensor(hidden) def forward(self, input, seq_lengths): # input shape: B x S -> S x B input = input.t() # 转置 batch_size = input.size(1) # 保存batch_size以便构造初始隐层 hidden = self._init_hidden(batch_size) # result of embedding with shape:(seqLen, batchSize, hiddenSize) embedding = self.embedding(input) # pack them up. 为了提高运行效率 gru_input = pack_padded_sequence(embedding, seq_lengths) # gru输出 output, hidden = self.gru(gru_input, hidden) if self.n_directions == 2: hidden_cat = torch.cat([hidden[-1], hidden[-2]], dim=1) else: hidden_cat = hidden[-1] fc_output = self.fc(hidden_cat) return fc_output名字如何转换成张量:
def make_tensors(names, countries): sequences_and_lengths = [name2list(name) for name in names] name_sequences = [s1[0] for s1 in sequences_and_lengths] seq_lengths = torch.LongTensor([s1[1] for s1 in sequences_and_lengths]) countries = countries.long() # make tensor of name, BatchSize x SeqLen seq_tensor = torch.zeros(len(name_sequences), seq_lengths.max()).long() for idx, (seq, seq_len) in enumerate(zip(name_sequences, seq_lengths), 0): seq_tensor[idx, :seq_len] = torch.LongTensor(seq) # sort by length to use pack_padded_sequence seq_lengths, perm_idx = seq_lengths.sort(dim=0, descending=True) seq_tensor = seq_tensor[perm_idx] countries = countries[perm_idx] return create_tensor(seq_tensor), create_tensor(seq_tensor), create_tensor(countries) -
-
One Epoch Training
def trainModel(): total_loss = 0 for i, (names, countries) in enumerate(trainLoader, 1): inputs, seq_lengths, target = make_tensors(names, countries) output = classifier(inputs, seq_lengths) loss = criterion(output, target) optimizer.zero_grad() loss.backward() optimizer.step() total_loss += loss.item() if i % 10 == 0: print(f' [{time_since(start)}] Epoch {epoch} ', end='') print(f' [{i * len(inputs)} / {len(trainset)}] ', end='') print(f' loss = {total_loss / (i * len(inputs))}', end='') return total_loss # 测试 def testModel(): correct = 0 total = len(testset) print("evaluating trained model ...") # 不需要求梯度 with torch.no_grad(): for i, (names, countries) in enumerate(testloader, 1): inputs, seq_lengths, target = make_tensors(names, countries) output = classifier(inputs, seq_lengths) pred = output.max(dim=1, keepdim=True)[1] correct += pred.eq(target.view_as(pred)).sum().item() precent = '%.2f' % (100 * correct / total) print(f'Test set: Accuracy {correct} / {total} {precent}%') return correct / total完整代码:
import csv import gzip import torch import time import math import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from torch.utils.data import Dataset, DataLoader from torch.nn.utils.rnn import pack_padded_sequence # 参数 HIDDEN_SIZE = 100 BATCH_SIZE = 256 N_LAYER = 2 # GRU层数 N_EPOCHS = 100 # 训练轮数 N_CHARS = 128 USE_GPU = False # 有GPU的支持则设置为True,没有则False # 构造数据集。NameDataset类继承自Dataset class NameDataset(Dataset): def __init__(self, is_train_set=True): # 读取数据集数据 filename = 'D:/pycharm_workspace/Liuer_lecturer/dataset/names_train.csv.gz' if is_train_set else 'D:/pycharm_workspace/Liuer_lecturer/dataset/names_test.csv.gz' with gzip.open(filename, 'rt') as f: reader = csv.reader(f) rows = list(reader) # (name, countries)元组 self.names = [row[0] for row in rows] # 将名字(数据)提取出来 self.len = len(self.names) # 计算字符长度 self.countries = [row[1] for row in rows] # 将名字(数据)对应的标签(国家)提取出来 # 获取国家的索引 # set将列表转成集合,即去除重复元素;sorted进行排序;list转成列表 self.country_list = list(sorted(set(self.countries))) self.country_dict = self.getCountryDict() # 将country_list这个列表转成字典 self.country_num = len(self.country_list) # 得到国家数量 def __getitem__(self, index): # 为数据集提供索引访问 return self.names[index], self.country_dict[self.countries[index]] def __len__(self): # 返回数据集长度 return self.len def getCountryDict(self): # 将列表转成字典 country_dict = dict() for idx, country_name in enumerate(self.country_list, 0): # 对country_list进行遍历,然后构造键值对 country_dict[country_name] = idx return country_dict def idx2country(self, index): # 根据索引index返回国家的字符串 return self.country_list[index] def getCountriesNum(self): # 获取国家数量 return self.country_num # 实例化数据集 trainset = NameDataset(is_train_set=True) trainLoader = DataLoader(trainset, batch_size=BATCH_SIZE, shuffle=True) testset = NameDataset(is_train_set=False) testloader = DataLoader(testset, batch_size=BATCH_SIZE, shuffle=False) # 模型输出的维度 N_COUNTRY = trainset.getCountriesNum() # RNN模型 class RNNClassifier(torch.nn.Module): def __init__(self, input_size, hidden_size, output_size, n_layers=1, bidirectional=True): super(RNNClassifier, self).__init__() # GRU参数 self.hidden_size = hidden_size self.n_layers = n_layers # 如果GRU是双向即为2,单向的则为1 self.n_directions = 2 if bidirectional else 1 # 构造嵌入层。input是(seqLen, batchSize) ; output是(seqLen, batchSize, hiddenSize) self.embedding = torch.nn.Embedding(input_size, hidden_size) # 构造GRU。 # input:(seqLen, batchSize, hiddenSize); hidden:(nLayers * nDirections, batchSize, hiddenSize) # output:(seqLen, batchSize, hiddenSize * nDirections); hidden:(nLayers * nDirections, batchSize, hiddenSize) # 第一个hidden_size是输入维度,第二个是输出维度,n_layers是层数,bidirectional用于说明是单向还是双向 self.gru = torch.nn.GRU(hidden_size, hidden_size, n_layers, bidirectional=bidirectional) # 如果是双向的则要乘上self.n_directions self.fc = torch.nn.Linear(hidden_size * self.n_directions, output_size) def _init_hidden(self, batch_size): # 根据batch_size构成一个全零的张量hidden hidden = torch.zeros(self.n_layers * self.n_directions, batch_size, self.hidden_size) return create_tensor(hidden) def forward(self, input, seq_lengths): # input shape: B x S -> S x B input = input.t() # 转置 batch_size = input.size(1) # 保存batch_size以便构造初始隐层 hidden = self._init_hidden(batch_size) # result of embedding with shape:(seqLen, batchSize, hiddenSize) embedding = self.embedding(input) # pack them up. 为了提高运行效率 gru_input = pack_padded_sequence(embedding, seq_lengths) # gru输出 output, hidden = self.gru(gru_input, hidden) if self.n_directions == 2: hidden_cat = torch.cat([hidden[-1], hidden[-2]], dim=1) else: hidden_cat = hidden[-1] fc_output = self.fc(hidden_cat) return fc_output def name2list(name): arr = [ord(c) for c in name] return arr, len(arr) # 判定是否要使用GPU def create_tensor(tensor): if USE_GPU: device = torch.device("cuda:0") tensor = tensor.to(device) return tensor def make_tensors(names, countries): sequences_and_lengths = [name2list(name) for name in names] name_sequences = [s1[0] for s1 in sequences_and_lengths] seq_lengths = torch.LongTensor([s1[1] for s1 in sequences_and_lengths]) countries = countries.long() # make tensor of name, BatchSize x SeqLen seq_tensor = torch.zeros(len(name_sequences), seq_lengths.max()).long() for idx, (seq, seq_len) in enumerate(zip(name_sequences, seq_lengths), 0): seq_tensor[idx, :seq_len] = torch.LongTensor(seq) # sort by length to use pack_padded_sequence seq_lengths, perm_idx = seq_lengths.sort(dim=0, descending=True) seq_tensor = seq_tensor[perm_idx] countries = countries[perm_idx] return create_tensor(seq_tensor), create_tensor(seq_tensor), create_tensor(countries) def time_since(sice): s = time.time() - sice # 当前时间减去开始时间,s为单位 m = math.floor(s / 60) # 转成分钟 s -= m*60 return '%dm %ds' % (m, s) # 一轮训练 def trainModel(): total_loss = 0 for i, (names, countries) in enumerate(trainLoader, 1): inputs, seq_lengths, target = make_tensors(names, countries) output = classifier(inputs, seq_lengths) loss = criterion(output, target) optimizer.zero_grad() loss.backward() optimizer.step() total_loss += loss.item() if i % 10 == 0: print(f' [{time_since(start)}] Epoch {epoch} ', end='') print(f' [{i * len(inputs)} / {len(trainset)}] ', end='') print(f' loss = {total_loss / (i * len(inputs))}', end='') return total_loss # 测试 def testModel(): correct = 0 total = len(testset) print("evaluating trained model ...") # 不需要求梯度 with torch.no_grad(): for i, (names, countries) in enumerate(testloader, 1): inputs, seq_lengths, target = make_tensors(names, countries) output = classifier(inputs, seq_lengths) pred = output.max(dim=1, keepdim=True)[1] correct += pred.eq(target.view_as(pred)).sum().item() precent = '%.2f' % (100 * correct / total) print(f'Test set: Accuracy {correct} / {total} {precent}%') return correct / total if __name__ == '__main__': # 初始化分类模型 # N_CHARS是字母表的大小,HIDDEN_SIZE是GRU输出隐层的维度,N_COUNTRY分类数量,N_LAYER是GRU层数 classifier = RNNClassifier(N_CHARS, HIDDEN_SIZE, N_COUNTRY, N_LAYER) # 是否要使用GPU if USE_GPU: device = torch.device("cuda:0") classifier.to(device) # Loss(交叉熵) and Optimizer criterion = torch.nn.CrossEntropyLoss() optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(classifier.parameters(), lr=0.001) # 记录训练开始时间 start = time.time() print("Training for %d epochs..." % N_EPOCHS) acc_list = [] for epoch in range(1, N_EPOCHS + 1): # Train cycle trainModel() # 模型训练 acc = testModel() # 模型测试 acc_list.append(acc) # 存储测试准确率 # 绘制测试准确率曲线 epoch = np.arange(1, len(acc_list) + 1, 1) acc_list = np.array(acc_list) plt.plot(epoch, acc_list) plt.xlabel('Epoch') plt.ylabel('Accuracy') plt.grid() plt.show()因为pytorch版本升级的原因代码里面有一个错误,目前还没跑通。有时间解决后再更新……
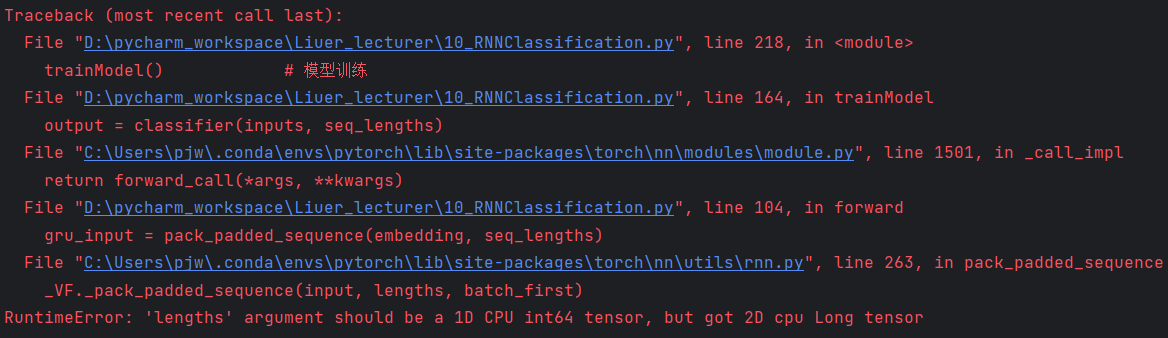
https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_45084253/article/details/122269699








 本文详细介绍了循环神经网络的基础和高级概念,包括RNNCell的工作原理、LSTM的优势以及GRU作为RNN和LSTM的折中选择。通过具体的PyTorch代码示例,展示了如何使用这些模型处理序列数据,如天气预测和名字分类问题,并讨论了数据预处理和模型训练的过程。
本文详细介绍了循环神经网络的基础和高级概念,包括RNNCell的工作原理、LSTM的优势以及GRU作为RNN和LSTM的折中选择。通过具体的PyTorch代码示例,展示了如何使用这些模型处理序列数据,如天气预测和名字分类问题,并讨论了数据预处理和模型训练的过程。














 1万+
1万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








