【项目-警察和厨师】
(1)根据下面的类图,定义各个类:
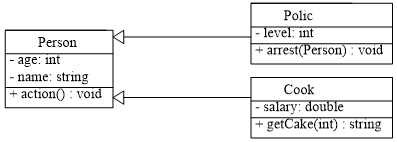
要求:
各个成员函数,只要输出相关的信息即可,暂不深究其业务功能
请为各个类增加构造函数
在实现中,可以增加需要的其他函数
自行编制main函数,完成初步的测试
[参考解答1]
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Person
{
public:
Person(int, string);
void action();
string getName()
{
return name;
}
private:
int age;
string name;
};
Person::Person(int a, string n):age(a), name(n) {}
void Person::action()
{
cout<<name<<" do some action"<<endl;
}
class Police: public Person
{
public:
Police(int, string, int);
void arrest(Person);
private:
int level; //级别
};
Police::Police(int a, string n, int l):Person(a,n),level(l) {}
void Police::arrest(Person p)
{
cout<<" Police "<<getName()<<" arrest " <<p.getName()<<endl;
}
class Cook: public Person
{
public:
Cook(int, string, double);
void getCake(int);
private:
double salary; //薪水
};
Cook::Cook(int a, string n, double s):Person(a,n),salary(s) {}
void Cook::getCake(int n)
{
cout<<" Cook "<<getName()<<" gave me " <<n<<" cakes."<<endl;
}
int main()
{
Person tom(120,"Tom");
Police jack(30,"Jack",2);
Cook john(24,"John",5000);
jack.arrest(tom);
john.getCake(4);
return 0;
}(2)下面的类图,为Polic类和Cook类增加了对象成员,请扩充代码,完成上述各项要求
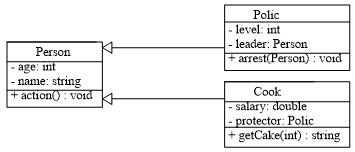
[参考解答1]
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Person
{
public:
Person(int, string);
void action();
string getName()
{
return name;
}
private:
int age;
string name;
};
Person::Person(int a, string n):age(a), name(n) {}
void Person::action()
{
cout<<name<<" do some action"<<endl;
}
class Police: public Person
{
public:
Police(int a, string n, int l, int la, string ln);
void arrest(Person);
void show();
private:
int level; //级别
Person leader; //领导
};
Police::Police(int a, string n, int l, int la, string ln):Person(a,n),level(l),leader(la,ln) {}
void Police::arrest(Person p)
{
cout<<"Police "<<getName()<<" arrest " <<p.getName()<<endl;
}
void Police::show()
{
cout<<"Police "<<getName()<<", leader is " <<leader.getName()<<endl;
}
class Cook: public Person
{
public:
Cook(int a, string n, double s,int pa, string pn, int pl, int pla, string pln);
void getCake(int);
void show();
private:
double salary; //薪水
Police protector; //厨师小店的片区警察
};
Cook::Cook(int a, string n, double s,int pa, string pn, int pl, int pla, string pln):
Person(a,n),salary(s),protector(pa,pn,pl,pla,pln) {}
void Cook::getCake(int n)
{
cout<<"Cook "<<getName()<<" gave me " <<n<<" cakes."<<endl;
}
void Cook::show()
{
cout<<"Cook "<<getName()<<" is protected by Police "<<protector.getName()<<endl;
}
int main()
{
Person tom(120,"Tom");
Police jack(30,"Jack",2,43,"Jerry");
Cook john(24,"John",5000,30,"Jack",2,43,"Jerry");
jack.show();
john.show();
return 0;
}评价:
- 这些代码是完成是题目的要求,但是,并不好。
- 每个构造函数带上一长串的参数,难写,难看,这本身就是质量问题。
- 这种写法,也根本未体现对象的“封装”——都是一串散乱的基本类型数据在工作。
- 我们希望看到jack警察的上司就是一个人,john厨师的保卫者,就是一个警察。
- 需要做的是,利用对象作为构造函数的参数,使结构清晰。
- 当然,这时需要增加相关的复制构造函数了。
[参考解答2]
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Person
{
public:
Person(int, string);
void action();
string getName()
{
return name;
}
private:
int age;
string name;
};
Person::Person(int a, string n):age(a), name(n) {}
void Person::action()
{
cout<<name<<" do some action"<<endl;
}
class Police: public Person
{
public:
Police(int a, string n, int l, Person);
void arrest(Person);
void show();
private:
int level; //级别
Person leader; //领导
};
Police::Police(int a, string n, int l, Person p):Person(a,n),level(l),leader(p) {}
void Police::arrest(Person p)
{
cout<<"Police "<<getName()<<" arrest " <<p.getName()<<endl;
}
void Police::show()
{
cout<<"Police "<<getName()<<", leader is " <<leader.getName()<<endl;
}
class Cook: public Person
{
public:
Cook(int a, string n, double s,Police p);
void getCake(int);
void show();
private:
double salary; //薪水
Police protector; //厨师小店的片区警察
};
Cook::Cook(int a, string n, double s,Police p):
Person(a,n),salary(s),protector(p) {}
void Cook::getCake(int n)
{
cout<<"Cook "<<getName()<<" gave me " <<n<<" cakes."<<endl;
}
void Cook::show()
{
cout<<"Cook "<<getName()<<" is protected by Police "<<protector.getName()<<endl;
}
int main()
{
Person jerry(43,"Jerry");
Police jack(30,"Jack",2,jerry);
Cook john(24,"John",5000,jack);
jack.show();
john.show();
return 0;
}评论:
这样做,是不是在逻辑上很清楚了?
Person、Police类中该定义复制构造函数,在这里没有写,用其默认复制构造函数了。相关类中没有定义指针型成员,不必要深复制,所以,可以使用默认复制构造函数。























 2万+
2万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










