1、旋转矩阵了解
在旋转坐标轴之前,要先了解对于x,y,z轴的变换矩阵
对于x轴

[
[1, 0, 0],
[0, np.cos(theta_x), -np.sin(theta_x)],
[0, np.sin(theta_x), np.cos(theta_x)]
]对于y轴
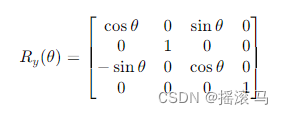
[
[np.cos(theta_y), 0, np.sin(theta_y)],
[0, 1, 0],
[-np.sin(theta_y), 0, np.cos(theta_y)]
]对于z轴

[
[np.cos(theta_z), -np.sin(theta_z), 0],
[np.sin(theta_z), np.cos(theta_z), 0],
[0, 0, 1]
]同样如果需要平移缩放等操作,则需要利用对应的变换矩阵
平移

缩放

2、旋转与组合变换
2.1、旋转变换
有了变换矩阵,我们只需要将我们的点云数据转为numpy格式设为N,再与变换矩阵R做矩阵乘法即可。
旋转后的矩阵为S
S = N * R
整体代码如下:
def point_cloud_rotation(pcd, elev_y, elev_z, elev_x):
# 将点云对象转换为 NumPy 数组
points = np.asarray(pcd.points)
# 将点云旋转到指定角度
theta_z = np.radians(elev_z)
theta_y = np.radians(elev_y)
theta_x = np.radians(elev_x)
rotation_matrix_x = np.array([
[1, 0, 0],
[0, np.cos(theta_x), np.sin(theta_x)],
[0, -np.sin(theta_x), np.cos(theta_x)]
])
rotation_matrix_y = np.array([
[np.cos(theta_y), 0, np.sin(theta_y)],
[0, 1, 0],
[-np.sin(theta_y), 0, np.cos(theta_y)]
])
rotation_matrix_z = np.array([
[np.cos(theta_z), np.sin(theta_z), 0],
[-np.sin(theta_z), np.cos(theta_z), 0],
[0, 0, 1]
])
# 根据自己的需要,对x,y,z轴旋转
rotated_points = np.dot(points, rotation_matrix_z.T)
rotated_points = np.dot(rotated_points, rotation_matrix_y.T)
# rotated_points = np.dot(rotated_points, rotation_matrix_x.T)其中elev_y, elev_z, elev_x为各个轴需要旋转的角度
2.2、组合变换
组合变换矩阵可以通过将上述矩阵相乘来实现。例如,先旋转再平移可以表示为:
𝑀=𝑇⋅𝑅
其中 𝑇是平移矩阵,𝑅 是旋转矩阵。






















 286
286











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








