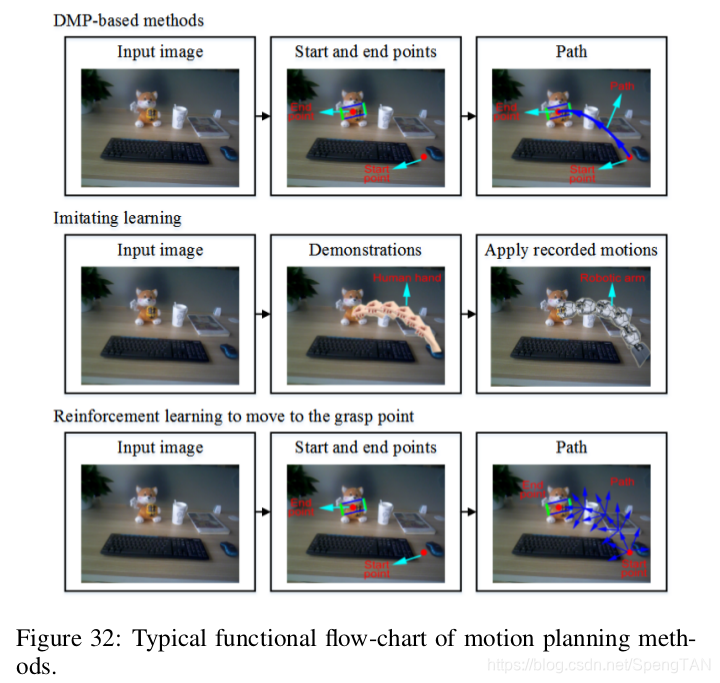
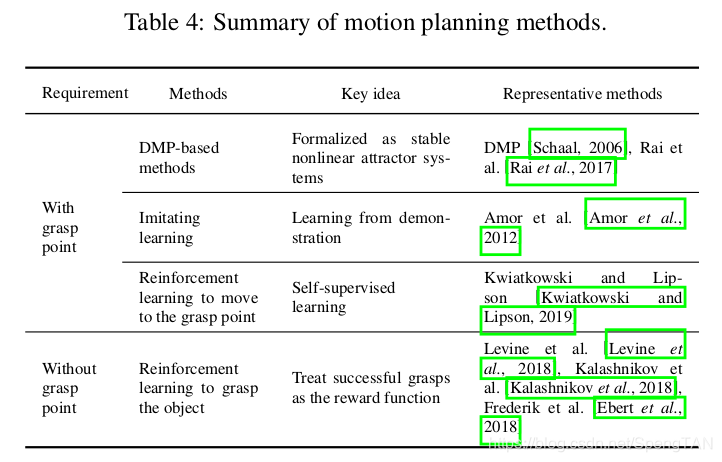
This section introduces the open-loop methods where the grasp points are assumed to have been detected with the above mentioned procedures. These methods design the path from the robot hand to the grasp points on the target object. Here motion representation is the key problem. Although there exist an infinite number of trajectories from the robotic hand to the target grasp points, many areas could not be reached due to the limitations of the robotic arm. Therefore, the trajectories need to be planned. There exist three kinds of methods in the literatures, which are traditional DMP-based methods, imitating learning-based methods, and reinforcement learning-based methods, as shown in 4. Typical functional flow-charts of DMP-based methods, imitating learning-based methods, and reinforcement learning-based methods to move to the grasp point, are illustrated in Fig. 32.
本节介绍开环方法,其中假定已通过上述过程检测到目标点。 这些方法设计了从机器人手到目标物体上抓点的路径。 在这里,运动表示是关键问题。 尽管从机械手到目标抓握点的轨迹是无限的,但由于机械臂的限制,无法到达许多区域。 因此,需要计划轨迹。 文献中存在三种方法,分别是传统的基于DMP的方法,基于模仿学习的方法和基于强化学习的方法,如表4所示。基于DMP的方法,基于模仿学习的方法和基于强化学习的方法将机器人手移至抓点的典型功能流程图如图32所示。

Traditional methods
传统方法
Traditional methods consider the dynamics of the motion and generate motion primitives. The Dynamic Movement Primitives (DMPs) [Schaal, 2006] are one of the most popular motion representations that can serve as an reactive feedback controller. DMPs are units of action that are formalized as stable nonlinear attractor systems. They encode kinematic control policies as differential equations with the goal as the attractor [Rai et al., 2017]. A nonlinear forcing term allows shaping the transient behavior to the attractor without endangering the well-defined attractor properties. Once this nonlinear term has been initialized, e.g., via imitation learning, this movement representation can be generalized with respect to task parameters such as start, goal, and duration of the movement.
传统方法考虑运动的动力学并生成运动图元。 动态运动基元(DMP)[Schaal,2006]是可以用作反应反馈控制器的最受欢迎的运动表示之一。 DMP是作用单元,被形式化为稳定的非线性吸引系统。 他们将运动控制策略编码为微分方程,目标是吸引子[Rai等,2017]。 非线性强迫项可以使吸引子的瞬态行为成形,而不会危及明确定义的吸引子特性。 一旦该非线性项已经被初始化,例如,通过模仿学习,就可以相对于任务参数,例如运动的开始,目标和持续时间,来概括该运动表示。
DMPs have been successfully used to in imitation learning, reinforcement learning, movement recognition and so on. Colomé et al. [Colomé and Torras, 2018] addressed the process of simultaneously learning a DMP-characterized robot motion and its underlying joint couplings through linear dimensionality reduction, whi
Motion Plan
最新推荐文章于 2023-10-16 22:05:17 发布








 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章















 515
515











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








