- 🍨 本文为🔗365天深度学习训练营 中的学习记录博客
- 🍖 作者:K同学啊
- 电脑系统:Windows 10
- 语言环境:Python 3.8.5
- 编译器:Pycharm 2022.02
- 深度学习环境:TensorFlow 2.10.0
- 显卡及显存:RTX 3060 12G
目录
目录
前言
RNN原理:在标准 RNN 中,这个重复模块将具有非常简单的结构,例如单个 tanh 层

LSTM原理:通过门控状态来选择调整传输的信息,简单的来说就是记住需要长时间记忆的信息,忘记不重要的信息,其结构如下:

一、数据集

其中每个数据的标签含义为:
- Time:时间
- Tem1:火灾温度
- CO 1:一氧化碳浓度
- Soot 1:烟雾浓度
二、前期工作
1、默认启动GPU,没有的话则使用CPU
代码如下(示例):
import tensorflow as tf
gpus = tf.config.list_physical_devices("GPU")
if gpus:
gpu0 = gpus[0] #如果有多个GPU,仅使用第0个GPU
tf.config.experimental.set_memory_growth(gpu0, True) #设置GPU显存用量按需使用
tf.config.set_visible_devices([gpu0],"GPU")
2、读入数据
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
df = pd.read_csv("E:\DL_data\Day21\heart.csv")
dataFrame = df.iloc[:,1:]
dataFrame

3、数据可视化
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import seaborn as sns
plt.rcParams['savefig.dpi'] = 500 #图片像素
plt.rcParams['figure.dpi'] = 500 #分辨率
fig, ax =plt.subplots(1,3,constrained_layout=True, figsize=(14, 3))
sns.lineplot(data=df["Tem1"], ax=ax[0])
sns.lineplot(data=df["CO 1"], ax=ax[1])
sns.lineplot(data=df["Soot 1"], ax=ax[2])
plt.show()

三、数据预处理
1.设置X,y
width_X = 8
width_y = 1
X = []
y = []
in_start = 0
for _, _ in df.iterrows():
in_end = in_start + width_X
out_end = in_end + width_y
if out_end < len(dataFrame):
X_ = np.array(dataFrame.iloc[in_start:in_end , ])
X_ = X_.reshape((len(X_)*3))
y_ = np.array(dataFrame.iloc[in_end :out_end, 0])
X.append(X_)
y.append(y_)
in_start += 1
X = np.array(X)
y = np.array(y)
X.shape, y.shape
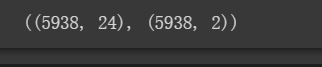
2、划分数据集
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
x = df.iloc[:,:-1]
y = df.iloc[:,-1]
x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(x, y, test_size=0.1, random_state=1)
x_train.shape, y_train.shape
2、数据归一化
from sklearn.preprocessing import MinMaxScaler
#将数据归一化,范围是0到1
sc = MinMaxScaler(feature_range=(0, 1))
X_scaled = sc.fit_transform(X)
X_scaled = X_scaled.reshape(len(X_scaled),width_X,3)
X_scaled.shape

四、构建LSTM网络
1、函数模型
tf.keras.layers.LSTM(
units,
activation='tanh',
recurrent_activation='sigmoid',
use_bias=True,
kernel_initializer='glorot_uniform',
recurrent_initializer='orthogonal',
bias_initializer='zeros',
unit_forget_bias=True,
kernel_regularizer=None,
recurrent_regularizer=None,
bias_regularizer=None,
activity_regularizer=None,
kernel_constraint=None,
recurrent_constraint=None,
bias_constraint=None,
dropout=0.0,
recurrent_dropout=0.0,
return_sequences=False,
return_state=False,
go_backwards=False,
stateful=False,
time_major=False,
unroll=False,
**kwargs
)
2、构建函数模型
from tensorflow.keras.models import Sequential
from tensorflow.keras.layers import Dense,LSTM
# 多层 LSTM
model_lstm = Sequential()
model_lstm.add(LSTM(units=64, activation='relu', return_sequences=True,
input_shape=(X_train.shape[1], 3)))
model_lstm.add(LSTM(units=64, activation='relu'))
model_lstm.add(Dense(width_y))

五、训练模型
1、超参数
opt = tf.keras.optimizers.Adam(learning_rate=1e-4)
model.compile(loss='binary_crossentropy', optimizer=opt,metrics=['accuracy'])
2、训练函数
history = model_lstm.fit(X_train, y_train, batch_size = 64, epochs = 40, validation_data = (X_test, y_test), validation_freq = 1)
3、模型评估
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
acc = history.history['accuracy']
val_acc = history.history['val_accuracy']
loss = history.history['loss']
val_loss = history.history['val_loss']
epochs_range = range(epochs)
plt.figure(figsize=(14, 4))
plt.subplot(1, 2, 1)
plt.plot(epochs_range, acc, label='Training Accuracy')
plt.plot(epochs_range, val_acc, label='Validation Accuracy')
plt.legend(loc='lower right')
plt.title('Training and Validation Accuracy')
plt.subplot(1, 2, 2)
plt.plot(epochs_range, loss, label='Training Loss')
plt.plot(epochs_range, val_loss, label='Validation Loss')
plt.legend(loc='upper right')
plt.title('Training and Validation Loss')
plt.show()

4、测试集预测

5、均方根误差和R2
from sklearn import metrics
"""
RMSE :均方根误差,对均方误差开方
R2 :决定系数,可以简单理解为反映模型拟合优度的重要的统计量
"""
RMSE_lstm = metrics.mean_squared_error(predicted_y_lstm, y_test)**0.5
R2_lstm = metrics.r2_score(predicted_y_lstm, y_test)
print('均方根误差: %.5f' % RMSE_lstm)
print('R2: %.5f' % R2_lstm)

RMSE均方根误差是预测值与真实值的误差平方根的均值,它用来估计模型预测目标值的性能(准确度),值越小,模型的质量越好。
R2是将预测值跟只使用均值的情况下相比,看能好多少。其区间通常在(0,1)之间。0表示还不如什么都不预测,直接取均值的情况,而1表示所有预测跟真实结果完美匹配的情况,值越接近1,模型的质量越好
总结
文章主要包括以下几个部分:
- 数据集介绍:介绍了所使用的火灾数据集,包括数据集的标签含义等。
- 前期工作:包括默认启动GPU,读入数据以及对数据进行可视化的操作。
- 数据预处理:对数据进行归一化操作,并将数据集划分为训练集和测试集。
- 构建LSTM网络:介绍了如何使用TensorFlow中的LSTM函数来构建函数模型。
- 训练模型:介绍了模型的超参数设置以及如何进行模型训练。








 该文介绍了通过LSTM网络进行火灾温度预测的过程,包括数据集的读取、数据预处理、模型构建和训练,以及使用均方根误差和R2指标评估模型性能。
该文介绍了通过LSTM网络进行火灾温度预测的过程,包括数据集的读取、数据预处理、模型构建和训练,以及使用均方根误差和R2指标评估模型性能。

















 5074
5074

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








