本文转载自:http://blog.csdn.net/luoshixian099/article/details/48244255
本文采用的是opencv2.4.3中的源码。
Harris角点检测
人眼对角点的识别通常是通过一个局部的小窗口内完成的,如果在各个方向上移动这个小窗口,窗口内的灰度发生了较大的变化,那么说明窗口内存在角点。
如果在各个方向移动,灰度几乎不变,说明是平坦区域;
如果只沿着某一个方向移动,灰度几乎不变,说明是直线;
如果沿各个方向移动,灰度均发生变化,说明是角点。
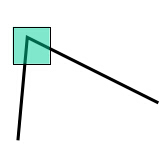
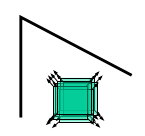
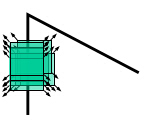
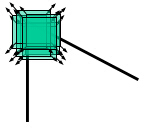
平坦区域 直线 角点
图像I(x,y),在点(x,y)处平移(u,v)后的自相似性,可以用灰度变化函数E(u,v)表示
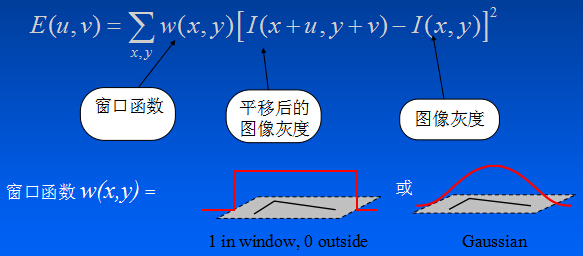

泰勒展开:
代入得到:

其中:

二次项函数本质上就是一个椭圆函数,椭圆的扁平率和尺寸是由矩阵M的两个特征值决定的。

矩阵M的两个特征值与图像中的角点,边缘,平坦区域的关系:

Harris定义角点响应函数即 ,即R=Det(M)-k*trace(M)*trace(M),k为经验常数0.04~0.06 。
,即R=Det(M)-k*trace(M)*trace(M),k为经验常数0.04~0.06 。
定义当R>threshold时且为局部极大值的点时,定义为角点。
Harris角点检测算子对图像亮度和对比度具有部分不变性,且具有旋转不变性,但不具有尺度不变性。

OpenCV中调用cornerHarris函数检测角点:
blockSize:为邻域大小,对每个像素,考虑blockSize×blockSize大小的邻域S(p),在邻域上计算图像的差分的相关矩阵;
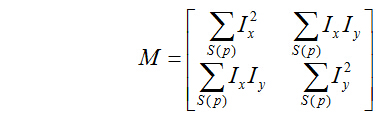
ksize: 为Soble算子核尺寸,如果小于0,采用3×3的Scharr滤波器;
k:为角点响应函数中的经验常数(0.04~0.06);
- int blockSize = 2;
- int apertureSize =3;
- double k = 0.04;
-
- cornerHarris( src_gray, dst, blockSize, apertureSize, k, BORDER_DEFAULT );
- void cv::cornerHarris( InputArray _src, OutputArray _dst, int blockSize, int ksize, double k, int borderType )
- {
- Mat src = _src.getMat();
- _dst.create( src.size(), CV_32F );
- Mat dst = _dst.getMat();
- cornerEigenValsVecs( src, dst, blockSize, ksize, HARRIS, k, borderType );
- }
- static void
- cornerEigenValsVecs( const Mat& src, Mat& eigenv, int block_size,
- int aperture_size, int op_type, double k=0.,
- int borderType=BORDER_DEFAULT )
- {
- #ifdef HAVE_TEGRA_OPTIMIZATION
- if (tegra::cornerEigenValsVecs(src, eigenv, block_size, aperture_size, op_type, k, borderType))
- return;
- #endif
-
-
- int depth = src.depth();
- double scale = (double)(1 << ((aperture_size > 0 ? aperture_size : 3) - 1)) * block_size;
- if( aperture_size < 0 )
- scale *= 2.;
- if( depth == CV_8U )
- scale *= 255.;
- scale = 1./scale;
- CV_Assert( src.type() == CV_8UC1 || src.type() == CV_32FC1 );
-
-
- Mat Dx, Dy;
- if( aperture_size > 0 )
- {
- Sobel( src, Dx, CV_32F, 1, 0, aperture_size, scale, 0, borderType );
- Sobel( src, Dy, CV_32F, 0, 1, aperture_size, scale, 0, borderType );
- }
- else
- {
- Scharr( src, Dx, CV_32F, 1, 0, scale, 0, borderType );
- Scharr( src, Dy, CV_32F, 0, 1, scale, 0, borderType );
- }
-
-
- Size size = src.size();
- Mat cov( size, CV_32FC3 );
- int i, j;
-
-
- for( i = 0; i < size.height; i++ )
- {
- float* cov_data = (float*)(cov.data + i*cov.step);
- const float* dxdata = (const float*)(Dx.data + i*Dx.step);
- const float* dydata = (const float*)(Dy.data + i*Dy.step);
-
-
- for( j = 0; j < size.width; j++ )
- {
- float dx = dxdata[j];
- float dy = dydata[j];
-
-
- cov_data[j*3] = dx*dx;
- cov_data[j*3+1] = dx*dy;
- cov_data[j*3+2] = dy*dy;
- }
- }
-
-
- boxFilter(cov, cov, cov.depth(), Size(block_size, block_size),
- Point(-1,-1), false, borderType );
-
-
- if( op_type == MINEIGENVAL )
- calcMinEigenVal( cov, eigenv );
- else if( op_type == HARRIS )
- calcHarris( cov, eigenv, k );
- else if( op_type == EIGENVALSVECS )
- calcEigenValsVecs( cov, eigenv );
- }
- static void
- calcHarris( const Mat& _cov, Mat& _dst, double k )
- {
- int i, j;
- Size size = _cov.size();
- if( _cov.isContinuous() && _dst.isContinuous() )
- {
- size.width *= size.height;
- size.height = 1;
- }
-
- for( i = 0; i < size.height; i++ )
- {
- const float* cov = (const float*)(_cov.data + _cov.step*i);
- float* dst = (float*)(_dst.data + _dst.step*i);
- j = 0;
- for( ; j < size.width; j++ )
- {
- float a = cov[j*3];
- float b = cov[j*3+1];
- float c = cov[j*3+2];
- dst[j] = (float)(a*c - b*b - k*(a + c)*(a + c));
- }
- }
- }
Shi-Tomasi角点检测
由于Harris算法的稳定性和k值有关,Shi-Tomasi发现,角点的稳定性和矩阵M的较小特征值有关,改进的Harris算法即直接计算出矩阵M的特征值,用较小的特征值与阈值比较,大于阈值的即为强特征点。
opencv中对其实现算法在goodFeaturesToTrack()函数中:
- CV_EXPORTS_W void goodFeaturesToTrack( InputArray image, OutputArray corners,
- int maxCorners, double qualityLevel, double minDistance,
- InputArray mask=noArray(), int blockSize=3,
- bool useHarrisDetector=false, double k=0.04 );
image:输入图像
corners:输出图像数组
maxCorners:需要的角点数目
qualityLevel:最大,最小特征值的乘法因子。定义可接受图像角点的最小质量因子。
minDistance:容忍距离。角点之间的最小距离,采用欧氏距离。
mask:掩码
blockSize:邻域大小
useHarrisDetector:采用Harris角点检测
k:采用Harris角点检测时的经验常数k(0.04~0.06)
算法原理:调用cornerMinEigenVal()函数求出每个像素点自适应矩阵M的较小特征值,保存在矩阵eig中,然后找到矩阵eig中最大的像素值记为maxVal,然后阈值处理,小于qualityLevel*maxVal的特征值排除掉,最后函数确保所有发现的角点之间具有足够的距离。
- void cv::goodFeaturesToTrack( InputArray _image, OutputArray _corners,
- int maxCorners, double qualityLevel, double minDistance,
- InputArray _mask, int blockSize,
- bool useHarrisDetector, double harrisK )
- {
- Mat image = _image.getMat(), mask = _mask.getMat();
-
- CV_Assert( qualityLevel > 0 && minDistance >= 0 && maxCorners >= 0 );
- CV_Assert( mask.empty() || (mask.type() == CV_8UC1 && mask.size() == image.size()) );
-
- Mat eig, tmp;
- if( useHarrisDetector )
- cornerHarris( image, eig, blockSize, 3, harrisK );
- else
- cornerMinEigenVal( image, eig, blockSize, 3 );
-
- double maxVal = 0;
- minMaxLoc( eig, 0, &maxVal, 0, 0, mask );
- threshold( eig, eig, maxVal*qualityLevel, 0, THRESH_TOZERO );
- dilate( eig, tmp, Mat());
-
- Size imgsize = image.size();
-
- vector<const float*> tmpCorners;
-
-
- for( int y = 1; y < imgsize.height - 1; y++ )
- {
- const float* eig_data = (const float*)eig.ptr(y);
- const float* tmp_data = (const float*)tmp.ptr(y);
- const uchar* mask_data = mask.data ? mask.ptr(y) : 0;
-
- for( int x = 1; x < imgsize.width - 1; x++ )
- {
- float val = eig_data[x];
- if( val != 0 && val == tmp_data[x] && (!mask_data || mask_data[x]) )
- tmpCorners.push_back(eig_data + x);
- }
- }
-
- sort( tmpCorners, greaterThanPtr<float>() );
- vector<Point2f> corners;
- size_t i, j, total = tmpCorners.size(), ncorners = 0;
-
-
-
-
- if(minDistance >= 1)
- {
-
- int w = image.cols;
- int h = image.rows;
-
- const int cell_size = cvRound(minDistance);
- const int grid_width = (w + cell_size - 1) / cell_size;
- const int grid_height = (h + cell_size - 1) / cell_size;
-
- std::vector<std::vector<Point2f> > grid(grid_width*grid_height);
-
- minDistance *= minDistance;
-
- for( i = 0; i < total; i++ )
- {
- int ofs = (int)((const uchar*)tmpCorners[i] - eig.data);
- int y = (int)(ofs / eig.step);
- int x = (int)((ofs - y*eig.step)/sizeof(float));
-
- bool good = true;
-
- int x_cell = x / cell_size;
- int y_cell = y / cell_size;
-
- int x1 = x_cell - 1;
- int y1 = y_cell - 1;
- int x2 = x_cell + 1;
- int y2 = y_cell + 1;
-
-
- x1 = std::max(0, x1);
- y1 = std::max(0, y1);
- x2 = std::min(grid_width-1, x2);
- y2 = std::min(grid_height-1, y2);
-
- for( int yy = y1; yy <= y2; yy++ )
- {
- for( int xx = x1; xx <= x2; xx++ )
- {
- vector <Point2f> &m = grid[yy*grid_width + xx];
-
- if( m.size() )
- {
- for(j = 0; j < m.size(); j++)
- {
- float dx = x - m[j].x;
- float dy = y - m[j].y;
- if( dx*dx + dy*dy < minDistance )
- {
- good = false;
- goto break_out;
- }
- }
- }
- }
- }
-
- break_out:
-
- if(good)
- {
-
-
- grid[y_cell*grid_width + x_cell].push_back(Point2f((float)x, (float)y));
-
- corners.push_back(Point2f((float)x, (float)y));
- ++ncorners;
-
- if( maxCorners > 0 && (int)ncorners == maxCorners )
- break;
- }
- }
- }
- else
- {
- for( i = 0; i < total; i++ )
- {
- int ofs = (int)((const uchar*)tmpCorners[i] - eig.data);
- int y = (int)(ofs / eig.step);
- int x = (int)((ofs - y*eig.step)/sizeof(float));
-
- corners.push_back(Point2f((float)x, (float)y));
- ++ncorners;
- if( maxCorners > 0 && (int)ncorners == maxCorners )
- break;
- }
- }
-
- Mat(corners).convertTo(_corners, _corners.fixedType() ? _corners.type() : CV_32F);
-
- }
求矩阵M最小的特征值
- static void
- calcMinEigenVal( const Mat& _cov, Mat& _dst )
- {
- int i, j;
- Size size = _cov.size();
- if( _cov.isContinuous() && _dst.isContinuous() )
- {
- size.width *= size.height;
- size.height = 1;
- }
-
- for( i = 0; i < size.height; i++ )
- {
- const float* cov = (const float*)(_cov.data + _cov.step*i);
- float* dst = (float*)(_dst.data + _dst.step*i);
- j = 0;
- for( ; j < size.width; j++ )
- {
- float a = cov[j*3]*0.5f;
- float b = cov[j*3+1];
- float c = cov[j*3+2]*0.5f;
- dst[j] = (float)((a + c) - std::sqrt((a - c)*(a - c) + b*b));
- }
- }
- }
参考:http://blog.csdn.net/xw20084898/article/details/21180729
http://wenku.baidu.com/view/f61bc369561252d380eb6ef0.html
http://blog.csdn.net/crzy_sparrow/article/details/7391511






 ,即R=Det(M)-k*trace(M)*trace(M),k为经验常数0.04~0.06 。
,即R=Det(M)-k*trace(M)*trace(M),k为经验常数0.04~0.06 。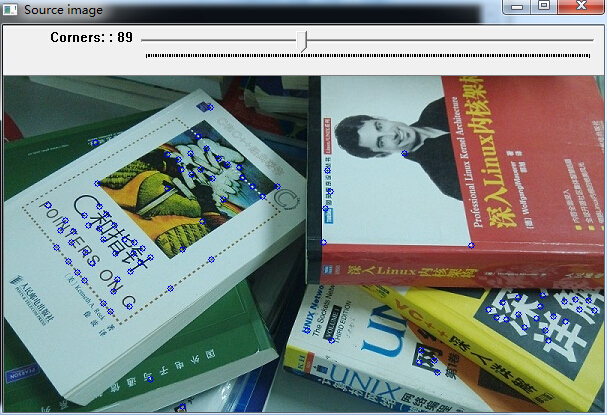

















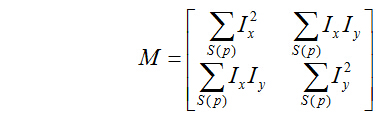














 1万+
1万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








