目录
2.1 Harris角点检测器
Harris角点检测算法是一个极为简单的角点检测算法。该算法的主要思想是,如果像素周围显示存在多于一个方向的边,我们认为该点为兴趣点。该点就称为角点。
图像域中点x上的对称半正定矩阵定义为:
卷积:
取决于该区域的值,harris矩阵
的特征值有三种情况:
- 如果 λ1 和 λ2 都是很大的正数,则该 x 点为角点;
- 如果 λ1 很大,λ2 ≈ 0,则该区域内存在一个边,该区域内的平均 MI 的特征值不会变化太大;
- 如果 λ1≈λ2≈0,该区域内为空。
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
from pylab import *
from PIL import Image
from PCV.localdescriptors import harris
# 读入图像
im = array(Image.open('8.jpg').convert('L'))
# 检测harris角点
harrisim = harris.compute_harris_response(im)
# Harris响应函数
harrisim1 = 255 - harrisim
figure()
gray()
# 画出Harris响应图
subplot(141)
imshow(harrisim1)
print ('harrisim1.shape')
axis('off')
axis('equal')
threshold = [0.01, 0.05, 0.1]
for i, thres in enumerate(threshold):
filtered_coords = harris.get_harris_points(harrisim, 6, thres)
subplot(1, 4, i + 2)
imshow(im)
print ('im.shape')
plot([p[1] for p in filtered_coords], [p[0] for p in filtered_coords], '*')
axis('off')
# 原书采用的PCV中PCV harris模块
# harris.plot_harris_points(im, filtered_coords)
# plot only 200 strongest
# harris.plot_harris_points(im, filtered_coords[:200])
show()
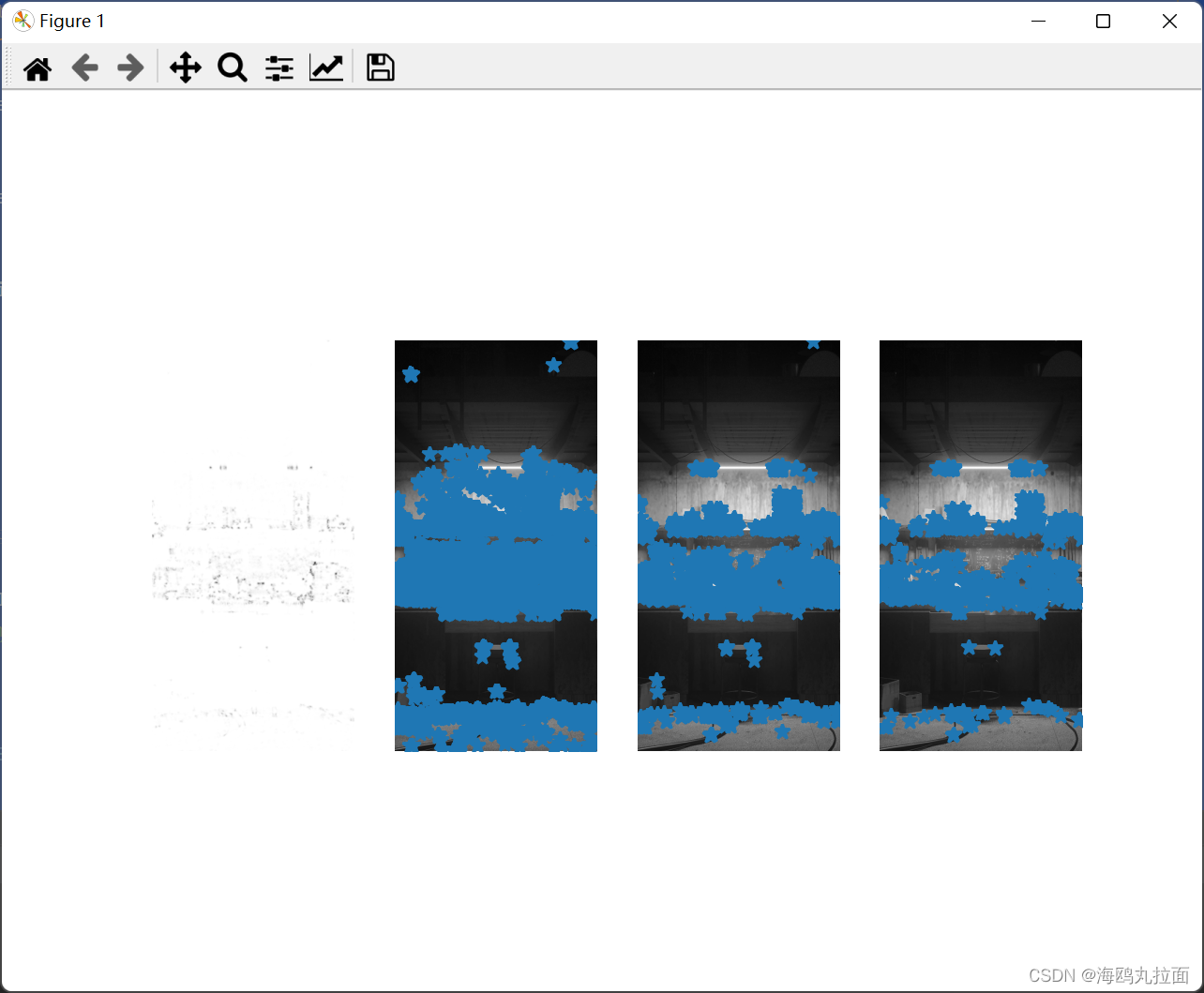
由图像结果可直观看出,减小角点响应值,降低角点检测的灵性,减少被检测角点的数量;增大角点响应值,增加角点检测的灵敏性,增加被检测角点的数量。
在图像间寻找对应点
Harris 角点检测器仅仅能够检测出图像中的兴趣点,但是没有给出通过比较图像间的兴趣点来寻找匹配角点的方法。我们需要在每个点上加入描述子信息,并给出一 个比较这些描述子的方法。
兴趣点描述子是分配给兴趣点的一个向量,描述该点附近的图像的表观信息。描述子越好,寻找到的对应点越好。我们用对应点或者点的对应来描述相同物体和场景点在不同图像上形成的像素点。
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
from pylab import *
from PIL import Image
from PCV.localdescriptors import harris
from PCV.tools.imtools import imresize
im1 = array(Image.open("15.jpg").convert("L"))
im2 = array(Image.open("15.1.jpg").convert("L"))
# resize加快匹配速度
wid = 5
harrisim = harris.compute_harris_response(im1, 5)
filtered_coords1 = harris.get_harris_points(harrisim, wid + 1)
d1 = harris.get_descriptors(im1, filtered_coords1, wid)
harrisim = harris.compute_harris_response(im2, 5)
filtered_coords2 = harris.get_harris_points(harrisim, wid + 1)
d2 = harris.get_descriptors(im2, filtered_coords2, wid)
print ('starting matching')
matches = harris.match_twosided(d1, d2)
figure()
gray()
harris.plot_matches(im1, im2, filtered_coords1, filtered_coords2, matches)
show()
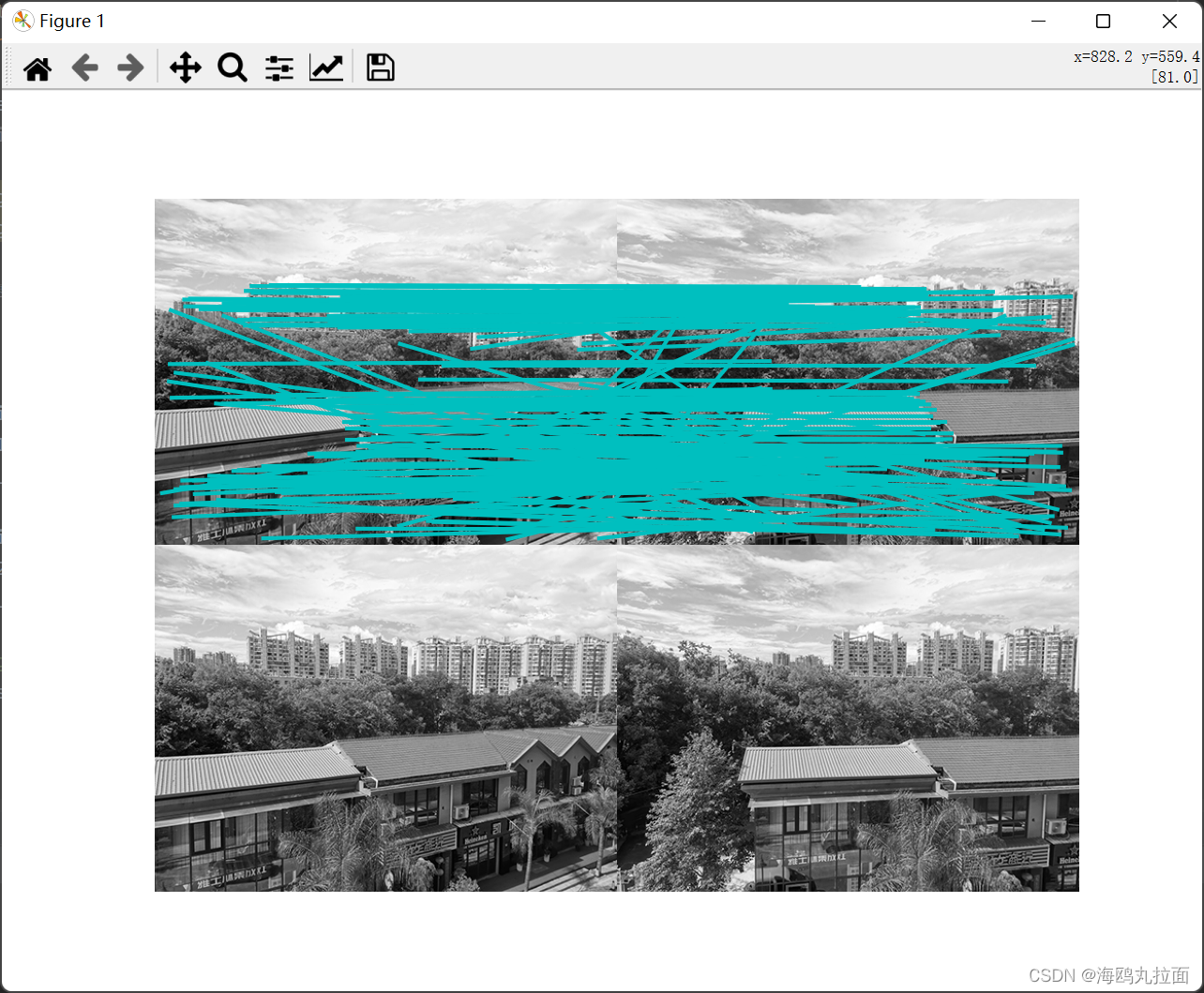
算法结果存在着不正确匹配,可能是由于图像像素的互相关矩阵具有较弱的描述性。同时,若图像尺寸较大,处理图像时长会非常长。
2.2 SIFT(尺寸不变特征变换)
SIFT特征包括兴趣点检测器和描述子。SIFT描述子具有非常强的稳健性,这在很大程度上也是SIFT特征能够成功和流行的主要原因。
2.2.1 兴趣点
SIFT特征使用高斯差分函数来定位兴趣点:
其中,Gδ是二维高斯核,Iδ是使用Gδ模糊的灰度图像。兴趣点是在图像位置和尺度变化下D(x,σ)的最大值和最小值点,这些候选位置点通过滤波去除不稳定点。
2.2.2 描述子
为了实现旋转不变性,基于每个点周围图像梯度的方向和大小,SIFT 描述子又引入了参考方向。SIFT 描述子使用主方向描述参考方向。主方向使用方向直方图(以大小为权重)来度量。
2.2.3 检测兴趣点
使用开源工具包VLFeat提供的二进制文件来计算图像的SIFT特征。
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
from PIL import Image
from pylab import *
from PCV.localdescriptors import sift
from PCV.localdescriptors import harris
# 添加中文字体支持
from matplotlib.font_manager import FontProperties
font = FontProperties(fname=r"c:\windows\fonts\SimSun.ttc", size=14)
imname = '8.jpg'
im = array(Image.open(imname).convert('L'))
sift.process_image(imname, 'empire.sift')
l1, d1 = sift.read_features_from_file('empire.sift')
figure()
gray()
subplot(131)
sift.plot_features(im, l1, circle=False)
title(u'(a)SIFT特征', fontproperties=font)
subplot(132)
sift.plot_features(im, l1, circle=True)
title(u'(b)用圆圈表示SIFT特征尺度', fontproperties=font)
# 检测harris角点
harrisim = harris.compute_harris_response(im)
subplot(133)
filtered_coords = harris.get_harris_points(harrisim, 6, 0.1)
imshow(im)
plot([p[1] for p in filtered_coords], [p[0] for p in filtered_coords], '*')
axis('off')
title(u'(c)Harris角点', fontproperties=font)
show()
报错如下:
网络搜索教程:
没能解决问题,暂时搁置该算法。
后记:将版本切换回自己安装的python3.7.2,再把PCV-matser解压后的PCV文件夹拷贝到项目根目录,从而自动识别应用PCV,问题得到解决。

比较结果可以看出,SIFT和harris两种算法选择特征点有很大不同。
2.2.4 匹配描述子
对于将一幅图像中的特征匹配到另一幅图像的特征,一种稳健的准则(同样是由 Lowe 提出的)是使用这两个特征距离和两个最匹配特征距离的比率。相比于图像中的其他特征,该准则保证能够找到足够相似的唯一特征。使用该方法可以使错误的匹配数降低。
from PIL import Image
from pylab import *
import sys
from PCV.localdescriptors import sift
if len(sys.argv) >= 3:
im1f, im2f = sys.argv[1], sys.argv[2]
else:
im1f = '15.jpg'
im2f = '15.1.jpg'
im1 = array(Image.open(im1f))
im2 = array(Image.open(im2f))
sift.process_image(im1f, 'out_sift_1.txt')
l1, d1 = sift.read_features_from_file('out_sift_1.txt')
figure()
gray()
subplot(121)
sift.plot_features(im1, l1, circle=False)
sift.process_image(im2f, 'out_sift_2.txt')
l2, d2 = sift.read_features_from_file('out_sift_2.txt')
subplot(122)
sift.plot_features(im2, l2, circle=False)
# matches = sift.match(d1, d2)
matches = sift.match_twosided(d1, d2)
print ('{} matches'.format(len(matches.nonzero()[0])))
figure()
gray()
sift.plot_matches(im1, im2, l1, l2, matches, show_below=True)
show()
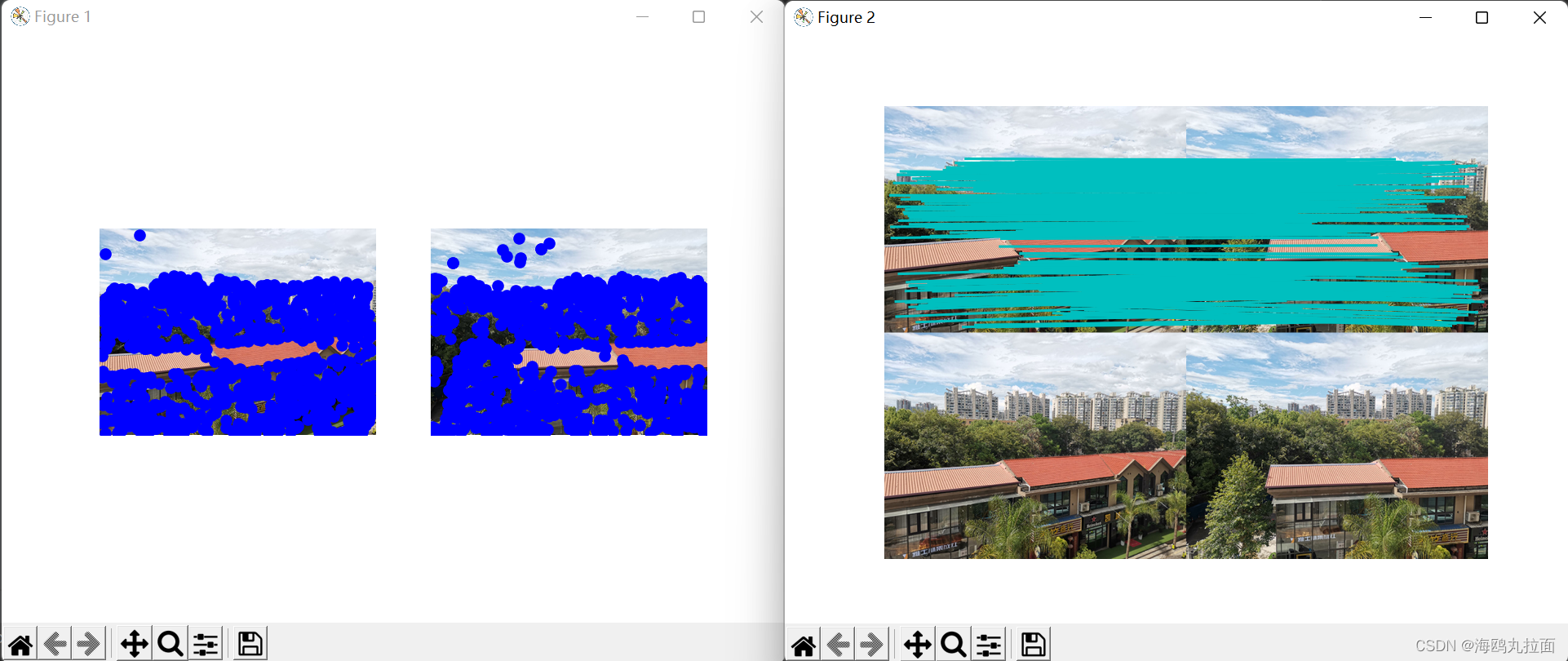
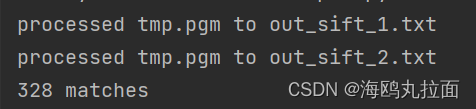
SIFT算法查找关键点,计算关键点位置,根据特征距离和两个最匹配特征距离的比率进行特征匹配。这种方式使匹配的精确性提高了。
2.3 匹配地理标记图像
2.3.1 从Panoramio下载地理标记图像
谷歌提供的照片共享服务 Panoramio(http://www.panoramio.com/) 已停止运营,暂时搁置该算法。
2.3.2 使用局部描述子匹配
在固定位置拍摄若干张图片进行处理
import json
import os
import urllib
# import urlparse
# from pylab import *
from PIL import Image
from PCV.localdescriptors import sift
from PCV.tools import imtools
from numpy import *
# import pydot
download_path = "G:\\picture\\path"
# path = "G:\\picture\\"
imlist = imtools.get_imlist(download_path)
nbr_images = len(imlist)
featlist = [imname[:-3] + 'sift' for imname in imlist]
for i, imname in enumerate(imlist):
sift.process_image(imname, featlist[i])
matchscores = zeros((nbr_images, nbr_images))
for i in range(nbr_images):
for j in range(i, nbr_images): # only compute upper triangle
print('comparing ', imlist[i], imlist[j])
l1, d1 = sift.read_features_from_file(featlist[i])
l2, d2 = sift.read_features_from_file(featlist[j])
matches = sift.match_twosided(d1, d2)
nbr_matches = sum(matches > 0)
print('number of matches = ', nbr_matches)
matchscores[i, j] = nbr_matches
# copy values
for i in range(nbr_images):
for j in range(i + 1, nbr_images): # no need to copy diagonal
matchscores[j, i] = matchscores[i, j]
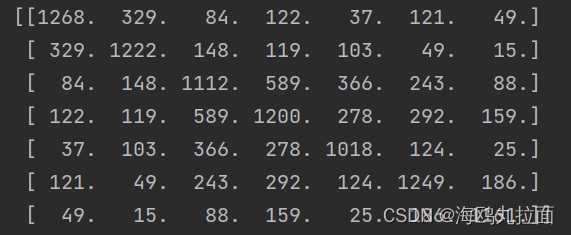
运行输出如下:
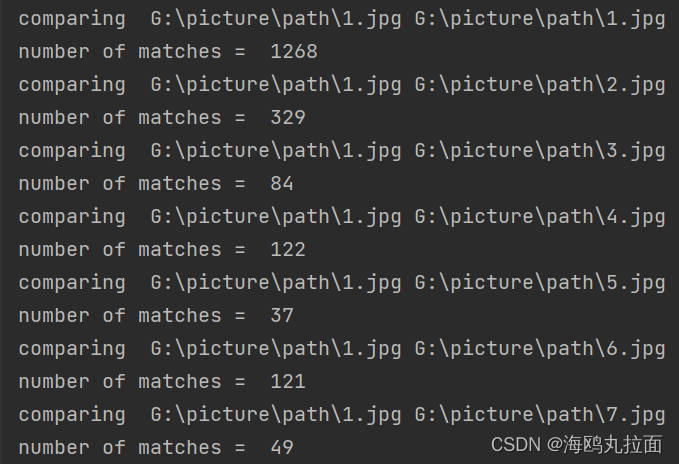
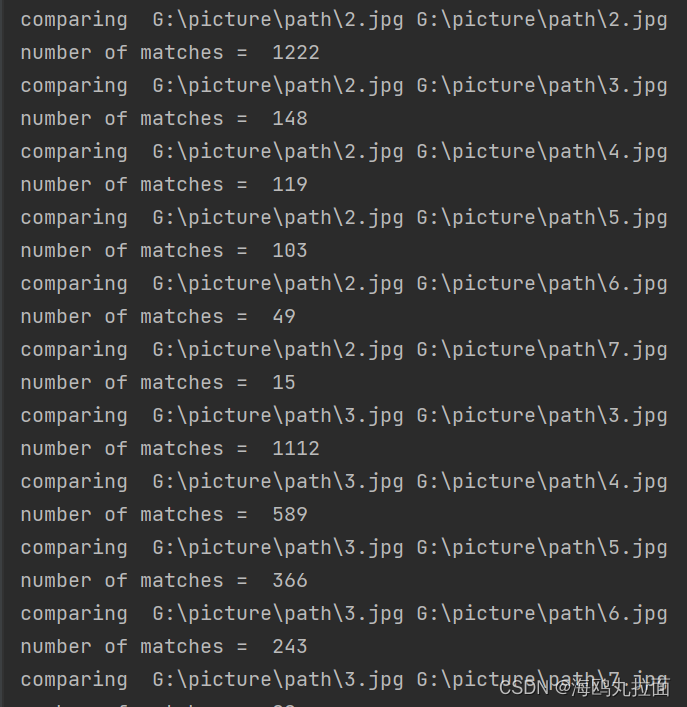
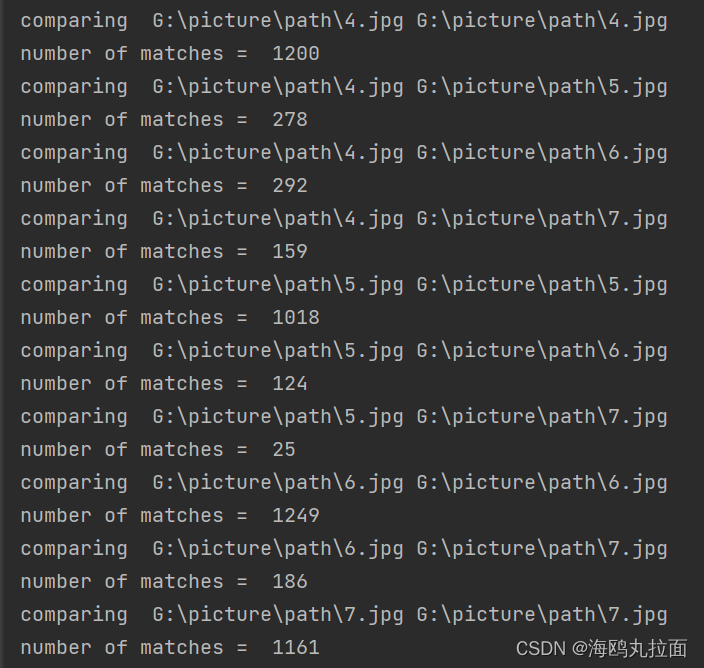
在代码末尾加上
print(mathscores)得到mathscroes矩阵,存储了每队图像间的匹配特征数。
2.3.3 可视化连接的图像
首先通过图像间是否具有匹配的局部描述子来定义图像间的连接,然后可视化这些连接情况。为了完成可视化,我们可以在图中显示这些图像,图的边代表连接。 可以使用pydot 工具包 (http://code.google.com/p/pydot/)。配置过程在此省略,该工具包是功能强大的GraphViz图像库的Python借口。
为了创建显示可能图像组的图,如果匹配的数目高于一个阈值,我们使用边来连接相应的图像节点。为了得到图中的 图像,需要使用图像的全路径(在下面例子中,使用 path 变量表示)。为了使图像看起来漂亮,我们需要将每幅图像尺度化为缩略图形式,缩略图的最大边为 100 像素。
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import json
import os
import urllib
# import urlparse
from pylab import *
from PIL import Image
from PCV.localdescriptors import sift
from PCV.tools import imtools
import pydot
from numpy import *
import os
# os.environ["PATH"] += os.pathsep + 'C:/Program Files (x86)/Graphviz2.38/bin/'
download_path = "G:\\picture\\path2"
path = "G:\\picture\\path2\\"
imlist = imtools.get_imlist(download_path)
nbr_images = len(imlist)
featlist = [imname[:-3] + 'sift' for imname in imlist]
for i, imname in enumerate(imlist):
sift.process_image(imname, featlist[i])
matchscores = zeros((nbr_images, nbr_images))
for i in range(nbr_images):
for j in range(i, nbr_images): # only compute upper triangle
print('comparing ', imlist[i], imlist[j])
l1, d1 = sift.read_features_from_file(featlist[i])
l2, d2 = sift.read_features_from_file(featlist[j])
matches = sift.match_twosided(d1, d2)
nbr_matches = sum(matches > 0)
print('number of matches = ', nbr_matches)
matchscores[i, j] = nbr_matches
# copy values
for i in range(nbr_images):
for j in range(i + 1, nbr_images): # no need to copy diagonal
matchscores[j, i] = matchscores[i, j]
# 可视化
threshold = 2 # min number of matches needed to create link
g = pydot.Dot(graph_type='graph') # don't want the default directed graph
for i in range(nbr_images):
for j in range(i + 1, nbr_images):
if matchscores[i, j] > threshold:
# first image in pair
im = Image.open(imlist[i])
im.thumbnail((100, 100))
filename = path + str(i) + '.jpg'
im.save(filename) # need temporary files of the right size
g.add_node(pydot.Node(str(i), fontcolor='transparent', shape='rectangle', image=filename))
# second image in pair
im = Image.open(imlist[j])
im.thumbnail((100, 100))
filename = path + str(j) + '.jpg'
im.save(filename) # need temporary files of the right size
g.add_node(pydot.Node(str(j), fontcolor='transparent', shape='rectangle', image=filename))
g.add_edge(pydot.Edge(str(i), str(j)))
g.write_jpg(r'G:\picture\path2\result.jpg')
配置好环境后可能会出现报错:
dot" not found in path解决参考 :
如还不行,登录 (Download | Graphviz)下载安装Graphviz,找到安装目录下dot.exe文件,再在pydot.py中对如下语句进行修改:
self.prog = ‘dot’
------修改为-------
self.prog = r'D:\Graphviz\bin\dot.exe'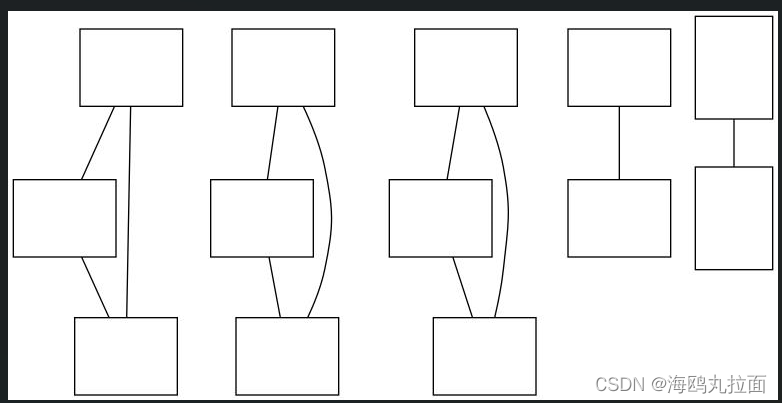
处理后目录中缩略图生成,连接情况正常,但是结果图中没有缩略图。没想明白是为什么,暂时搁置。





















 662
662











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








