一、背景
为何选择svm来尝试解决多分类问题,以下为决策树和svm用于多分类的表现上的差异:
决策树
优化后的决策树(随机森林)
svm
详见:http://blog.jobbole.com/98635/
二、SVM支持向量机(Support vector machine)
SVM原理:http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Support_vector_machine
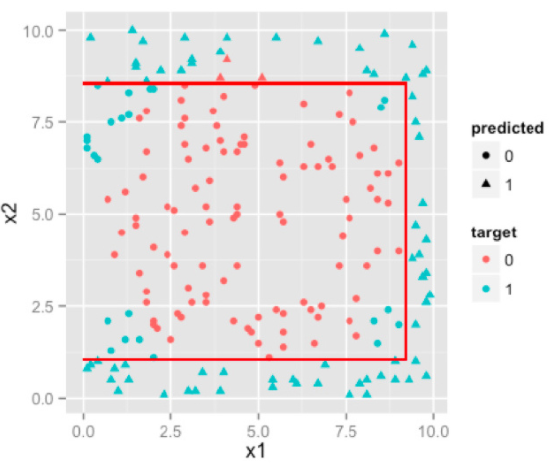
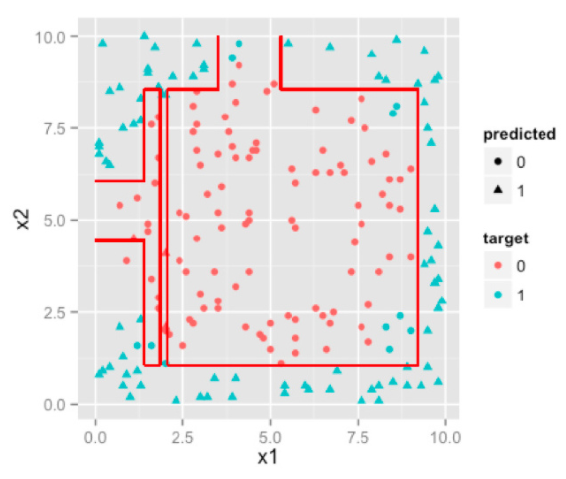
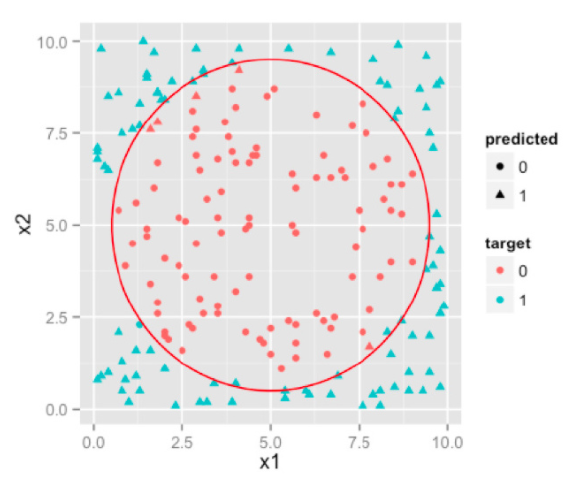
SVM是两类分类器;对于k类的多分类问题的处理方式如下
- 设计k个SVM两类分类器;
- 设计两两k(k-1)/2个SVM两类分类器。
- 在线性方程后加高阶项:采用一次优化求解解决问题。对于每一类,设计w_i与b_i,约束真实类别对应的w_i x + b_i大于其他类别的w_i x + b_i进行训练,求解目标是所有w_i的范数之和最小,也可以引入 样本数乘以类别数 个松驰变量
三、SVR支持向量回归(Support vector Regression)
原理:用核函数代替线性方程中的线性项可以使原来的线性算法“非线性化”,即能做非线性回归。引进核函数达到了“升维”的目的,而增加的可调参数使得过拟合依然能控制。
- 所谓回归(regression),基本上就是拟合,用一个函数拟合x与y的关系。对于SVR来说,x是向量,y是标量,拟合的函数形式为y=W^T*g(x)+b,其中g(x)为核函数对应的特征空间向量。
- SVR认为,只要估计的y在实际的y的两侧一个固定的范围(epsilon)之内,就认为是估计正确,没有任何损失;
- SVR的优化目标,是|W|最小,这样y-x曲线的斜率最小,这个function最flat,这样据说可以增加估计的鲁棒性。
- 之后的事情就很自然了,和SVM一样:可以有soft margin,用一个小正数控制。用对偶式来解;但有一个不同,控制范围的epsilon的值难于确定,在最小优化目标中加入一项C*\nu*\epsilon,其中epsilon是一个变量,nu是一个预先给定的正数。
四、svm设置参数
-s svm类型:SVM设置类型(默认0)
0 -- C-SVC
1 --v-SVC
2 – 一类SVM
3 -- e -SVR
4 -- v-SVR-t 核函数类型:核函数设置类型(默认2)
0 – 线性:u'v
1 – 多项式:(r*u'v + coef0)^degree
2 – RBF函数:exp(-r|u-v|^2)
3 –sigmoid:tanh(r*u'v + coef0)-d degree:核函数中的degree设置(默认3)
-g r(gama):核函数中的函数设置(默认1/ k)
-r coef0:核函数中的coef0设置(默认0)
-c cost:设置C-SVC, -SVR和-SVR的参数(默认1)
-n nu:设置SVC,一类SVM和 SVR的参数(默认0.5)
-p e:设置 -SVR 中损失函数的值(默认0.1)
-m cachesize:设置cache内存大小,以MB为单位(默认40)
-e :设置允许的终止判据(默认0.001)
-h shrinking:是否使用启发式,0或1(默认1)
-wi weight:设置第几类的参数C为weightC(C-SVC中的C)(默认1)
-v n: n-fold交互检验模式
五、svm模型参数
- svm_type:所选择的svm类型,默认为c_svc
- kernel_type rbf:训练采用的核函数类型,此处为RBF核
- gamma 0.0078125:RBF核的参数γ
- nr_class 6:类别数,此处为6分类问题
- total_sv 18:支持向量总个数
- rho 0.004423136341674322 -0.02055338568924989 0.03588086612165208 0.24771746047322893 0.00710699773513259 -0.008734834466328766 0.02297409269106355 0.24299467083662166 -0.07400614425237287 -0.0050679463881033344 0.18446534035305884 0.004123018419961004 0.22127259896446397 -0.012677989710344693 -0.2178023679167552 :判决函数的偏置项b
- label 0 9 99 999 100 101:原始文件中的类别标识
- nr_sv 2 2 3 3 4 4:每个类的支持向量机的个数
- SV :以下为各个类的权系数及相应的支持向量
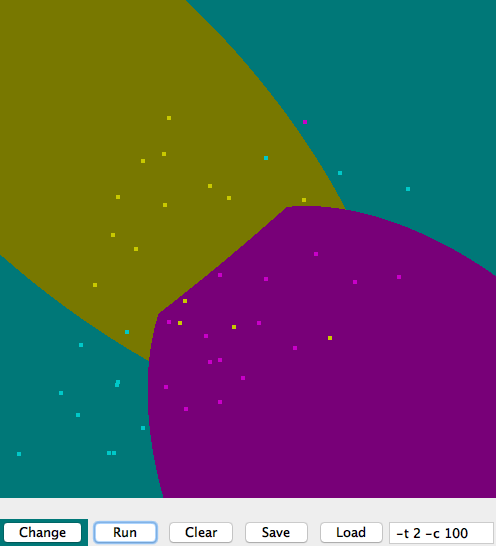
六、分类样例
七、参考链接
- libsvm使用方法总结
- svm-toy
- svm-scale 使用方法介绍
- http://renhongchao.iteye.com/blog/2061664
- 代码结构及c-SVC过程
- libSVM简介及核函数模型选择
- 支持向量机通俗导论(理解SVM的三层境界)
- 数据挖掘十大算法详解
- 拉格朗日对偶
- Stanford机器学习—第八讲. 支持向量机SVM
- Stanford公开课
- http://www.csie.ntu.edu.tw/~cjlin/libsvm/
- http://blog.jasonding.top/2015/05/01/Machine%20Learning/%E3%80%90%E6%9C%BA%E5%99%A8%E5%AD%A6%E4%B9%A0%E5%9F%BA%E7%A1%80%E3%80%91%E6%94%AF%E6%8C%81%E5%90%91%E9%87%8F%E5%9B%9E%E5%BD%92/
- http://mpi2.alibaba-inc.com/doc/SVM
- http://www.atatech.org/articles/65337
- http://blog.csdn.net/zy_zhengyang/article/details/45009431
- http://renhongchao.iteye.com/blog/2061664
- http://www.csdn.net/article/2015-12-02/2826374?reload=1
- http://blog.csdn.net/dxy_1110/article/details/43851955
八、具体代码
public class SvmTest3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String []arg ={ "trainfile/train1.txt", //存放SVM训练模型用的数据的路径
"trainfile/model_r.txt"}; //存放SVM通过训练数据训练出来的模型的路径
String []parg={
"trainfile/test2.txt", //这个是存放测试数据
"trainfile/model_r.txt", //调用的是训练以后的模型
"trainfile/out_r.txt"}; //生成的结果的文件的路径
System.out.println("........SVM运行开始..........");
//创建一个训练对象
SvmTrain t = new SvmTrain();
//创建一个预测或者分类的对象
SvmPredict p= new SvmPredict();
//归一化
SvmScale svm_scale = new SvmScale();
try {
//String[] testArgs = {"-l","0", "-u","1","-s","trainfile/trainscale.txt","trainfile/train.txt"};
//svm_scale.main(testArgs);
//String[] argvScaleTest ={"-r","trainfile/trainscale.txt","trainfile/train.txt"};
//svm_scale.main(argvScaleTest);
t.main(arg); //调用
p.main(parg); //调用
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
/**归一化调用示例
* String[] testArgs = {"-l","0", "-u","1","-s","chao-test-scale","UCI-breast-cancer-tra"};
svm_scale.main(testArgs);
String[] argvScaleTest ={"-r","chao-test-scale","UCI-breast-cancer-test"};
svm_scale.main(testArgs);
svm_scale无直接生成归一化后的文件方法,控制台实现命令 :
java svm_scale -s chao-test-scale train>train.scale
java svm_scale -s chao-test-scale test>test.scale
*/public class SvmTrain {
private svm_parameter param; // set by parse_command_line
private svm_problem prob; // set by read_problem
private svm_model model;
private String input_file_name; // set by parse_command_line
private String model_file_name; // set by parse_command_line
private String error_msg;
private int cross_validation;
private int nr_fold;
private static svm_print_interface svm_print_null = new svm_print_interface()
{
public void print(String s) {}
};
private static void exit_with_help()
{
System.out.print(
"Usage: svm_train [options] training_set_file [model_file]\n"
+"options:\n"
+"-s svm_type : set type of SVM (default 0)\n"
+" 0 -- C-SVC (multi-class classification)\n"
+" 1 -- nu-SVC (multi-class classification)\n"
+" 2 -- one-class SVM\n"
+" 3 -- epsilon-SVR (regression)\n"
+" 4 -- nu-SVR (regression)\n"
+"-t kernel_type : set type of kernel function (default 2)\n"
+" 0 -- linear: u'*v\n"
+" 1 -- polynomial: (gamma*u'*v + coef0)^degree\n"
+" 2 -- radial basis function: exp(-gamma*|u-v|^2)\n"
+" 3 -- sigmoid: tanh(gamma*u'*v + coef0)\n"
+" 4 -- precomputed kernel (kernel values in training_set_file)\n"
+"-d degree : set degree in kernel function (default 3)\n"
+"-g gamma : set gamma in kernel function (default 1/num_features)\n"
+"-r coef0 : set coef0 in kernel function (default 0)\n"
+"-c cost : set the parameter C of C-SVC, epsilon-SVR, and nu-SVR (default 1)\n"
+"-n nu : set the parameter nu of nu-SVC, one-class SVM, and nu-SVR (default 0.5)\n"
+"-p epsilon : set the epsilon in loss function of epsilon-SVR (default 0.1)\n"
+"-m cachesize : set cache memory size in MB (default 100)\n"
+"-e epsilon : set tolerance of termination criterion (default 0.001)\n"
+"-h shrinking : whether to use the shrinking heuristics, 0 or 1 (default 1)\n"
+"-b probability_estimates : whether to train a SVC or SVR model for probability estimates, 0 or 1 (default 0)\n"
+"-wi weight : set the parameter C of class i to weight*C, for C-SVC (default 1)\n"
+"-v n : n-fold cross validation mode\n"
+"-q : quiet mode (no outputs)\n"
);
System.exit(1);
}
private void do_cross_validation()
{
int i;
int total_correct = 0;
double total_error = 0;
double sumv = 0, sumy = 0, sumvv = 0, sumyy = 0, sumvy = 0;
double[] target = new double[prob.l];
libsvm.svm.svm_cross_validation(prob, param, nr_fold, target);
if(param.svm_type == svm_parameter.EPSILON_SVR ||
param.svm_type == svm_parameter.NU_SVR)
{
for(i=0;i<prob.l;i++)
{
double y = prob.y[i];
double v = target[i];
total_error += (v-y)*(v-y);
sumv += v;
sumy += y;
sumvv += v*v;
sumyy += y*y;
sumvy += v*y;
}
System.out.print("Cross Validation Mean squared error = "+total_error/prob.l+"\n");
System.out.print("Cross Validation Squared correlation coefficient = "+
((prob.l*sumvy-sumv*sumy)*(prob.l*sumvy-sumv*sumy))/
((prob.l*sumvv-sumv*sumv)*(prob.l*sumyy-sumy*sumy))+"\n"
);
}
else
{
for(i=0;i<prob.l;i++)
if(target[i] == prob.y[i])
++total_correct;
System.out.print("Cross Validation Accuracy = "+100.0*total_correct/prob.l+"%\n");
}
}
private void run(String argv[]) throws IOException
{
parse_command_line(argv);
read_problem();
error_msg = libsvm.svm.svm_check_parameter(prob, param);
if(error_msg != null)
{
System.err.print("ERROR: "+error_msg+"\n");
System.exit(1);
}
if(cross_validation != 0)
{
do_cross_validation();
}
else
{
model = libsvm.svm.svm_train(prob, param);
libsvm.svm.svm_save_model(model_file_name, model);
}
}
public static void main(String argv[]) throws IOException
{
SvmTrain t = new SvmTrain();
t.run(argv);
}
private static double atof(String s)
{
double d = Double.valueOf(s).doubleValue();
if (Double.isNaN(d) || Double.isInfinite(d))
{
System.err.print("NaN or Infinity in input\n");
System.exit(1);
}
return(d);
}
private static int atoi(String s)
{








 本文探讨了使用SVM解决多分类问题的背景和方法,包括SVM支持向量机和SVR支持向量回归的原理。详细介绍了SVM的参数设置,如核函数类型、gamma和C参数等,并提供了分类样例及参考资料链接。
本文探讨了使用SVM解决多分类问题的背景和方法,包括SVM支持向量机和SVR支持向量回归的原理。详细介绍了SVM的参数设置,如核函数类型、gamma和C参数等,并提供了分类样例及参考资料链接。

 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章















 3918
3918

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








