Fsm3comb
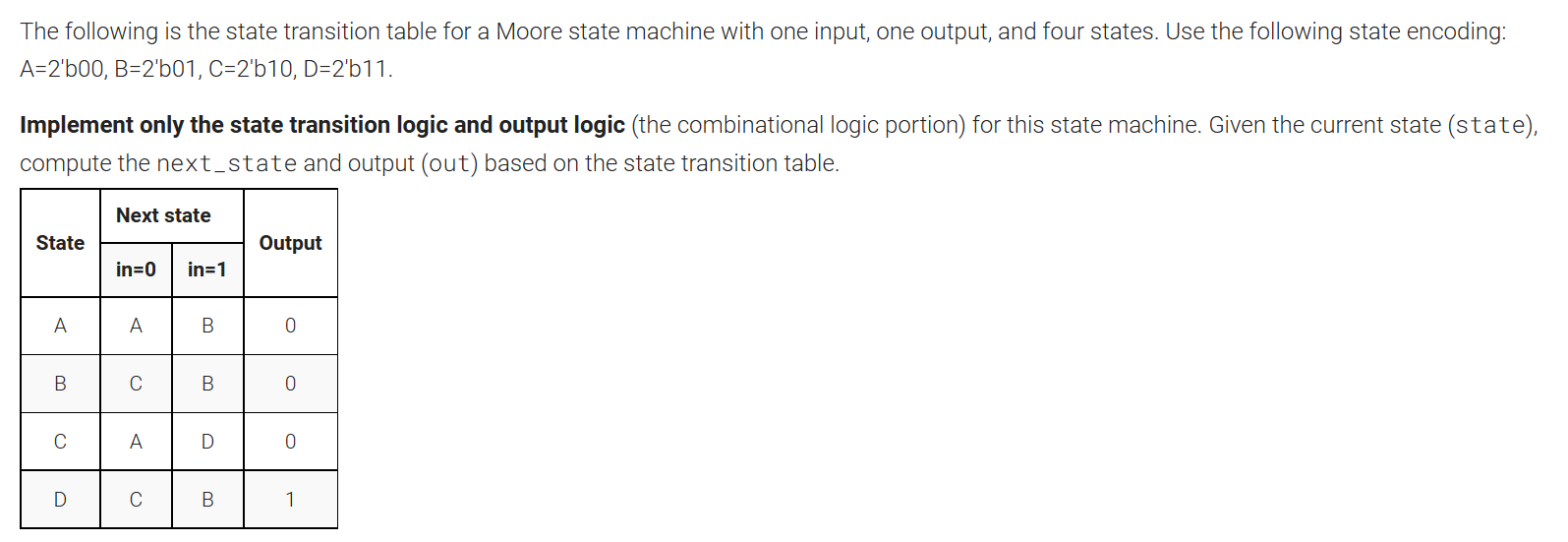
module top_module(
input in,
input [1:0] state,
output [1:0] next_state,
output out); //
parameter A=0, B=1, C=2, D=3;
// State transition logic: next_state = f(state, in)
always@(*) begin
case(state)
A: next_state=in?B:A;
B: next_state=in?B:C;
C: next_state=in?D:A;
D: next_state=in?B:C;
endcase
// Output logic: out = f(state) for a Moore state machine
case(state)
A: out=0;
B: out=0;
C: out=0;
D: out=1;
endcase
end
endmoduleFsm3onehot (根据每一位的逻辑关系)

module top_module(
input in,
input [3:0] state,
output [3:0] next_state,
output out); //
parameter A=0, B=1, C=2, D=3;
// State transition logic: Derive an equation for each state flip-flop.
assign next_state[A] = (~in)&(state[A]||state[C] );
assign next_state[B] = in&(state[A]||state[B]||state[D]);
assign next_state[C] = (~in)&(state[B]||state[D] );
assign next_state[D] = in&(state[C]);
//不能用state==A,要用state[A]
// Output logic:
assign out = (state[D])?1:0;
endmodule“通过检查得出方程”:
One-hot 状态机编码保证恰好有一个状态位为 1。这意味着可以通过仅检查一个状态位而不是所有状态位来确定状态机是否处于特定状态。通过检查状态转换图中每个状态的输入边,这导致了状态转换的简单逻辑方程。
Fsm3 (异步复位)

module top_module(
input clk,
input in,
input areset,
output out); //
reg [4:0]state;//开始写成reg state, 结果报错,因为状态大于两种,需要至少两位表示
reg [4:0]next_state;
parameter A=0,B=1,C=2,D=3;
// State transition logic
always@(*) begin
case(state)
A:next_state=in?B:A;
B:next_state=in?B:C;
C:next_state=in?D:A;
D:next_state=in?B:C;
endcase
end
// State flip-flops with asynchronous reset
always@(posedge clk or posedge areset) begin
if(areset) state<=A;
else state<=next_state;
end
// Output logic
assign out=(state==D);
endmoduleFsm3s (同步复位)

module top_module(
input clk,
input in,
input reset,
output out); //
reg [1:0]state;
reg [1:0]next_state;
parameter A=0, B=1, C=2, D=3;
// State transition logic
always@(*) begin
case(state)
A:next_state=in?B:A;
B:next_state=in?B:C;
C:next_state=in?D:A;
D:next_state=in?B:C;
endcase
end
// State flip-flops with synchronous reset
always@(posedge clk) begin
if(reset) state<=A;
else state<=next_state;
end
// Output logic
assign out=(state==D);
endmodule



















 206
206











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








