最近这一两周看到不少互联网公司都已经开始秋招发放Offer。
不同以往的是,当前职场环境已不再是那个双向奔赴时代了。求职者在变多,HC 在变少,岗位要求还更高了。
最近,我们又陆续整理了很多大厂的面试题,帮助一些球友解惑答疑,分享技术面试中的那些弯弯绕绕。
喜欢本文记得收藏、关注、点赞。更多实战和面试交流,文末加入我们
技术交流

在一个通用的AI系统中,核心模型应该能够理解不同模态的信息。当前的大语言模型现在已经能够理解语言并进行推理,并且已经扩展到了更多的模态,包括视觉和音频。
此前团队陆续发布了多个 Qwen 语言模型系列以及 Qwen-VL 和 Qwen-Audio 等多模态模型。
今天,团队正式发布 Qwen2-Audio。这是 Qwen-Audio 的下一代版本,它能够接受音频和文本输入,并生成文本输出。Qwen2-Audio 具有以下特点:
-
语音聊天: 用户可以使用语音向音频语言模型发出指令,无需通过自动语音识别(ASR)模块。
-
音频分析: 该模型能够根据文本指令分析音频信息,包括语音、声音、音乐等。
-
多语言支持: 该模型支持超过8种语言和方言,例如中文、英语、粤语、法语、意大利语、西班牙语、德语和日语。
模型效果
团队已经在一系列基准数据集上进行了实验,包括 LibriSpeech、Common Voice 15、Fleurs、Aishell2、CoVoST2、Meld、Vocalsound 以及 AIR-Benchmark,以评估 Qwen2-Audio 与团队之前发布的 Qwen-Audio 以及各项任务中的最先进模型相比的表现。
下面团队将展示一张图表来说明 Qwen2-Audio 相对于竞争对手的表现。在所有任务中,Qwen2-Audio 都显著超越了先前的最佳模型或是 Qwen-Audio。

结构与训练范式
下图展示了模型结构及训练方法。具体来说,通义千问团队使用 Qwen 语言模型和音频编码器这两个基础模型,接着依次进行多任务预训练以实现音频与语言的对齐,以及 SFT 和 DPO 来掌握下游任务的能力并捕捉人类的偏好。

目前,Qwen2-Audio可在魔搭社区进行下载和Demo体验,社区还为开发者们同步推出了推理和微调的实战教程,欢迎体验 ⬇️
模型体验

模型下载和推理
transformers推理
Qwen2-Audio 的代码已在最新的 Hugging face transformers 中,环境安装
pip install git+https://github.com/huggingface/transformers
语音聊天推理
from io import BytesIO
from urllib.request import urlopen
import librosa
from transformers import Qwen2AudioForConditionalGeneration, AutoProcessor
from modelscope import snapshot_download
import torch
model_dir = snapshot_download("Qwen/Qwen2-Audio-7B-Instruct")
processor = AutoProcessor.from_pretrained(model_dir)
model = Qwen2AudioForConditionalGeneration.from_pretrained(model_dir, device_map="auto",torch_dtype=torch.bfloat16)
conversation = [
{"role": "user", "content": [
{"type": "audio", "audio_url": "https://qianwen-res.oss-cn-beijing.aliyuncs.com/Qwen2-Audio/audio/guess_age_gender.wav"},
]},
{"role": "assistant", "content": "Yes, the speaker is female and in her twenties."},
{"role": "user", "content": [
{"type": "audio", "audio_url": "https://qianwen-res.oss-cn-beijing.aliyuncs.com/Qwen2-Audio/audio/translate_to_chinese.wav"},
]},
]
text = processor.apply_chat_template(conversation, add_generation_prompt=True, tokenize=False)
audios = []
for message in conversation:
if isinstance(message["content"], list):
for ele in message["content"]:
if ele["type"] == "audio":
audios.append(librosa.load(
BytesIO(urlopen(ele['audio_url']).read()),
sr=processor.feature_extractor.sampling_rate)[0]
)
inputs = processor(text=text, audios=audios, return_tensors="pt", padding=True)
inputs = inputs.to("cuda")
generate_ids = model.generate(**inputs, max_length=256)
generate_ids = generate_ids[:, inputs.input_ids.size(1):]
response = processor.batch_decode(generate_ids, skip_special_tokens=True, clean_up_tokenization_spaces=False)[0]
音频分析推理:
from io import BytesIO
from urllib.request import urlopen
import librosa
from transformers import Qwen2AudioForConditionalGeneration, AutoProcessor
from modelscope import snapshot_download
import torch
model_dir = snapshot_download("Qwen/Qwen2-Audio-7B-Instruct")
processor = AutoProcessor.from_pretrained(model_dir)
model = Qwen2AudioForConditionalGeneration.from_pretrained(model_dir, device_map="auto",torch_dtype=torch.bfloat16)
conversation = [
{'role': 'system', 'content': 'You are a helpful assistant.'},
{"role": "user", "content": [
{"type": "audio", "audio_url": "https://qianwen-res.oss-cn-beijing.aliyuncs.com/Qwen2-Audio/audio/glass-breaking-151256.mp3"},
{"type": "text", "text": "What's that sound?"},
]},
{"role": "assistant", "content": "It is the sound of glass shattering."},
{"role": "user", "content": [
{"type": "text", "text": "What can you do when you hear that?"},
]},
{"role": "assistant", "content": "Stay alert and cautious, and check if anyone is hurt or if there is any damage to property."},
{"role": "user", "content": [
{"type": "audio", "audio_url": "https://qianwen-res.oss-cn-beijing.aliyuncs.com/Qwen2-Audio/audio/1272-128104-0000.flac"},
{"type": "text", "text": "What does the person say?"},
]},
]
text = processor.apply_chat_template(conversation, add_generation_prompt=True, tokenize=False)
audios = []
for message in conversation:
if isinstance(message["content"], list):
for ele in message["content"]:
if ele["type"] == "audio":
audios.append(
librosa.load(
BytesIO(urlopen(ele['audio_url']).read()),
sr=processor.feature_extractor.sampling_rate)[0]
)
inputs = processor(text=text, audios=audios, return_tensors="pt", padding=True)
inputs = inputs.to("cuda")
generate_ids = model.generate(**inputs, max_length=256)
generate_ids = generate_ids[:, inputs.input_ids.size(1):]
response = processor.batch_decode(generate_ids, skip_special_tokens=True, clean_up_tokenization_spaces=False)[0]
显存占用:

vllm推理
# 从源码安装vllm(大约安装20分钟)
pip install git+https://github.com/faychu/vllm.git@qwen2-audio
# 安装transformers
pip install git+https://github.com/huggingface/transformers
import argparseimport requests
from transformers import AutoTokenizer, AutoProcessor
from transformers.pipelines.audio_utils import ffmpeg_read
from vllm import LLM, SamplingParams
from modelscope import snapshot_download
model_dir = snapshot_download('qwen/Qwen2-Audio-7B-Instruct')
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
parser.add_argument('path', type=str, nargs='?',
default=model_dir)
args = parser.parse_args()
path = args.path
if not path.endswith('/'):
path += '/'
def qwen2_audio_batch():
processor = AutoProcessor.from_pretrained(args.path)
conversation1 = [
{"role": "user", "content": [
{"type": "audio", "audio_url": "https://qianwen-res.oss-cn-beijing.aliyuncs.com/Qwen2-Audio/audio/glass-breaking-151256.mp3"},
{"type": "text", "text": "What's that sound?"},
]},
{"role": "assistant", "content": "It is the sound of glass shattering."},
{"role": "user", "content": [
{"type": "audio", "audio_url": "https://qianwen-res.oss-cn-beijing.aliyuncs.com/Qwen2-Audio/audio/f2641_0_throatclearing.wav"},
{"type": "text", "text": "What can you hear?"},
]}
]
conversation2 = [
{"role": "user", "content": [
{"type": "audio", "audio_url": "https://qianwen-res.oss-cn-beijing.aliyuncs.com/Qwen2-Audio/audio/1272-128104-0000.flac"},
{"type": "text", "text": "What does the person say?"},
]},
]
conversations = [conversation1, conversation2]
text = [processor.apply_chat_template(conversation, add_generation_prompt=True, tokenize=False, add_audio_id = True) for conversation in conversations]
audios = []
for conversation in conversations:
audio_infos_vllm = []
for message in conversation:
if isinstance(message["content"], list):
for ele in message["content"]:
if ele["type"] == "audio":
audio_infos_vllm.append(ffmpeg_read(requests.get(ele['audio_url']).content, sampling_rate=processor.feature_extractor.sampling_rate))
audios.append(audio_infos_vllm)
inputs = [
{
'prompt': text[i],
'multi_modal_data': {
'audio': audios[i]
}
} for i in range(len(conversations))
]
return inputs
def main():
llm = LLM(
model=path, trust_remote_code=True, gpu_memory_utilization=0.98,
enforce_eager=True, # Disable CUDA graph, force call forward in every decode step.
)
sampling_params = SamplingParams(
temperature=0.7, top_p=0.01, top_k=1, repetition_penalty=1.1, max_tokens=256,
stop_token_ids=[],
)
inputs = qwen2_audio_batch()
print(inputs)
outputs = llm.generate(inputs, sampling_params=sampling_params)
for i, output in enumerate(outputs):
generated_text = output.outputs[0].text
print()
print('=' * 40)
print(f"Inputs[{i}]: {inputs[i]['prompt']!r}")
print(f"Generated text: {generated_text!r}")
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
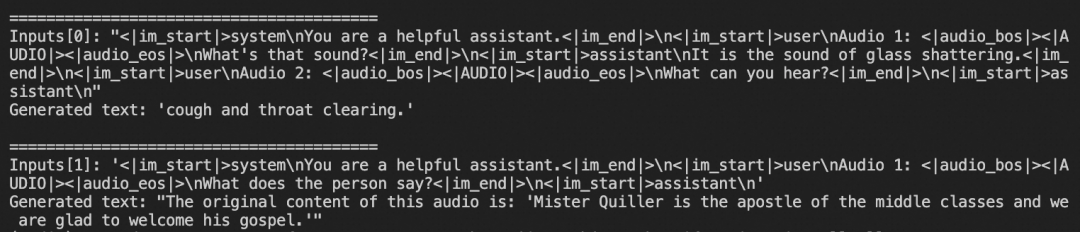
模型微调
我们使用ms-swift对Qwen2-Audio-7B-Instruct进行微调。ms-swift是魔搭社区官方提供的大模型与多模态大模型微调推理框架。
swift开源地址:https://github.com/modelscope/ms-swift
通常,多模态大模型微调会使用自定义数据集进行微调。在这里,我们将展示可直接运行的demo。我们使用aishell1-zh-mini数据集进行微调,您可以在 modelscope 上找到该数据集:https://modelscope.cn/datasets/speech_asr/speech_asr_aishell1_trainsets
在开始微调之前,请确保您的环境已准备妥当。
# 安装ms-swift
pip install git+https://github.com/modelscope/swift.git#egg=ms-swift[llm]
# 安装最新的transformers
pip install git+https://github.com/huggingface/transformers.git
pip install librosa
使用python:
import os
os.environ['CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES'] = '0'
from swift.llm import sft_main, SftArguments, ModelType, DatasetName
# 如果是本地路径需要指定model_id_or_path
sft_main(SftArguments(model_type=ModelType.qwen2_audio_7b_instruct,
model_id_or_path=None,
dataset=[DatasetName.aishell1_zh_mini]))
ZeRO2:
# 如果是本地路径需要增加:`--model_id_or_path <local_path>`
NPROC_PER_NODE=4 CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0,1,2,3 swift sft \
--model_type qwen2-audio-7b-instruct \
--dataset aishell1-zh-mini \
--deepspeed default-zero2
如果要使用自定义数据集,按以下方式进行指定:
# val_dataset可选,如果不指定,则会从dataset中切出一部分数据集作为验证集
--dataset train.jsonl \
--val_dataset val.jsonl \
自定义数据集支持json和jsonl样式。以下提供了两种自定义数据集格式:
格式1:
[
{"conversations": [
{"from": "user", "value": "<audio>audio_path</audio>11111"},
{"from": "assistant", "value": "22222"}
]},
{"conversations": [
{"from": "user", "value": "<audio>audio_path</audio><audio>audio_path2</audio><audio>audio_path3</audio>aaaaa"},
{"from": "assistant", "value": "bbbbb"},
{"from": "user", "value": "<audio>audio_path</audio>ccccc"},
{"from": "assistant", "value": "ddddd"}
]},
{"conversations": [
{"from": "user", "value": "AAAAA"},
{"from": "assistant", "value": "BBBBB"},
{"from": "user", "value": "CCCCC"},
{"from": "assistant", "value": "DDDDD"}
]}
]
格式2:
{"query": "<audio>55555", "response": "66666", "audios": ["audio_path"]}
{"query": "<audio><audio>eeeee", "response": "fffff", "history": [], "audios": ["audio_path1", "audio_path2"]}
{"query": "EEEEE", "response": "FFFFF", "history": [["query1", "response1"], ["query2", "response2"]]}
显存占用:

微调后对验证集推理:
CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0 swift infer \
--ckpt_dir output/qwen2-audio-7b-instruct/vx-xxx/checkpoint-xxx \
--load_dataset_config true
# merge-lora and inference
CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0 swift infer \
--ckpt_dir output/qwen2-audio-7b-instruct/vx-xxx/checkpoint-xxx \
--load_dataset_config true --merge_lora true
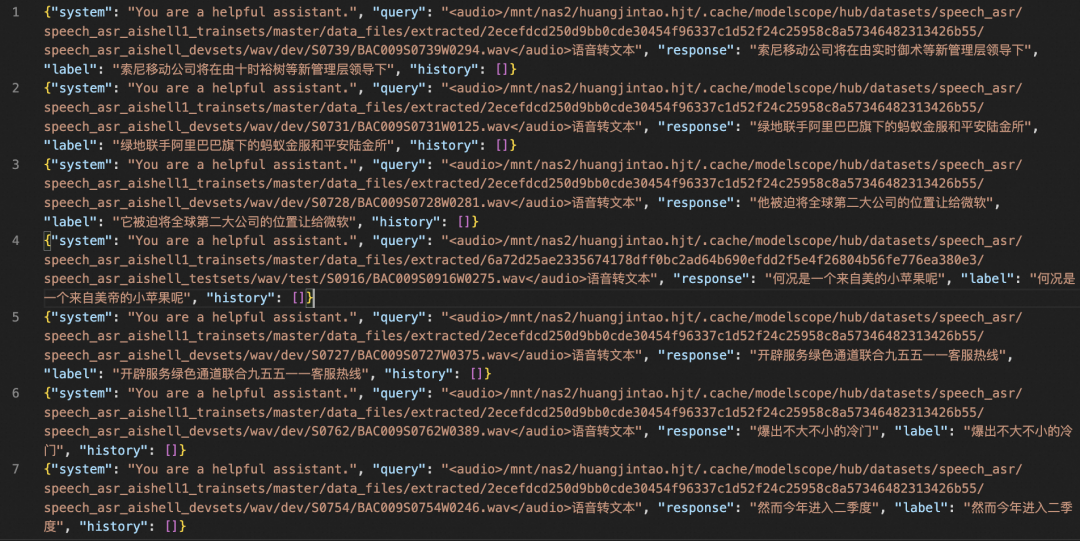
微调后模型对验证集进行推理的示例,时间原因,只跑了400个steps:






















 1137
1137

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








