编译器=翻译器
编译器是每个软件开发人员每天都会使用几次的工具。这是因为网络绝大部分基于客户端的代码执行,并且许多这种客户端的程序都以源代码的形式被传递给浏览器。
这里我们就有一个比较重要的概念:尽管源代码通常是人类可读的,对于我们的CPU来说它们就像垃圾。在另一方面,虽然机器码是机器可读的,但是它几乎是人类不可读的。因此我们需要执行一步翻译过程。
最简单的编译器执行单步编译:从源代码到机器码。然而,实际上大多数编译器都会经过至少两阶段:从源代码到AST,再从AST到机器码。AST在这种情况下作为IR,它仅仅是源代码的另外一种组织形式。
对于阶段数并没有明确限定,每个新的阶段都会将源程序变得更像机器码。
优化阶段
然而,并不是所有的阶段都仅被用来翻译。许多编译器同样尝试来优化我们所写的代码。(我们所写的代码通常需要在高性能和代码优雅间取一个均衡)。
以下面的JavaScript代码为例子:
for (var i = 0, acc = 0; i < arr.length; i++)
acc += arr[i];
如果编译器直接将它从AST翻译到机器码,那么它可能类似如下的形式(in very abstract and detached from reality instruction set):
acc = 0;
i = 0;
loop {
// Load `.length` field of arr
tmp = loadArrayLength(arr);
if (i >= tmp)
break;
// Check that `i` is between 0 and `arr.length`
// (NOTE: This is necessary for fast loads and
// stores).
checkIndex(arr, i);
// Load value
acc += load(arr, i);
// Increment index
i += 1;
}
上述代码还有很大的优化空间,在循环期间数组长度不变,并且范围检查不是必要的,理想情况下,代码应当如下所示:
acc = 0;
i = 0;
len = loadArrayLength(arr);
loop {
if (i >= len)
break;
acc += load(arr, i);
i += 1;
}
假设我们现有一个AST,并且我们想要直接从AST中生成机器码(注意,下面生成自esprima)。
{ type: 'ForStatement',
//
// This is `var i = 0;`
//
init:
{ type: 'VariableDeclaration',
declarations:
[ { type: 'VariableDeclarator',
id: { type: 'Identifier', name: 'i' },
init: { type: 'Literal', value: 0, raw: '0' } },
{ type: 'VariableDeclarator',
id: { type: 'Identifier', name: 'acc' },
init: { type: 'Literal', value: 0, raw: '0' } }],
kind: 'var' },
//
// `i < arr.length`
//
test:
{ type: 'BinaryExpression',
operator: '<',
left: { type: 'Identifier', name: 'i' },
right:
{ type: 'MemberExpression',
computed: false,
object: { type: 'Identifier', name: 'arr' },
property: { type: 'Identifier', name: 'length' } } },
//
// `i++`
//
update:
{ type: 'UpdateExpression',
operator: '++',
argument: { type: 'Identifier', name: 'i' },
prefix: false },
//
// `arr[i] += 1;`
//
body:
{ type: 'ExpressionStatement',
expression:
{ type: 'AssignmentExpression',
operator: '+=',
left: { type: 'Identifier', name: 'acc' },
right:
{ type: 'MemberExpression',
computed: true,
object: { type: 'Identifier', name: 'arr' },
property: { type: 'Identifier', name: 'i' } } } }
上述JSON表示也可以通过如下方式进行可视化:

这是一个树形结构,因此我们可以很自然地从顶部到底部进行遍历,在我们访问AST节点的同时生成机器码。这种方式的问题在于the information about variables is very sparse, and is spread through the different tree nodes.
Again, to safely move the length lookup out of the loop we need to know that the array length does not change between the loop’s iterations. Humans can do it easily just by looking at the source code, but the compiler needs to do quite a lot of work to confidently extract those facts directly from the AST.
Like many other compiler problems, this is often solved by lifting the data into a more appropriate abstraction layer, i.e. intermediate representation. In this particular case that choice of IR is known as a data-flow graph (DFG). Instead of talking about syntax-entities (like for loops, expressions, …), we should talk about the data itself (read, variables values), and how it changes through the program.
数据流图
在我们的例子中,我们感兴趣的是变量arr的值。我们想要能够很轻易的观察到所有使用它的地方从而证明没有越界访问或者任何修改它的长度的操作。
This is accomplished by introducing “def-use” (definition and uses) relationship between the different data values. Concretely, it means that the value has been declared once (node), and that it has been used somewhere to create new values (edge for every use). Obviously, connecting different values together will form a data-flow graph like this:

我们着重关注图中红色的部分。从它伸出的实线代表对这个值的使用,通过遍历这些边,编译器可以推断出array的值用在:
- loadArrayLength
- checkIndex
- load
这种图
Such graphs are constructed in the way that explicitly “clones” the array node, if its value was accessed in a destructive manner (i.e. stores, length sizes). Whenever we see array node and observe its uses - we are always certain that its value does not change.
It may sound complicated, but this property of the graph is quite easy to achieve. The graph should follow Single Static Assignment (SSA) rules. In short, to convert any program to SSA the compiler needs to rename all assignments and later uses of the variables, to make sure that each variable is assigned only once.
Example, before SSA:
var a = 1;
console.log(a);
a = 2;
console.log(a);
After SSA:
var a0 = 1;
console.log(a0);
var a1 = 2;
console.log(a1);
通过这种方式,我们可以确定当我们讨论a0时,we are actually talking about a single assignment to it. This is really close to how people do things in the functional languages!
Seeing that loadArrayLength has no control dependency (i.e. no dashed lines; we will talk about them in a bit), compiler may conclude that this node is free to move anywhere it wants to be and can be placed outside of the loop. By going through the graph further, we may observe that the value of ssa:phi node is always between 0 and arr.length, so the checkIndex may be removed altogether.
控制流图(Control Flow Graph,CFG)
We just used some form of data-flow analysis to extract information from the program. This allows us to make safe assumptions about how it could be optimized.
数据流表达在其他方面也是十分有用的。仅有的一个问题是通过将代码转化为这种图,我们其实在我们最终转化为机器码的过程中后退了一步。这种IR相比AST甚至更不适合生成机器码。
通常而言,这个问题通过将图中的节点组合为块来进行解决。这种表达方式被称为控制流图,下面是一个例子:
b0 {
i0 = literal 0
i1 = literal 0
i3 = array
i4 = jump ^b0
}
b0 -> b1
b1 {
i5 = ssa:phi ^b1 i0, i12
i6 = ssa:phi ^i5, i1, i14
i7 = loadArrayLength i3
i8 = cmp "<", i6, i7
i9 = if ^i6, i8
}
b1 -> b2, b3
b2 {
i10 = checkIndex ^b2, i3, i6
i11 = load ^i10, i3, i6
i12 = add i5, i11
i13 = literal 1
i14 = add i6, i13
i15 = jump ^b2
}
b2 -> b1
b3 {
i16 = exit ^b3
}
It is called a graph not without the reason. For example, the bXX blocks represent nodes, and the bXX -> bYY arrows represent edges. Let’s visualize it:
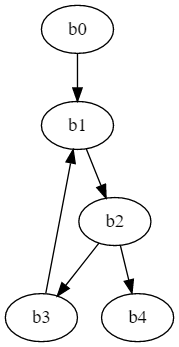
As you can see, there is code before the loop in block b0, loop header in b1, loop test in b2, loop body in b3, and exit node in b4.
Translation to machine code is very easy from this form. We just replace iXX identifiers with CPU register names (in some sense, CPU registers are sort of variables, the CPU has a limited amount of registers, so we need to be careful to not run out of them), and generating machine code for each instruction, line-by-line.
To recap, CFG has data-flow relations and also ordering. This allows us to utilize it for both data-flow analysis and machine code generation. However, attempting to optimize the CFG, by manipulating the blocks and their contents contained within it, can quickly become complex and error-prone.
Instead, Clifford Click and Keith D. Cooper proposed to use an approach called sea-of-nodes, the very topic of this blog post!
Sea-of-Nodes
Remember our fancy data-flow graph with dashed lines? Those dashed-lines are actually what make that graph a sea-of-nodes graph.
Instead of grouping nodes in blocks and ordering them, we choose to declare the control dependencies as the dashed edges in a graph. If we will take that graph, remove everything non-dashed, and group things a bit we will get:

With a bit of imagination and node reordering, we can see that this graph is the same as the simplified CFG graphs that we have just seen above:

Let’s take another look at the sea-of-nodes representation:

The striking difference between this graph and CFG is that there is no ordering of the nodes, except the ones that have control dependencies (in other words, the nodes participating in the control flow).
This representation is very powerful way to look at the code. It has all insights of the general data-flow graph, and could be changed easily without constantly removing/replacing nodes in the blocks.





















 8325
8325











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








