实验二 数据库的基本查询和高级查询
一、实验目的:
- 掌握SQL程序设计基本规范,熟练运用SQL语言实现数据基本查询,包括单表查询、分组统计查询和连接查询。
- 掌握SQL嵌套查询和集合查询等各种高级查询的设计方法等,加深SQL语言的嵌套查询语句的理解,熟练掌握数据查询中的分组、统计、计算和集合的操作方法。
二、实验要求:
- 针对实验一设计的“学生课程”数据库设计各种单表查询SQL语句、分组统计查询语句;设计单个表针对自身的连接查询,设计多个表的连接查询。理解和掌握SQL查询语句各个子句的特点和作用,按照SQL程序设计规范写出具体的SQL查询语句,并调试通过。
- 正确分析用户查询要求,设计各种嵌套查询和集合查询。
- SQL程序设计规范包含SQL关键字大写、表名、属性名、存储过程名等标示符大小写混合、SQL程序书写缩进排列等编程规范。
三、实验重点和难点:
实验重点:
1)分组统计查询、单表自身连接查询、多表连接查询、嵌套查询。
实验难点:
- 区分元组过滤条件和分组过滤条件;确定连接属性,正确设计连接条件。
- 相关子查询、多层EXIST嵌套查询。
四、实验内容:(P87-P113)
(一)简单查询操作
该实验包括投影、选择条件表达,数据排序,使用临时表等。
具体完成以下题目,将它们转换为SQL语句表示,在学生课程数据库中实现其数据查询操作。
例:(1)查询描述:查询所有学生的姓名与学号
SQL语句:select sno,sname from student
查询结果:截图或文本
题目:
1.求数学系学生的学号和姓名。
from student
where Sdept='MA';

2.求选修了课程的学生学号。
select distinct Sno
from sc;(可将重复的合并成一行)
或者
select Sno
from sc;

3.求选修课程号为‘1’的学生号和成绩,并要求对查询结果按成绩的降序排列,如果成绩相同按学号的升序排列。
select Sno,Grade
from sc
where Cno='1'
order by Grade desc,Sno;

4.求选修课程号为‘1’且成绩在80~90之间的学生学号和成绩,并将成绩乘以0.8输出。
select Sno,Grade*0.8
from sc
where Cno='1'and Grade between 80 and 90;

5.求数学系或计算机系姓“张”的学生的信息。
select *
from student
where Sdept in('MA','CS') and Sname like '张%';
查询计算机科学系;
select *
from student
where Sdept in('MA','IS') and Sname like '张%';
查询信息系;

6.求缺少了成绩的学生的学号和课程号。
select Sno,Cno
from sc
where grade is null;

(二)连接查询操作。
该实验包括等值连接、自然连接、求笛卡儿积、一般连接、外连接、内连接、左连接、右连接和自连接等。
题目:
1.查询每个学生的情况以及他所选修的课程。
select student.*,Cname
from student,sc,course
where student.Sno=sc.Sno
and sc.Cno=course.Cno;

2.求学生的学号、姓名、选修的课程及成绩。
select student.Sno,Sname,Cname,Grade
from student,sc,course
where student.Sno=sc.Sno
and sc.Cno=course.Cno;

3.求选修课程号为‘1’且成绩在90以上的学生学号、姓名和成绩。
select student.Sno,Sname,Grade
from student,sc
where student.Sno=sc.Sno
and sc.Cno='1' and sc.Grade>90;

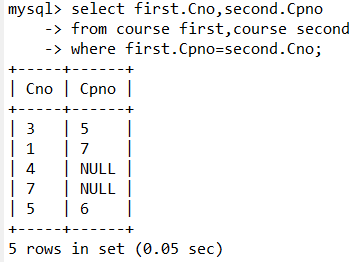
4.查询每一门课程的间接先行课(即先行课的先行课)。
select first.Cno,second.Cpno
from course first,course second
where first.Cpno=second.Cno;
(三)嵌套查询操作:
该实验包括在SQL Server查询分析器中使用IN、比较符、ANY或ALL和EXISTS操作符进行嵌套查询操作。具体完成以下各题。将它们用SQL语句表示,在学生选课中实现其数据嵌套查询操作。
题目:
1.求选修了高等数学的学号和姓名。
select Sno,Sname
from student
where Sno in
(select Sno
from sc
where Cno in
(select Cno
from course
where Cname='数学'
)
);
或者
select student.Sno,Sname
from student,sc,course
where student.Sno=sc.Sno
and sc.Cno=course.Cno
and Cname='数学';

2.求‘2’课程的成绩高于刘晨的学生学号和成绩。
select Sno,Grade
from sc
where Grade>
(select Grade
from sc
where Sno=
(select Sno
from student
where Sname='刘晨')
and Cno='2'
)
and Cno='2';

3.求其他系中比计算机系某一学生年龄小的学生(即年龄小于计算机系年龄最大者的学生)。
select *
from student
where Sage<any(
select Sage
from student
where Sdept='CS'
)
and Sdept<>'CS';

4.求其他系中比计算机系学生年龄都小的学生。
select *
from student
where Sage<all(
select Sage
from student
where Sdept='CS'
)
and Sdept<>'CS';

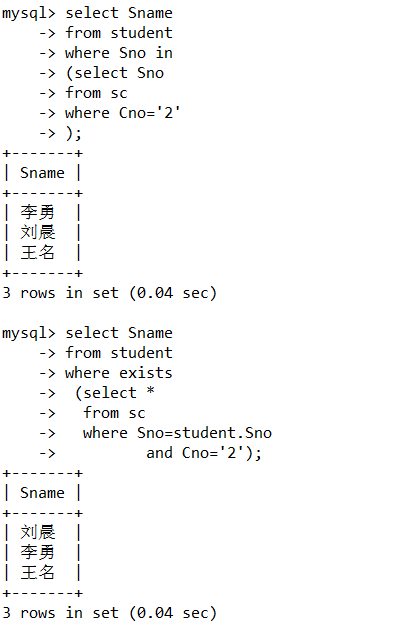
5.求选修了‘2’课程的学生姓名。
select Sname
from student
where Sno in
(select Sno
from sc
where Cno='2'
);
或者
select Sname
from student
where exists
(select *
from sc
where Sno=student.Sno
and Cno='2');
6.求没有选修‘2’课程的学生姓名。
select Sname
from student
where not exists
(select *
from sc
where Sno=student.Sno
and Cno='2');

7.查询选修了全部课程的学生姓名。
select Sname
from student
where not exists
(select *
from course
where not exists
(select *
from sc
where Sno=student.Sno
and Cno=course.Cno
)
);

8.求至少选修了学号为“95002”的学生所选修全部课程的学生学号和姓名。
select distinct Sno
from sc scx
where not exists
(select *
from sc scy
where scy.Sno='95002'and
not exists
(select *
from sc scz
where scz.Sno=scx.Sno and
scz.Cno=scy.Cno
)
);

(四)集合查询和统计查询:
- 分组查询实验。该实验包括分组条件表达、选择组条件表达的方法。
- 使用函数查询的实验。该实验包括统计函数和分组统计函数的使用方法。
- 集合查询实验。该实验并操作UNION、交操作INTERSECT和差操作MINUS的实现方法。
具体完成以下例题,将它们用SQL语句表示,在学生选课中实现其数据查询操作。
题目:
1.求学生的总人数。
select count(*)
from student;

2.求选修了课程的学生人数。
select count(distinct Sno)
from sc;

3.求课程和选修了该课程的学生人数。
select Cno,count(Sno)
from sc
group by Cno;

4.求选修超过3门课的学生学号。
select Sno
from sc
group by Sno
having count(*)>3;(更改条件>=确认结果是否正确)

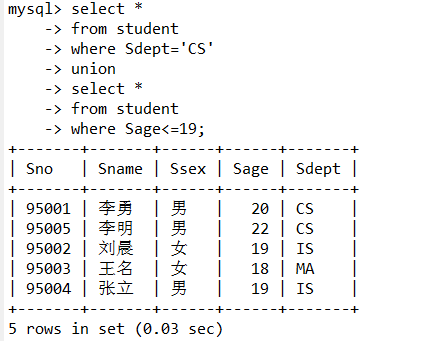
5.查询计算机科学系的学生及年龄不大于19岁的学生。
select *
from student
where Sdept='CS'
union
select *
from student
where Sage<=19;
6.查询计算机科学系的学生与年龄不大于19岁的学生的交集。
select *
from student
where Sdept='CS'
intersect
select *
from student
where Sage<=19;(navicat中mysql没有intersect关键词)
或者
select *
from student
where Sdept='CS' and
Sage<=19;

7.查询计算机科学系的学生与年龄不大于19岁的学生的差集。
select *
from student
where Sdept='CS'
except
select *
from student
where Sage<=19; (navicat中mysql没有excep关键词)
或者
select *
from student
where Sdept='CS'and Sage>19;

8.查询选修课程‘1’的学生集合与选修课程‘2’的学生集合的交集。
select Sno
from sc
where Cno='1' and Sno in
(select Sno
from sc
where Cno='2');

9.查询选修课程‘1’的学生集合与选修课程‘2’的学生集合的差集。
select Sno
from sc
where Cno='1' and Sno in
(select Sno
from sc
where Cno<>'2');

五、实验方法:
将查询需求用SQL语言表示;在SQL Server查询编辑器的输入区中输入SQL查询语句;设置查询分析器的结果区为Standard Execute(标准执行)或Execute to Grid(网格执行)方式;发布执行命令,并在结果区中查看查询结果;如果结果不正确,要进行修改,直到正确为止。所使用的学生管理库中的三张表为:
1.STUDENT(学生信息表)
| SNO(学号) | SNAME(姓名) | SEX(性别) | SAGE(年龄) | SDEPT(所在系) |
| 95001 | 李勇 | 男 | 20 | CS |
| 95002 | 刘晨 | 女 | 19 | IS |
| 95003 | 王名 | 女 | 18 | MA |
| 95004 | 张立 | 男 | 19 | IS |
| 95005 | 李明 | 男 | 22 | CS |
| 95006 | 张小梅 | 女 | 23 | IS |
| 95007 | 封晓文 | 女 | 20 | MA |
2.COURSE(课程表)
| CNO(课程号) | CNAME(课程名) | CPNO(先行课) | CCREDIT(学分) |
| 1 | 数据库 | 5 | 4 |
| 2 | 数学 | 2 | |
| 3 | 信息系统 | 1 | 4 |
| 4 | 操作系统 | 6 | 3 |
| 5 | 数据结构 | 7 | 4 |
| 6 | 数据处理 | 2 | |
| 7 | PASCAL语言 | 6 | 4 |
3.SC(选修表)
| SNO(学号) | CNO(课程号) | Grade(成绩) |
| 95001 | 1 | 92 |
| 95001 | 2 | 85 |
| 95001 | 3 | 88 |
| 95002 | 2 | 90 |
| 95002 | 3 | 80 |
| 95003 | 1 | 78 |
| 95003 | 2 | 80 |
| 95004 | 1 | 90 |
| 95004 | 4 | 60 |
| 95005 | 1 | 80 |
| 95005 | 3 | 89 |
| 95006 | 3 | 80 |
| 95007 | 4 | 65 |
六、实验结果与分析(概括、分析与总结):
有些题有多种解法,上述结果中,部分题写出了两种方法,在两种方法中可以运用到不同的查询,其中运用到了and、distinct(可以把重复的行合并成一行)、order by(排序)等关键词,可以轻松的解决题目。
七、实验心得:
本次实验,将本节的数据查询进行实践。通过实践,可以加强对查询语句的记忆以及其他关键词的用法,使得mysql语句有了更深的记忆。对本次实验,收获颇多,对于今后的学习有了更好的理解和帮助。

























 2750
2750

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










