http://blog.csdn.net/pipisorry/article/details/30277861
C++ 中 map 提供的是一种键值对容器。
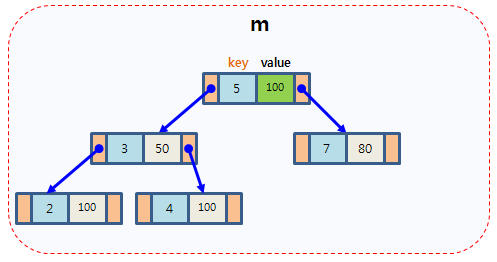
map以模板(泛型)方式实现,可以存储任意类型的数据,包括使用者自定义的数据类型。Map主要用于资料一对一映射(one-to-one)的情況,map內部的实现自建一颗红黑树,这颗树具有对数据自动排序的功能。在map内部所有的数据都是有序的。
unordered_map 与 map 的区别
STL中,map 对应的数据结构是 红黑树。红黑树是一种近似于平衡的二叉查找树,里面的数据是有序的。在红黑树上做查找操作的时间复杂度为 O(logN)。而 unordered_map 对应 哈希表,哈希表的特点就是查找效率高,时间复杂度为常数级别 O(1), 而额外空间复杂度则要高出许多。所以对于需要高效率查询的情况,使用 unordered_map 容器。而如果对内存大小比较敏感或者数据存储要求有序的话,则可以用 map 容器。
使用
需要导入头文件
#include <map> // STL头文件没有扩展名.h
map 的基本操作函数
C++ Maps 是一种关联式容器,包含“关键字/值”对
begin() 返回指向 map 头部的迭代器
clear() 删除所有元素
count() 返回指定元素出现的次数
empty() 如果 map 为空则返回 true
end() 返回指向 map 末尾的迭代器
equal_range() 返回特殊条目的迭代器对
erase() 删除一个元素
find() 查找一个元素
get_allocator() 返回map的配置器
insert() 插入元素
key_comp() 返回比较元素key的函数
lower_bound() 返回键值>=给定元素的第一个位置
max_size() 返回可以容纳的最大元素个数
rbegin() 返回一个指向map尾部的逆向迭代器
rend() 返回一个指向map头部的逆向迭代器
size() 返回map中元素的个数
swap() 交换两个map
upper_bound() 返回键值>给定元素的第一个位置
value_comp() 返回比较元素value的函数
初始化
map 对象是一个模版类,需要关键字和存储对象两个模版参数
std::map<int , std::string> person;
可以对模版进行类型定义使其使用方便
typedef std::map<int , std::string> MAP_INI_STRING;
MAP_INI_STRING person;
创建空的 unordered_map 容器:
std::unordered_map<std::string, std::string> umap;
在创建 unordered_map 容器的同时,可以完成初始化操作:
std::unordered_map<int32_t, std::string> map1 = {{1, "1"}};
将现有 unordered_map 容器中存储的键值对,复制给新建 unordered_map 容器:
std::unordered_map<std::string, std::string> umap2(umap);
由此,umap2 容器中就包含有 umap 容器中所有的键值对。
[[c++]-unordered_map用法及成员方法_c++ map作为类成员-CSDN博客]
map 添加数据/赋值
1 用数组方式插入数据(推荐)
map<int, string> mapStudent;
mapStudent[1] = "student_one";
2 insert 函数插入 pair 数据
std::map < int , std::string > mapPerson;
mapPerson.insert(pair < int,string > (1,"Jim"));
3 insert 函数插入 value_type 数据
mapPerson.insert(std::map < int, std::string > ::value_type (2, "Tom"));
map嵌套list赋值
map<int, vector<int>> myMap;
myMap[1] = vec1; // 这里vec1不能是list<int>类型,只能是vector<int>!
myMap[2] = vec2;
map嵌套list添加数据
map<int, list<int>> myMap;
myMap[1].push_back(10);
myMap[1].push_back(20);
myMap[2].push_back(40);
myMap[2].push_back(50);
Map 数据的遍历
1)前向迭代器
std::map<int, std::string> myMap;
myMap[1] = "apple";// 向 map 中插入元素
// 使用迭代器遍历 map
for (std::map<int, std::string>::iterator it = myMap.begin(); it != myMap.end(); ++it) {
std::cout << it->first << ": " << it->second << std::endl;
}
2)使用 C++11 的新特性 range-based for 循环来遍历 std::map
for (const auto& [key, value] : myMap) {
std::cout << key << ": " << value << std::endl;
}
3)直接pair(推荐)
for (const auto& pair : myMap) {
std::cout << pair.first << " -> " << pair.second << std::endl;
}
[C++ 中使用 std::map 的一个示例-CSDN博客]
map 中元素的查找find
find() 函数返回一个迭代器指向键值为 key 的元素,如果没找到就返回指向 map 尾部的迭代器。
示例:
// Map should be std::map or std::unordered_map.
template <typename Map, typename Key>
auto map_get(const Map& container, const Key& key, const typename Map::mapped_type& default_value) -> const typename Map::mapped_type& {
auto it = container.find(key);
if (it == container.end()) {
return default_value;
} else {
return it->second;
}}
template <typename Map, typename Key>
auto map_get(Map& container, const Key& key, typename Map::mapped_type& default_value) -> typename Map::mapped_type& {
auto it = container.find(key);
if (it == container.end()) {
return default_value;
} else {
return it->second;
}}
示例2:
if (myMap.find(str1) != myMap.end()) {myMap.at(str1)}
或者
if (myMap.count(a) > 0) { myMap.at(str1) }
[c++ map取值的find、[]、at方法特性对比_c++ 用[]和at取值-CSDN博客]
map 中元素的删除
iterator erase(iterator it) ;//通过一个条目对象删除
iterator erase(iterator first,iterator last); //删除一个范围
size_type erase(const Key&key); //通过关键字删除
clear();//就相当于enumMap.erase(enumMap.begin(),enumMap.end());map 中 swap 的用法
Map 中的 swap 不是一个容器中的元素交换,而是两个容器交换;
m1.swap( m2 );
[C++ map用法_w3cschool:6、map 中 swap 的用法]
map sort 问题
Map 中的元素是自动按 key 升序排序,所以不能对 map 用 sort 函数
示例
取参示例
template <typename T>
std::unordered_map<std::string, T> get_map_conf_with_entranceid(
const SortRequestContext& ctx, const std::string& key1,
const std::string& key2, std::unordered_map<std::string, T> default_value) {
std::unordered_map<std::string, T> value = default_value;
if (ctx.params->has({key1, fmt::to_string(ctx.entranceid), key2})) {
value = ctx.params->get_umap<T>({key1, fmt::to_string(ctx.entranceid), key2});
} else if (ctx.params->has({key1, key2})) {
value = ctx.params->get_umap<T>({key1, key2});
}
return value;
}
std::unordered_map<std::string, int32_t> trans_map =
get_map_conf_with_entranceid<int32_t>(
ctx, "sort", "trans_map", std::unordered_map<std::string, int32_t>{});
from:http://blog.csdn.net/pipisorry/article/details/30277861
ref:























 1万+
1万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








