一、变换规则
对于三维旋转theta*a是向量fai
对于三维变换,左上角的R仍然是相同公式,右上角J由新公式给出

二、求导
由于在实际计算时,往往要计算误差函数对于R或者T的导数,提出了扰动模型,p为旋转之前的点,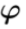 是微小扰动
是微小扰动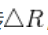 的李代数
的李代数

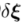 是微小扰动
是微小扰动 T的李代数,最后的结果有一个运算符
T的李代数,最后的结果有一个运算符
三、使用Sophus进行李群和李代数的运算
#include < iostream>
#include < cmath>
#include <Eigen/Core>
#include <Eigen/Geometry>
#include “sophus/se3.hpp”
using namespace std;
using namespace Eigen;
/// 本程序演示sophus的基本用法
int main(int argc, char **argv) {
// 沿Z轴转90度的旋转矩阵
Matrix3d R = AngleAxisd(M_PI / 2, Vector3d(0, 0, 1)).toRotationMatrix();
// 或者四元数
Quaterniond q ( R) ;
Sophus::SO3d SO3_R( R); // SO3d初始化可以直接从旋转矩阵构造
Sophus::SO3d SO3_q( q); // 也可以通过四元数构造,也可以exp(向量)=R
// 二者是等价的
cout << “SO(3) from matrix:\n” << SO3_R.matrix() << endl;
cout << “SO(3) from quaternion:\n” << SO3_q.matrix() << endl;
cout << “they are equal” << endl;
// 使用对数映射获得它的李代数
Vector3d so3 = SO3_R.log();做log运算获取R对应的李代数向量,exp(向量的反对称矩阵)=R
cout << "so3 = " << so3.transpose() << endl;
// hat 为向量到反对称矩阵
cout << “so3 hat=\n” << Sophus::SO3d::hat(so3)hat函数从向量构造向量对应的反对称矩阵 << endl;
// 相对的,vee为反对称到向量
cout << "so3 hat vee= " << Sophus::SO3d::vee(Sophus::SO3d::hat(so3))vee函数从反对称矩阵到对应的向量.transpose() << endl;
// 增量扰动模型的更新
Vector3d update_so3(1e-4, 0, 0); //假设更新量为这么多
Sophus::SO3d SO3_updated = Sophus::SO3d::exp(update_so3) exp函数,把向量直接转换为SO3d* SO3_R;
cout << “SO3 updated = \n” << SO3_updated.matrix() << endl;
cout << “*******************************” << endl;
// 对SE(3)操作大同小异
Vector3d t(1, 0, 0); // 沿X轴平移1
Sophus::SE3d SE3_Rt(R, t); // 从R,t构造SE(3)
Sophus::SE3d SE3_qt(q, t); // 从q,t构造SE(3)
cout << “SE3 from R,t= \n” << SE3_Rt.matrix() << endl;
cout << “SE3 from q,t= \n” << SE3_qt.matrix() << endl;
// 李代数se(3) 是一个六维向量,方便起见先typedef一下
typedef Eigen::Matrix<double, 6, 1> Vector6d;
Vector6d se3 = SE3_Rt.log();做log运算获取T对应的李代数向量
cout << "se3 = " << se3.transpose() << endl;
// 观察输出,会发现在Sophus中,se(3)的平移在前,旋转在后.
// 同样的,有hat和vee两个算符
cout << “se3 hat = \n” << Sophus::SE3d::hat(se3) << endl;
cout << "se3 hat vee = " << Sophus::SE3d::vee(Sophus::SE3d::hat(se3)).transpose() << endl;
// 最后,演示一下更新
Vector6d update_se3; //更新量
update_se3.setZero();
update_se3(0, 0) = 1e-4d;
Sophus::SE3d SE3_updated = Sophus::SE3d::exp(update_se3) * SE3_Rt;
cout << "SE3 updated = " << endl << SE3_updated.matrix() << endl;
return 0;
}
四、
#include < iostream>
#include < fstream>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <pangolin/pangolin.h>
#include <sophus/se3.hpp>
using namespace Sophus;
using namespace std;
string groundtruth_file = “./example/groundtruth.txt”;
string estimated_file = “./example/estimated.txt”;
typedef vector<Sophus::SE3d, Eigen::aligned_allocator< Sophus::SE3d>> TrajectoryType;
void DrawTrajectory(const TrajectoryType >, const TrajectoryType &esti);
TrajectoryType ReadTrajectory(const string &path);
int main(int argc, char **argv) {
TrajectoryType groundtruth = ReadTrajectory(groundtruth_file);
TrajectoryType estimated = ReadTrajectory(estimated_file);
assert(!groundtruth.empty() && !estimated.empty());
assert(groundtruth.size() == estimated.size());
// compute rmse
double rmse = 0;
for (size_t i = 0; i < estimated.size(); i++) {
Sophus::SE3d p1 = estimated[i], p2 = groundtruth[i];
double error = (p2.inverse() * p1).log().norm()绝对轨迹误差公式,。norm返回向量的二范数,例如norm(3,4)=5;
rmse += error * error;去掉二范数的根号
}
rmse = rmse / double(estimated.size());除以分母N
rmse = sqrt(rmse);开根号
cout << "RMSE = " << rmse << endl;
DrawTrajectory(groundtruth, estimated);
return 0;
}
TrajectoryType ReadTrajectory(const string &path) {
ifstream fin(path);
TrajectoryType trajectory;
if (!fin) {
cerr << “trajectory " << path << " not found.” << endl;
return trajectory;
}
while (!fin.eof()) {
double time, tx, ty, tz, qx, qy, qz, qw;
fin >> time >> tx >> ty >> tz >> qx >> qy >> qz >> qw;
Sophus::SE3d p1(Eigen::Quaterniond(qw, qx, qy, qz), Eigen::Vector3d(tx, ty, tz));
trajectory.push_back(p1);
}
return trajectory;
}
void DrawTrajectory(const TrajectoryType >, const TrajectoryType &esti) {
// create pangolin window and plot the trajectory
pangolin::CreateWindowAndBind(“Trajectory Viewer”, 1024, 768);
glEnable(GL_DEPTH_TEST);
glEnable(GL_BLEND);
glBlendFunc(GL_SRC_ALPHA, GL_ONE_MINUS_SRC_ALPHA);
pangolin::OpenGlRenderState s_cam(
pangolin::ProjectionMatrix(1024, 768, 500, 500, 512, 389, 0.1, 1000),
pangolin::ModelViewLookAt(0, -0.1, -1.8, 0, 0, 0, 0.0, -1.0, 0.0)
);
pangolin::View &d_cam = pangolin::CreateDisplay()
.SetBounds(0.0, 1.0, pangolin::Attach::Pix(175), 1.0, -1024.0f / 768.0f)
.SetHandler(new pangolin::Handler3D(s_cam));
while (pangolin::ShouldQuit() == false) {
glClear(GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT | GL_DEPTH_BUFFER_BIT);
d_cam.Activate(s_cam);
glClearColor(1.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f);
glLineWidth(2);
for (size_t i = 0; i < gt.size() - 1; i++) {
glColor3f(0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f); // blue for ground truth
glBegin(GL_LINES);
auto p1 = gt[i], p2 = gt[i + 1];
glVertex3d(p1.translation()[0], p1.translation()[1], p1.translation()[2]);
glVertex3d(p2.translation()[0], p2.translation()[1], p2.translation()[2]);
glEnd();
}
for (size_t i = 0; i < esti.size() - 1; i++) {
glColor3f(1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f); // red for estimated
glBegin(GL_LINES);
auto p1 = esti[i], p2 = esti[i + 1];
glVertex3d(p1.translation()[0], p1.translation()[1], p1.translation()[2]);
glVertex3d(p2.translation()[0], p2.translation()[1], p2.translation()[2]);
glEnd();
}
pangolin::FinishFrame();
usleep(5000); // sleep 5 ms
}
}




















 666
666











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








