我的配置:
I7-9750H;
核显;
Tensorflow1.14—cpu;
Anacode3;
VS2017;
我的文件结构:
ssd_mobilenet_v1_coco_2017_11_17网上有很多资源下载
不得不说配置Object Detection API就是一项浩大工程,非常之麻烦,配置好了Object Detection API,现在开始训练自己的SSD模型,并用C++调用(数据集只有20张图片,效果不太好)。(过程非常复杂,自己摸索很痛苦);
- 利用labelImg将自己的图片样本(保存在images文件中)标注标签并保存为xml格式,保存在merged_xml文件中。
- 新建train_test_split.py把xml数据集分为了train 、test、 validation三部分,并存储在annotations文件夹中,train为训练集占76.5%,test为测试集10%,validation为验证集13.5%,train_test_split.py代码如下:
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
Created on Tue Apr 7 13:54:20 2020
@author: 27522
"""
import os
import random
import time
import shutil
xmlfilepath = r'merged_xml'
saveBasePath = r"./annotations"
trainval_percent = 0.9
train_percent = 0.85
total_xml = os.listdir(xmlfilepath)
num = len(total_xml)
list = range(num)
tv = int(num * trainval_percent)
tr = int(tv * train_percent)
trainval = random.sample(list, tv)
train = random.sample(trainval, tr)
print("train and val size", tv)
print("train size", tr)
# print(total_xml[1])
start = time.time()
# print(trainval)
# print(train)
test_num = 0
val_num = 0
train_num = 0
# for directory in ['train','test',"val"]:
# xml_path = os.path.join(os.getcwd(), 'annotations/{}'.format(directory))
# if(not os.path.exists(xml_path)):
# os.mkdir(xml_path)
# # shutil.copyfile(filePath, newfile)
# print(xml_path)
for i in list:
name = total_xml[i]
# print(i)
if i in trainval: # train and val set
# ftrainval.write(name)
if i in train:
# ftrain.write(name)
# print("train")
# print(name)
# print("train: "+name+" "+str(train_num))
directory = "train"
train_num += 1
xml_path = os.path.join(os.getcwd(), 'annotations/{}'.format(directory))
if (not os.path.exists(xml_path)):
os.mkdir(xml_path)
filePath = os.path.join(xmlfilepath, name)
newfile = os.path.join(saveBasePath, os.path.join(directory, name))
shutil.copyfile(filePath, newfile)
else:
# fval.write(name)
# print("val")
# print("val: "+name+" "+str(val_num))
directory = "validation"
xml_path = os.path.join(os.getcwd(), 'annotations/{}'.format(directory))
if (not os.path.exists(xml_path)):
os.mkdir(xml_path)
val_num += 1
filePath = os.path.join(xmlfilepath, name)
newfile = os.path.join(saveBasePath, os.path.join(directory, name))
shutil.copyfile(filePath, newfile)
# print(name)
else: # test set
# ftest.write(name)
# print("test")
# print("test: "+name+" "+str(test_num))
directory = "test"
xml_path = os.path.join(os.getcwd(), 'annotations/{}'.format(directory))
if (not os.path.exists(xml_path)):
os.mkdir(xml_path)
test_num += 1
filePath = os.path.join(xmlfilepath, name)
newfile = os.path.join(saveBasePath, os.path.join(directory, name))
shutil.copyfile(filePath, newfile)
# print(name)
# End time
end = time.time()
seconds = end - start
print("train total : " + str(train_num))
print("validation total : " + str(val_num))
print("test total : " + str(test_num))
total_num = train_num + val_num + test_num
print("total number : " + str(total_num))
print("Time taken : {0} seconds".format(seconds))
- 把xml转换成csv文件,新建xml_to_csv.py,运行代码前,需要建一个data目录,用来放生成的csv文件,结果和代码如下:
import os
import glob
import pandas as pd
import xml.etree.ElementTree as ET
def xml_to_csv(path):
xml_list = []
for xml_file in glob.glob(path + '/*.xml'):
tree = ET.parse(xml_file)
root = tree.getroot()
for member in root.findall('object'):
value = (root.find('filename').text,
int(root.find('size')[0].text),
int(root.find('size')[1].text),
member[0].text,
int(member[4][0].text),
int(member[4][1].text),
int(member[4][2].text),
int(member[4][3].text)
)
xml_list.append(value)
column_name = ['filename', 'width', 'height', 'class', 'xmin', 'ymin', 'xmax', 'ymax']
xml_df = pd.DataFrame(xml_list, columns=column_name)
return xml_df
def main():
for folder in ['train','test','validation']:
image_path = os.path.join(os.getcwd(), ('annotations/' + folder))
xml_df = xml_to_csv(image_path)
xml_df.to_csv(('data/' + folder + '_labels.csv'), index=None)
print('Successfully converted xml to csv.')
main()
- 生成tfrecords文件,python文件名为generate_tfrecord.py,代码如下:
from __future__ import division
from __future__ import print_function
from __future__ import absolute_import
import os
import io
import pandas as pd
import tensorflow as tf
from PIL import Image
from object_detection.utils import dataset_util
from collections import namedtuple, OrderedDict
flags = tf.app.flags
flags.DEFINE_string('csv_input', '', 'Path to the CSV input')
flags.DEFINE_string('output_path', '', 'Path to output TFRecord')
FLAGS = flags.FLAGS
# TO-DO replace this with label map
def class_text_to_int(row_label,filename):
#类型根据自己的需要改
if row_label == 'white':
return 1
elif row_label == 'black':
return 2
elif row_label == 'orange':
return 3
elif row_label == 'blue':
return 4
else:
print("------------------nonetype:", filename)
None
def split(df, group):
data = namedtuple('data', ['filename', 'object'])
gb = df.groupby(group)
return [data(filename, gb.get_group(x))
for filename, x in zip(gb.groups.keys(), gb.groups)]
def create_tf_example(group, path):
with tf.gfile.GFile(os.path.join(path, '{}'.format(group.filename)), 'rb') as fid:
encoded_jpg = fid.read()
encoded_jpg_io = io.BytesIO(encoded_jpg)
image = Image.open(encoded_jpg_io)
width, height = image.size
filename = group.filename.encode('utf8')
image_format = b'jpg'
xmins = []
xmaxs = []
ymins = []
ymaxs = []
classes_text = []
classes = []
for index, row in group.object.iterrows():
xmins.append(row['xmin'] / width)
xmaxs.append(row['xmax'] / width)
ymins.append(row['ymin'] / height)
ymaxs.append(row['ymax'] / height)
classes_text.append(row['class'].encode('utf8'))
classes.append(class_text_to_int(row['class'], group.filename))
tf_example = tf.train.Example(features=tf.train.Features(feature={
'image/height': dataset_util.int64_feature(height),
'image/width': dataset_util.int64_feature(width),
'image/filename': dataset_util.bytes_feature(filename),
'image/source_id': dataset_util.bytes_feature(filename),
'image/encoded': dataset_util.bytes_feature(encoded_jpg),
'image/format': dataset_util.bytes_feature(image_format),
'image/object/bbox/xmin': dataset_util.float_list_feature(xmins),
'image/object/bbox/xmax': dataset_util.float_list_feature(xmaxs),
'image/object/bbox/ymin': dataset_util.float_list_feature(ymins),
'image/object/bbox/ymax': dataset_util.float_list_feature(ymaxs),
'image/object/class/text': dataset_util.bytes_list_feature(classes_text),
'image/object/class/label': dataset_util.int64_list_feature(classes),
}))
return tf_example
def main(_):
writer = tf.python_io.TFRecordWriter(FLAGS.output_path)
path = os.path.join(os.getcwd(), 'images')
examples = pd.read_csv(FLAGS.csv_input)
grouped = split(examples, 'filename')
num=0
for group in grouped:
num+=1
tf_example = create_tf_example(group, path)
writer.write(tf_example.SerializeToString())
if(num%2==0):
#每完成2个转换,打印一次
print(num)
writer.close()
output_path = os.path.join(os.getcwd(), FLAGS.output_path)
print('Successfully created the TFRecords: {}'.format(output_path))
if __name__ == '__main__':
tf.app.run()
注意:17行和80行根据自己需要修改;
现将训练集转换为tfrecord格式,输入如下命令:
python generate_tfrecord.py --csv_input=data/whsyxt_train_labels.csv --output_path=data/whsyxt_train.tfrecord类似的,我们可以输入如下命令,将验证集和测试集也转换为tfrecord格式,
python generate_tfrecord.py --csv_input=data/whsyxt_validation_labels.csv --output_path=data/whsyxt_validation.tfrecord
python generate_tfrecord.py --csv_input=data/whsyxt_test_labels.csv --output_path=data/whsyxt_test.tfrecord
5、配置管道配置文件,找到 D:\Program Files (x86)\anaconda\Lib\site-packages\tensorflow\models\research\object_detection\samples\configs\ssd_mobilenet_v1_pets.config文件,复制到data文件夹下,修改之后代码如下:
# SSD with Mobilenet v1, configured for Oxford-IIIT Pets Dataset.
# Users should configure the fine_tune_checkpoint field in the train config as
# well as the label_map_path and input_path fields in the train_input_reader and
# eval_input_reader. Search for "PATH_TO_BE_CONFIGURED" to find the fields that
# should be configured.
model {
ssd {
#改为自己的类别数,不包括background
num_classes: 4
box_coder {
faster_rcnn_box_coder {
y_scale: 10.0
x_scale: 10.0
height_scale: 5.0
width_scale: 5.0
}
}
//匹配规则
matcher {
argmax_matcher {
matched_threshold: 0.5
unmatched_threshold: 0.5
ignore_thresholds: false
negatives_lower_than_unmatched: true
force_match_for_each_row: true
}
}
//区域相似度度量规则
similarity_calculator {
iou_similarity {
}
}
//预测用的default boxes
anchor_generator {
ssd_anchor_generator {
num_layers: 6
min_scale: 0.2
max_scale: 0.95
aspect_ratios: 1.0
aspect_ratios: 2.0
aspect_ratios: 0.5
aspect_ratios: 3.0
aspect_ratios: 0.3333
}
}
image_resizer {
fixed_shape_resizer {
//输入图片高度
height: 300
//输入图片宽度
width: 300
}
}
//卷积预测层参数
box_predictor {
convolutional_box_predictor {
min_depth: 0
max_depth: 0
num_layers_before_predictor: 0
use_dropout: false
dropout_keep_probability: 0.8
kernel_size: 1
box_code_size: 4
apply_sigmoid_to_scores: false
conv_hyperparams {
activation: RELU_6,
regularizer {
l2_regularizer {
weight: 0.00004
}
}
initializer {
truncated_normal_initializer {
stddev: 0.03
mean: 0.0
}
}
batch_norm {
train: true,
scale: true,
center: true,
decay: 0.9997,
epsilon: 0.001,
}
}
}
}
//卷积特征提取
feature_extractor {
type: 'ssd_mobilenet_v1'
min_depth: 16
depth_multiplier: 1.0
conv_hyperparams {
activation: RELU_6,
regularizer {
l2_regularizer {
weight: 0.00004
}
}
initializer {
truncated_normal_initializer {
stddev: 0.03
mean: 0.0
}
}
batch_norm {
train: true,
scale: true,
center: true,
decay: 0.9997,
epsilon: 0.001,
}
}
}
loss {
//分类损失函数
classification_loss {
weighted_sigmoid {
}
}
//定位损失函数
localization_loss {
weighted_smooth_l1 {
}
}
//难样本挖掘规则
hard_example_miner {
num_hard_examples: 3000
iou_threshold: 0.99
loss_type: CLASSIFICATION
max_negatives_per_positive: 3
min_negatives_per_image: 0
}
classification_weight: 1.0
localization_weight: 1.0
}
//归一化参数
normalize_loss_by_num_matches: true
//图像后处理,只参与验证,不参与训练
post_processing {
batch_non_max_suppression {
score_threshold: 1e-8
iou_threshold: 0.6
max_detections_per_class: 100
max_total_detections: 100
}
score_converter: SIGMOID
}
}
}
train_config: {
#视CPU情况而定,每次迭代输入的图片数量
batch_size: 2
optimizer {
rms_prop_optimizer: {
learning_rate: {
exponential_decay_learning_rate {
initial_learning_rate: 0.004
decay_steps: 100#学习率以基数0.95每100步进行衰减
decay_factor: 0.95
}
}
momentum_optimizer_value: 0.9
decay: 0.9
epsilon: 1.0
}
}
#改为自己应用的SSD模型的kept路径
fine_tune_checkpoint: "D:/python project/SSD mobilenet/ssd_mobilenet_v1_coco_2017_11_17/model.ckpt"
from_detection_checkpoint: false
#load_all_detection_checkpoint_vars: true
# Note: The below line limits the training process to 200K steps, which we
# empirically found to be sufficient enough to train the pets dataset. This
# effectively bypasses the learning rate schedule (the learning rate will
# never decay). Remove the below line to train indefinitely.
#步数200
num_steps: 20000
data_augmentation_options {
random_horizontal_flip {
}
}
data_augmentation_options {
ssd_random_crop {
}
}
}
train_input_reader: {
tf_record_input_reader {
#改为自己路径
input_path: "D:/python project/SSD mobilenet/data/whsyxt_train.tfrecord"
}
label_map_path: "D:/python project/SSD mobilenet/data/label_map.pbtxt"
}
eval_config: {
metrics_set: "coco_detection_metrics"
num_examples: 1#改成自己validation的样本数量
}
eval_input_reader: {
tf_record_input_reader {
#改为自己路径
input_path: "D:/python project/SSD mobilenet/data/whsyxt_validation.tfrecord"
}
# label_map.pbtxt自己构建
label_map_path: "D:/python project/SSD mobilenet/data/label_map.pbtxt"
shuffle: false
num_readers: 1
}
注意:修改路径一定要认真仔细,不然训练时会出现错误:
Windows fatal exception: access violation
label_map.pbtxt代码如下:
item {
id: 1
name: 'white'
}
item {
id: 2
name: 'black'
}
item {
id: 3
name: 'orange'
}
item {
id: 4
name: 'blue'
}
- 打开D:\Program Files (x86)\anaconda\Lib\site-packages\tensorflow\models\research\object_detection,将model_main.py、nets复制到D:\python project\SSD mobilenet下;打开D:\Program Files (x86)\anaconda\Lib\site-packages\tensorflow\models\research\slim,将datasets、deployment文件复制到D:\python project\SSD mobilenet下;
在D:\python project\SSD mobilenet目录下输入以下命令:
python model_main.py --logtostderr --model_dir=data/ --pipeline_config_path=data/ssd_mobilenet_v1_pets.config在data目录下得到文件:model.ckpt-200.data-00000-of-00001、model.ckpt-200.index、
model.ckpt-200.meta
评价模型:
python eval.py --logtostderr --checkpoint_dir=mydata1/ --pipeline_config_path=data/faster_rcnn_inception_v2_coco.config \ --eval_dir eval1
7、将kept文件转换成pb文件:将D:\Program Files (x86)\anaconda\Lib\site-packages\tensorflow\models\research\object_detection目录下的export_inference_graph.py复制到D:\python project\SSD mobilenet目录下:
执行如下命令:
python export_inference_graph.py \ --input_type image_tensor \ --pipeline_config_path data/ssd_mobilenet_v1_pets.config \ --trained_checkpoint_prefix data/model.ckpt-200 \ --output_directory result8、何获得ssd_mobilenet_v1_pets.pbtxt:打开D:\python project\SSD mobilenet\pb2pbtxt,将上面得到的frozen_inference_graph.pb和ssd_mobilenet_v1_pets.config复制到该目录下,tf_text_graph_ssd.py可以在D:\opencv4.2\opencv4.2.0\samples\dnn下找到。
执行如下命令:
python tf_text_graph_ssd.py --input frozen_inference_graph.pb --config ssd_mobilenet_v1_pets.config --output ssd_mobilenet_v1_pets.pbtxt得到ssd_mobilenet_v1_pets.pbtxt
pb2pbtxt文件的资源可以私聊
9、VS2017环境配置(opencv4.2已经配置好了),下面进行python环境的配置:
(1)VC++目录——库目录

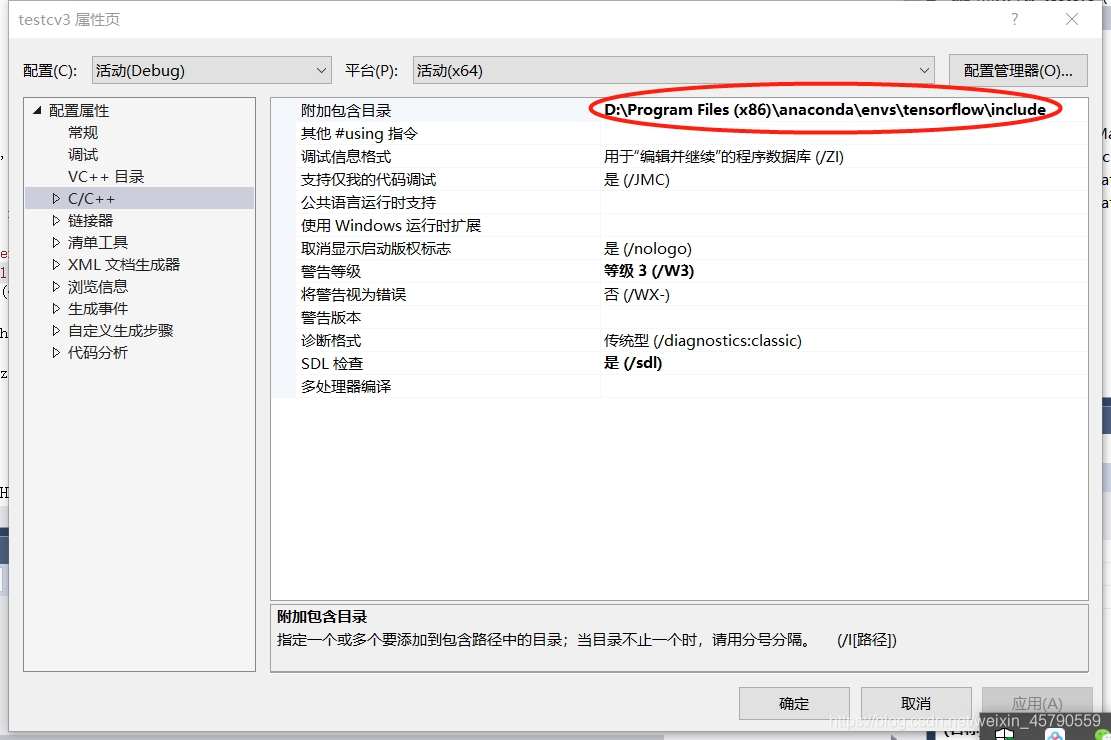
2)C/C++——附加包含目录
(3)链接器——输入——附加依赖项,输入python36_d.lib
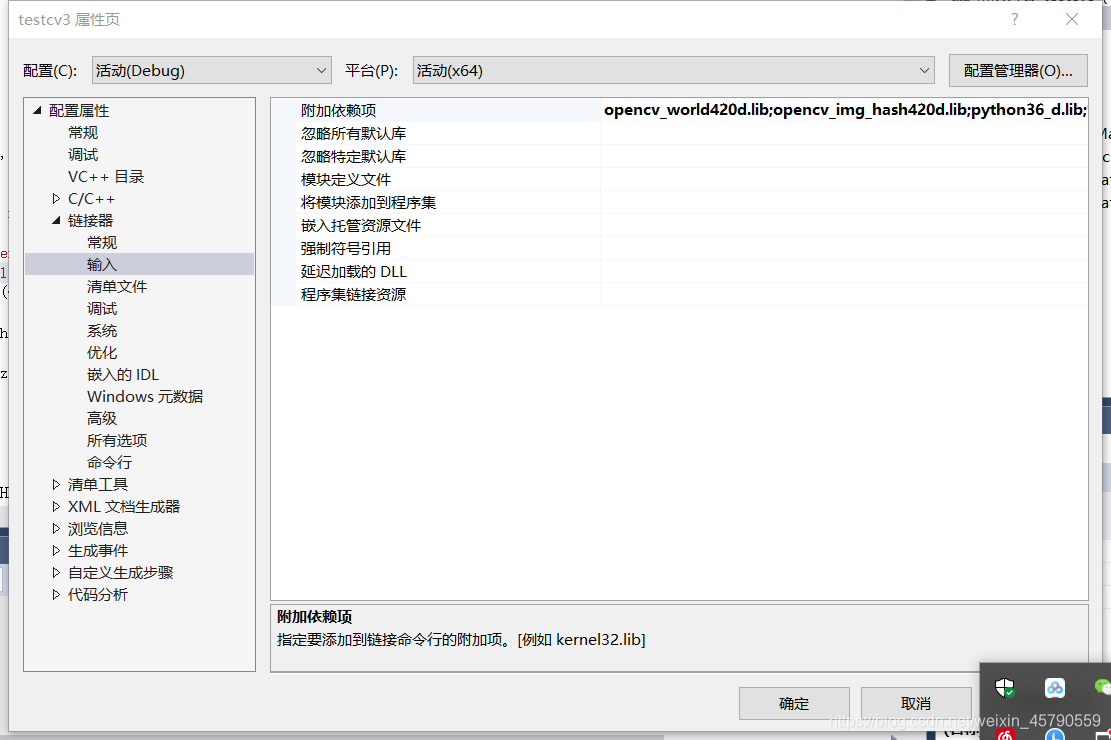
注意:其实打开
D:\Program Files (x86)\anaconda\envs\tensorflow\libs目录下并没有python36_d.lib,将python36.lib复制一份改名字就好
至此,环境配置好了
10:调用程序:
#include <iostream>
#include<opencv2/opencv.hpp>
#include<opencv2/dnn.hpp>
#include <opencv2/highgui/highgui_c.h>
#include "opencv2/imgproc/types_c.h"
using namespace std;
using namespace cv;
const size_t inWidth = 300;
const size_t inHeight = 300;
const float WHRatio = inWidth / (float)inHeight;
const char* classNames[] = { "background","white","black","orange","blue" };//这个需要根据训练的类别定义
int main()
{
Mat frame = cv::imread("D:/python/SSD mobilenet/cat3.jpg");
Size frame_size = frame.size();
String weights = "D:/python/SSD mobilenet/result/frozen_inference_graph.pb";//注意"/"和"\"
String prototxt = "D:/python/SSD mobilenet/pb2pbtxt/ssd_mobilenet_v1_pets.pbtxt";
dnn::Net net = cv::dnn::readNetFromTensorflow(weights, prototxt);
Size cropSize;
//将输入图片尺寸进行修改
if (frame_size.width / (float)frame_size.height > WHRatio)
{
cropSize = Size(static_cast<int>(frame_size.height * WHRatio),
frame_size.height);
}
else
{
cropSize = Size(frame_size.width,
static_cast<int>(frame_size.width / WHRatio));
}
//Rect类用于存储矩形框左上角坐标、宽度和高度
Rect crop(Point((frame_size.width - cropSize.width) / 2,
(frame_size.height - cropSize.height) / 2),
cropSize);
//blobFromImage函数进行图片预处理:均减值、缩放和通道交换(图片归一化)
cv::Mat blob = cv::dnn::blobFromImage(frame, 1. / 255, Size(300, 300));//我觉得可以把(300,300)去掉,实验发现加上(300,300)会造成图片显示不全
//cout << "blob size: " << blob.size << endl;
net.setInput(blob);//将图片输入到网络中
Mat output = net.forward();//获得向前传播结果
//cout << "output size: " << output.size << endl;
Mat detectionMat(output.size[2], output.size[3], CV_32F, output.ptr<float>());
frame = frame(crop);
float confidenceThreshold = 0.55;//该参数与能否生成框有关系
//根据置信度绘制矩形框
for (int i = 0; i < detectionMat.rows; i++)
{
float confidence = detectionMat.at<float>(i, 2);//置信度
if (confidence > confidenceThreshold)
{
size_t objectClass = (size_t)(detectionMat.at<float>(i, 1));//标签文件的索引号
int xLeftBottom = static_cast<int>(detectionMat.at<float>(i, 3) * frame.cols);//矩形框左上点横坐标
int yLeftBottom = static_cast<int>(detectionMat.at<float>(i, 4) * frame.rows);//矩形框左上点纵坐标
int xRightTop = static_cast<int>(detectionMat.at<float>(i, 5) * frame.cols);//矩形框右下横坐标
int yRightTop = static_cast<int>(detectionMat.at<float>(i, 6) * frame.rows);//矩形框右下纵坐标
//ostringstream是C++的一个字符集操作模板类,定义在sstream.h头文件中。ostringstream类通常用于执行C风格的串流的输出操作,格式化字符串,避免申请大量的缓冲区,替代sprintf。
ostringstream ss;
ss << confidence;
String conf(ss.str());
Rect object((int)xLeftBottom, (int)yLeftBottom,
(int)(xRightTop - xLeftBottom),
(int)(yRightTop - yLeftBottom));
rectangle(frame, object, Scalar(0, 0, 255), 2);
String label = String(classNames[objectClass]) + ": " + conf;
int baseLine = 0;
Size labelSize = getTextSize(label, FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.5, 1, &baseLine);
rectangle(frame, Rect(Point(xLeftBottom, yLeftBottom - labelSize.height),
Size(labelSize.width, labelSize.height + baseLine)),
Scalar(0, 255, 255), -1);
putText(frame, label, Point(xLeftBottom, yLeftBottom),
FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.5, Scalar(0, 0, 0));
}
}
imshow("image", frame);
cv::waitKey(0);
destroyAllWindows();
return 0;
}
pb2pbtxt文件的百度云盘链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1FRXt4v8UM4Z9i-qP9eXeaQ
提取码:x4v3





















 506
506











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








