本文内容整理自西安交通大学软件学院李晨老师的课件,仅供学习使用,请勿转载
计算机组成原理系列笔记汇总:计算机组成原理笔记及思维导图汇总附复习建议_Qlz的博客-CSDN博客
文章目录
文章目录
本章思维导图
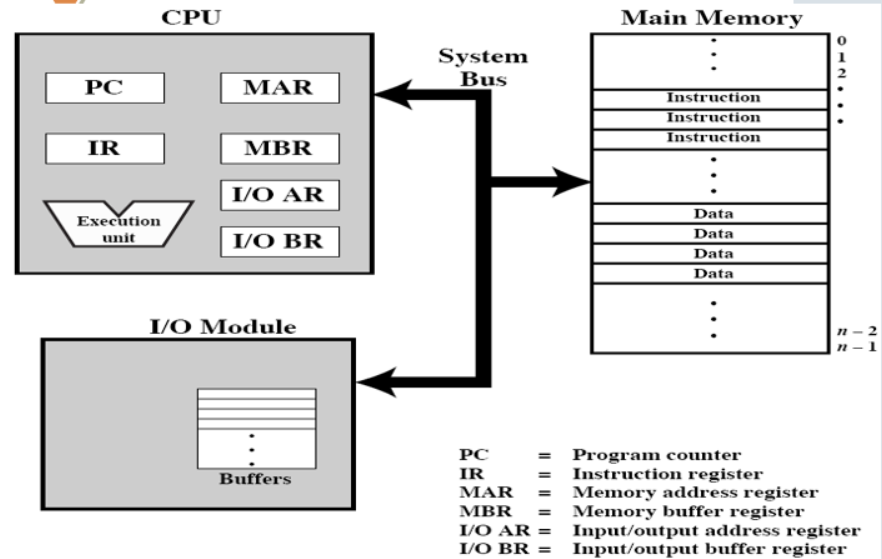
Computer components
Three key concepts in von Neuman architecture
- Data and instruction are stored in a single read-write memory
- The contents of the memory are addressed by location
- Execution occurs in a sequential fashion
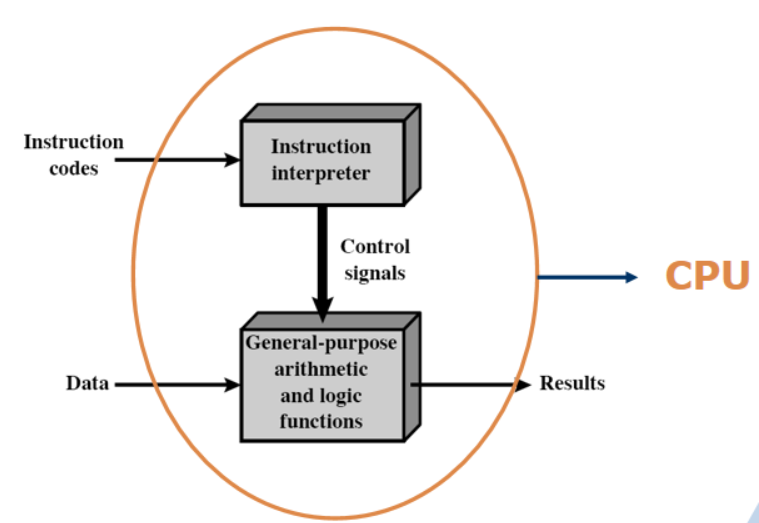
Main Components
- the Central Processing Unit-CPU
- Input/output—I/O
- Main memory
- System bus
内部结构图
Computer Function
Basic function of a computer is executing program (a sequence of instructions), to complete special tasks
- CPU is a component of executing instruction
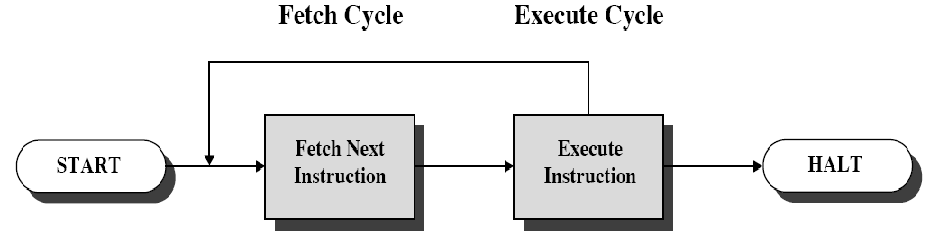
- The CPU time of processing an instruction is called Instruction Cycle 处理指令的CPU时间称为指令周期
- An execution of instruction can be simply viewed as two steps:
- Fetch instruction - Fetch cycle (取指)
- execute instruction - Execute cycle (执行)
Fetch Cycle
- Processor fetches instruction from memory location pointed to by PC
- Increment PC
- Unless told otherwise
- Instruction loaded into Instruction Register (IR)
- Processor interprets instruction and performs required actions
Execute Cycle
- Processor-memory
- data transfer between CPU and main memory
- Processor- I/O
- Data transfer between CPU and I/O module
- Data processing
- Some arithmetic or logical operation on data
- Control
- Alteration of sequence of operations
- e.g. jump
- Combination of above
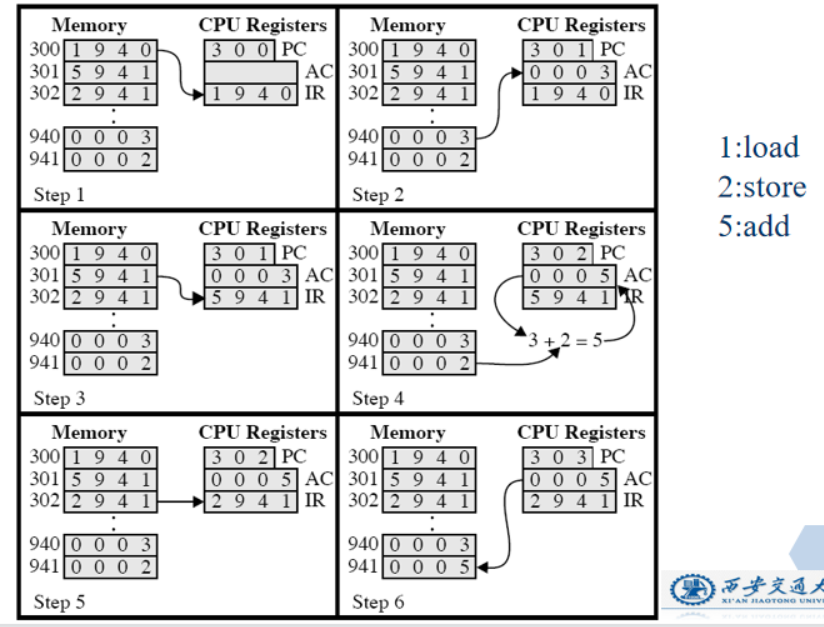
例子
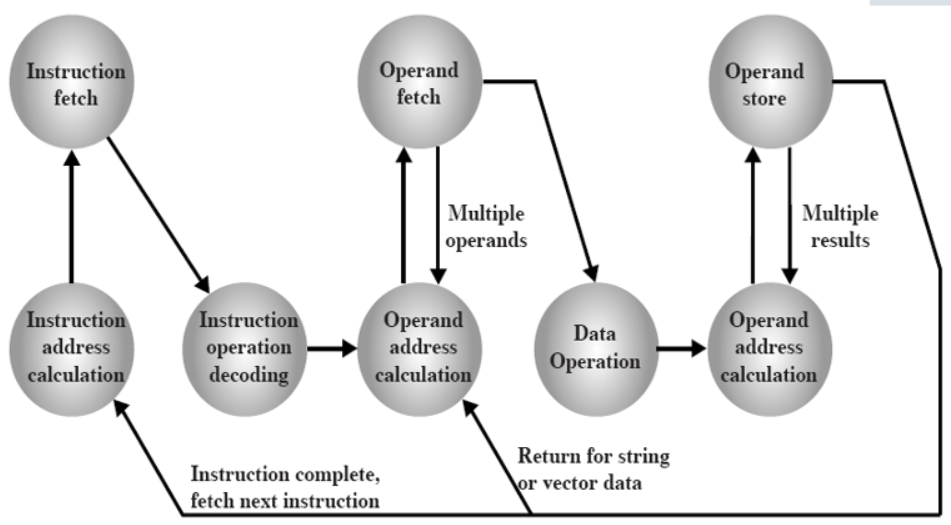
Flow of an Instruction(指令流程)
- Instruction address calculation
- Instruction fetch
- Instruction operation decoding
- operand address calculation (操作数地址计算)
- Operand fetch
- Data operation
- Operand storage
(未考虑中断时) 计算指令地址->取指->译码->执行->操作数地址计算->取操作数->数据运算->操作数地址计算->存操作数->返回数据->计算下一条指令地址
Interrupts
Def
a mechanism allowing other module to break CPU executing sequence 一种允许其他模块打断CPU运行的机制
Goal
- to improve the utility of the CPU 提升效率
- to allow CPU to **process urgent events ** 处理紧急事件
Classification
- Program
- e.g. overflow, division by zero,illegal instruction, outside reference
- Timer
- Generated by internal processor timer
- Used in pre-emptive multi-tasking?
- I/O
- from I/O controller
- Hardware failure
- e.g. memory parity error (存储器奇偶误差)
Comparison
- If interrupt is pending, the processor does the following:
- Suspend execution of the current program being executed and save its context 停止执行当前程序,并保存其上下文
- Save current context of PC and other data
- Set the PC to starting address of an interrupt handler routine 将PC指向异常处理程序的开始地址
- Suspend execution of the current program being executed and save its context 停止执行当前程序,并保存其上下文
- The user program does not have to contain any special code to accommodate interrupts 用户程序无需包含任何特殊代码来实现中断
- The processor and OS are responsible for suspending the user program and resuming it 处理器和操作系统负责中断以及恢复用户程序
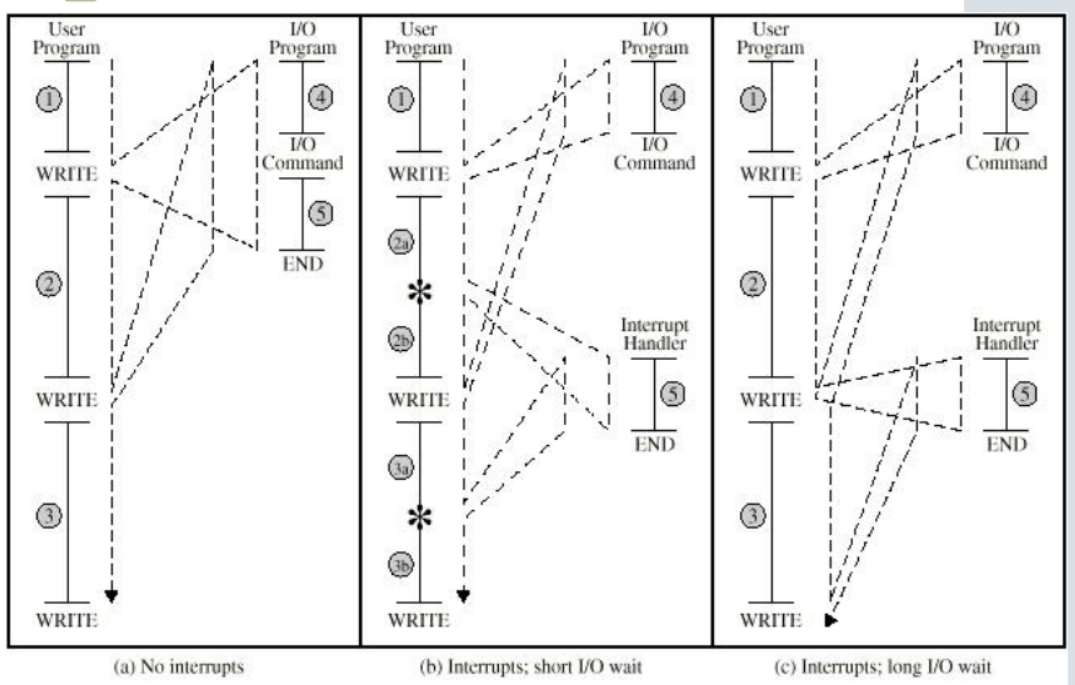
short I/O wait
I/O等待时间较短时,CPU会转而执行其他程序,待I/O处理完成发生中断通知CPU,此时会去处理I/O部分剩余的内容(例如恢复某些寄存器的设置)完成后继续执行程序
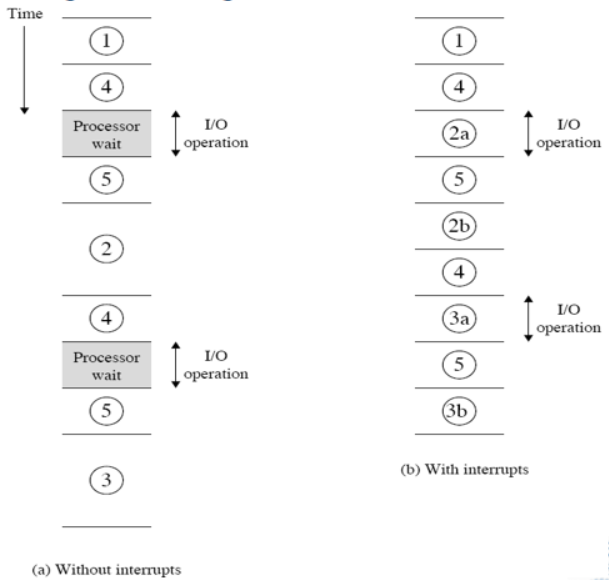
long I/O wait
I/O等待时间较长时,CPU如果在执行过程中碰到另一个I/O请求时会等待上一个I/O请求完成时才继续执行
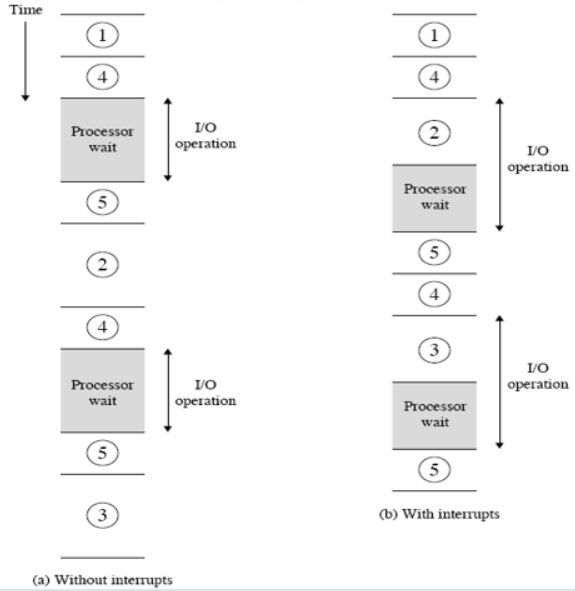
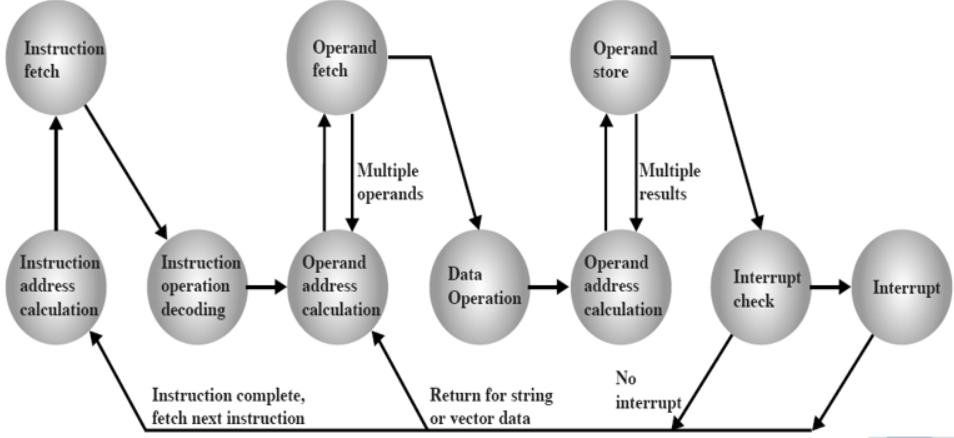
考虑中断后的指令处理流程
- An interrupt cycle is added to instruction cycle (在每个指令周期中加入了一个中断周期)
- After an instruction cycle, processor checks for interrupt, Indicated by an interrupt signal (每一次指令周期后处理器都会检查一下是否有中断信号)
- If no interrupt, fetch next instruction 如果没有,则继续取下一条指令
- If interrupt : 如果有,停止当前程序运行并保存现场转而去处理异常,异常处理结束后恢复现场
- Suspend execution of current program
- Save context
- Set PC to start address of interrupt handler routine
- Process interrupt
- Restore context and continue interrupted program
须在每个指令结束后取检查一下是否有异常产生,如果没有则继续程序执行,如果有,则处理异常
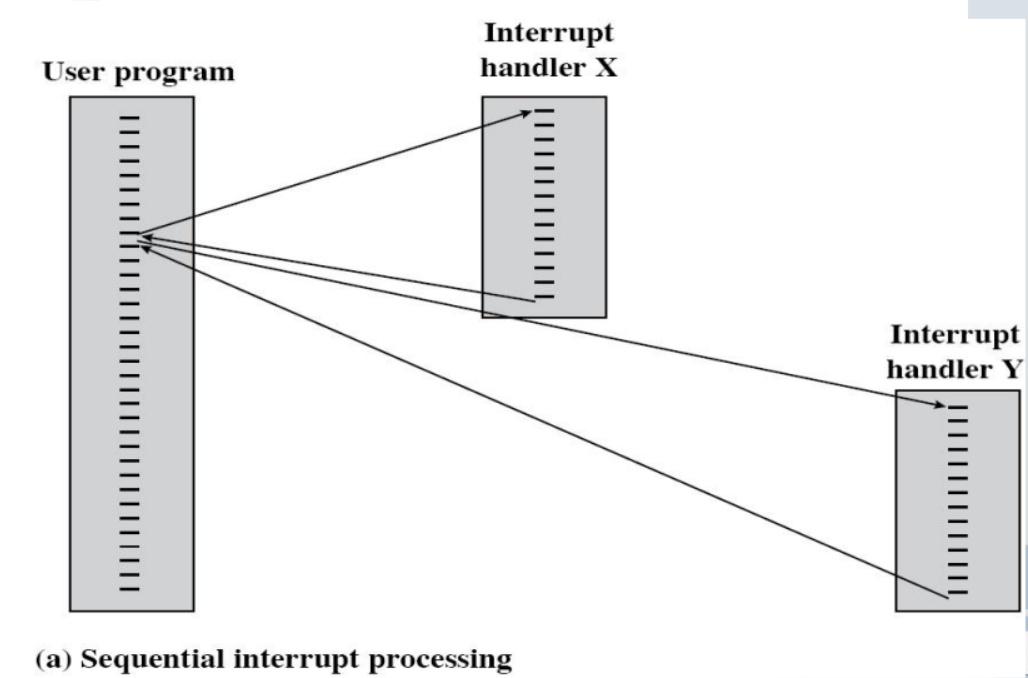
Multiple Interrupts
Def
multiple interrupts occur at the same time
methods
- Disable interrupts 一个中断处理过程中禁用中断
- Processor will ignore further interrupts whilst processing one interrupt 当处理一个中断时CPU会暂时忽略另一个中断的产生
- Interrupts remain pending and are checked after first interrupt has been processed 当一个中断处理完成后才会继续处理另一个中断
- Interrupts handled in sequence as they occur 类似队列的处理方式
- Define priorities 设置优先级
- Low priority interrupts can be interrupted by higher priority interrupts
- When higher priority interrupt has been processed, processor returns to previous interrupt
顺序执行中断程序
为不同的中断设置优先级
I/O function
- Exchange data directly with the processor
- Exchange data directly with the memory, in some case
- Direct memory access (DMA) - chapter 7
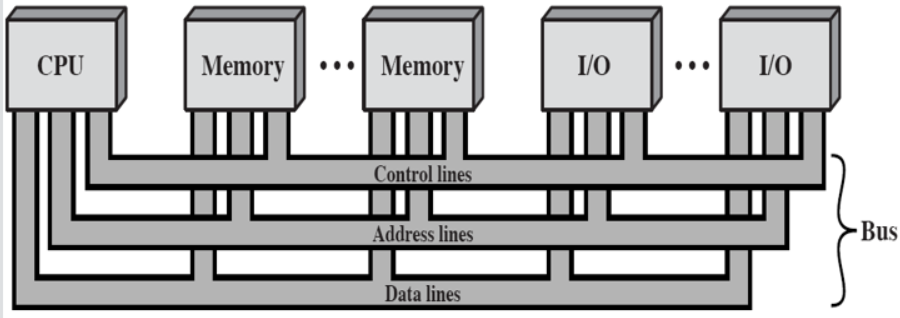
Interconnection structures(互连结构)
Def
The collection of paths connecting the various modules
Port: Each of the interface to an external device
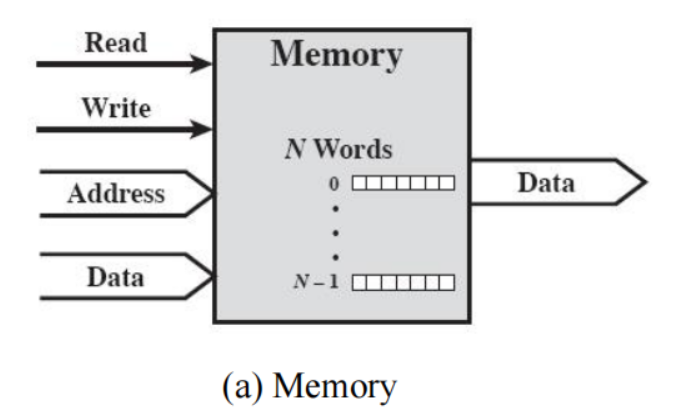
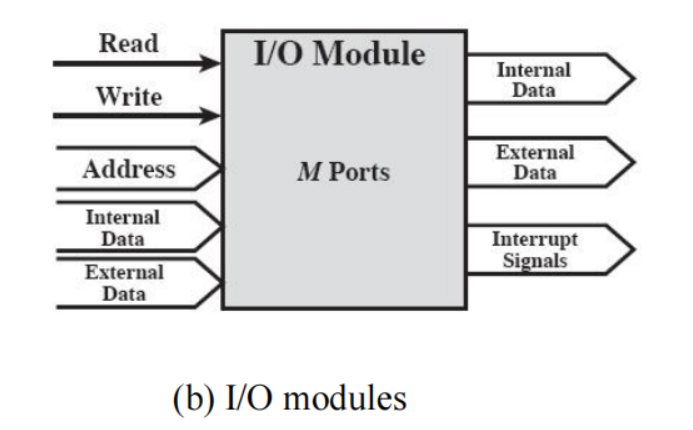
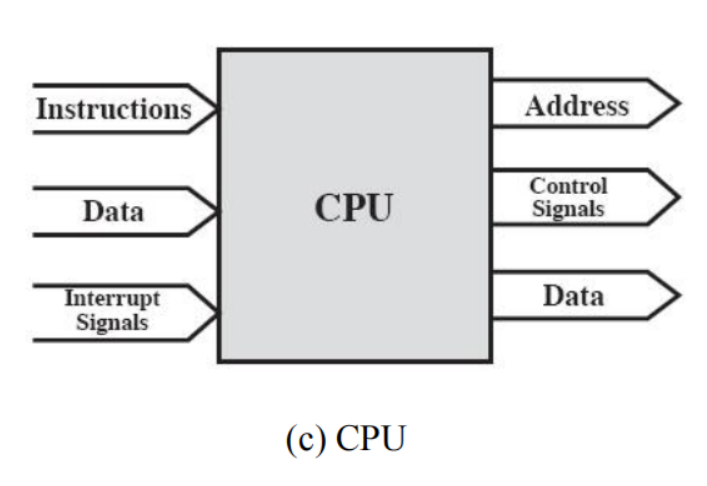
Types of transfer
- Memory to processor
- Processor to memory
- I/O to processor
- Processor to I/O
- I/O to or from memory - DMA
内存与处理器间传输,I/O与处理器间传输,I/O直接与内存传输(DMA)
Bus interconnection
Introduction
Def
communication paths connecting two or more components
Key feature
providing shared transferring media (提供共享的传输媒体)
A number of channels in one bus, e.g. 32 bit data bus is 32 separate single bit channels
Bus width: the number of lines
Type
-
system bus,
-
peripheral buses,
-
internal bus
System Bus:
bus connecting main components of computer
- Data Bus
- Address Bus
- Control Bus
Bus Interconnection Scheme
Data bus
- Function: carry data
- Remember that there is no difference between “data” and “instruction” at this level
- Each line can carry only 1 bit at a time
- Data bus width is a key factor in determining of system performance
- 8, 16, 32, 64 bit
- Machine word-length: The most binary bits which machine can process in the integer operation 机器在整数操作中可以处理的最多的二进制位
- Data bus width = Machine word-length = major Register length
- 数据总线线宽=机器字长=主寄存器长度
Address bus
- Function: identify the source or destination of data
- e.g. CPU needs to read an instruction (data) from a given location in memory
- Address bus width determines maximum memory capacity of system 地址总线的线宽决定内存的最大容量
- e.g. 8088 has 20 bit address bus giving 1M address space
Control bus
- Function: transfer control signals
- Control use of data and address bus 控制数据和地址总线的使用
- Control signals: command and timing information
- Memory read/write signal
- I/O read/write
- Transfer ACK
- Bus Request
- Bus grant
- Interrupt request & ACK
- Clock signals
- Reset
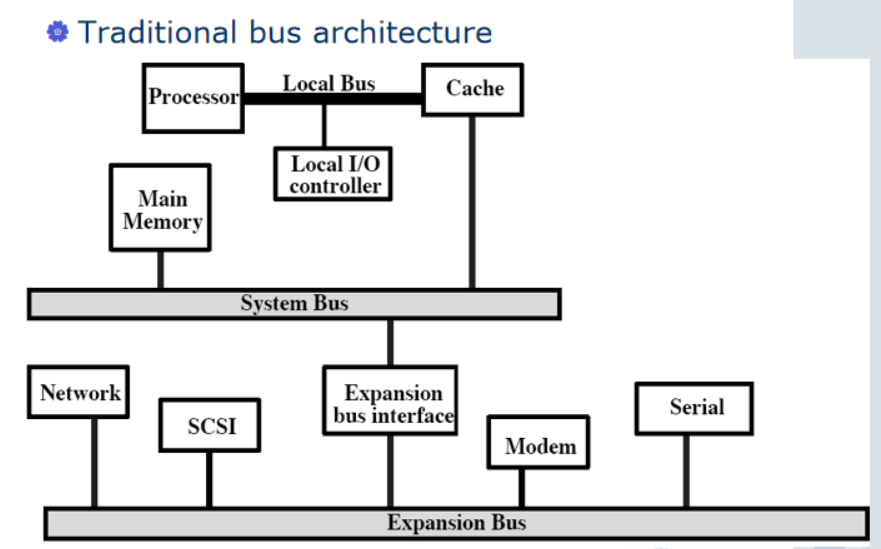
Physical structure
Multiple-bus Hierarchies
- Single Bus Problems
- Lots of devices on one bus leads to:
- Propagation delays(bottleneck)
- More device mean more long bus, and this leads greater delay. Long data paths mean that co-ordination of bus use can adversely affect performance
- If aggregate data transfer approaches bus capacity
- Propagation delays(bottleneck)
- Lots of devices on one bus leads to:
- Most systems use multiple buses to overcome these problems
Elements of Bus Design
Bus Types
- Dedicated Bus:
- Multiple buses, e.g, Separate data & address lines
- Advantage: high throughput(高吞吐量)
- Disadvantage: scale and cost increases
- Multiplexed Bus:
- Time multiplexing(复用), shared lines
- Address valid or data valid control line
- Advantage - fewer lines, space, cost
- Disadvantages
- More complex control
- Ultimate performance
Bus Arbitration(仲裁)
- More than one module using the bus
- e.g. CPU and DMA controller
- Only one module may control bus at one time
- Arbitration method:
- Distributed: no centralized controller, every module contains a access control logic
- Centralized: a bus controller/arbiter is responsible for bus usage and time. A separate module or part of CPU
- Separate request(单独的请求)
- Chain polling(链轮询)
- Counter timing polling(计时器定时轮询)
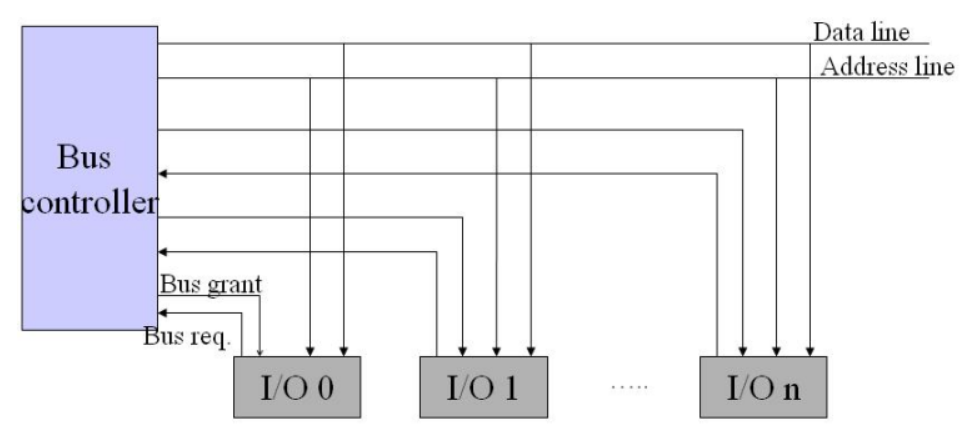
Separate request
每一个I/O设备都直接连接到总线控制器上,直接发送并接收总线的处理结果
- Advantage: rapid response, flexible priority
- Disadvantage: too many lines, complex control
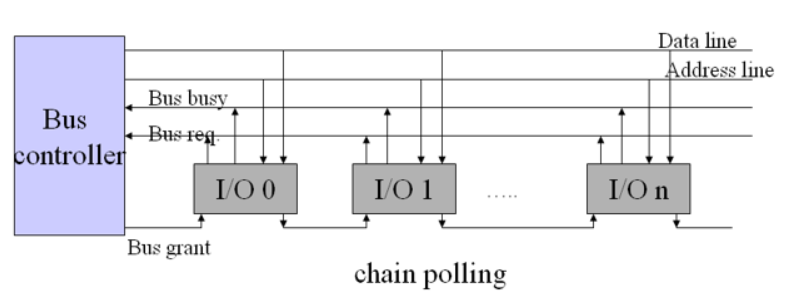
Chain polling
新增加 Bus busy线,用来通知每个线总线现在是否被占用,如果没被占用的话,则可以发送一个Bus req,总线控制器经Bus grant发出同意信号,每个I/O设备根据自己的请求状态判断是否被分配到总线使用权,这种模式下离总线控制器越近优先级越高
- Advantage: scalable
- Disadvantage: sensitive to circuit failure
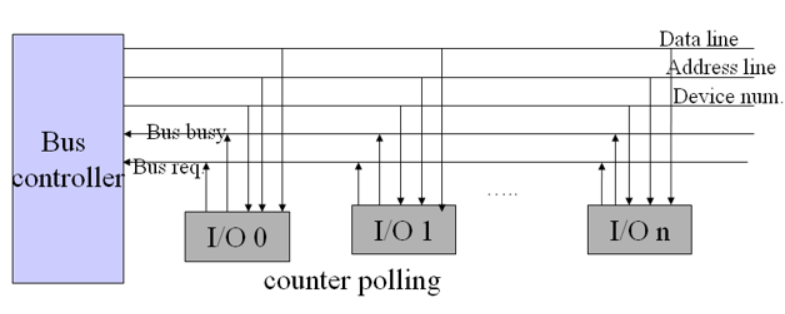
Counter timing polling
新增加Device num线,用来轮询I/O设备的序号,并且这种方式轮询的次序可自己设置,因此有比较灵活的优先权,但是控制比较复杂
- Advantage : flexible priority, insensitive to circuit failure
- Disadvantage : complex control
Communication Control Modes of Bus
- Communication control (通信控制): addressing how to start and end transmission, how to coordinate master and slave module 解决如何启动和结束传输,如何协调主从模块
- According to timing, four communication modes can usually be used
- Synchronous
- Asynchronous
- Half-synchronous
- Separated
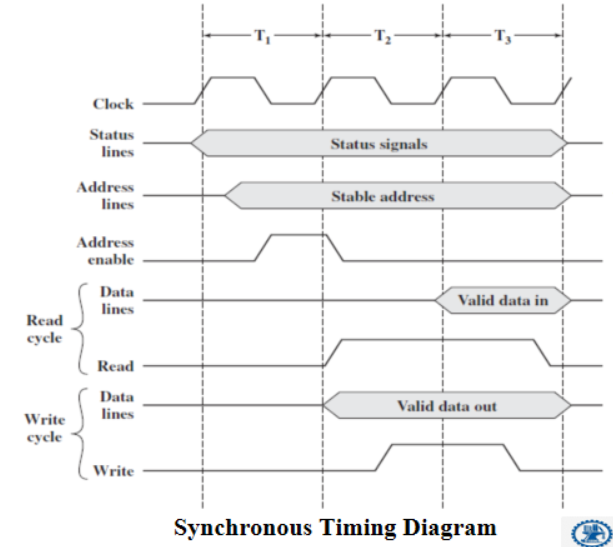
Timing
-
Def: the way in which events are coordination(协调) on bus -
Synchronous timing: the occurrence of events is determined by clock signals
- Control bus includes clock line
- A single 1-0 transmission is a bus cycle
- All devices can read clock line
-
Asynchronous timing: the occurrence of one event on a bus follows and depends on the occurrence of a previous event
总线上一个事件的发生跟随,并取决于前一个事件的发生
-
Half-synchronous
-
Separate Communication
Synchronous timing
- Advantage: simple, easy to implement
- Disadvantage: inflexible, bottleneck
Asynchronous timing
- Advantage: request-response, allowing fast and slow devices
- Disadvantage: control complex
Types of Asynchronous Communication
非联锁
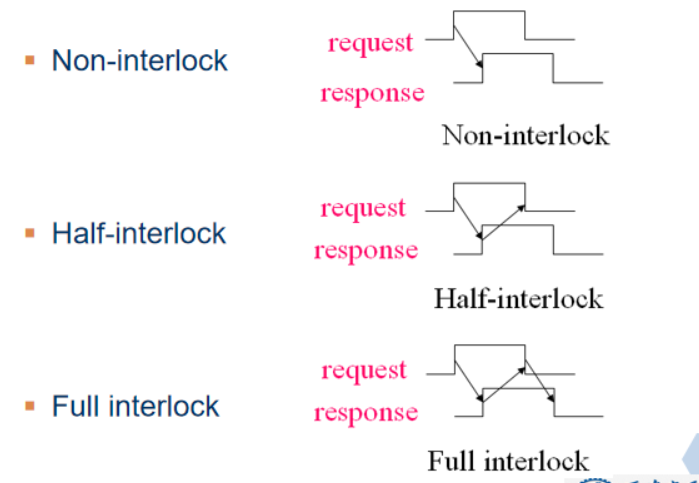
Half-synchronous Communication
- Clock is needed
- Wait line is needed
- Allowing various speed modules to communicate harmoniously
- Used for connecting low speed and larger speed difference devices
Separate Communication
- Basic idea is:
- Separate bus cycle into two sub-cycles
- In the first sub-cycle, master puts command, address and other information into the bus, then abandons the bus
- In the second sub-cycle, slave begins to prepare data (select, decode, load), then applies the bus and sends the data
- Advantage: avoiding bus idle waiting
- Used for large computer
Bus width and Bus bandwidth
Bus width
-
The width of data bus has an impact on system performance, bit
-
The width of address bus has an impact on system capacity, bit
Bus bandwidth
- The transmitting rate of bus, b/s
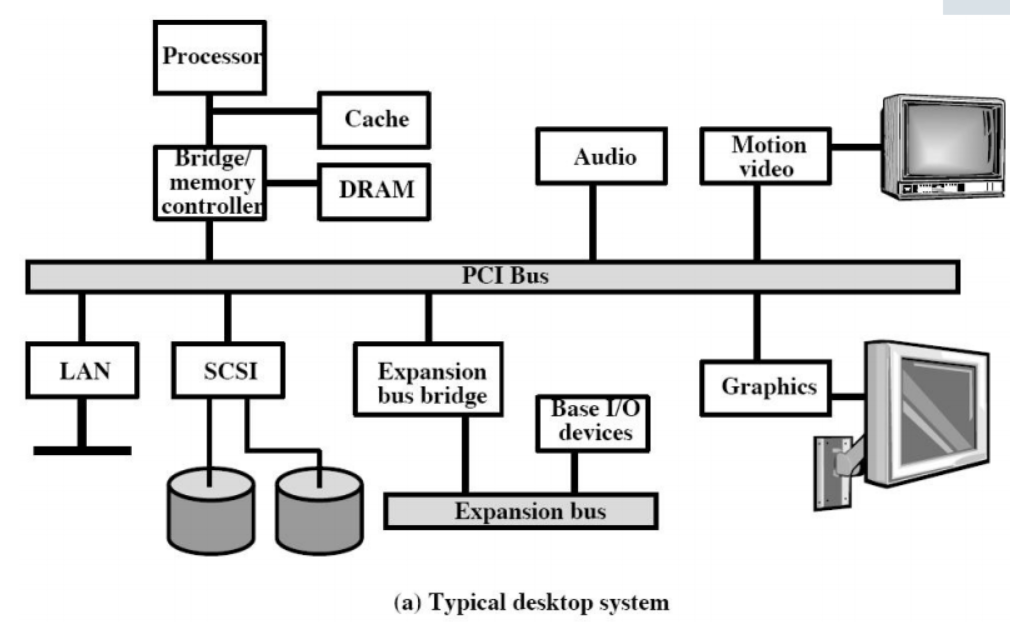
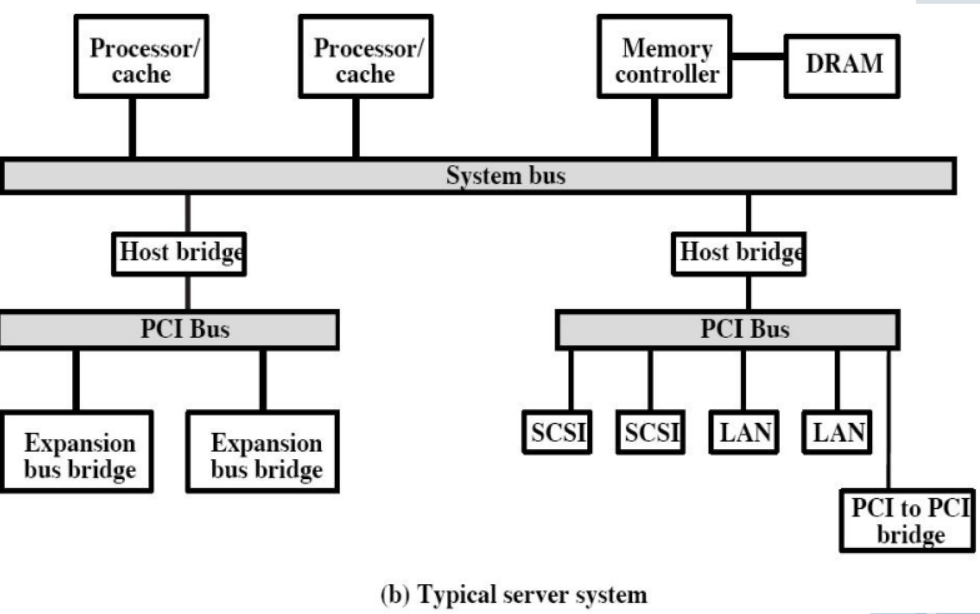
PCI
PCI (Peripheral Component Interconnection 外围设备组件互联) :also called high speed I/O bus
Vocabulary
- Hardwired program:硬布线编程
- Interrupt request:中断请求
- Interrupt handler routine:中断处理程序
- Multiple interrupts:多重中断
- DMA(direct memory access):直接存储器访问
- Port:端口
- Module:模块
- Fast Ethernet:快速以太网
- Packet-switching network:分组交换网
- LAN:局域网
- Time(frequency) multiplexing:时(频)分复用
- Adapter:适配器
- Arbitration:仲裁
- Synchronous (Asynchronous) timing:同(异)步时序
- Master (slave) synchronous:主(辅)同步
- Multiprogramming system:多道程序系统
- PCI(peripheral component interconnect):外设互连(总线)
Key points
- Interrupt and instruction cycles
- Multiple interrupts
- System bus
- Multiple bus hierarchy
- Key elements of bus






















 288
288











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










