目录
5、IPOPT的initial gauss 以及 warm star
优化,在Apollo规划模块中占据了重要的地位
Apollo中 OSQP 和 IPOPT 的应用:
| OSQP | IPOPT |
| 参考线:discrete_points_smoother( FemPosSmooth) 参考线:qp_spline_smoother | 参考线:spiral_smoother 分段五次螺旋线非线性优化拟合 参考线:discrete_points_smoother(CosThetaSmooth) ipopt+adol-c |
| Lattice中横向规划中使用的基于二次规划的轨迹规划 | Hybrid A*的轨迹优化 |
| 路径规划的QP 速度规划中DP之后的QP | 速度规划中DP之后的IPOPT |
其中OSQP在之前的文章中测试过,这篇文章主要进行IPOPT的相关实践
非线性优化的一般形式为:
IPOPT是一种常用的非线性优化求解器,使用内点法进行求解
对于复杂问题,需要借助自动微分工具,帮助求解梯度、Yacobian矩阵、Hessian矩阵,
如ADOL-C,CppAD
1、IPOPT的安装(简洁版本)
(1).安装apt包
sudo apt-get install gcc g++ gfortran git patch wget pkg-config liblapack-dev libmetis-dev(2).安装BLAS and LAPACK
即为前面apt安装的liblapack-dev
(3).安装HSL 官网注册申请下载
需要教育网邮箱申请,
同时下载如下库.并将前面下载的HSL包解压后改名为coinhsl(例如coinhsl-archive-2021.05.05 => coinhsl)后复制到ThirdParty-HSL文件夹中,最后进行编译安装.
git clone https://github.com/coin-or-tools/ThirdParty-HSL.git
cd ThirdParty-HSL
./configure
make
sudo make install
sudo ldconfig(4).安装IPOPT
mkdir build
cd build
sudo ../configure --prefix=/usr/local/ #安装到指定位置
sudo make
sudo make test
sudo make installmake test的输出应该如下:
Running unitTests...
Testing AMPL Solver Executable...
Test passed!
Testing C++ Example...
Test passed!
Testing C Example...
Test passed!
Testing Fortran Example...
Test passed!
Skip testing Java Example (Java interface not build)
Testing sIpopt Example parametric_cpp...
Test passed!
Testing sIpopt Example redhess_cpp...
Test passed!
Testing EmptyNLP Example...
Test passed!
Testing GetCurr Example...
Test passed!(5).安装成功与否
进入IPOPT源码文件夹如下位置,用官方例子测试
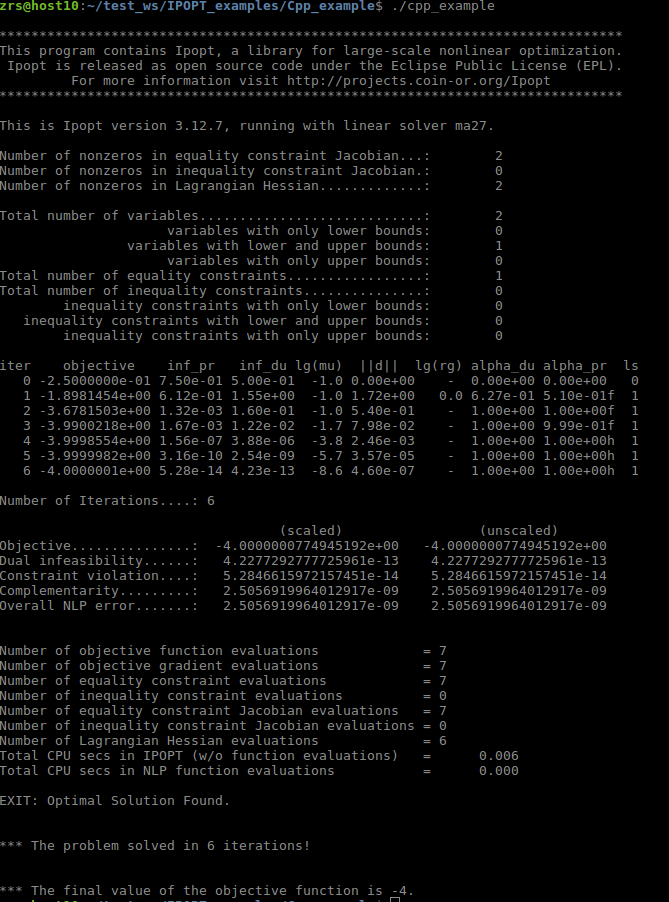
cd Ipopt-releases-3.14.2/build/examples/Cpp_example
sudo make
./solverUbuntu 16.04 安装Ipopt 3.12.7 和 CppAD - 简书
Ubuntu18.04配置Ipopt,CppAD 通过C++求解最优控制_小朱 智能驾驶的博客-CSDN博客_c++ ipopt
2、IPOPT测试案例
#include "IpIpoptApplication.hpp"
#include "IpSolveStatistics.hpp"
#include "MyNLP.hpp"
#include <iostream>
using namespace Ipopt;
int main(int argv, char* argc[])
{
// Create an instance of your nlp...
SmartPtr<TNLP> mynlp = new MyNLP();
// Create an instance of the IpoptApplication
//
// We are using the factory, since this allows us to compile this
// example with an Ipopt Windows DLL
SmartPtr<IpoptApplication> app = IpoptApplicationFactory();
// Initialize the IpoptApplication and process the options
ApplicationReturnStatus status;
status = app->Initialize();
if (status != Solve_Succeeded) {
std::cout << std::endl << std::endl << "*** Error during initialization!" << std::endl;
return (int) status;
}
status = app->OptimizeTNLP(mynlp);
if (status == Solve_Succeeded) {
// Retrieve some statistics about the solve
Index iter_count = app->Statistics()->IterationCount();
std::cout << std::endl << std::endl << "*** The problem solved in " << iter_count << " iterations!" << std::endl;
Number final_obj = app->Statistics()->FinalObjective();
std::cout << std::endl << std::endl << "*** The final value of the objective function is " << final_obj << '.' << std::endl;
}
return (int) status;
} 
3、ADOL-C的使用
ADOL-C是一个自动求解微分的库,通过给出目标函数、自变量值,求解雅克比矩阵和黑塞矩阵,省去了手工推导偏导数的麻烦。
细节待补充
4、CppAD的使用
CppAD是一个用于自动微分(Automatic Differentiation,AD)的C++库,全称是"Computational Differentiation in C++ using Operator Overloading"。
AD 的工作原理基于链式法则(Chain Rule)和计算图的概念。有两种主要的自动微分方法:前向模式(Forward Mode)和反向模式(Reverse Mode)。
#include <iostream>
#include <cppad/ipopt/solve.hpp>
using namespace std;
namespace {
using CppAD::AD;
class FG_eval {
public:
typedef CPPAD_TESTVECTOR(AD<double>) ADvector;
//
void operator()(ADvector& fg, const ADvector& x)
{
assert(fg.size() == 3);
assert(x.size() == 4);
// variables 优化变量
AD<double> x1 = x[0];
AD<double> x2 = x[1];
AD<double> x3 = x[2];
AD<double> x4 = x[3];
// f(x) objective function 目标函数
fg[0] = x1 * x4 * (x1 + x2 + x3) + x3;
// constraints 约束条件
fg[1] = x1 * x2 * x3 * x4;
fg[2] = x1 * x1 + x2 * x2 + x3 * x3 + x4 * x4;
return;
}
};
} //end namespace
bool get_started(void)
{
bool ok = true;
size_t i;
typedef CPPAD_TESTVECTOR(double) Dvector;
size_t nx = 4; // number of varibles
size_t ng = 2; // number of constraints
Dvector x0(nx); // initial condition of varibles 初始?
x0[0] = 1.0;
x0[1] = 5.0;
x0[2] = 5.0;
x0[3] = 1.0;
// lower and upper bounds for varibles
Dvector xl(nx), xu(nx);
for(i = 0; i < nx; i++)
{
xl[i] = 1.0;
xu[i] = 5.0;
}
//不等式上下界
Dvector gl(ng), gu(ng);
gl[0] = 25.0; gu[0] = 1.0e19;
gl[1] = 40.0; gu[1] = 40.0;
// object that computes objective and constraints
FG_eval fg_eval;
// options
string options;
// turn off any printing
options += "Integer print_level 0\n";
options += "String sb yes\n";
// maximum iterations
options += "Integer max_iter 10\n";
//approximate accuracy in first order necessary conditions;
// see Mathematical Programming, Volume 106, Number 1,
// Pages 25-57, Equation (6)
options += "Numeric tol 1e-6\n";
//derivative tesing
options += "String derivative_test second-order\n";
// maximum amount of random pertubation; e.g.,
// when evaluation finite diff
options += "Numeric point_perturbation_radius 0.\n";
//定义solution并求解
CppAD::ipopt::solve_result<Dvector> solution; // solution
CppAD::ipopt::solve<Dvector, FG_eval>(options, x0, xl, xu, gl, gu, fg_eval, solution); // solve the problem
cout << "solution: " << solution.x << endl;
//check some of the solution values 这个check有什么用?
ok &= solution.status == CppAD::ipopt::solve_result<Dvector>::success;
double check_x[] = {1.000000, 4.743000, 3.82115, 1.379408};
double check_zl[] = {1.087871, 0., 0., 0. };
double check_zu[] = {0., 0., 0., 0. };
double rel_tol = 1e-6; // relative tolerance
double abs_tol = 1e-6; // absolute tolerance
for(i = 0; i < nx; i++)
{
ok &= CppAD::NearEqual(check_x[i], solution.x[i], rel_tol, abs_tol);
ok &= CppAD::NearEqual(check_zl[i], solution.zl[i], rel_tol, abs_tol);
ok &= CppAD::NearEqual(check_zu[i], solution.zu[i], rel_tol, abs_tol);
}
return ok;
}
int main()
{
cout << "CppAD : Hello World Demo!" << endl;
bool res = get_started();
cout << "CppAD res:" << res << endl;
return 0;
}CMakeList.txt
project(ipopt_test)
cmake_minimum_required (VERSION 3.5)
add_definitions(-std=c++11 -O3)
add_executable(ipopt_test main.cpp)
target_link_libraries(ipopt_test ipopt) 
5、IPOPT的initial gauss 以及 warm star
参考链接:
非线性优化求解器IPOPT的使用学习 - Challenging-eXtraordinary
基础理论:
Chapter 11 导数、梯度、 Jacobian、Hessian {Gradient Related Concepts} | 数值分析笔记
梯度向量、Jacobian、Hessian矩阵_Alinooo的博客-CSDN博客_梯度向量怎么求
自动微分工具:ADOL-C、CppAD
自动微分的理论:
ipopt CppAD 非线性规划_梦醒时分1218的博客-CSDN博客_cppad
无人车系统(十):c++与python非线性规(优)划(化)工具_昔风不起,唯有努力生存!-CSDN博客 C++自动微分(Automatic differentiation)原理1_Daniel 的技术笔记 不积跬步无以至千里,不积小流无以成江海。-CSDN博客_c++ 自动微分
自动微分的使用 - propagator的个人空间 - OSCHINA - 中文开源技术交流社区
后记:关于非线性优化,,我只在CasADi(MATLAB,Python)中进行过简单的测试
SX、MX以及Opti方法(像在写数学表达式),使用最基本的Opti方法
还有一种方式是AMPL,我在讲座中看到过
以上方案可以作为研究中初步的仿真测试,实际运行还是要用C++








 本文详细介绍了如何在Ubuntu上安装IPOPT非线性优化求解器,包括依赖库的安装,HSL库的获取与编译,以及IPOPT的编译与测试。此外,文章还提及了IPOPT在Apollo自动驾驶系统中的应用,并给出了一个简单的IPOPT测试案例。同时,提到了自动微分工具ADOL-C和CppAD在求解梯度和矩阵时的作用。
本文详细介绍了如何在Ubuntu上安装IPOPT非线性优化求解器,包括依赖库的安装,HSL库的获取与编译,以及IPOPT的编译与测试。此外,文章还提及了IPOPT在Apollo自动驾驶系统中的应用,并给出了一个简单的IPOPT测试案例。同时,提到了自动微分工具ADOL-C和CppAD在求解梯度和矩阵时的作用。


















 237
237

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










