一、 Multiplier
1.1 概述
乘法器顾名思义,用来做乘法运算。
1.2 端口说明
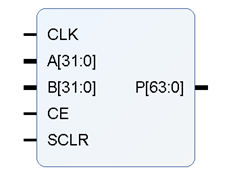

1.3 ip核的生成
(1)在ip catalog里面选择multiplier

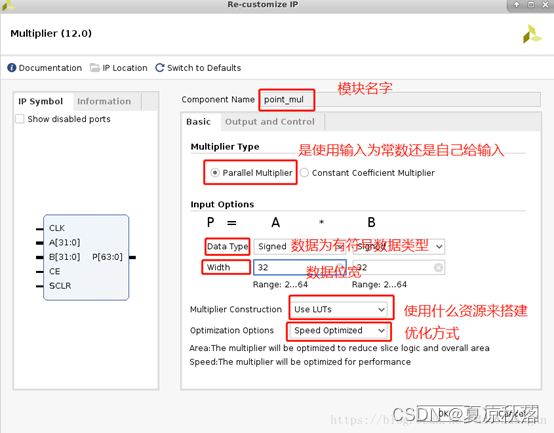
(2)basic的具体配置以及含义如下:
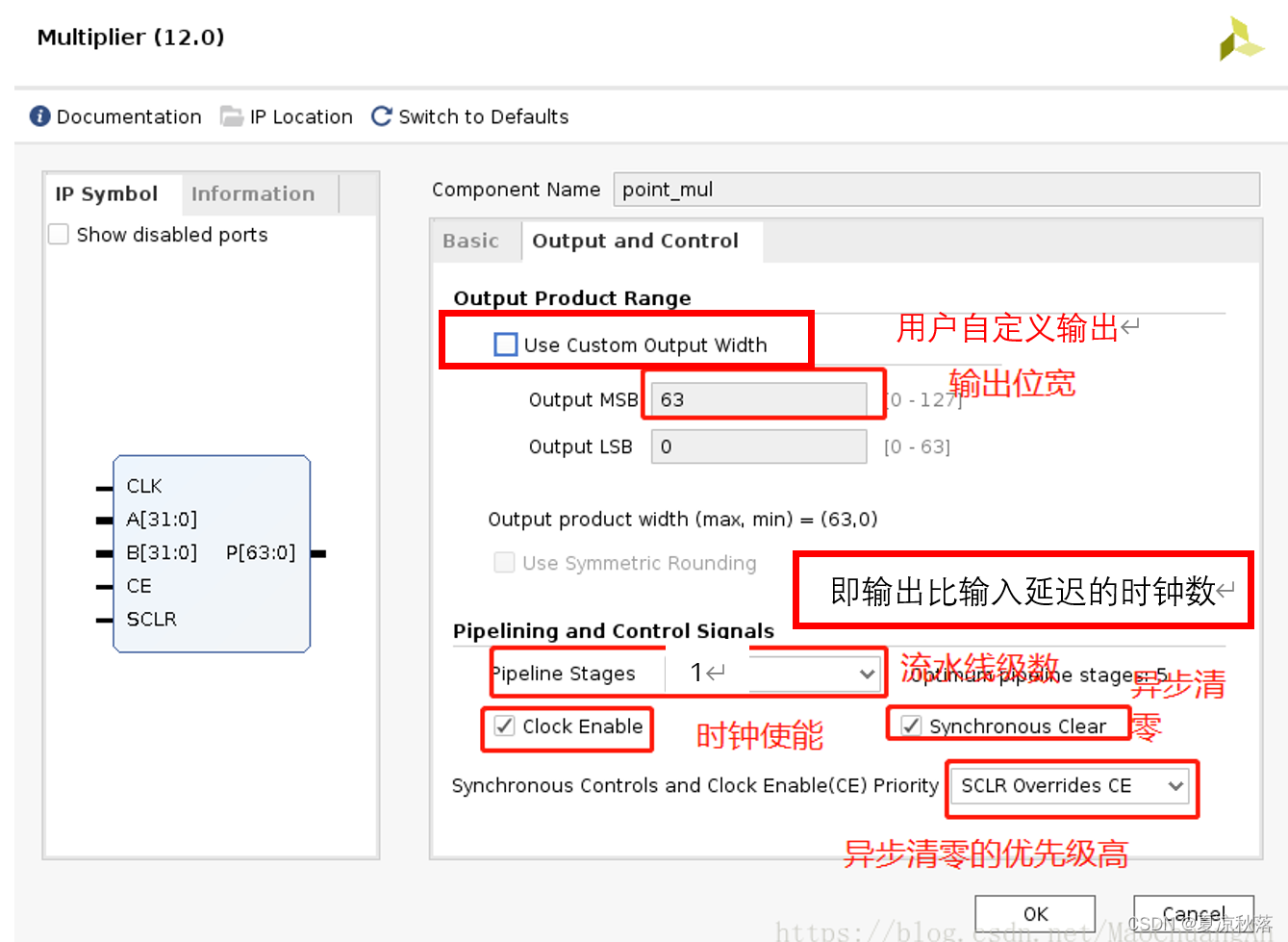
(3)output and control的配置如下:
1.4 代码实现
主程序:
library IEEE;
use IEEE.STD_LOGIC_1164.ALL;
-- Uncomment the following library declaration if using
-- arithmetic functions with Signed or Unsigned values
--use IEEE.NUMERIC_STD.ALL;
-- Uncomment the following library declaration if instantiating
-- any Xilinx leaf cells in this code.
--library UNISIM;
--use UNISIM.VComponents.all;
entity Multiplier is
Port (
CLK: in std_logic;
A : IN STD_LOGIC_VECTOR(31 DOWNTO 0);
B : IN STD_LOGIC_VECTOR(31 DOWNTO 0);
CE : IN STD_LOGIC;
SCLR : IN STD_LOGIC;
P : OUT STD_LOGIC_VECTOR(63 DOWNTO 0)
);
end Multiplier;
architecture Behavioral of Multiplier is
COMPONENT mult_gen_0
PORT (
CLK : IN STD_LOGIC;
A : IN STD_LOGIC_VECTOR(31 DOWNTO 0);
B : IN STD_LOGIC_VECTOR(31 DOWNTO 0);
CE : IN STD_LOGIC;
SCLR : IN STD_LOGIC;
P : OUT STD_LOGIC_VECTOR(63 DOWNTO 0)
);
END COMPONENT;
begin
signed32_signed32 : mult_gen_0
PORT MAP (
CLK => CLK,
A => A,
B => B,
CE => CE,
SCLR => SCLR,
P => P
);
end Behavioral;
测试文件(VHDL):
library IEEE;
use IEEE.STD_LOGIC_1164.ALL;
use IEEE.STD_LOGIC_ARITH.ALL;
-- Uncomment the following library declaration if using
-- arithmetic functions with Signed or Unsigned values
--use IEEE.NUMERIC_STD.ALL;
-- Uncomment the following library declaration if instantiating
-- any Xilinx leaf cells in this code.
--library UNISIM;
--use UNISIM.VComponents.all;
entity multiplier_tb is
-- Port ( );
end multiplier_tb;
architecture Behavioral of multiplier_tb is
signal clk : std_logic;
signal a : std_logic_vector(31 downto 0);
signal b : std_logic_vector(31 downto 0);
signal cs : std_logic;
signal sclr : std_logic;
signal result : std_logic_vector(63 downto 0);
COMPONENT multiplier
Port (
CLK: in std_logic;
A : IN STD_LOGIC_VECTOR(31 DOWNTO 0);
B : IN STD_LOGIC_VECTOR(31 DOWNTO 0);
CE : IN STD_LOGIC;
SCLR : IN STD_LOGIC;
P : OUT STD_LOGIC_VECTOR(63 DOWNTO 0)
);
END COMPONENT;
begin
multiplier_inst0: multiplier
Port map (
CLK => clk,
A => a,
B => b,
CE => cs,
SCLR => sclr,
P => result
);
clk_gen: process
begin
clk <='1';
wait for 5ns;
clk <= '0';
wait for 5ns;
end process;
process
begin
a <= (others=>'0') ; -- 必须加括号否则会报错
b <= (others=>'0');
cs <= '0';
sclr <='1';
wait for 20ns;
a <= conv_std_logic_vector(11,32);
b <= conv_std_logic_vector(10,32);
cs <= '1';
sclr <='0';
wait for 100ns;
a <= conv_std_logic_vector(-11,32);
b <= conv_std_logic_vector(10,32);
wait for 100ns;
cs <='0';
wait; -- 一直等待下去
end process;
end Behavioral;
测试文件(Verilog):
module multiplier_tb1();
reg clk;
reg signed [31:0] a;
reg signed [31:0] b;
reg cs;
reg sclr;
wire signed [63:0] result ;
Multiplier Multiplier_inst0
(
.CLK (clk),
.A (a),
.B (b ),
.CE (cs ),
.SCLR (sclr ),
.P (result)
);
initial clk=1;
always #5 clk=~clk;
initial begin
a = 0 ;
b = 0;
cs = 0;
sclr =1;
#20;
a = 32'd11;
b = 32'd10;
cs = 1;
sclr = 0;
#100;
a = $signed(-11);
b = 32'd10;
#100;
cs =0;
end
endmodule
1.5 仿真结果
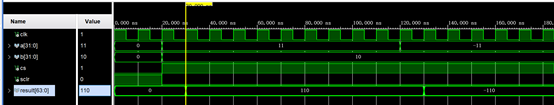
从图中可以看出,输出比输入延时了一个时钟周期,这与ip核中pipeline stages设置一样,而且乘法运算结果正确。







 本文介绍了一种使用VHDL实现的乘法器设计方法,并详细阐述了其端口定义、IP核生成过程及代码实现细节。通过仿真验证了设计的正确性。
本文介绍了一种使用VHDL实现的乘法器设计方法,并详细阐述了其端口定义、IP核生成过程及代码实现细节。通过仿真验证了设计的正确性。

















 1221
1221

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








