1712_ShffleNet:
图:

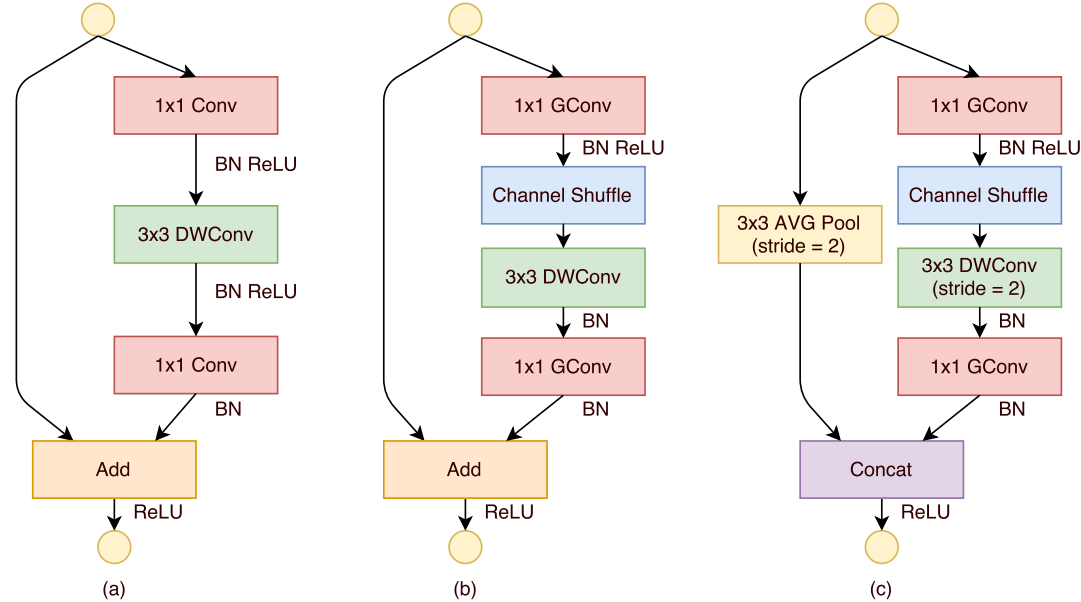
图.ShuffleNet Units (a)具有深度卷积(depthwise convolution)的瓶颈单元;(b)具有分组逐点卷积(GConv)和通道重排的ShuffleNet单元;(c)具有stride=2的ShuffleNet单元。
网络描述:
表中展示了整个ShuffleNet架构。该网络主要由一组分为三个阶段的ShuffleNet单元组成。每个阶段的第一个构建块使用stride=2。一个阶段中的其他超参数保持不变,下一个阶段的输出通道加倍。为每个ShuffleNet单元将瓶颈通道的数量设置为输出通道的1/4。我们的目的是提供一个尽可能简单的参考设计,尽管发现进一步的超参数调优可能会产生更好的结果。在ShuffleNet单元中,组数g控制逐点卷积的连接稀疏性。表探索了不同的组数,调整了输出通道,以确保总体计算成本大致不变。显然,对于给定的复杂度约束,较大的组数会产生更多的输出通道(因此会产生更多的卷积滤波器),这有助于编码更多的信息,但由于相应的输入通道有限,这也可能导致单个卷积滤波器的性能下降 。
利用通道重排的优点,提出了一种专为小型网络设计的新型ShuffleNet单元。从图(a)中瓶颈单元的设计原理出发,它是一个残差块。在其残差分支中,对于3×3层,我们在瓶颈特征图上应用了计算量较少的3×3深度卷积。然后,我们将第一个1×1层替换为分组逐点卷积,然后进行通道重排操作,形成一个ShuffleNet单元,如图(b)所示。第二个分组逐点卷积的目的是恢复通道维数以匹配shortcut路径。为了简单起见,我们不在第二个逐点卷积层之后应用额外的通道重排操作,因为它已产生可比较的成绩。批归一化(BN)和非线性的使用与[Deep residual learning for image recognition, Aggregated residual transformations for deep neural networks]相似,只是我们没有按照[Xception: Deep learning with depthwise separable convolutions]建议的在深度卷积后使用ReLU。对于将stride应用于ShuffleNet的情况,只做了两个修改(见图(c)):(i)在shortcut路径上添加一个3×3的平均池化;(ii)用通道级联替换元素相加,这样可以很容易地扩大通道尺寸,而几乎无需额外的计算成本。
特点,优点:
(1) 使用逐点群卷积来减小 1x1 卷积的计算复杂度
(2) 为了克服群卷积带来的副作用,提出了通道清洗来帮助信息流通,增强通道之间的相关性
(3) shufflenet units可以看作是部分深度可分离卷积(depthwise convolution)和通道注意力机制(通道重排)的组合。
代码:
keras实现:
def _group_conv(x, filters, kernel, stride, groups):
"""
Group convolution
# Arguments
x: Tensor, input tensor of with `channels_last` or 'channels_first' data format
filters: Integer, number of output channels
kernel: An integer or tuple/list of 2 integers, specifying the
width and height of the 2D convolution window.
strides: An integer or tuple/list of 2 integers,
specifying the strides of the convolution along the width and height.
Can be a single integer to specify the same value for
all spatial dimensions.
groups: Integer, number of groups per channel
# Returns
Output tensor
"""
channel_axis = 1 if K.image_data_format() == 'channels_first' else -1
in_channels = K.int_shape(x)[channel_axis]
# number of input channels per group
nb_ig = in_channels // groups
# number of output channels per group
nb_og = filters // groups
gc_list = []
# Determine whether the number of filters is divisible by the number of groups
assert filters % groups == 0
for i in range(groups):
if channel_axis == -1:
x_group = Lambda(lambda z: z[:, :, :, i * nb_ig: (i + 1) * nb_ig])(x)
else:
x_group = Lambda(lambda z: z[:, i * nb_ig: (i + 1) * nb_ig, :, :])(x)
gc_list.append(Conv2D(filters=nb_og, kernel_size=kernel, strides=stride,
padding='same', use_bias=False)(x_group))
return Concatenate(axis=channel_axis)(gc_list)
def _channel_shuffle(x, groups):
"""
Channel shuffle layer
# Arguments
x: Tensor, input tensor of with `channels_last` or 'channels_first' data format
groups: Integer, number of groups per channel
# Returns
Shuffled tensor
"""
if K.image_data_format() == 'channels_last':
height, width, in_channels = K.int_shape(x)[1:]
channels_per_group = in_channels // groups
pre_shape = [-1, height, width, groups, channels_per_group]
dim = (0, 1, 2, 4, 3)
later_shape = [-1, height, width, in_channels]
else:
in_channels, height, width = K.int_shape(x)[1:]
channels_per_group = in_channels // groups
pre_shape = [-1, groups, channels_per_group, height, width]
dim = (0, 2, 1, 3, 4)
later_shape = [-1, in_channels, height, width]
x = Lambda(lambda z: K.reshape(z, pre_shape))(x)
x = Lambda(lambda z: K.permute_dimensions(z, dim))(x)
x = Lambda(lambda z: K.reshape(z, later_shape))(x)
return x
def _shufflenet_unit(inputs, filters, kernel, stride, groups, stage, bottleneck_ratio=0.25):
"""
ShuffleNet unit
# Arguments
inputs: Tensor, input tensor of with `channels_last` or 'channels_first' data format
filters: Integer, number of output channels
kernel: An integer or tuple/list of 2 integers, specifying the
width and height of the 2D convolution window.
strides: An integer or tuple/list of 2 integers,
specifying the strides of the convolution along the width and height.
Can be a single integer to specify the same value for
all spatial dimensions.
groups: Integer, number of groups per channel
stage: Integer, stage number of ShuffleNet
bottleneck_channels: Float, bottleneck ratio implies the ratio of bottleneck channels to output channels
# Returns
Output tensor
# Note
For Stage 2, we(authors of shufflenet) do not apply group convolution on the first pointwise layer
because the number of input channels is relatively small.
"""
channel_axis = 1 if K.image_data_format() == 'channels_first' else -1
in_channels = K.int_shape(inputs)[channel_axis]
bottleneck_channels = int(filters * bottleneck_ratio)
if stage == 2:
x = Conv2D(filters=bottleneck_channels, kernel_size=kernel, strides=1,
padding='same', use_bias=False)(inputs)
else:
x = _group_conv(inputs, bottleneck_channels, (1, 1), 1, groups)
x = BatchNormalization(axis=channel_axis)(x)
x = ReLU()(x)
x = _channel_shuffle(x, groups)
x = DepthwiseConv2D(kernel_size=kernel, strides=stride, depth_multiplier=1,
padding='same', use_bias=False)(x)
x = BatchNormalization(axis=channel_axis)(x)
if stride == 2:
x = _group_conv(x, filters - in_channels, (1, 1), 1, groups)
x = BatchNormalization(axis=channel_axis)(x)
avg = AveragePooling2D(pool_size=(3, 3), strides=2, padding='same')(inputs)
x = Concatenate(axis=channel_axis)([x, avg])
else:
x = _group_conv(x, filters, (1, 1), 1, groups)
x = BatchNormalization(axis=channel_axis)(x)
x = add([x, inputs])
return x
def _stage(x, filters, kernel, groups, repeat, stage):
"""
Stage of ShuffleNet
# Arguments
x: Tensor, input tensor of with `channels_last` or 'channels_first' data format
filters: Integer, number of output channels
kernel: An integer or tuple/list of 2 integers, specifying the
width and height of the 2D convolution window.
strides: An integer or tuple/list of 2 integers,
specifying the strides of the convolution along the width and height.
Can be a single integer to specify the same value for
all spatial dimensions.
groups: Integer, number of groups per channel
repeat: Integer, total number of repetitions for a shuffle unit in every stage
stage: Integer, stage number of ShuffleNet
# Returns
Output tensor
"""
x = _shufflenet_unit(x, filters, kernel, 2, groups, stage)
for i in range(1, repeat):
x = _shufflenet_unit(x, filters, kernel, 1, groups, stage)
return x
def ShuffleNet(input_shape, classes):
"""
ShuffleNet architectures
# Arguments
input_shape: An integer or tuple/list of 3 integers, shape
of input tensor
k: Integer, number of classes to predict
# Returns
A keras model
"""
inputs = Input(shape=input_shape)
x = Conv2D(24, (3, 3), strides=2, padding='same', use_bias=True, activation='relu')(inputs)
x = MaxPooling2D(pool_size=(3, 3), strides=2, padding='same')(x)
x = _stage(x, filters=384, kernel=(3, 3), groups=8, repeat=4, stage=2)
x = _stage(x, filters=768, kernel=(3, 3), groups=8, repeat=8, stage=3)
x = _stage(x, filters=1536, kernel=(3, 3), groups=8, repeat=4, stage=4)
x = GlobalAveragePooling2D()(x)
x = Dense(classes)(x)
predicts = Activation('softmax')(x)
model = Model(inputs, predicts)
return model
if __name__ == '__main__':
model = ShuffleNet((224, 224, 3), 1000)
pytorch实现:
def conv3x3(in_channels, out_channels, stride=1,
padding=1, bias=True, groups=1):
"""3x3 convolution with padding
"""
return nn.Conv2d(
in_channels,
out_channels,
kernel_size=3,
stride=stride,
padding=padding,
bias=bias,
groups=groups)
def conv1x1(in_channels, out_channels, groups=1):
"""1x1 convolution with padding
- Normal pointwise convolution When groups == 1
- Grouped pointwise convolution when groups > 1
"""
return nn.Conv2d(
in_channels,
out_channels,
kernel_size=1,
groups=groups,
stride=1)
def channel_shuffle(x, groups):
batchsize, num_channels, height, width = x.data.size()
channels_per_group = num_channels // groups
# reshape
x = x.view(batchsize, groups,
channels_per_group, height, width)
# transpose
# - contiguous() required if transpose() is used before view().
# See https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/764
x = torch.transpose(x, 1, 2).contiguous()
# flatten
x = x.view(batchsize, -1, height, width)
return x
class ShuffleUnit(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels, groups=3,
grouped_conv=True, combine='add'):
super(ShuffleUnit, self).__init__()
self.in_channels = in_channels
self.out_channels = out_channels
self.grouped_conv = grouped_conv
self.combine = combine
self.groups = groups
self.bottleneck_channels = self.out_channels // 4
# define the type of ShuffleUnit
if self.combine == 'add':
# ShuffleUnit Figure 2b
self.depthwise_stride = 1
self._combine_func = self._add
elif self.combine == 'concat':
# ShuffleUnit Figure 2c
self.depthwise_stride = 2
self._combine_func = self._concat
# ensure output of concat has the same channels as
# original output channels.
self.out_channels -= self.in_channels
else:
raise ValueError("Cannot combine tensors with \"{}\"" \
"Only \"add\" and \"concat\" are" \
"supported".format(self.combine))
# Use a 1x1 grouped or non-grouped convolution to reduce input channels
# to bottleneck channels, as in a ResNet bottleneck module.
# NOTE: Do not use group convolution for the first conv1x1 in Stage 2.
self.first_1x1_groups = self.groups if grouped_conv else 1
self.g_conv_1x1_compress = self._make_grouped_conv1x1(
self.in_channels,
self.bottleneck_channels,
self.first_1x1_groups,
batch_norm=True,
relu=True
)
# 3x3 depthwise convolution followed by batch normalization
self.depthwise_conv3x3 = conv3x3(
self.bottleneck_channels, self.bottleneck_channels,
stride=self.depthwise_stride, groups=self.bottleneck_channels)
self.bn_after_depthwise = nn.BatchNorm2d(self.bottleneck_channels)
# Use 1x1 grouped convolution to expand from
# bottleneck_channels to out_channels
self.g_conv_1x1_expand = self._make_grouped_conv1x1(
self.bottleneck_channels,
self.out_channels,
self.groups,
batch_norm=True,
relu=False
)
@staticmethod
def _add(x, out):
# residual connection
return x + out
@staticmethod
def _concat(x, out):
# concatenate along channel axis
return torch.cat((x, out), 1)
def _make_grouped_conv1x1(self, in_channels, out_channels, groups,
batch_norm=True, relu=False):
modules = OrderedDict()
conv = conv1x1(in_channels, out_channels, groups=groups)
modules['conv1x1'] = conv
if batch_norm:
modules['batch_norm'] = nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channels)
if relu:
modules['relu'] = nn.ReLU()
if len(modules) > 1:
return nn.Sequential(modules)
else:
return conv
def forward(self, x):
# save for combining later with output
residual = x
if self.combine == 'concat':
residual = F.avg_pool2d(residual, kernel_size=3,
stride=2, padding=1)
out = self.g_conv_1x1_compress(x)
out = channel_shuffle(out, self.groups)
out = self.depthwise_conv3x3(out)
out = self.bn_after_depthwise(out)
out = self.g_conv_1x1_expand(out)
out = self._combine_func(residual, out)
return F.relu(out)
class ShuffleNet(nn.Module):
"""ShuffleNet implementation.
"""
def __init__(self, groups=3, in_channels=3, num_classes=1000):
"""ShuffleNet constructor.
Arguments:
groups (int, optional): number of groups to be used in grouped
1x1 convolutions in each ShuffleUnit. Default is 3 for best
performance according to original paper.
in_channels (int, optional): number of channels in the input tensor.
Default is 3 for RGB image inputs.
num_classes (int, optional): number of classes to predict. Default
is 1000 for ImageNet.
"""
super(ShuffleNet, self).__init__()
self.groups = groups
self.stage_repeats = [3, 7, 3]
self.in_channels = in_channels
self.num_classes = num_classes
# index 0 is invalid and should never be called.
# only used for indexing convenience.
if groups == 1:
self.stage_out_channels = [-1, 24, 144, 288, 567]
elif groups == 2:
self.stage_out_channels = [-1, 24, 200, 400, 800]
elif groups == 3:
self.stage_out_channels = [-1, 24, 240, 480, 960]
elif groups == 4:
self.stage_out_channels = [-1, 24, 272, 544, 1088]
elif groups == 8:
self.stage_out_channels = [-1, 24, 384, 768, 1536]
else:
raise ValueError(
"""{} groups is not supported for
1x1 Grouped Convolutions""".format(num_groups))
# Stage 1 always has 24 output channels
self.conv1 = conv3x3(self.in_channels,
self.stage_out_channels[1], # stage 1
stride=2)
self.maxpool = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=1)
# Stage 2
self.stage2 = self._make_stage(2)
# Stage 3
self.stage3 = self._make_stage(3)
# Stage 4
self.stage4 = self._make_stage(4)
# Global pooling:
# Undefined as PyTorch's functional API can be used for on-the-fly
# shape inference if input size is not ImageNet's 224x224
# Fully-connected classification layer
num_inputs = self.stage_out_channels[-1]
self.fc = nn.Linear(num_inputs, self.num_classes)
self.init_params()
def init_params(self):
for m in self.modules():
if isinstance(m, nn.Conv2d):
init.kaiming_normal(m.weight, mode='fan_out')
if m.bias is not None:
init.constant(m.bias, 0)
elif isinstance(m, nn.BatchNorm2d):
init.constant(m.weight, 1)
init.constant(m.bias, 0)
elif isinstance(m, nn.Linear):
init.normal(m.weight, std=0.001)
if m.bias is not None:
init.constant(m.bias, 0)
def _make_stage(self, stage):
modules = OrderedDict()
stage_name = "ShuffleUnit_Stage{}".format(stage)
# First ShuffleUnit in the stage
# 1. non-grouped 1x1 convolution (i.e. pointwise convolution)
# is used in Stage 2. Group convolutions used everywhere else.
grouped_conv = stage > 2
# 2. concatenation unit is always used.
first_module = ShuffleUnit(
self.stage_out_channels[stage-1],
self.stage_out_channels[stage],
groups=self.groups,
grouped_conv=grouped_conv,
combine='concat'
)
modules[stage_name+"_0"] = first_module
# add more ShuffleUnits depending on pre-defined number of repeats
for i in range(self.stage_repeats[stage-2]):
name = stage_name + "_{}".format(i+1)
module = ShuffleUnit(
self.stage_out_channels[stage],
self.stage_out_channels[stage],
groups=self.groups,
grouped_conv=True,
combine='add'
)
modules[name] = module
return nn.Sequential(modules)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.conv1(x)
x = self.maxpool(x)
x = self.stage2(x)
x = self.stage3(x)
x = self.stage4(x)
# global average pooling layer
x = F.avg_pool2d(x, x.data.size()[-2:])
# flatten for input to fully-connected layer
x = x.view(x.size(0), -1)
x = self.fc(x)
return F.log_softmax(x, dim=1)
























 4170
4170











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








