📝个人主页:研学社的博客
💥💥💞💞欢迎来到本博客❤️❤️💥💥
🏆博主优势:🌞🌞🌞博客内容尽量做到思维缜密,逻辑清晰,为了方便读者。
⛳️座右铭:行百里者,半于九十。
目录
💥1 概述
文献来源:

极限学习机(ELM)已被证明是模式分类和回归的高效学习机制。然而,ELM主要应用于监督学习问题。只有少数现有的研究论文使用ELM来探索未标记的数据。在本文中,我们基于流形正则化将ELM扩展到半监督和无监督任务,从而极大地扩展了ELM的适用性。所提算法的主要优点是:1)半监督ELM(SS-ELM)和无监督ELM(US-ELM)都表现出ELM的学习能力和计算效率;2)两种算法都自然地处理多类分类或多集群聚类;3)两种算法都是归纳的,可以直接在测试时处理看不见的数据。此外,本文表明,所有有监督、半监督和无监督的ELM实际上都可以放入一个统一的框架中。这为理解随机特征映射的机制提供了新的视角,这是ELM理论中的关键概念。对各种数据集的实证研究表明,所提出的算法在准确性和效率方面与最先进的半监督或无监督学习算法具有竞争力。
📚2 运行结果
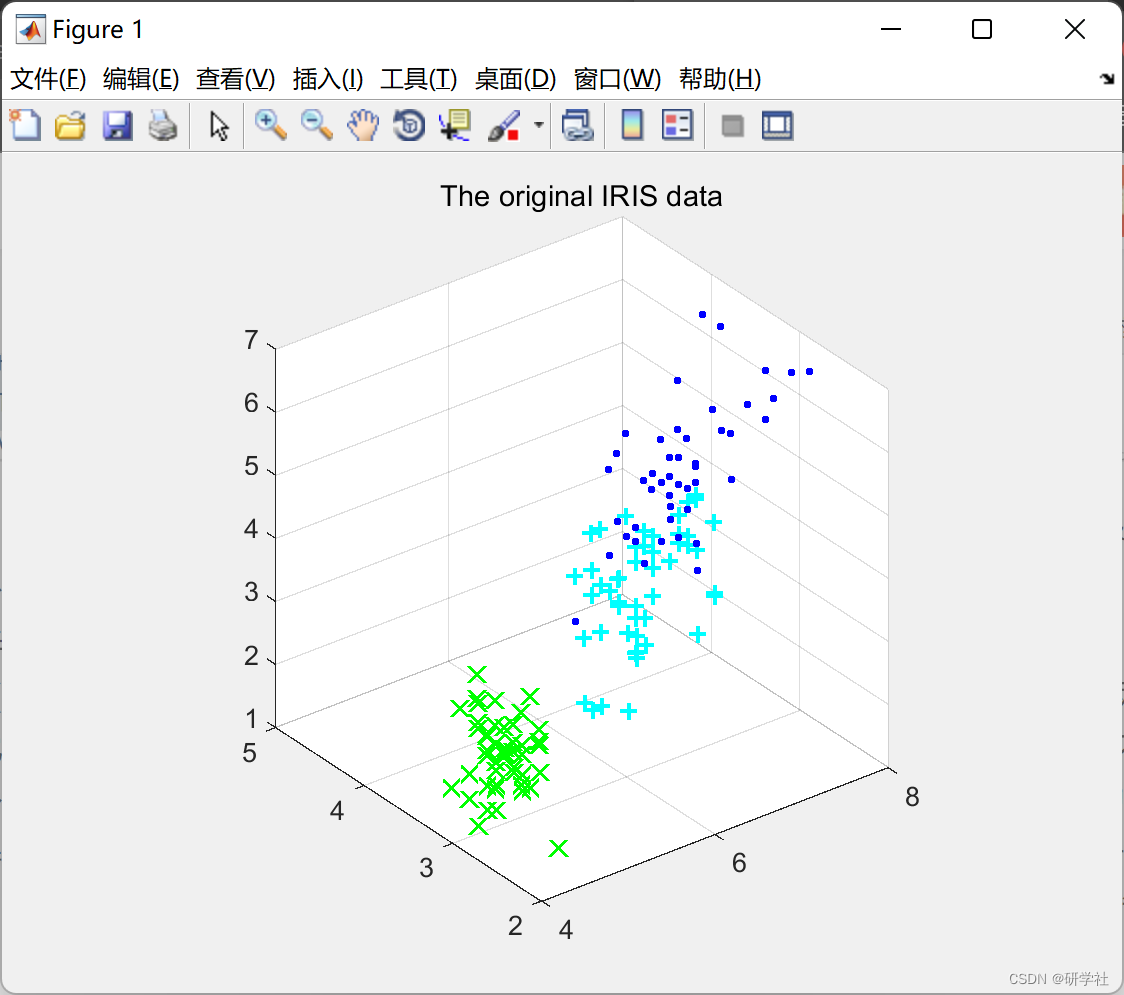
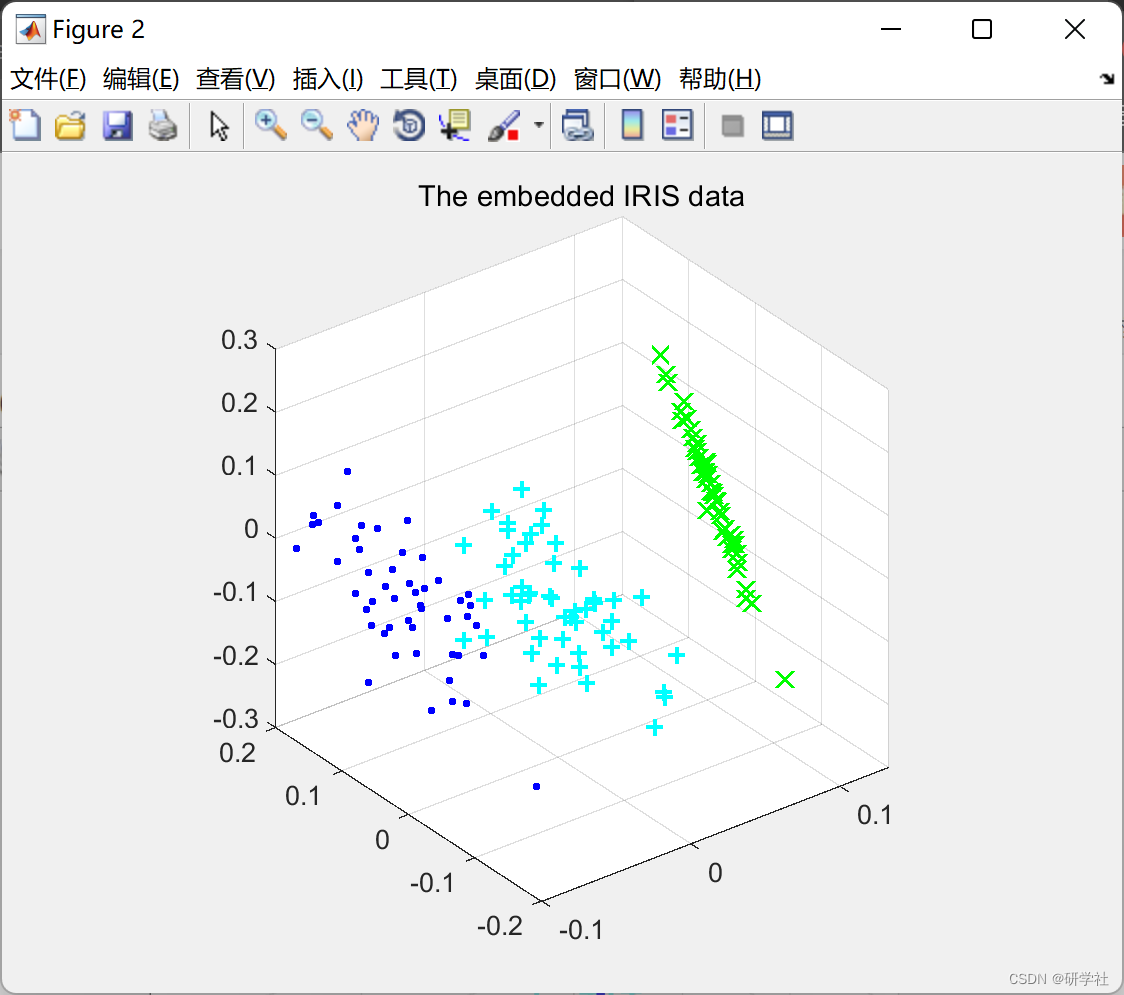
部分代码:
function [P_cond,stepnum] = step1(P_cond)
P_size = length(P_cond);
% Loop throught each row
for ii = 1:P_size
rmin = min(P_cond(ii,:));
P_cond(ii,:) = P_cond(ii,:)-rmin;
end
stepnum = 2;
%**************************************************************************
% STEP 2: Find a zero in P_cond. If there are no starred zeros in its
% column or row start the zero. Repeat for each zero
%**************************************************************************
function [r_cov,c_cov,M,stepnum] = step2(P_cond)
% Define variables
P_size = length(P_cond);
r_cov = zeros(P_size,1); % A vector that shows if a row is covered
c_cov = zeros(P_size,1); % A vector that shows if a column is covered
M = zeros(P_size); % A mask that shows if a position is starred or primed
for ii = 1:P_size
for jj = 1:P_size
if P_cond(ii,jj) == 0 && r_cov(ii) == 0 && c_cov(jj) == 0
M(ii,jj) = 1;
r_cov(ii) = 1;
c_cov(jj) = 1;
end
end
end
% Re-initialize the cover vectors
r_cov = zeros(P_size,1); % A vector that shows if a row is covered
c_cov = zeros(P_size,1); % A vector that shows if a column is covered
stepnum = 3;
%**************************************************************************
% STEP 3: Cover each column with a starred zero. If all the columns are
% covered then the matching is maximum
%**************************************************************************
function [c_cov,stepnum] = step3(M,P_size)
c_cov = sum(M,1);
if sum(c_cov) == P_size
stepnum = 7;
else
stepnum = 4;
end
%**************************************************************************
% STEP 4: Find a noncovered zero and prime it. If there is no starred
% zero in the row containing this primed zero, Go to Step 5.
% Otherwise, cover this row and uncover the column containing
% the starred zero. Continue in this manner until there are no
% uncovered zeros left. Save the smallest uncovered value and
% Go to Step 6.
%**************************************************************************
function [M,r_cov,c_cov,Z_r,Z_c,stepnum] = step4(P_cond,r_cov,c_cov,M)
P_size = length(P_cond);
zflag = 1;
while zflag
% Find the first uncovered zero
row = 0; col = 0; exit_flag = 1;
ii = 1; jj = 1;
while exit_flag
if P_cond(ii,jj) == 0 && r_cov(ii) == 0 && c_cov(jj) == 0
row = ii;
col = jj;
exit_flag = 0;
end
jj = jj + 1;
if jj > P_size; jj = 1; ii = ii+1; end
if ii > P_size; exit_flag = 0; end
end
% If there are no uncovered zeros go to step 6
if row == 0
stepnum = 6;
zflag = 0;
Z_r = 0;
Z_c = 0;
else
% Prime the uncovered zero
M(row,col) = 2;
% If there is a starred zero in that row
% Cover the row and uncover the column containing the zero
if sum(find(M(row,:)==1)) ~= 0
r_cov(row) = 1;
zcol = find(M(row,:)==1);
c_cov(zcol) = 0;
else
stepnum = 5;
zflag = 0;
Z_r = row;
Z_c = col;
end
end
end
%**************************************************************************
% STEP 5: Construct a series of alternating primed and starred zeros as
% follows. Let Z0 represent the uncovered primed zero found in Step 4.
% Let Z1 denote the starred zero in the column of Z0 (if any).
% Let Z2 denote the primed zero in the row of Z1 (there will always
% be one). Continue until the series terminates at a primed zero
% that has no starred zero in its column. Unstar each starred
% zero of the series, star each primed zero of the series, erase
% all primes and uncover every line in the matrix. Return to Step 3.
%**************************************************************************
function [M,r_cov,c_cov,stepnum] = step5(M,Z_r,Z_c,r_cov,c_cov)
zflag = 1;
ii = 1;
while zflag
% Find the index number of the starred zero in the column
rindex = find(M(:,Z_c(ii))==1);
if rindex > 0
% Save the starred zero
ii = ii+1;
% Save the row of the starred zero
Z_r(ii,1) = rindex;
% The column of the starred zero is the same as the column of the
% primed zero
Z_c(ii,1) = Z_c(ii-1);
else
zflag = 0;
end
% Continue if there is a starred zero in the column of the primed zero
if zflag == 1;
% Find the column of the primed zero in the last starred zeros row
cindex = find(M(Z_r(ii),:)==2);
ii = ii+1;
Z_r(ii,1) = Z_r(ii-1);
Z_c(ii,1) = cindex;
end
end
% UNSTAR all the starred zeros in the path and STAR all primed zeros
for ii = 1:length(Z_r)
if M(Z_r(ii),Z_c(ii)) == 1
M(Z_r(ii),Z_c(ii)) = 0;
else
M(Z_r(ii),Z_c(ii)) = 1;
end
end
% Clear the covers
r_cov = r_cov.*0;
c_cov = c_cov.*0;
% Remove all the primes
M(M==2) = 0;
stepnum = 3;
% *************************************************************************
% STEP 6: Add the minimum uncovered value to every element of each covered
% row, and subtract it from every element of each uncovered column.
% Return to Step 4 without altering any stars, primes, or covered lines.
%**************************************************************************
function [P_cond,stepnum] = step6(P_cond,r_cov,c_cov)
a = find(r_cov == 0);
b = find(c_cov == 0);
minval = min(min(P_cond(a,b)));
P_cond(find(r_cov == 1),:) = P_cond(find(r_cov == 1),:) + minval;
P_cond(:,find(c_cov == 0)) = P_cond(:,find(c_cov == 0)) - minval;
stepnum = 4;
function cnum = min_line_cover(Edge)
% Step 2
[r_cov,c_cov,M,stepnum] = step2(Edge);
% Step 3
[c_cov,stepnum] = step3(M,length(Edge));
% Step 4
[M,r_cov,c_cov,Z_r,Z_c,stepnum] = step4(Edge,r_cov,c_cov,M);
% Calculate the deficiency
cnum = length(Edge)-sum(r_cov)-sum(c_cov);
🎉3 参考文献
部分理论来源于网络,如有侵权请联系删除。
[1]G. Huang, S. Song, J. N. D. Gupta and C. Wu, "Semi-Supervised and Unsupervised Extreme Learning Machines," in IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, vol. 44, no. 12, pp. 2405-2417, Dec. 2014, doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2014.2307349.





















 4206
4206

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








