逻辑回归
介绍
逻辑回归是用来进行分类的。二分类问题下,采用逻辑回归的分类算法,这个算法的性质是:它的输出值永远在 0 到 1 之间。
它适用于标签 y 取值离散的情况,如:1 0 0 1。
回归模型表达式
sigmoid函数
Sigmoid函数是一种阶跃函数。在数学中,如果实数域上的某个函数可以用半开区间上的指示函数的有限次线性组合来表示,那么这个函数就是阶跃函数。而数学中指示函数是定义在某集合X上的函数,表示其中有哪些元素属于某一子集A。
为了实现Logistic回归分类器,我们在每个特征上都乘以一个回归系数,然后把所有的结果值相加,将这个总和代人Sigmoid函数中,进而得到一个范围在0~1之间的数值。任何大于0.5的数据被分入1类,小于0.5即被归入0类。所以,Logistic回归也可以被看成是一种概率估计。

hθ(x)ℎ𝜃(𝑥) 的作用是,对于给定的输入变量,根据选择的参数计算输出变量为 1 的可能性 (estimated probablity),即 hθ(x)=P(y=1|x;θ)ℎ𝜃(𝑥)=𝑃(𝑦=1|𝑥;𝜃)。例如,如果对于给定的 x,通过已经确定的参数计算得出 hθ(x)ℎ𝜃(𝑥)=0.7,则表示有 70% 的几率 y 为正向类,相应地 y 为负向类的几率为 1-0.7=0.3
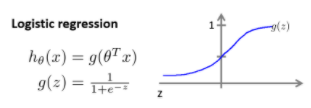
z = 0 时 g(z) = 0.5
z > 0 时 g(z) > 0.5
z < 0 时 g(z) < 0.5
当 hθ(x)ℎ𝜃(𝑥)大于等于 0.5 时,预测 y=1。 当hθ(x)ℎ𝜃(𝑥)小于 0.5 时,预测 y=0 。
梯度下降法
梯度下降法在逻辑回归中起到了优化模型参数、寻找最优解、调节学习率和处理大规模数据的作用。它是逻辑回归模型中常用的优化算法之一,能够有效地提升模型的性能.。
代价函数
我们该如何选择 θ𝜃,这时候我们将引入代价函数的这个概念,这个概念是让函数拟合,逐渐确定 θ𝜃。
我们定义线性回归模型的代价函数是所有模型误差的平方和。理论上来说,对逻辑回归模型也可以沿用这个定义,但是问题在于,当我们将 hθ(x)=11+e−θTXℎ𝜃(𝑥)=11+𝑒−𝜃𝑇𝑋 带入到这样的代价函数中时,得到的代价函数将是一个非凸函数(non-convex function)。
这意味着我们的代价函数有许多局部最小值,这将影响梯度下降算法寻找全局最小值。
定义逻辑回归的代价函数为:
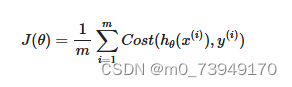
其中:
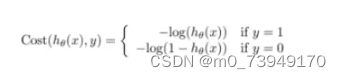
hθ(x)ℎ𝜃(𝑥)与Cost(hθ(x),y)𝐶𝑜𝑠𝑡(ℎ𝜃(𝑥),𝑦)之间的关系如下图所示:
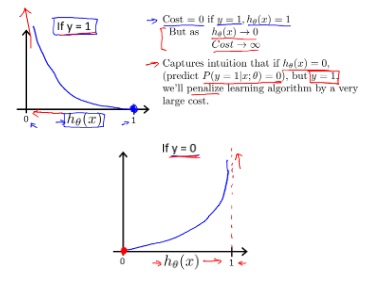
这样构建的Cost(hθ(x),y)𝐶𝑜𝑠𝑡(ℎ𝜃(𝑥),𝑦)函数的特点是:
当实际的 y=1 且hθ(x)ℎ𝜃(𝑥)也为1 时误差为 0,当 y=1 但hθ(x)ℎ𝜃(𝑥)不为 1 时误差随着hθ(x)ℎ𝜃(𝑥)的变小而变大;
当实际的 y=0 且hθ(x)ℎ𝜃(𝑥)也为 0 时代价为 0,当 y=0 但hθ(x)ℎ𝜃(𝑥)不为 0 时误差随着 hθ(x)ℎ𝜃(𝑥)的变大而变大。
将构建的Cost(hθ(x),y)𝐶𝑜𝑠𝑡(ℎ𝜃(𝑥),𝑦)简化如下:
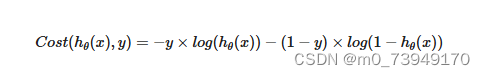
带入代价函数得到:
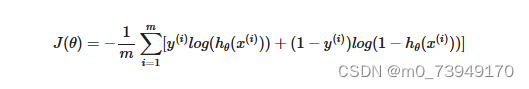
现在,我们要做的事情就是找出让 J(θ)𝐽(𝜃) 取得最小值的参数 θ𝜃 。
梯度下降
最小化代价函数的方法,是使用梯度下降法(gradient descent)。这是通常用的梯度下降法的模板:

反复更新每个参数,用这个式子减去学习率 α 乘以后面的微分项。求导后得到:
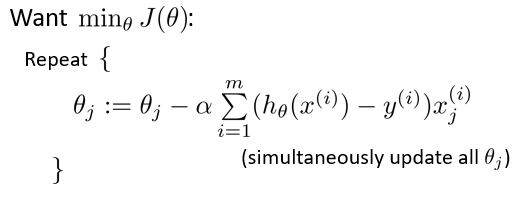
计算得到等式:
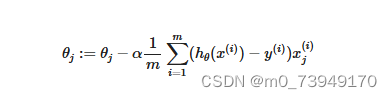
来它同时更新所有θ𝜃的值。
代码
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import time
path = "LogiReg_data.txt"
pdData = pd.read_csv(path, header=None, names=['exam_1', 'exam_2', 'admitted'])
pdData.head()
pdData.shape
positive = pdData[pdData['admitted'] == 1] # returns the subset of rows such Admitted = 1, i.e. the set of *positive* examples
negative = pdData[pdData['admitted'] == 0] # returns the subset of rows such Admitted = 0, i.e. the set of *negative* examples
plt.subplots(figsize=(10,5))
plt.scatter(positive['exam_1'], positive['exam_2'], s=30, c='b', marker='o', label='Admitted')
plt.scatter(negative['exam_1'], negative['exam_2'], s=30, c='r', marker='x', label='Not Admitted')
plt.legend()
plt.xlabel('Exam_1 Score')
plt.ylabel('Exam_2 Score')
图像
逻辑回归类
class LogisticRegression():
"""逻辑回归类"""
def __init__(self, n):
self.STOP_ITER = 0
self.STOP_COST = 1
self.STOP_GRAD = 2
self.n = n
def sigmoid(self, z):
"""
sigmoid函数
将预测值映射成概率
"""
return 1 / (1 + np.exp(-z))
def model(self, X, theta):
"""
预测函数:返回预测值
"""
return self.sigmoid(np.dot(X, theta.T))
def cost(self, X, y, theta):
"""损失函数"""
left = np.multiply(-y, np.log(self.model(X, theta)))
right = np.multiply(1 - y, np.log(1 - self.model(X, theta)))
return np.sum(left - right) / (len(X))
def gradient(self, X, y, theta):
"""计算梯度"""
grad = np.zeros(theta.shape)
error = (self.model(X, theta)- y).ravel()
for j in range(len(theta.ravel())): #for each parmeter
term = np.multiply(error, X[:,j])
grad[0, j] = np.sum(term) / len(X)
return grad
def stopCriterion(self, type, value, threshold):
"""
停止标准函数:
1.迭代次数
2.损失值变化
3.梯度变化
"""
if type == self.STOP_ITER:
return value > threshold
elif type == self.STOP_COST:
return abs(value[-1]-value[-2]) < threshold
elif type == self.STOP_GRAD:
return np.linalg.norm(value) < threshold
def shuffleData(self, data):
"""洗牌"""
np.random.shuffle(data)
cols = data.shape[1]
X = data[:, 0:cols-1]
y = data[:, cols-1:]
return X, y
def descent(self, data, theta, batchSize, stopType, thresh, alpha):
"""梯度下降求解"""
init_time = time.time()
i = 0 # 迭代次数
k = 0 # batch
X, y = self.shuffleData(data)
grad = np.zeros(theta.shape) # 计算的梯度
costs = [self.cost(X, y, theta)] # 损失值
while True:
grad = self.gradient(X[k:k+batchSize], y[k:k+batchSize], theta)
k += batchSize #取batch数量个数据
if k >= self.n:
k = 0
X, y = self.shuffleData(data) #重新洗牌
theta = theta - alpha*grad # 参数更新
costs.append(self.cost(X, y, theta)) # 计算新的损失
i += 1
if stopType == self.STOP_ITER:
value = i
elif stopType == self.STOP_COST:
value = costs
elif stopType == self.STOP_GRAD:
value = grad
if self.stopCriterion(stopType, value, thresh):
break
return theta, i-1, costs, grad, time.time() - init_time
def predict(self, X, theta):
return [1 if x >= 0.5 else 0 for x in self.model(X, theta)]
处理数据
pdData.insert(0, 'Ones', 1) # in a try / except structure so as not to return an error if the block si executed several times
# set X (training data) and y (target variable)
orig_data = pdData.as_matrix() # convert the Pandas representation of the data to an array useful for further computations
cols = orig_data.shape[1]
X = orig_data[:,0:cols-1]
y = orig_data[:,cols-1:cols]
# convert to numpy arrays and initalize the parameter array theta
theta = np.zeros([1, 3])
print(X[:5])
print(y[:5])
print(theta)
查看准确度
scaled_X = orig_data[:, :3]
y = orig_data[:, 3]
predictions = lr.predict(scaled_X, theta)
correct = [1 if ((a == 1 and b == 1) or (a == 0 and b == 0)) else 0 for (a, b) in zip(predictions, y)]
accuracy = (sum(map(int, correct)) % len(correct))
print ('accuracy = {0}%'.format(accuracy))
accuracy = 60%





















 1548
1548

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








