1、前言
最近在做转录组分析时遇到个问题,由于本人是半路出家学习的生信,所以在做注释分析时主要采用的都是近几年比较主流的软件,比如Y叔的clusterProfiler, g:Profiler 等软件,对于之前出现的软件几乎都不了解,所以当碰到近几年主流的软件无法进行注释的时候就无从下手了。
注释、可视化和集成发现数据库(DAVID)为研究人员提供了一套全面的功能注释工具,以了解大型基因列表背后的生物学意义。这些工具由建立在DAVID基因概念基础上的全面的DAVID知识库提供支持,该知识库汇集了功能注释的多个来源。
2、使用
1、获取差异基因
我们此次实验做的是细菌,但是由于实验前没有做详尽的调查,导致在完成转录组测序后无法找到对用菌种的参考基因组信息,并且该菌种亚型的注释信息也比较少,所以这里就退而求其次选择了NCBI提供的参考基因组进行分析,在分析完之后得到了228个上调基因、290个下调基因。
2、使用DAVID进行注释
1、首先进入DAVID分析网站:
2、进入注释页面:
首先上传自己的基因ID,接着选择ID类型,并选择参考基因组对应的物种、最后提交进行分析

注释速度很快,在注释完成后会弹出结果页面,结果页面左侧显示有多少基因没有注释成功,结果页面右侧显示注释结果,其中包括注释后的分簇结果、通路表格、以及各个基因对应的通路。用户可以点击对应的结果文件进行查看以及下载;
 对于14个未知基因,用户可以点击ID转换模块进行转换
对于14个未知基因,用户可以点击ID转换模块进行转换
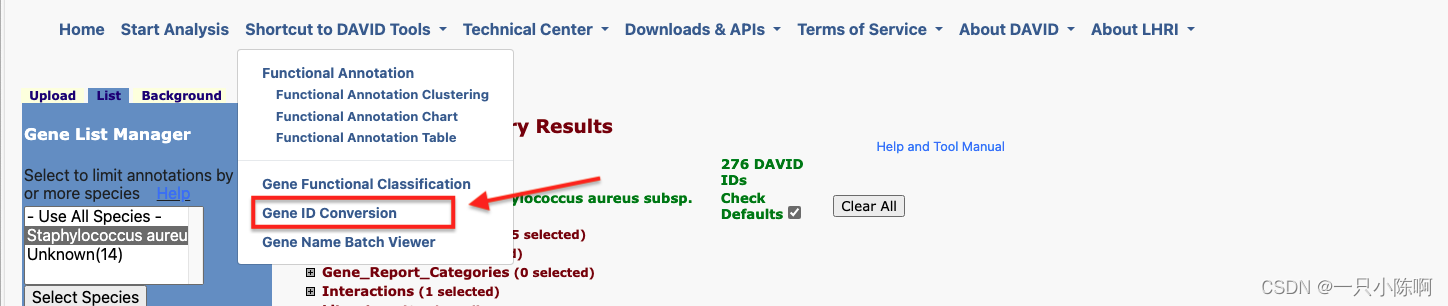
首先选择对应的ID类型,然后再选择对应的物种类型,最后进行转换。
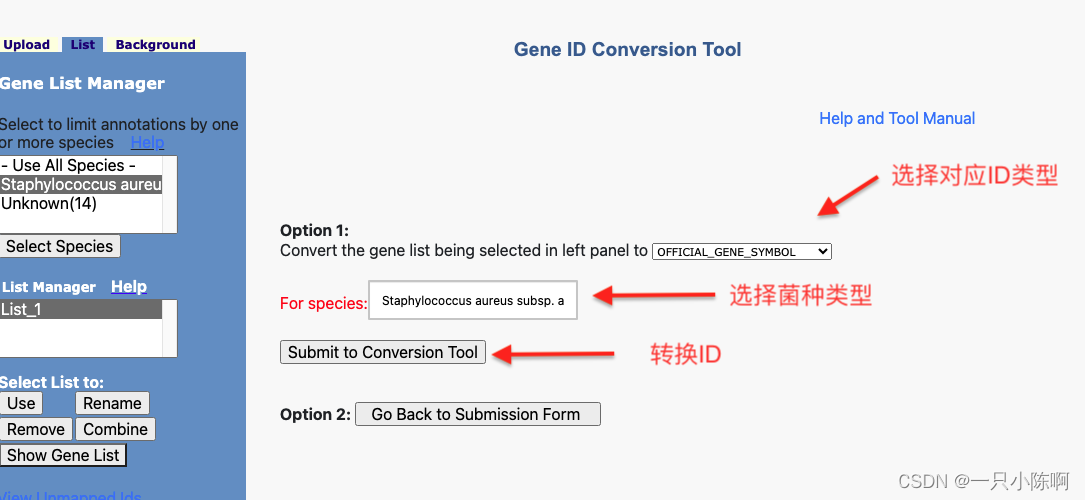
在完成转换之后,再进行注释分析。
生信真的是一门需要积累的学科!很多软件、方法需要在学习的过程中逐渐积累!







 本文介绍了在转录组分析中遇到的问题,如何使用DAVID工具对差异基因进行注释,包括获取NCBI参考基因组、上传基因ID、注释过程和处理未知基因的方法。强调生信领域的学习积累重要性。
本文介绍了在转录组分析中遇到的问题,如何使用DAVID工具对差异基因进行注释,包括获取NCBI参考基因组、上传基因ID、注释过程和处理未知基因的方法。强调生信领域的学习积累重要性。
















 4万+
4万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








