1
Introduction
spectral graph theory
graph signal processing (GSP)
Fourier basis
eigenvalue decomposition (EVD)

2
Proposed Technique
Generalizing CNNs to graphs requires three fundamental steps:
(i) the design of localized convolutional fifilters on graphs
(ii) a graph coarsening procedure that groups together similar vertices
(iii) a graph pooling operation that trades spatial resolution for higher fifilter resolution.
2.1
Learning Fast Localized Spectral Filters
There are two strategies to defifine convolutional fifilters; either from a spatial approach or from a spectral approach.
Graph Fourier Transform
A signal
x : V → R defined on the nodes of the graph may be regarded as a vector
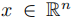
x
i
is the value of
x
at the
i
th node
![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]()
(这个D也就是每个点有几条边,加权)
L标准化定义:
As L is a real symmetric positive semidefifinite matrix(实对称半正定矩阵
),it has a complete set of orthonormal eigenvectors
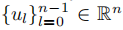 (一组完全正交的特征向量),known as the graph Fourier modes, and their associated ordered real nonnegative eigenvalues
(一组完全正交的特征向量),known as the graph Fourier modes, and their associated ordered real nonnegative eigenvalues
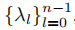 (相关的有序实非负特征值),
identified as the frequencies of the graph.
(相关的有序实非负特征值),
identified as the frequencies of the graph.
L分解:
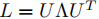 ,
,
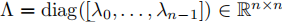 ,
,
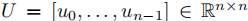
所以:把一个信号x的图傅里叶变换定义为:
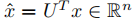
反过来:
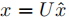
Spectral fifiltering of graph signals
Polynomial parametrization for localized fifilters
non-parametric fifilters两个局限:
(i) they are not localized in space
(ii) their learning complexity is in
O
(
n
), the dimensionality of the data.
所以,用下面这个
polynomial fifilter
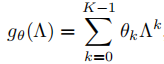 ,
,
(可能内容不全)








 本文介绍了一种将卷积神经网络应用于图信号处理的技术,包括设计局部化图滤波器、图分块和池化操作。重点讨论了从频域角度定义滤波器的方法,以及使用多项式参数化解决非局部化和高复杂度问题。
本文介绍了一种将卷积神经网络应用于图信号处理的技术,包括设计局部化图滤波器、图分块和池化操作。重点讨论了从频域角度定义滤波器的方法,以及使用多项式参数化解决非局部化和高复杂度问题。














 2393
2393











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








