前置题条件:
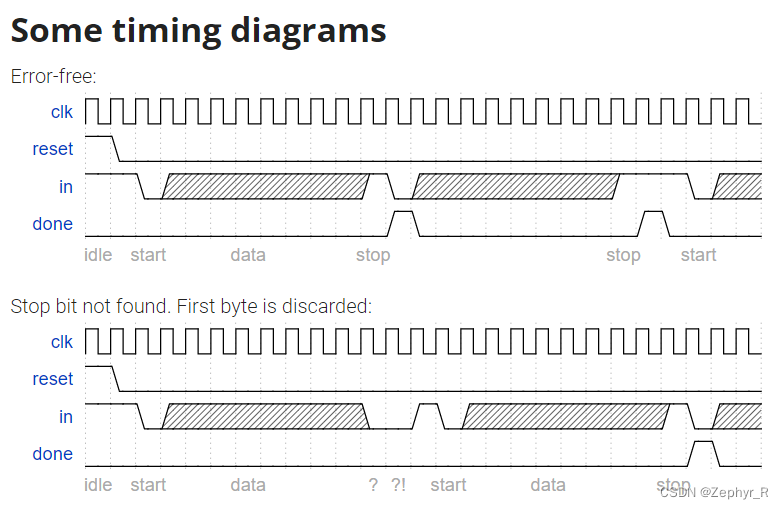
In many (older) serial communications protocols, each data byte is sent along with a start bit and a stop bit, to help the receiver delimit bytes from the stream of bits. One common scheme is to use one start bit (0), 8 data bits, and 1 stop bit (1). The line is also at logic 1 when nothing is being transmitted (idle).
Design a finite state machine that will identify when bytes have been correctly received when given a stream of bits. It needs to identify the start bit, wait for all 8 data bits, then verify that the stop bit was correct. If the stop bit does not appear when expected, the FSM must wait until it finds a stop bit before attempting to receive the next byte.
Now that you have a finite state machine that can identify when bytes are correctly received in a serial bitstream, add a datapath that will output the correctly-received data byte. out_byte needs to be valid when done is 1, and is don't-care otherwise.
Note that the serial protocol sends the least significant bit first.
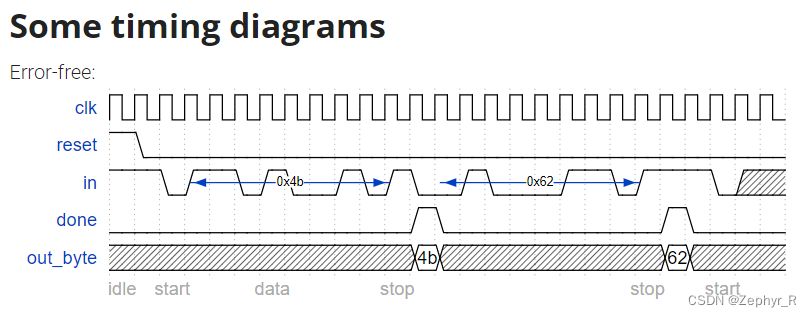
See also: Serial receiver and datapath
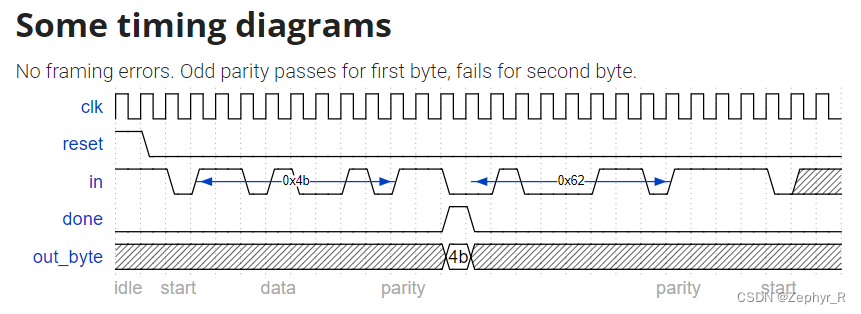
We want to add parity checking to the serial receiver. Parity checking adds one extra bit after each data byte. We will use odd parity, where the number of 1s in the 9 bits received must be odd. For example, 101001011 satisfies odd parity (there are 5 1s), but 001001011 does not.
Change your FSM and datapath to perform odd parity checking. Assert the done signal only if a byte is correctly received and its parity check passes. Like the serial receiver FSM, this FSM needs to identify the start bit, wait for all 9 (data and parity) bits, then verify that the stop bit was correct. If the stop bit does not appear when expected, the FSM must wait until it finds a stop bit before attempting to receive the next byte.
You are provided with the following module that can be used to calculate the parity of the input stream (It's a TFF with reset). The intended use is that it should be given the input bit stream, and reset at appropriate times so it counts the number of 1 bits in each byte.
module parity (
input clk,
input reset,
input in,
output reg odd);
always @(posedge clk)
if (reset) odd <= 0;
else if (in) odd <= ~odd;
endmoduleNote that the serial protocol sends the least significant bit first, and the parity bit after the 8 data bits.
//Fsm serialdp
module top_module(
input clk,
input in,
input reset, // Synchronous reset
output [7:0] out_byte,
output done
);
reg[4:0]state,next_state;
parameter idle=5'd0, s1=5'd1, s2=5'd2, s3=5'd3, s4=5'd4 ,s5=5'd5 ,s6=5'd6, s7=5'd7, s8=5'd8;
parameter d=5'd9, wait_d=5'd10,discard=5'd11,wait_finish=5'd12, check=5'd13,wait_discard=5'd14;
reg[7:0] rec_data;
wire odd;
wire odd_check;
wire odd_reset;
always @(*)
begin
case(state)
idle: next_state = (in ? idle : s1); //in为0时,下个周期开始接收数据
s1: next_state = s2; //s1代表正在接收第一个数据
s2: next_state = s3;
s3: next_state = s4;
s4: next_state = s5;
s5: next_state = s6;
s6: next_state = s7;
s7: next_state = s8;
s8: next_state = check; //接收完8个bits后进入odd check
check: next_state = (in==odd_check ? wait_finish : wait_d); //check失败则当停止信号到来时进入discard状态
wait_finish: next_state = (in ? d : wait_d);
d: next_state = (in ? idle : s1);
wait_d: next_state = (in ? discard : wait_d);
discard: next_state = (in ? idle : s1); //在接收到停止信号后恢复正常,但丢弃前一个字节信息,且不输出done信号
endcase
end
always @(posedge clk)
if (reset)
state <= idle;
else
state <= next_state;
assign done = (state==d);
// New: Datapath to latch input bits.
always @(posedge clk)
begin
case(state)
s1: rec_data[0] <= in; //时钟沿到来时,若为正在接收数据状态,将in的值保存到对应的寄存器
s2: rec_data[1] <= in;
s3: rec_data[2] <= in;
s4: rec_data[3] <= in;
s5: rec_data[4] <= in;
s6: rec_data[5] <= in;
s7: rec_data[6] <= in;
s8: rec_data[7] <= in;
endcase
end
assign out_byte = rec_data;
// New: Add parity checking.
assign odd_reset = ~(state==s1|state==s2|state==s3|state==s4|state==s5|state==s6|state==s7|state==s8); //不在接收数据状态时,保持清零
parity check1 (.clk(clk),.reset(odd_reset),.in(in),.odd(odd));
assign odd_check = ~odd; //odd为1时代表前八个数据为奇数,odd_check应为0;数据为偶数,odd_check应为1
endmodule





















 2067
2067











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








