打算好好啃ORB-SLAM源代码,接下来的LSD、SVO其实就是从特征点法换成了光流法(直接法),但是整体的框架大同小异,所以打算两周时间啃完,并将学习到的C++技巧总结下来,这样对于C++也会有新的理解。
每章5个技巧,怕什么真理无穷,进一寸有进一寸的欢喜。
一、多线程Thread
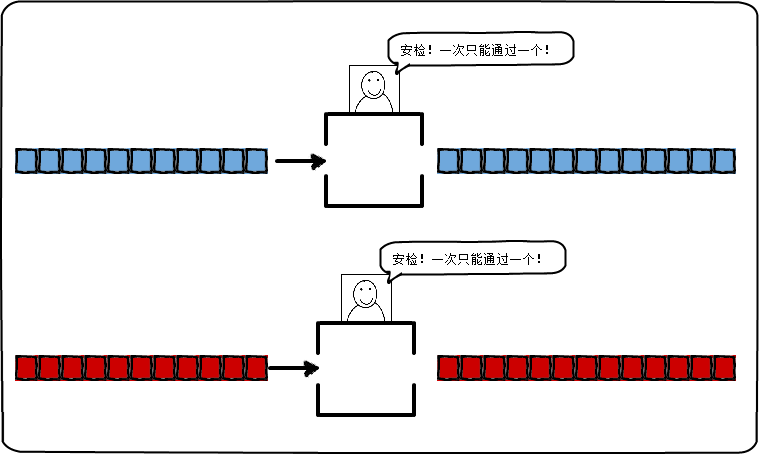
并发:某一个时刻只能处理一个操作,但是交替进行。大脑的设计:看显示器同时打字
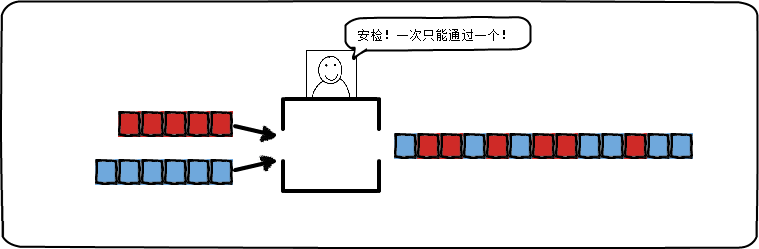
并行:某个时间点上处理两个或以上的操作。
实例代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <thread>
using namespace std;
void t1()
{
for (int i = 0; i < 20; ++i)
{
cout << "t1111\n";
}
}
void t2()
{
for (int i = 0; i < 20; ++i)
{
cout << "t22222\n";
}
}
int main()
{
thread th1(t1);//新线程要有初始函数
thread th2(t2);
th1.join(); //等待th1执行完
th2.join(); //等待th2执行完
cout << "here is main\n\n";
return 0;
} 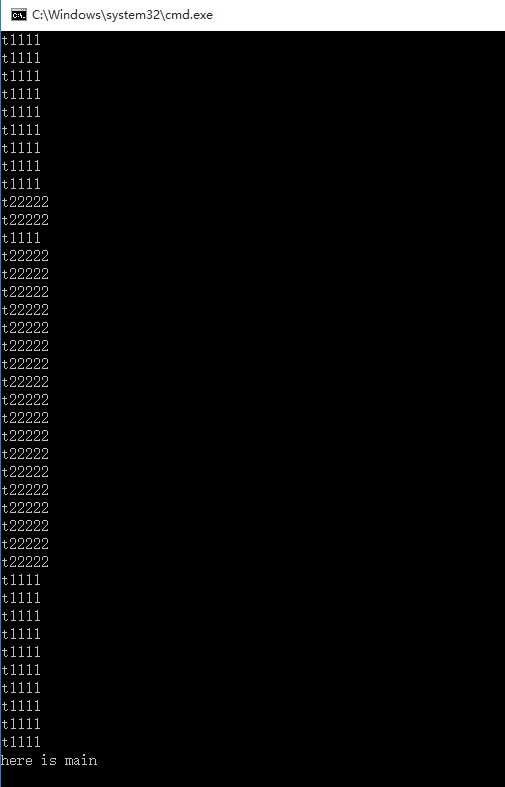
(1)三个线程,一个主线程(main),两个子线程(th1,th2),三者并发执行,共用CPU。
(2)join的作用是保证子程序执行结束再退出主线程,this is main最后才执行。否则会出Bug。
System.cpp
// System.h
// 3个线程: Local Mapping, Loop Closing, Viewer.
// Tracking线程在System主程序线程中
std::thread* mptLocalMapping;
std::thread* mptLoopClosing;
std::thread* mptViewer;
// System.cpp
//5.1初始化 Tracking
//(it will live in the main thread of execution, the one that called this constructor)
mpTracker = new Tracking(this, mpVocabulary, mpFrameDrawer, mpMapDrawer,
mpMap, mpKeyFrameDatabase, strSettingsFile, mSensor);
//5.2初始化并发布 Local Mapping 线程
mpLocalMapper = new LocalMapping(mpMap, mSensor==MONOCULAR);
mptLocalMapping = new thread(&ORB_SLAM2::LocalMapping::Run,mpLocalMapper);
//5.3初始化并发布 Loop Closing 线程
mpLoopCloser = new LoopClosing(mpMap, mpKeyFrameDatabase, mpVocabulary, mSensor!=MONOCULAR);
mptLoopClosing = new thread(&ORB_SLAM2::LoopClosing::Run, mpLoopCloser);
//5.4初始化并发布 Viewer 线程
mpViewer = new Viewer(this, mpFrameDrawer,mpMapDrawer,mpTracker,strSettingsFile);
if(bUseViewer)
mptViewer = new thread(&Viewer::Run, mpViewer);Frame.cpp
// ORB extraction
//提取特征加入双线程同步提取,0,1代表左目和右目
//两张提取的特征点会放在不同的vector中
//对单目和RGBD来说,右目不用,以左为准
thread threadLeft(&Frame::ExtractORB,this,0,imLeft);
thread threadRight(&Frame::ExtractORB,this,1,imRight);
//该函数在线程执行完成是返回
//在调用这个函数之后,线程对象变为不可连接的并且可以被安全地销毁
threadLeft.join();
threadRight.join();
二、unique_lock与lock_guard关系
多线程编程会对共享的数据进行写保护,防止多线程对共享数据成员进行读写时造成资源争抢,做法:加锁—mutex
unique_lock与lock_guard两种数据结构实现自动unlock,unique_lock更灵活但占用空间。
mutex是用来保证线程同步的,防止不同的线程同时操作同一个共享数据。
lock_guard能够自解锁,当生命周期结束时,它会自动析构(unlock),
mutex m;
lock_guard<mutex> lockGuard(m);
三、Public、Protected、Private
public:可以被任意实体访问
protected:只允许子类及本类的成员函数访问,允许继承的派生类
private:只允许本类的成员函数访问(C++默认)
private是自己私有的,protected是可以让孩子知道的,public是公开的!
成员函数一般设置为Pubic,函数会被大量调用。
成员变量一般设置为Private,只是本类成员函数调用即可。
四、FileStorage类读写XML/YML文件
使用这个工具类,我们可以将 opencv 中的数据结构(或者int,float,string)保存到 XML/YAML 文件中去。或者从XML/YAML文件中加载这些数据。
构造函数:cv::FileStorage(const string& source, int flags, const string& encoding=string());
参数说明:
source –存储或读取数据的文件名(字符串),其扩展名(.xml 或 .yml或者.yaml)决定文件格式。
flags – 操作方式,包括:
FileStorage::READ 打开文件进行读操作
FileStorage::WRITE 打开文件进行写操作
FileStorage::APPEND打开文件进行附加操作,在已有内容的文件里添加
encoding:编码方式,用默认值就好。
写
#include <opencv2\opencv.hpp>
using namespace std;
using namespace cv;
typedef struct
{
int x;
int y;
string s;
} test_t;
int main()
{
FileStorage fs("test.yml", FileStorage::WRITE);
//普通数据
int a = 2;
char a1 = -1;
fs << "a" << a;
fs << "a1" << a1;
// Mat 类型
Mat cameraMatrix = (Mat_<double>(3,3) << 1000, 0, 320, 0, 1000, 240, 0, 0, 1); //又一种Mat初始化方式
Mat distCoeffs = (Mat_<double>(5,1) << 0.1, 0.01, -0.001, 0, 0);
fs << "cameraMatrix" << cameraMatrix << "distCoeffs" << distCoeffs;
//结构体
test_t t = { 3, 4, "hi hello" };
fs << "struct" << "{";
fs << "x" << t.x;
fs << "y" << t.y;
fs << "s" << t.s;
fs << "}";
//map关键字
map<string, int> m;
m["kobe"] = 90;
m["james"] = 80;
fs << "map" << "{";
map<string, int>::iterator it = m.begin();
for (; it != m.end(); it++)
{
fs << it->first << it->second;
}
fs << "}";
return 0;
}test.yml

读
#include <opencv2\opencv.hpp>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
using namespace cv;
typedef struct
{
int x;
int y;
string s;
} test_t;
int a, a1, arr[5];
Mat cameraMatrix2, distCoeffs2;
test_t t;
void data_info()
{
cout << "a" << a << endl;
cout << "a1" << a1 << endl;
cout << "cameraMatrix" << cameraMatrix2 << endl;
cout << " distCoeffs" << distCoeffs2 << endl;
cout << "t.x" << t.x << endl;
}
int main()
{
FileStorage fs("test.yml", FileStorage::READ);
//方式一:[]操作符
a = fs["a"];
a1 = (int)fs["a1"];
//数组,方式二:>> 流输出
fs["cameraMatrix"] >> cameraMatrix2;
fs["distCoeffs"] >> distCoeffs2;
//结构体,方式三:FileNode
FileNode struct_node = fs["struct"];
t.x = (int)struct_node["x"];
t.s = (string)struct_node["s"];
data_info();
return 0;
}























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








