⛄一、简介
路径规划是实现移动机器人自主导航的关键技术,是指在有障碍物的环境中,按照一定的评价标准(如距离、时间、能耗等),寻找到一条从起始点到目标点的无碰撞路径,这里选取最短距离路径规划的评价标准,即最短路径规划问题。
1.路径规划数学模型的建立
将移动机器人周围环境用一组数据进行抽象表达,建立二维或三维的环境模型,得到移动机器人能够理解分析的环境数据,是机器人路径规划的基本前提。我这里用的是栅格法,其原理是将周围环境看成一个二维平面,将平面分成一个个等面积大小的具有二值信息的栅格,每个栅格中存储着周围环境信息量,下图我给出了一个栅格法地图,方便大家更好的理解栅格地图。这里设计的栅格地图为一个20×20的地形矩阵,黑色的地方表示有障碍,白色的地方表示没有障碍。
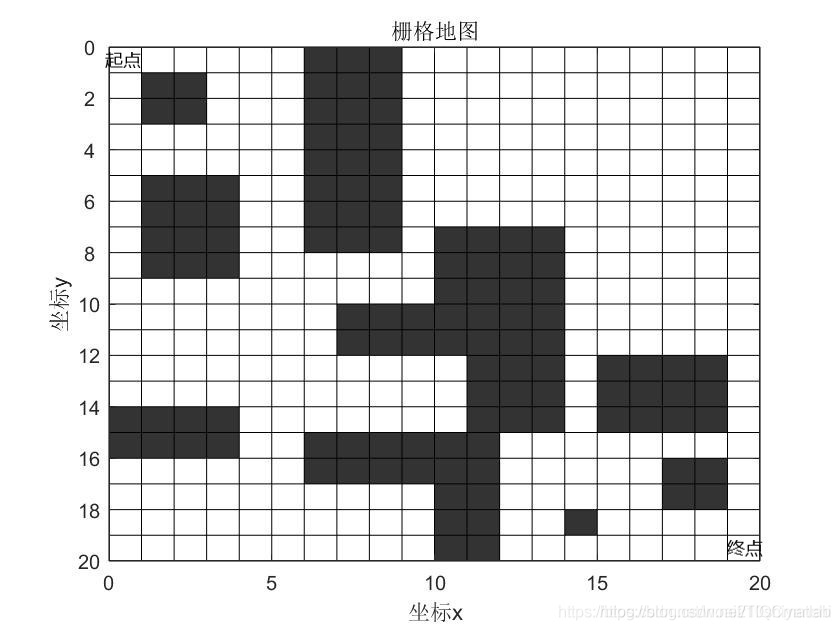
图1 栅格法地图
在用栅格法建立环境模型时,为了将环境信息转换成移动机器人可以识别的数据,一般采用序号法标记环境地图信息,即将栅格地图中一个个栅格从序号1依次累加直到标记到最后一个栅格。如图2所示。
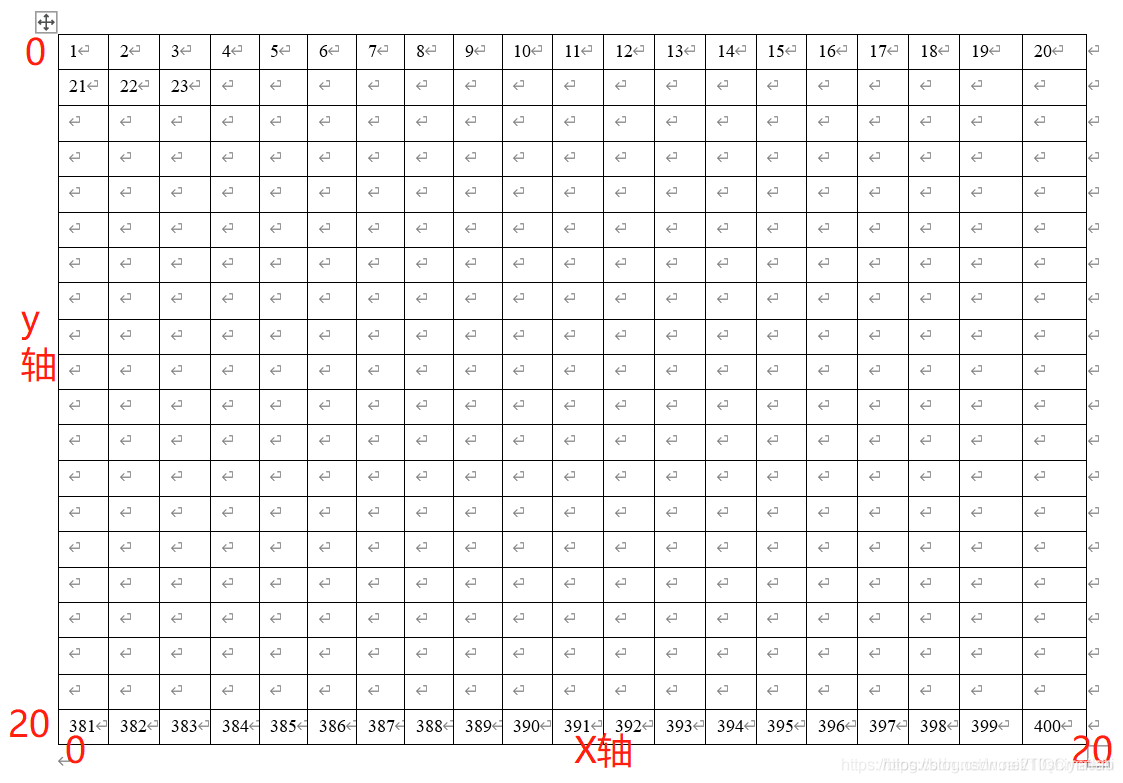
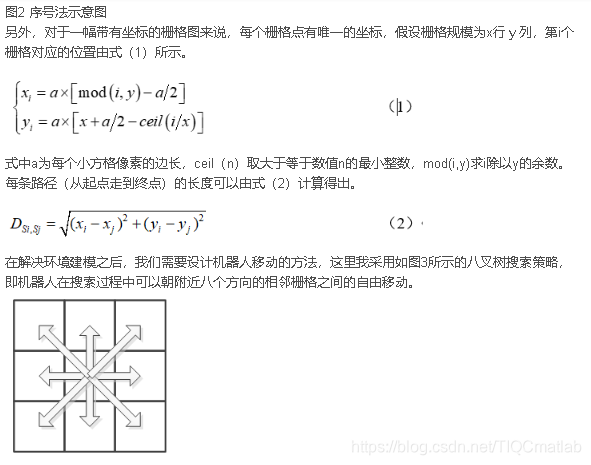
图3 八叉树搜索策略
那么,怎么判断一个栅格点是否为另一个栅格点的相邻栅格点呢,另外,又怎么判断是否为有障碍栅格呢。这就需建立矩阵D,记录每个栅格点至其相邻栅格点的代价值。本例中栅格地图有20×20个栅格点,则D的大小为400×400,其中列是起点栅格,行是局部终点栅格,各栅格点至其各相邻无障碍栅格点的代价值非零,而有障碍栅格及非相邻栅格设为0。
这里需要说明的是,我的MATLAB程序来自于:
版权声明:本文为CSDN博主「qq_40443076」的原创文章,遵循 CC 4.0 BY-SA 版权协议,转载请附上原文出处链接及本声明。
原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_40443076/article/details/88179836
这里主要介绍基于蚁群算法的机器人最短路径规划的思路,以及我在运行MALTLAB程序的时候,学到的内容。
2.机器人最短路径规划的实现步骤
蚁周模型实现机器人最短路径规划的流程图
为了方便大家更好地理解蚁群算法的原理及实现过程,其流程图如图4所示。(流程图较长,我截图了两段。)
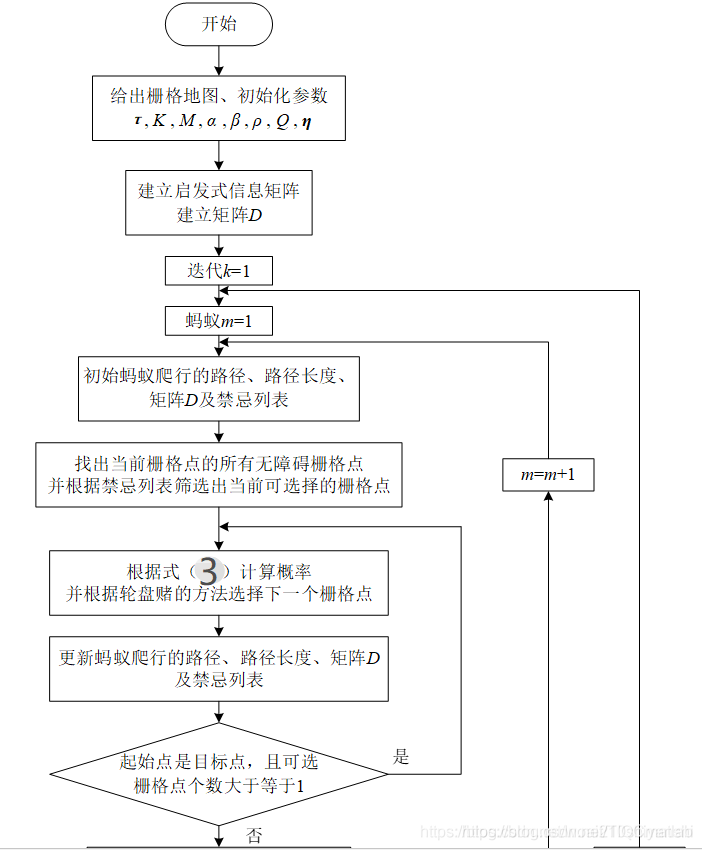
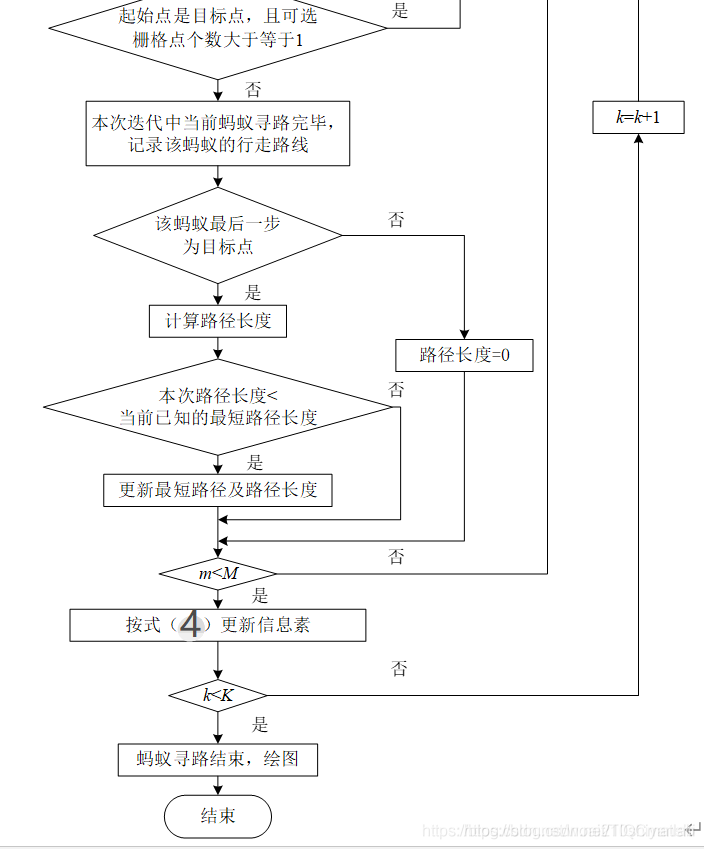
图4 基于蚁群算法的机器人最小路径规划流程图
图中公式(3)(4)的具体表达在下边的具体步骤里。
蚁周模型实现机器人最短路径规划的具体步骤
**步骤1:**给出栅格地图的地形矩阵;初始化信息素矩阵 Tau(记录每个栅格至其他栅格的信息素量),最大迭代次数K,蚂蚁个数M,表征信息素重要程度的参数 、表征启发式信息重要程度的参数 ,信息素蒸发系数 ,信息素增加强度系数Q及启发式信息矩阵
**步骤2:**构建启发式信息矩阵。按式(1)和式(2)计算每个栅格至目标点的距离,启发式信息素取为至目标点距离的倒数,距离越短,启发式因子越大,障碍物处的启发式信息为0。建立矩阵D,用以存储每个栅格点至各自相邻无障碍栅格点的代价值。
**步骤3:**对于每一只蚂蚁,初始化蚂蚁爬行的路径及路径长度,将禁忌列表全部初始化为1;蚂蚁从起始点出发开始搜索路径,找出当前栅格点的所有无障碍相邻栅格点(即矩阵D中相应元素不为0的栅格点),再根据禁忌列表筛选出当前可选择的栅格点。
**步骤4:**如果起始点是目标点,且可选栅格点个数大于等于1,则根据式(3)计算蚂蚁从当前栅格点转移到各相邻栅格点的概率,

⛄二、部分源代码
function varargout = main_GUI_xu(varargin)
% MAIN_GUI_XU MATLAB code for main_GUI_xu.fig
% MAIN_GUI_XU, by itself, create
function edit26_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to edit26 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% Hints: get(hObject,‘String’) returns contents of edit26 as text
% str2double(get(hObject,‘String’)) returns contents of edit26 as a double
% — Executes during object creation, after setting all properties.
function edit26_CreateFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to edit26 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles empty - handles not created until after all CreateFcns called
% Hint: edit controls usually have a white background on Windows.
% See ISPC and COMPUTER.
if ispc && isequal(get(hObject,‘BackgroundColor’), get(0,‘defaultUicontrolBackgroundColor’))
set(hObject,‘BackgroundColor’,‘white’);
end
function edit27_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to edit27 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% Hints: get(hObject,‘String’) returns contents of edit27 as text
% str2double(get(hObject,‘String’)) returns contents of edit27 as a double
% — Executes during object creation, after setting all properties.
function edit27_CreateFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to edit27 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles empty - handles not created until after all CreateFcns called
% Hint: edit controls usually have a white background on Windows.
% See ISPC and COMPUTER.
if ispc && isequal(get(hObject,‘BackgroundColor’), get(0,‘defaultUicontrolBackgroundColor’))
set(hObject,‘BackgroundColor’,‘white’);
end
function edit28_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to edit28 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% Hints: get(hObject,‘String’) returns contents of edit28 as text
% str2double(get(hObject,‘String’)) returns contents of edit28 as a double
% — Executes during object creation, after setting all properties.
function edit28_CreateFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to edit28 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles empty - handles not created until after all CreateFcns called
% Hint: edit controls usually have a white background on Windows.
% See ISPC and COMPUTER.
if ispc && isequal(get(hObject,‘BackgroundColor’), get(0,‘defaultUicontrolBackgroundColor’))
set(hObject,‘BackgroundColor’,‘white’);
end
function edit101_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to edit101 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% Hints: get(hObject,‘String’) returns contents of edit101 as text
% str2double(get(hObject,‘String’)) returns contents of edit101 as a double
% — Executes during object creation, after setting all properties.
function edit101_CreateFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to edit101 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles empty - handles not created until after all CreateFcns called
% Hint: edit controls usually have a white background on Windows.
% See ISPC and COMPUTER.
if ispc && isequal(get(hObject,‘BackgroundColor’), get(0,‘defaultUicontrolBackgroundColor’))
set(hObject,‘BackgroundColor’,‘white’);
end
function edit102_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to edit102 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% Hints: get(hObject,‘String’) returns contents of edit102 as text
% str2double(get(hObject,‘String’)) returns contents of edit102 as a double
% — Executes during object creation, after setting all properties.
function edit102_CreateFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to edit102 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles empty - handles not created until after all CreateFcns called
% Hint: edit controls usually have a white background on Windows.
% See ISPC and COMPUTER.
if ispc && isequal(get(hObject,‘BackgroundColor’), get(0,‘defaultUicontrolBackgroundColor’))
set(hObject,‘BackgroundColor’,‘white’);
end
function edit104_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to edit104 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% Hints: get(hObject,‘String’) returns contents of edit104 as text
% str2double(get(hObject,‘String’)) returns contents of edit104 as a double
% — Executes during object creation, after setting all properties.
function edit104_CreateFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to edit104 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles empty - handles not created until after all CreateFcns called
% Hint: edit controls usually have a white background on Windows.
% See ISPC and COMPUTER.
if ispc && isequal(get(hObject,‘BackgroundColor’), get(0,‘defaultUicontrolBackgroundColor’))
set(hObject,‘BackgroundColor’,‘white’);
end
function edit105_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to edit105 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% Hints: get(hObject,‘String’) returns contents of edit105 as text
% str2double(get(hObject,‘String’)) returns contents of edit105 as a double
% — Executes during object creation, after setting all properties.
function edit105_CreateFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to edit105 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles empty - handles not created until after all CreateFcns called
% Hint: edit controls usually have a white background on Windows.
% See ISPC and COMPUTER.
if ispc && isequal(get(hObject,‘BackgroundColor’), get(0,‘defaultUicontrolBackgroundColor’))
set(hObject,‘BackgroundColor’,‘white’);
end
function edit106_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to edit106 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% Hints: get(hObject,‘String’) returns contents of edit106 as text
% str2double(get(hObject,‘String’)) returns contents of edit106 as a double
% — Executes during object creation, after setting all properties.
function edit106_CreateFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to edit106 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles empty - handles not created until after all CreateFcns called
% Hint: edit controls usually have a white background on Windows.
% See ISPC and COMPUTER.
if ispc && isequal(get(hObject,‘BackgroundColor’), get(0,‘defaultUicontrolBackgroundColor’))
set(hObject,‘BackgroundColor’,‘white’);
end
% — Executes on button press in pushbutton5.
function pushbutton5_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to pushbutton5 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% — Executes on button press in pushbutton6.
function pushbutton6_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to pushbutton6 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% — Executes on button press in pushbutton7.
function pushbutton7_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to pushbutton7 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% — Executes on button press in pushbutton8.
function pushbutton8_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to pushbutton8 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% — Executes on button press in radiobutton9.
function radiobutton9_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to radiobutton9 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% Hint: get(hObject,‘Value’) returns toggle state of radiobutton9
⛄三、运行结果


⛄四、matlab版本及参考文献
1 matlab版本
2014a
2 参考文献
[1]周东健,张兴国,马海波,李成浩,郭旭.基于栅格地图-蚁群算法的机器人最优路径规划[J].南通大学学报(自然科学版). 2013,12(04)
3 备注
简介此部分摘自互联网,仅供参考,若侵权,联系删除






















 1993
1993











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








