解决.tiff文件转.pcd文件滤波后转回.tiff文件点的序列被打乱的问题
解决思路
1、.tiff转点云.pcd格式,定义数据结构记录对应点的三轴坐标与对应的行列信息
.tiff存放点云信息,将点的三轴坐标作为Mat的三个通道的值,三个通道分别对应了点的Z、Y、X坐标
struct pointindex{
float x;
float y;
float z;
int i;
int j;
};
std::vector<pointindex> pointList;
//tiff转点云
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr tiff2Cloud(cv::Mat src)
{
//创建点云
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr cloud (new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>);
if (src.type() == CV_32FC3){
for (int i = 0; i < src.rows; i++){
const float *p_src = src.ptr<float>(i);
for (int j = 0; j < src.cols; j++){
if(p_src[3*j]!=0){
pcl::PointXYZ point;
point.x = p_src[3*j+2];
point.y = p_src[3*j+1];
point.z = p_src[3*j];
cloud->push_back(point);
pointindex point_;
point_.x = point.x = p_src[3*j+2];
point_.y = p_src[3*j+1];
point_.z = p_src[3*j];
point_.i = i;
point_.j = j;
pointList.push_back(point_);
}
}
}
}
return cloud;
}
2、点云离群滤波
点云的可视化尽量采用pcl::visualization::PCLVisualizer::Ptr这个类
//点云可视化
void showCloud(std::string windowname,pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr cloud){
pcl::visualization::PCLVisualizer::Ptr viewer (new pcl::visualization::PCLVisualizer (windowname));
viewer->setBackgroundColor (0.5, 0.5, 0.5); //设置背景
viewer->addPointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ> (cloud, "sample cloud"); //显示点云
viewer->setPointCloudRenderingProperties (pcl::visualization::PCL_VISUALIZER_POINT_SIZE, 1, "sample cloud"); //设置点尺寸
viewer->addCoordinateSystem (100.0); //设置坐标轴尺寸
// while (!viewer->wasStopped ())
// {
// viewer->spinOnce (100);
// boost::this_thread::sleep (boost::posix_time::microseconds (100000));
// }
cout<<"Point couting in "<<windowname<<": "<<cloud->size()<<endl;
}
//离群滤波
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr cloud_filtered (new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>);
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr remove (new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>);
pcl::StatisticalOutlierRemoval<pcl::PointXYZ> sor;
sor.setInputCloud (cloud);
sor.setMeanK (50);
sor.setStddevMulThresh (1.0);
sor.filter(*cloud_filtered);
showCloud("filtered",cloud_filtered);
sor.setNegative(true);
sor.filter(*remove);
3、拿离群点的X、Y、Z三轴坐标与前面记录的作比对,找出离群点在原Mat中对应的行列信息,复原离群点在原图中的情况
//点云转tiff
cv::Mat cloud2Tiff(std::vector<pointindex> list,int width,int height){
cv::Mat output = cv::Mat::zeros(cv::Size(height,width) ,CV_32FC3);
for(auto&p:list){
output.ptr<float>(p.i)[3*p.j+2] = p.x;
output.ptr<float>(p.i)[3*p.j+1] = p.y;
output.ptr<float>(p.i)[3*p.j] = p.z;
}
return output;
}
std::vector<pointindex> filteredpoints;
for(int num = 0;num<remove->points.size();num++){
for (int index = 0;index<pointList.size();index++){
if (std::abs(remove->points[num].x - pointList[index].x) < 0.000001
&& std::abs(remove->points[num].y - pointList[index].y) < 0.000001
&& std::abs(remove->points[num].z - pointList[index].z) < 0.000001){
filteredpoints.push_back(pointList[index]);
}
}
}
//离群点云转图
cv::Mat src = cloud2Tiff(filteredpoints,img.rows,img.cols);
4、离群点Mat与原Mat通道相减
//通道相减
cv::Mat channelSubtract(cv::Mat img,cv::Mat src){
if (src.rows==img.rows && src.cols==img.cols){
for(int i=0;i<src.rows;i++){
for(int j=0;j<src.cols;j++){
src.ptr<float>(i)[3*j] = img.ptr<float>(i)[3*j] - src.ptr<float>(i)[3*j];
src.ptr<float>(i)[3*j+1] = img.ptr<float>(i)[3*j+1] - src.ptr<float>(i)[3*j+1];
src.ptr<float>(i)[3*j+2] = img.ptr<float>(i)[3*j+2] - src.ptr<float>(i)[3*j+2];
}
}
}
return src;
}
//离群点云图与原图通道相减
src = channelSubtract(img,src);
效果
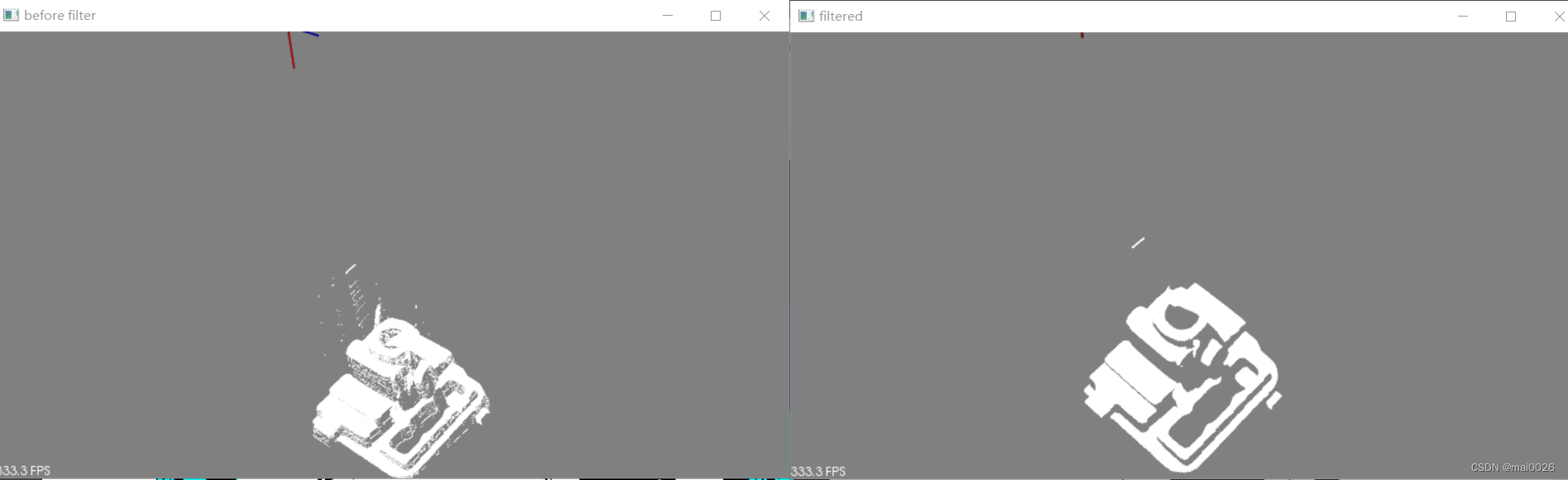
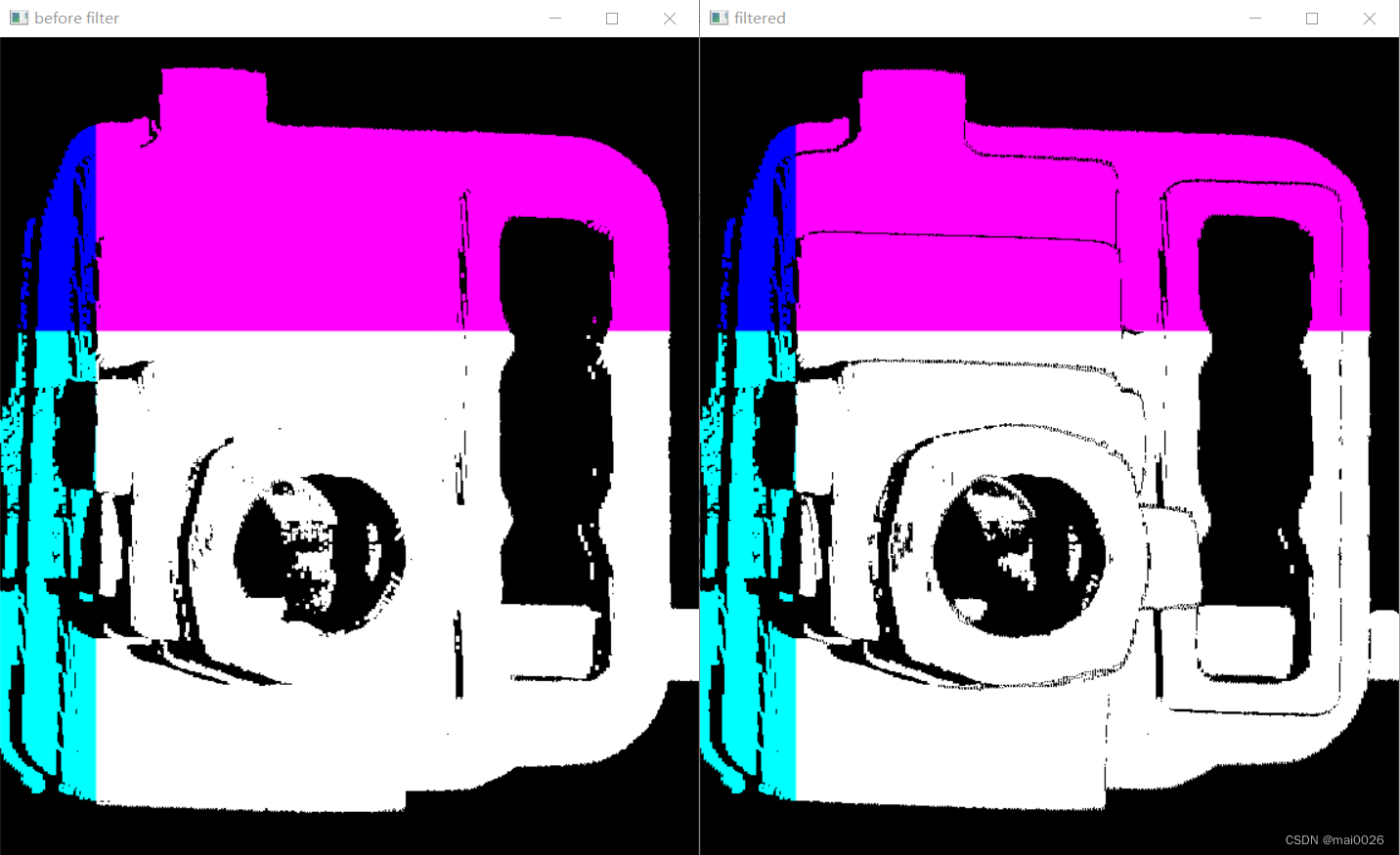
完整代码
#include <QCoreApplication>
#include<opencv2/opencv.hpp>
#include <pcl/visualization/pcl_visualizer.h>
#include<iostream>//标准C++库中的输入输出类相关头文件。
#include<pcl/io/io.h>
#include<pcl/io/pcd_io.h>//pcd 读写类相关的头文件。
#include<pcl/io/ply_io.h>
#include<pcl/point_types.h> //PCL中支持的点类型头文件。
#include <pcl/filters/statistical_outlier_removal.h>
#include <string.h>
struct pointindex{
float x;
float y;
float z;
int i;
int j;
};
std::vector<pointindex> pointList;
//tiff转点云
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr tiff2Cloud(cv::Mat src)
{
//创建点云
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr cloud (new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>);
if (src.type() == CV_32FC3){
for (int i = 0; i < src.rows; i++){
const float *p_src = src.ptr<float>(i);
for (int j = 0; j < src.cols; j++){
if(p_src[3*j+2]>0){
pcl::PointXYZ point;
point.x = p_src[3*j];
point.y = p_src[3*j+1];
point.z = p_src[3*j+2];
cloud->push_back(point);
pointindex point_;
point_.x = point.x = p_src[3*j];
point_.y = p_src[3*j+1];
point_.z = p_src[3*j+2];
point_.i = i;
point_.j = j;
pointList.push_back(point_);
}
}
}
}
return cloud;
}
//点云转tiff
cv::Mat cloud2Tiff(std::vector<pointindex> list,int width,int height){
cv::Mat output = cv::Mat::zeros(cv::Size(height,width) ,CV_32FC3);
for(auto&p:list){
output.ptr<float>(p.i)[3*p.j] = p.x;
output.ptr<float>(p.i)[3*p.j+1] = p.y;
output.ptr<float>(p.i)[3*p.j+2] = p.z;
}
return output;
}
//点云可视化
void showCloud(std::string windowname,pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr cloud){
pcl::visualization::PCLVisualizer::Ptr viewer (new pcl::visualization::PCLVisualizer (windowname));
viewer->setBackgroundColor (0.5, 0.5, 0.5); //设置背景
viewer->addPointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ> (cloud, "sample cloud"); //显示点云
viewer->setPointCloudRenderingProperties (pcl::visualization::PCL_VISUALIZER_POINT_SIZE, 1, "sample cloud"); //设置点尺寸
viewer->addCoordinateSystem (100.0); //设置坐标轴尺寸
// while (!viewer->wasStopped ())
// {
// viewer->spinOnce (100);
// boost::this_thread::sleep (boost::posix_time::microseconds (100000));
// }
cout<<"Point couting in "<<windowname<<": "<<cloud->size()<<endl;
}
//通道相减
cv::Mat channelSubtract(cv::Mat img,cv::Mat src){
if (src.rows==img.rows && src.cols==img.cols){
for(int i=0;i<src.rows;i++){
for(int j=0;j<src.cols;j++){
src.ptr<float>(i)[3*j] = img.ptr<float>(i)[3*j] - src.ptr<float>(i)[3*j];
src.ptr<float>(i)[3*j+1] = img.ptr<float>(i)[3*j+1] - src.ptr<float>(i)[3*j+1];
src.ptr<float>(i)[3*j+2] = img.ptr<float>(i)[3*j+2] - src.ptr<float>(i)[3*j+2];
}
}
}
return src;
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
QCoreApplication a(argc, argv);
//tiff转pcd
cv::Mat img = cv::imread("D:\\Qt_Project\\model123.tiff",cv::IMREAD_UNCHANGED|cv::IMREAD_ANYCOLOR|cv::IMREAD_ANYDEPTH);
cv::imshow("before filter",img);
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr cloud (new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>);
//图转点云
cloud = tiff2Cloud(img);
//显示点云
showCloud("before filter",cloud);
//离群滤波
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr cloud_filtered (new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>);
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr remove (new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>);
pcl::StatisticalOutlierRemoval<pcl::PointXYZ> sor;
sor.setInputCloud (cloud);
sor.setMeanK (50);
sor.setStddevMulThresh (1.0);
sor.filter(*cloud_filtered);
showCloud("filtered",cloud_filtered);
sor.setNegative(true);
sor.filter(*remove);
std::vector<pointindex> filteredpoints;
for(int num = 0;num<remove->points.size();num++){
for (int index = 0;index<pointList.size();index++){
if (std::abs(remove->points[num].x - pointList[index].x) < 0.000001
&& std::abs(remove->points[num].y - pointList[index].y) < 0.000001
&& std::abs(remove->points[num].z - pointList[index].z) < 0.000001){
filteredpoints.push_back(pointList[index]);
}
}
}
//离群点云转图
cv::Mat src = cloud2Tiff(filteredpoints,img.rows,img.cols);
//离群点云图与原图通道相减
src = channelSubtract(img,src);
cv::imshow("filtered",src);
return a.exec();
}
这篇博客解决的问题是如何将.tiff文件转.pcd文件滤波后再转回.tiff文件同时保持像素的一致,下方链接中的源码仅解决了将.tiff文件转.pcd文件这个问题,注意甄别。
tiff转PCL
里面有完整的tiff转pcl代码以及用到的数据集























 172
172











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










