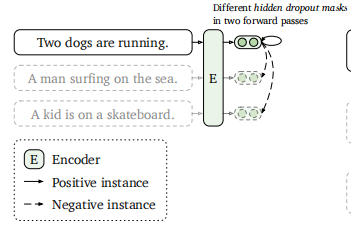
对比学习的思想是拉近同类样本的距离,增大不同类样本的距离,目标是要从样本中学习到一个好的语义表示空间。SimCSE是一种简单的无监督对比学习框架,它通过对同一句子两次Dropout得到一对正样例,将该句子与同一个batch内的其它句子作为一对负样例。模型结构如下所示:
损失函数为:
ℓ
i
=
−
log
e
sim
(
h
i
z
i
,
h
i
z
i
′
)
/
τ
∑
j
=
1
N
e
sim
(
h
i
z
i
,
h
j
z
j
′
)
/
τ
\ell_{i}=-\log \frac{e^{\operatorname{sim}\left(\mathbf{h}_{i}^{z_{i}}, \mathbf{h}_{i}^{z_{i}^{\prime}}\right) / \tau}}{\sum_{j=1}^{N} e^{\operatorname{sim}\left(\mathbf{h}_{i}^{z_{i}}, \mathbf{h}_{j}^{z_{j}^{\prime}}\right) / \tau}}
ℓi=−log∑j=1Nesim(hizi,hjzj′)/τesim(hizi,hizi′)/τ
代码实现
在作者的代码中,并不是将一个句子输入到模型中两次,而是复制一份放到同一个batch里。模型的核心是 cl_forward 函数:
def cl_forward(cls,
encoder,
input_ids=None,
attention_mask=None,
token_type_ids=None,
position_ids=None,
head_mask=None,
inputs_embeds=None,
labels=None,
output_attentions=None,
output_hidden_states=None,
return_dict=None,
mlm_input_ids=None,
mlm_labels=None,
):
return_dict = return_dict if return_dict is not None else cls.config.use_return_dict
ori_input_ids = input_ids # 形状为[bs, num_sent, sent_len], bs=32
batch_size = input_ids.size(0)
# Number of sentences in one instance
# 2: pair instance,[自己,自己]; 3: pair instance with a hard negative,[自己,自己,难例]
num_sent = input_ids.size(1)
mlm_outputs = None
# Flatten input for encoding
input_ids = input_ids.view((-1, input_ids.size(-1))) # [bs * num_sent, sent_len]
attention_mask = attention_mask.view((-1, attention_mask.size(-1))) # [bs * num_sent, sent_len]
if token_type_ids is not None:
token_type_ids = token_type_ids.view((-1, token_type_ids.size(-1))) # [bs * num_sent, sent_len]
# Get raw embeddings, [bs, num_sent, sent_len, hidden_size]
outputs = encoder(
input_ids,
attention_mask=attention_mask,
token_type_ids=token_type_ids,
position_ids=position_ids,
head_mask=head_mask,
inputs_embeds=inputs_embeds,
output_attentions=output_attentions,
output_hidden_states=True if cls.model_args.pooler_type in ['avg_top2', 'avg_first_last'] else False,
return_dict=True,
)
# MLM auxiliary objective
if mlm_input_ids is not None:
mlm_input_ids = mlm_input_ids.view((-1, mlm_input_ids.size(-1)))
mlm_outputs = encoder(
mlm_input_ids,
attention_mask=attention_mask,
token_type_ids=token_type_ids,
position_ids=position_ids,
head_mask=head_mask,
inputs_embeds=inputs_embeds,
output_attentions=output_attentions,
output_hidden_states=True if cls.model_args.pooler_type in ['avg_top2', 'avg_first_last'] else False,
return_dict=True,
)
# Pooling
pooler_output = cls.pooler(attention_mask, outputs)
pooler_output = pooler_output.view((batch_size, num_sent, pooler_output.size(-1))) # (bs, num_sent, hidden_size)
# If using "cls", we add an extra MLP layer
# (same as BERT's original implementation) over the representation.
if cls.pooler_type == "cls":
pooler_output = cls.mlp(pooler_output)
# Separate representation, [bs, hidden_size], 同一样本经过“两次Dropout”得到的两个句向量
z1, z2 = pooler_output[:,0], pooler_output[:,1]
# Hard negative
if num_sent == 3:
z3 = pooler_output[:, 2]
# Gather all embeddings if using distributed training
if dist.is_initialized() and cls.training:
# Gather hard negative
if num_sent >= 3:
z3_list = [torch.zeros_like(z3) for _ in range(dist.get_world_size())]
dist.all_gather(tensor_list=z3_list, tensor=z3.contiguous())
z3_list[dist.get_rank()] = z3
z3 = torch.cat(z3_list, 0)
# Dummy vectors for allgather
z1_list = [torch.zeros_like(z1) for _ in range(dist.get_world_size())]
z2_list = [torch.zeros_like(z2) for _ in range(dist.get_world_size())]
# Allgather
dist.all_gather(tensor_list=z1_list, tensor=z1.contiguous())
dist.all_gather(tensor_list=z2_list, tensor=z2.contiguous())
# Since allgather results do not have gradients, we replace the
# current process's corresponding embeddings with original tensors
z1_list[dist.get_rank()] = z1
z2_list[dist.get_rank()] = z2
# Get full batch embeddings: (bs x N, hidden)
z1 = torch.cat(z1_list, 0)
z2 = torch.cat(z2_list, 0)
# [bs, bs],计算该样本与其它样本的相似度
cos_sim = cls.sim(z1.unsqueeze(1), z2.unsqueeze(0))
# Hard negative
if num_sent >= 3:
z1_z3_cos = cls.sim(z1.unsqueeze(1), z3.unsqueeze(0))
cos_sim = torch.cat([cos_sim, z1_z3_cos], 1)
# [bs, ], 内容为[0,1,...,bs-1],表示每个样本最相似的样本下标
labels = torch.arange(cos_sim.size(0)).long().to(cls.device)
# 此处显示出对比学习loss和常规交叉熵loss的区别,
# 对比学习的label数是[bs,bs],而交叉熵的label数是[bs, label_nums]
loss_fct = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
# Calculate loss with hard negatives
if num_sent == 3:
# Note that weights are actually logits of weights
z3_weight = cls.model_args.hard_negative_weight
weights = torch.tensor(
[[0.0] * (cos_sim.size(-1) - z1_z3_cos.size(-1)) + [0.0] * i + [z3_weight] + [0.0] * (z1_z3_cos.size(-1) - i - 1) for i in range(z1_z3_cos.size(-1))]
).to(cls.device)
cos_sim = cos_sim + weights
loss = loss_fct(cos_sim, labels)
# Calculate loss for MLM
if mlm_outputs is not None and mlm_labels is not None:
mlm_labels = mlm_labels.view(-1, mlm_labels.size(-1))
prediction_scores = cls.lm_head(mlm_outputs.last_hidden_state)
masked_lm_loss = loss_fct(prediction_scores.view(-1, cls.config.vocab_size), mlm_labels.view(-1))
loss = loss + cls.model_args.mlm_weight * masked_lm_loss
if not return_dict:
output = (cos_sim,) + outputs[2:]
return ((loss,) + output) if loss is not None else output
return SequenceClassifierOutput(
loss=loss,
logits=cos_sim,
hidden_states=outputs.hidden_states,
attentions=outputs.attentions,
)
上述代码考虑诸多场景,比如分布式训练、难例三元组、mlm mask,写的较为复杂。
以下是简化版,更加符合论文的表述:
loss_func = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
def simcse_loss(batch_emb):
"""用于无监督SimCSE训练的loss
"""
batch_size = batch_emb.size(0) # [bs, hidden_size]
# 构造标签, [bs, 2], bs=64
y_true = torch.cat([torch.arange(1, batch_size, step=2, dtype=torch.long).unsqueeze(1),
torch.arange(0, batch_size, step=2, dtype=torch.long).unsqueeze(1)],
dim=1).reshape([batch_size,])
# 计算score和loss
norm_emb = F.normalize(batch_emb, dim=1, p=2)
# [bs, bs],计算该样本与其它样本的相似度
sim_score = torch.matmul(norm_emb, norm_emb.transpose(0,1))
# 对角线的位置,也就是自身的余弦相似度,肯定为1,不产生loss,需要mask掉
sim_score = sim_score - torch.eye(batch_size) * 1e12
sim_score = sim_score * 20 # 温度系数
loss = loss_func(sim_score, y_true)
return loss
FAQ
- 如果同一个batch里有其它语义相似的正样本,但在这里被当作了负样例处理,不是也拉远了同类样本的距离吗?





















 2万+
2万+











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








