主要依照个人对代码的理解。
所谓“正样本”,也就是需要计算位置损失的预测框,也可以认为是负责预测target的anchor(anchor与pred一一对应)。例如20*20,40*40,80*80三种尺寸的特征图,认为其中的anchor总数为20*20*3+40*40*3+80*80*3(等于预测框数量),从这大量anchor之中选出预测少量target的"正样本"。损失计算时(位置损失和分类损失),需要用到的是“正样本”对应的预测值与target。
一、原理
Step1. target与anchor:
真值框与9个anchor分别计算宽比(ratio_w)和高比(ratio_h),二者都介于(1/4,4)之间则认为该真值框与对应anchor匹配上。即该anchor与真值框形状大小相似,一般大部分anchor都符合,该步骤可以得到负责预测target的 0~9 个“正样本”。
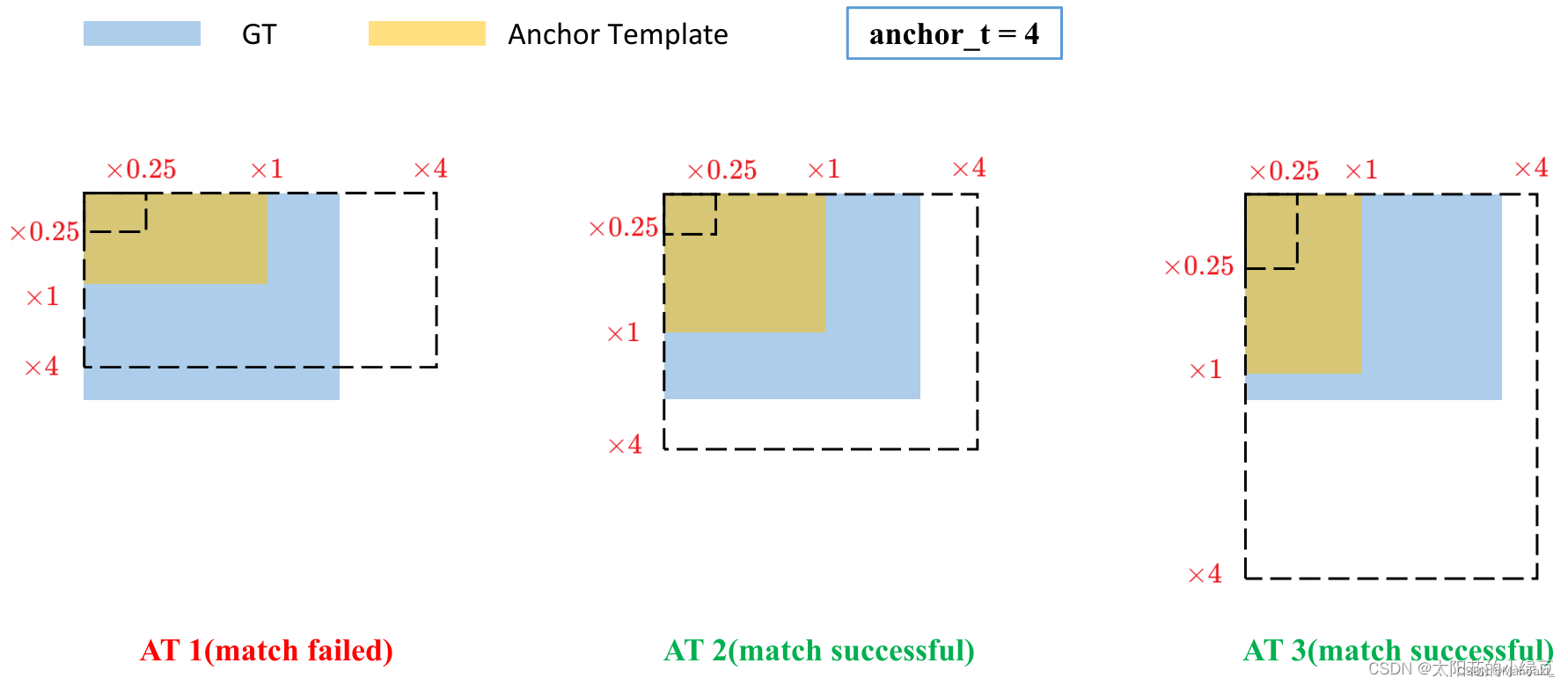 图源:YOLOv5网络详解_yolov5网络结构详解-CSDN博客
图源:YOLOv5网络详解_yolov5网络结构详解-CSDN博客
Step2. target与grid:
真值框中心点落在某grid的四个方位(左上、左下、右上、右下),则往相邻的两个方向扩展一个grid。除非精准地落在正中间,该步骤后每个target可以有3个grid负责预测,结合第一步筛选出来的anchor,可以得到负责预测该target的 0~27 个正样本。
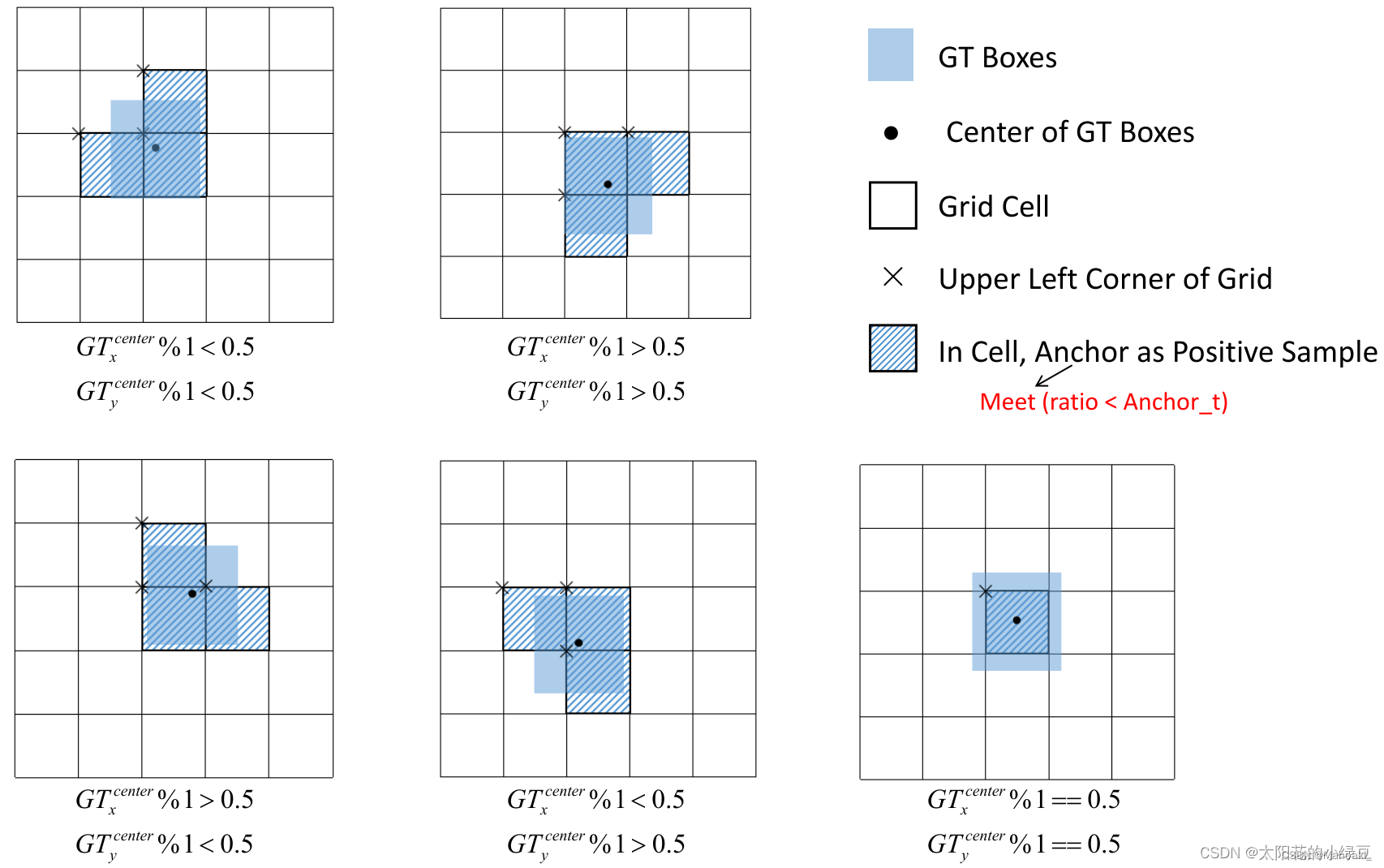
图源:YOLOv5网络详解_yolov5网络结构详解-CSDN博客
v5以及不含OTA的v7(代码可选)到这一步就结束了。
Step3. target与IoU(SimOTA):
需要注意,一个target可以由多个正样本预测,但一个正样本只能负责预测一个target。
(1)计算cost:计算该图像中的每个target与第二步中所有正样本对应的prediction的IoU,得到一个 nT*nP 的矩阵(其中很多值为0,因为不是该正样本负责预测的target);同时也可以计算出IoU_cost、分类损失class_cost 以及cost = class_cost + lmd * IoU_cost。该步骤最终需得到2个 nT*nP 的矩阵IoU、cost。
(2)获取dynamic_k:对于IoU矩阵,选取与每个target的IoU最大的前10(可调,如果不足10个,有多少取多少)个pred,得到 nT*10 的矩阵;对每一行求和并向下取整,得到nT个整数,即每个target最终由多少个正样本来预测。这么做的原因是,step1,2之后,正样本个数是增多了,但鱼龙混杂,有的预测框实在太差,与target的IoU非常小,我们也把它认为是负样本,不计算损失。每一行求和得到的整数大致可以代表与这个target的IoU较大的有多少个。
(3)得到dynamic_k个正样本:对于cost矩阵,取每个target对应的前dynamic_k个预测框作为最终“正样本”。可能会遇到其中有的正样本与多个target匹配,则选取与它IoU最小的target来预测。
总结
前两步筛选出的正样本只是anchor,没有预测值也可以获得,目的是为了增加正样本数量;第三步SimOTA精细化筛选,涉及预测值,需要经过前向传播得到pred后才能计算,第1,2步的正样本anchor,给第3步提供pred索引进行初筛,再经过cost筛选,此时的“正样本”可以直接认为是接下来用来计算loss的预测框了。
注意:train.py中,通常,训练时使用加simota的正样本匹配,验证时不加。
模型输出为tx, ty, tw, th,对应到实际预测框的中心点坐标以及宽高为:
可以看到中心点坐标位于(cx-0.5, cx+1.5)*(cy-0.5, cy+1.5)范围,即该grid向外扩了0.5个单位,一种解释是,若真值框中心点落在grid边界附近,原公式(v2论文给的)需要tx或ty无穷大或无穷小才能接近,对训练来说太难了,于是预测中心点可落范围向外扩了0.5个单位;
还有一种解释是,与正样本匹配第二步相呼应,若真值中心点落在(cx, cy)grid内,向邻近的两个方向扩一个grid,与中心点向上下左右四个方向分别取一个间隔0.5单位的点,这总共5个点所在的格子进行预测,效果是一样的,而从这个grid向外延伸出去的4个点,都会落在(cx-0.5, cx+1.5)*(cy-0.5, cy+1.5)范围内。
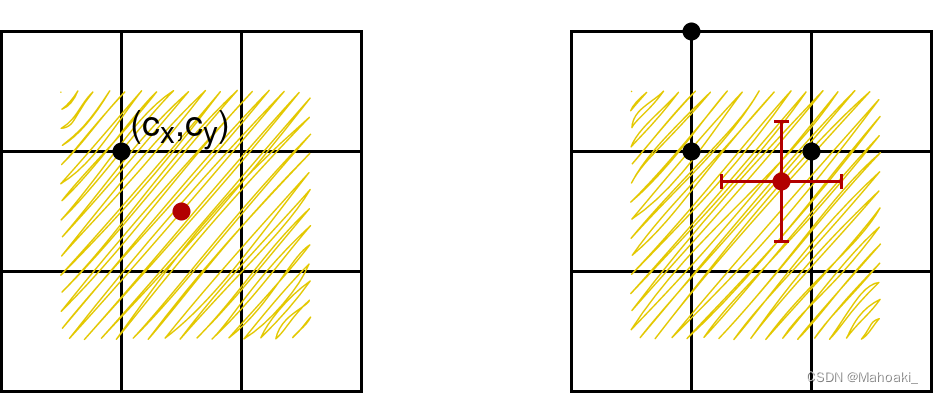
而对于宽高,原公式e^x,可能会出现梯度爆炸的问题,于是将其限制在了(0, 4)之间,而为什么是4呢,也可以理解为与上述正样本匹配的第一步宽比、高比筛选时的超参数4相呼应。
二、代码
源代码链接:https://github.com/WongKinYiu/yolov7
正样本匹配部分主要看 utils/loss.py/class ComputeLossOTA/__call__()中的一个函数build_targets(),接下来具体看一下build_targets()。
1、find_3_positive()
该函数对应原理中的前两步,也是class ComputeLoss(不含OTA)中build_targets()的全部内容,意思是class ComputeLossOTA的builid_targets()中的内容主要都是SimOTA。
indices, anch = self.find_3_positive(p, targets) # 一个batch的predictions和targets进到函数里面:
def find_3_positive(self, p, targets):
# p: {list:3}, 三个尺度的输出:N*C*H*W*(5+cls), 5表示(conf,tx,ty,tw,th)
# targets: n_targets*6, 6表示(img_index,cls_index,x,y,w,h), 其中x,y,w,h都是归一化后的
na, nt = self.na, targets.shape[0] # number of anchors, targets
indices, anch = [], []
# 用于使归一化的xywh转换到对应的网格坐标系1->number_grid
gain = torch.ones(7, device=targets.device).long() # normalized to grid_space gain
# 索引,ai.shape=(na,nt)=(3,nt),即第一行nt个0,第二行nt个1,第三行nt个2,只用于下一步append targets
ai = torch.arange(na, device=targets.device).float().view(na, 1).repeat(1, nt) # same as .repeat_interleave(nt)
# targets: nt*6 --> 3*nt*7, 7 means (img,cls,x,y,w,h,anchor), anchor represents this layer's 3 anchors
targets = torch.cat((targets.repeat(na, 1, 1), ai[:, :, None]), 2) # append anchor indices
g = 0.5 # bias
off = torch.tensor([[0, 0],
[1, 0], [0, 1], [-1, 0], [0, -1], # j,k,l,m
# [1, 1], [1, -1], [-1, 1], [-1, -1], # jk,jm,lk,lm
], device=targets.device).float() * g # offsets
# ---------------------------------------------one layer-----------------------------------------------------------
for i in range(self.nl):
anchors = self.anchors[i] # this layers' anchors: 3*2
gain[2:6] = torch.tensor(p[i].shape)[[3, 2, 3, 2]] # xyxy gain
# Match targets to anchors
t = targets * gain # (3,nt,7), 将xywh转换到网格坐标系下
if nt:
# Matches, 3 anchors vs. nt targets
r = t[:, :, 4:6] / anchors[:, None] # wh ratio, r.shape=(3,nt,2)
j = torch.max(r, 1. / r).max(2)[0] < self.hyp['anchor_t'] # compare, shape=(3,nt)
# j = wh_iou(anchors, t[:, 4:6]) > model.hyp['iou_t'] # iou(3,n)=wh_iou(anchors(3,2), gwh(n,2))
t = t[j] # filter, t.shape=(nPositive,7)
# Offsets
gxy = t[:, 2:4] # grid xy, 从左上数(nP,7)
gxi = gain[[2, 3]] - gxy # inverse, 从右下数(nP,7)
j, k = ((gxy % 1. < g) & (gxy > 1.)).T # bool(nP,), 落在格子左半边的,格子上半边的
l, m = ((gxi % 1. < g) & (gxi > 1.)).T # bool(nP,), 落在格子右半边的,格子下半边的
j = torch.stack((torch.ones_like(j), j, k, l, m)) # (5,nP)
t = t.repeat((5, 1, 1))[j] # (nOffset,7), nOffset=nP+nPl+nPu+nPr+nPd
offsets = (torch.zeros_like(gxy)[None] + off[:, None])[j] # (5,nP,2)[j]=(nOffset,2)
else:
t = targets[0]
offsets = 0
# Define
b, c = t[:, :2].long().T # image, class (nOffset,)
gxy = t[:, 2:4] # grid xy (nOffset,2)
gwh = t[:, 4:6] # grid wh (nOffset,2)
gij = (gxy - offsets).long() # (nOffset,2), 所在网格左上角坐标
gi, gj = gij.T # grid xy indices # (nOffset, )
# Append
a = t[:, 6].long() # anchor indices, (nOffset,)
indices.append((b, a, gj.clamp_(0, gain[3] - 1), gi.clamp_(0, gain[2] - 1))) # image, anchor, grid indices
anch.append(anchors[a]) # anchors
# ---------------------------------------------end layer-----------------------------------------------------------
return indices, anch # both {list:3}, indices[0]:{tuple:4}, anch[0]:{nOffset,2}主要经过matches和offsets两次筛选。经过step1. matches长比宽比阈值筛选,targets变为 nPositive*7;经过step2. offsets向外扩展2个grid,targets变为nOffset*7。一般nOffset=3*nPositive。
return的indices是按layer分的{list:3},可理解为是正样本索引[img, anch, gj, gi],包含从 t 中获取的image_index(nOffset,),anchor_index(nOffset,),gj(nOffset,),gi(nOffset,);
anch也是按layer分开的{list:3},储存anchor_index对应的每个anchor的尺寸。
2、build_targets()
作者主要定义了两种用来储存的变量 matching_, all_。all_用来储存一张image的信息,matching_按照layer,储存一个batch的信息,最终返回matching_用于计算损失。
def build_targets(self, p, targets, imgs):
# input batch_predictions, batch_labels(), batch_images
# indices, anch = self.find_positive(p, targets)
indices, anch = self.find_3_positive(p, targets)
# indices, anch = self.find_4_positive(p, targets)
# indices, anch = self.find_5_positive(p, targets)
# indices, anch = self.find_9_positive(p, targets)
device = torch.device(targets.device)
matching_bs = [[] for pp in p]
matching_as = [[] for pp in p]
matching_gjs = [[] for pp in p]
matching_gis = [[] for pp in p]
matching_targets = [[] for pp in p]
matching_anchs = [[] for pp in p]
nl = len(p)
# ------------------------------------------one image in the batch---------------------------------------------
for batch_idx in range(p[0].shape[0]):
b_idx = targets[:, 0] == batch_idx # 取该图像编号对应的targets
this_target = targets[b_idx] # nt_of_this_img * 6
if this_target.shape[0] == 0:
continue
txywh = this_target[:, 2:6] * imgs[batch_idx].shape[1] # 转换到像素坐标系(640*640)
txyxy = xywh2xyxy(txywh) # --> 左上右下顶点坐标
pxyxys = []
p_cls = []
p_obj = []
from_which_layer = []
all_b = []
all_a = []
all_gj = []
all_gi = []
all_anch = []
# ------------------------------------one layer of the image prediction------------------------------------
for i, pi in enumerate(p): # pi: N*C*H*W*(5+cls)
b, a, gj, gi = indices[i] # 这一层的正样本索引[b,a,gj,gi]
idx = (b == batch_idx)
b, a, gj, gi = b[idx], a[idx], gj[idx], gi[idx] # 这一层中对应该图像的正样本索引
all_b.append(b)
all_a.append(a)
all_gj.append(gj)
all_gi.append(gi)
all_anch.append(anch[i][idx])
from_which_layer.append((torch.ones(size=(len(b),)) * i).to(device))
# 根据索引获取正样本预测值
fg_pred = pi[b, a, gj, gi] # nPositive*85
p_obj.append(fg_pred[:, 4:5])
p_cls.append(fg_pred[:, 5:])
# 计算预测框实际位置(像素坐标系, 640*640)
grid = torch.stack([gi, gj], dim=1)
pxy = (fg_pred[:, :2].sigmoid() * 2. - 0.5 + grid) * self.stride[i] # / 8.
# pxy = (fg_pred[:, :2].sigmoid() * 3. - 1. + grid) * self.stride[i]
pwh = (fg_pred[:, 2:4].sigmoid() * 2) ** 2 * anch[i][idx] * self.stride[i] # / 8.
pxywh = torch.cat([pxy, pwh], dim=-1)
pxyxy = xywh2xyxy(pxywh) # nPositive*4
pxyxys.append(pxyxy) # list, append 3 layers' pxyxy
# ------------------------------------------end layer--------------------------------------------------
# three layers appended, pxyxys:{list:3}
pxyxys = torch.cat(pxyxys, dim=0) # {list:3} --> nPositive_3layers(nPrediction) * 4
if pxyxys.shape[0] == 0:
continue
p_obj = torch.cat(p_obj, dim=0)
p_cls = torch.cat(p_cls, dim=0)
from_which_layer = torch.cat(from_which_layer, dim=0)
all_b = torch.cat(all_b, dim=0)
all_a = torch.cat(all_a, dim=0)
all_gj = torch.cat(all_gj, dim=0)
all_gi = torch.cat(all_gi, dim=0)
all_anch = torch.cat(all_anch, dim=0)
# ---------------------------------SimOTA-----------------------------------
# IoU cost
pair_wise_iou = box_iou(txyxy, pxyxys) # (nTarget,nPrediction)
pair_wise_iou_loss = -torch.log(pair_wise_iou + 1e-8)
# class cost
gt_cls_per_image = (F.one_hot(this_target[:, 1].to(torch.int64), self.nc).float().unsqueeze(1)
.repeat(1, pxyxys.shape[0], 1)) # bool:(nT,nP,cls)
num_gt = this_target.shape[0]
cls_preds_ = (p_cls.float().unsqueeze(0).repeat(num_gt, 1, 1).sigmoid_() *
p_obj.unsqueeze(0).repeat(num_gt, 1, 1).sigmoid_()) # bool:(nT,nP,cls), cls_pred=cls*conf
y = cls_preds_.sqrt_()
pair_wise_cls_loss = F.binary_cross_entropy_with_logits(torch.log(y / (1 - y)), gt_cls_per_image,
reduction="none").sum(-1)
del cls_preds_
# cost
cost = pair_wise_cls_loss + 3.0 * pair_wise_iou_loss # (nT,nP)
matching_matrix = torch.zeros_like(cost, device=device) # (nT,nP), positive sample mask
# max_IoU topK
top_k, _ = torch.topk(pair_wise_iou, min(10, pair_wise_iou.shape[1]), dim=1) # (nT,10)
dynamic_ks = torch.clamp(top_k.sum(1).int(), min=1) # (nT,)
# min_cost topKs --> Positive Sample
for gt_idx in range(num_gt):
_, pos_idx = torch.topk(cost[gt_idx], k=dynamic_ks[gt_idx].item(), largest=False)
matching_matrix[gt_idx][pos_idx] = 1.0
del top_k, dynamic_ks
# 一个正样本不能预测多个target
anchor_matching_gt = matching_matrix.sum(0) # (nP,)
if (anchor_matching_gt > 1).sum() > 0: # 选与该anchor的cost最小的target进行预测
_, cost_argmin = torch.min(cost[:, anchor_matching_gt > 1], dim=0)
matching_matrix[:, anchor_matching_gt > 1] *= 0.0
matching_matrix[cost_argmin, anchor_matching_gt > 1] = 1.0
fg_mask_inboxes = (matching_matrix.sum(0) > 0.0).to(device) # bool:(nP,)负责预测的正样本
matched_gt_inds = matching_matrix[:, fg_mask_inboxes].argmax(0) # (nP_responsible).target_index
# ------------------------------end SimOTA----------------------------------
# (nP,) --> (nP_responsible,) 负责预测的正样本信息(经过SimOTA筛选)
from_which_layer = from_which_layer[fg_mask_inboxes]
all_b = all_b[fg_mask_inboxes]
all_a = all_a[fg_mask_inboxes]
all_gj = all_gj[fg_mask_inboxes]
all_gi = all_gi[fg_mask_inboxes]
all_anch = all_anch[fg_mask_inboxes]
# (nT,6) --> (nP_responsible,6) 被正样本预测的真值框
this_target = this_target[matched_gt_inds]
# matching_ 将 all_ 分三层储存,各层分别都append每张图片
for i in range(nl):
layer_idx = from_which_layer == i # bool:(nP_resp)
matching_bs[i].append(all_b[layer_idx])
matching_as[i].append(all_a[layer_idx])
matching_gjs[i].append(all_gj[layer_idx])
matching_gis[i].append(all_gi[layer_idx])
matching_targets[i].append(this_target[layer_idx])
matching_anchs[i].append(all_anch[layer_idx])
# ---------------------------------------------end image---------------------------------------------------
# now the matching_ are all {list:3}, every layer is a {list:16}
# if this layer's anchors are responsible for any targets, we concat all of this layer's info together
for i in range(nl):
if matching_targets[i]:
matching_bs[i] = torch.cat(matching_bs[i], dim=0)
matching_as[i] = torch.cat(matching_as[i], dim=0)
matching_gjs[i] = torch.cat(matching_gjs[i], dim=0)
matching_gis[i] = torch.cat(matching_gis[i], dim=0)
matching_targets[i] = torch.cat(matching_targets[i], dim=0)
matching_anchs[i] = torch.cat(matching_anchs[i], dim=0)
else:
matching_bs[i] = torch.tensor([], device='cuda:0', dtype=torch.int64)
matching_as[i] = torch.tensor([], device='cuda:0', dtype=torch.int64)
matching_gjs[i] = torch.tensor([], device='cuda:0', dtype=torch.int64)
matching_gis[i] = torch.tensor([], device='cuda:0', dtype=torch.int64)
matching_targets[i] = torch.tensor([], device='cuda:0', dtype=torch.int64)
matching_anchs[i] = torch.tensor([], device='cuda:0', dtype=torch.int64)
# now the matching_ are all {list:3}, but every layer is just a tensor
return matching_bs, matching_as, matching_gjs, matching_gis, matching_targets, matching_anchs主要通过matching_matrix矩阵来进行SimOTA提取,matching_matrix为初始 nT*nP 大小的0矩阵,对于每个target,最小cost的前dynamic_k个,对应正样本anchor位置赋值为1,列求和得到经过SimOTA之后的正样本掩模fg_mask_inboxes,bool变量,大小为(nP,)。
all_系列变量的储存内容变化:以all_b为例
# 1、首先定义为空
all_b = []
# 2、在图像的一个layer中
for i, pi in enumerate(p):
all_b.append(b)
# 经过3 layers后,all_b是一个{list:3},每一层都包含这一层中对应该图像的正样本索引信息
# 3、在第0维拼接,得到这张图像的所有正样本索引信息(layer信息存到了from_which_layer变量中)
all_b = torch.cat(all_b, dim=0)
# 4、SimOTA之后,得到筛选后的正样本索引信息
all_a = all_a[fg_mask_inboxes]matching_系列变量的储存内容变化:以matching_bs为例
# 1、首先定义为空
matching_bs = [[] for pp in p] # [[], [], []]
# 2、在一张img处理过程中,将最终的all_转化为按layer储存
layer_idx = from_which_layer == i
matching_bs[i].append(all_b[layer_idx])
# 处理过16张图片后,变成一个{list:3},每一层都有16个tensor,每个tensor中都是正样本索引信息
# 3、最后,将16张图像的内容concat成一个tensor,即{list:3}每一层只有一个tensor
for i in range(nl):
if matching_targets[i]:
matching_bs[i] = torch.cat(matching_bs[i], dim=0)return时的matching_bs, matching_as, matching_gjs, matching_gis都是最终的正样本索引,{list:3},每一层是16张图片的所有正样本索引信息;matching_targets和matching_anchs是batch中所有正样本对应的targets(当然会有重复)和anchor,都是{list:3}。





















 1643
1643











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








