前言
- 定义:OBB是相对于物体方向对齐的包围盒,不再局限于坐标轴对齐,因此包围点云时更加紧密。
- 优点:能够更好地贴合物体形状,减少空白区域。
- 缺点:计算较为复杂,需要计算物体的主方向,进行旋转和缩放变换。
算法原理
实现OBB通常涉及以下步骤:
- 计算凸包(Convex Hull)
- 使用主成分分析(Principal Component Analysis,简称PCA)找到最佳的旋转方向
- 根据这些方向确定包围盒的边界
步骤一:计算凸包
凸包是一组点的最小凸多边形,包含所有点,并且所有点都在多边形的边界上或内部。可以使用scipy库中的ConvexHull函数来计算。
import numpy as np
from scipy.spatial import ConvexHull
# 生成数据
mean = [0, 0]
cov = [[3, 1], [1, 2]]
points = np.random.multivariate_normal(mean, cov, 300)
# 计算凸包
convex_hull = ConvexHull(points)
# 可视化
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 8))
plt.scatter(points[:, 0], points[:, 1], s=10, alpha=0.5, label='Points')
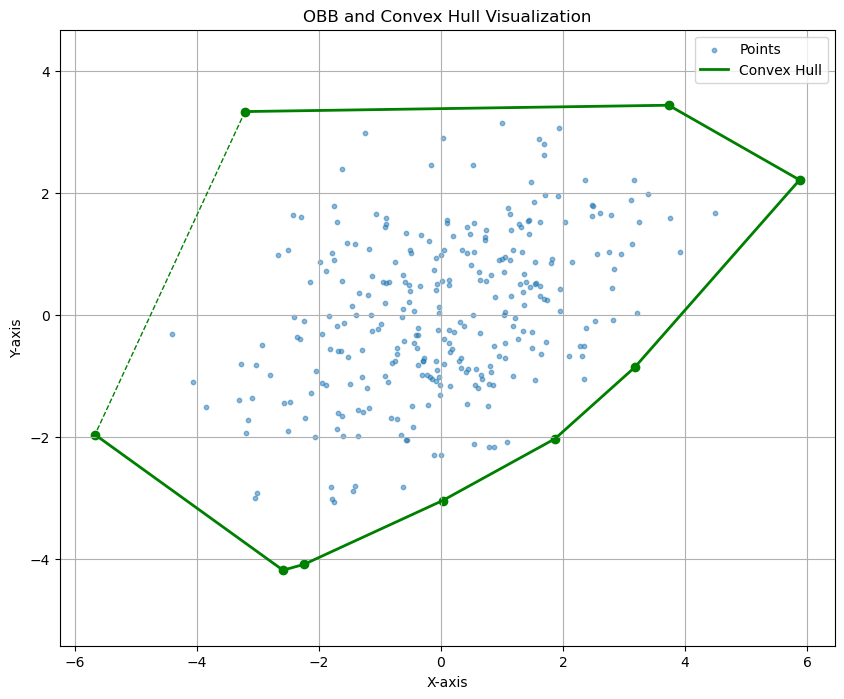
图 展示了图包得到的最外层点及其点之间的连线
步骤二:主成分分析(PCA)
PCA可以帮助我们找到数据的主方向。通过分析凸包顶点的协方差矩阵,我们可以得到主要的方向,这些方向定义了OBB的方向。
from sklearn.decomposition import PCA
pca = PCA(n_components=2)
pca.fit(points[convex_hull.vertices]) # 仅对凸包顶点进行PCA
步骤三:根据PCA方向计算OBB
根据PCA的结果,我们可以确定OBB的方向。然后,我们需要计算在这些方向上点的投影,以此来确定矩形的边界。
# OBB计算函数
def compute_obb(points):
# 使用PCA找到数据的主成分方向
pca = PCA(n_components=2)
pca.fit(points)
# 得到主轴
eigen_vectors = pca.components_
eigen_values = pca.explained_variance_
# 将点投影到主轴上
projected_points = np.dot(points, eigen_vectors.T)
# 计算包围盒的边界
min_proj = np.min(projected_points, axis=0)
max_proj = np.max(projected_points, axis=0)
# 通过主轴和包围盒的边界重构OBB顶点
obb_vertices = np.array([
[min_proj[0], min_proj[1]],
[min_proj[0], max_proj[1]],
[max_proj[0], max_proj[1]],
[max_proj[0], min_proj[1]]
])
# 将OBB顶点从PCA空间转换回原始空间
obb_vertices = np.dot(obb_vertices, eigen_vectors)
return obb_vertices
obb_vertices = compute_obb(points)
上述代码定义了计算OBB的整个过程,从计算凸包到应用PCA,最后确定边界框的角。每步都是基于数学原理进行建模,确保能找到最合适的包围盒。

完整代码
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.decomposition import PCA
from scipy.spatial import ConvexHull
# OBB计算函数
def compute_obb(points):
# 使用PCA找到数据的主成分方向
pca = PCA(n_components=2)
pca.fit(points)
# 得到主轴
eigen_vectors = pca.components_
eigen_values = pca.explained_variance_
# 将点投影到主轴上
projected_points = np.dot(points, eigen_vectors.T)
# 计算包围盒的边界
min_proj = np.min(projected_points, axis=0)
max_proj = np.max(projected_points, axis=0)
# 通过主轴和包围盒的边界重构OBB顶点
obb_vertices = np.array([
[min_proj[0], min_proj[1]],
[min_proj[0], max_proj[1]],
[max_proj[0], max_proj[1]],
[max_proj[0], min_proj[1]]
])
# 将OBB顶点从PCA空间转换回原始空间
obb_vertices = np.dot(obb_vertices, eigen_vectors)
return obb_vertices
np.random.seed(42)
mean = [0, 0]
cov = [[3, 1], [1, 2]]
points = np.random.multivariate_normal(mean, cov, 300)
# 计算OBB顶点
obb_vertices = compute_obb(points)
# 计算凸包
convex_hull = ConvexHull(points)
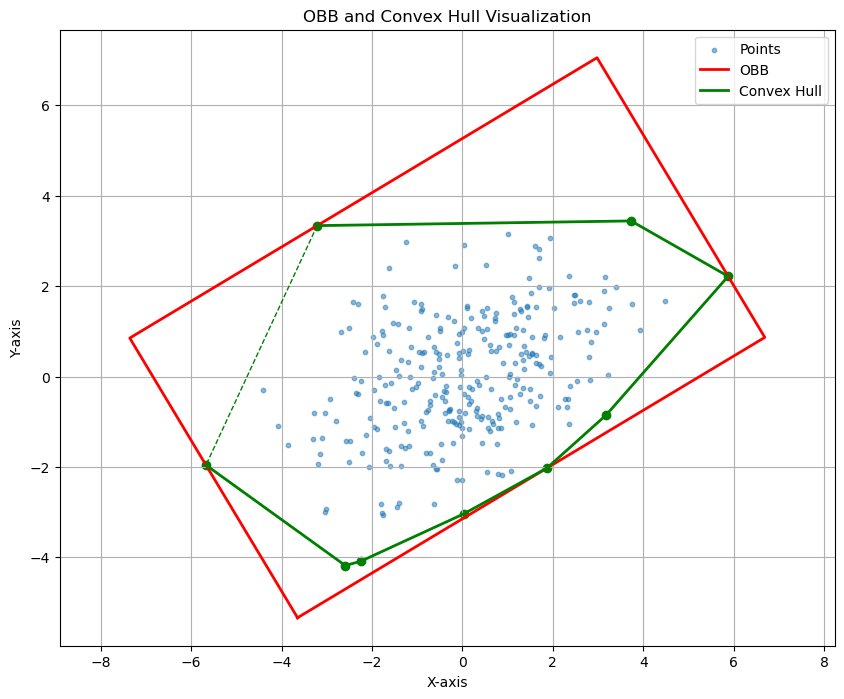
# 可视化点云、OBB和凸包
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 8))
plt.scatter(points[:, 0], points[:, 1], s=10, alpha=0.5, label='Points')
# 绘制OBB
obb_polygon = np.vstack([obb_vertices, obb_vertices[0]]) # 闭合OBB多边形
plt.plot(obb_polygon[:, 0], obb_polygon[:, 1], 'r-', linewidth=2, label='OBB')
# 绘制凸包
for simplex in convex_hull.simplices:
plt.plot(points[simplex, 0], points[simplex, 1], 'g--', linewidth=1)
plt.plot(points[convex_hull.vertices, 0], points[convex_hull.vertices, 1], 'g-', linewidth=2, label='Convex Hull')
plt.scatter(points[convex_hull.vertices, 0], points[convex_hull.vertices, 1], color='green')
plt.title('OBB and Convex Hull Visualization')
plt.xlabel('X-axis')
plt.ylabel('Y-axis')
plt.legend()
plt.axis('equal')
plt.grid(True)
plt.show()
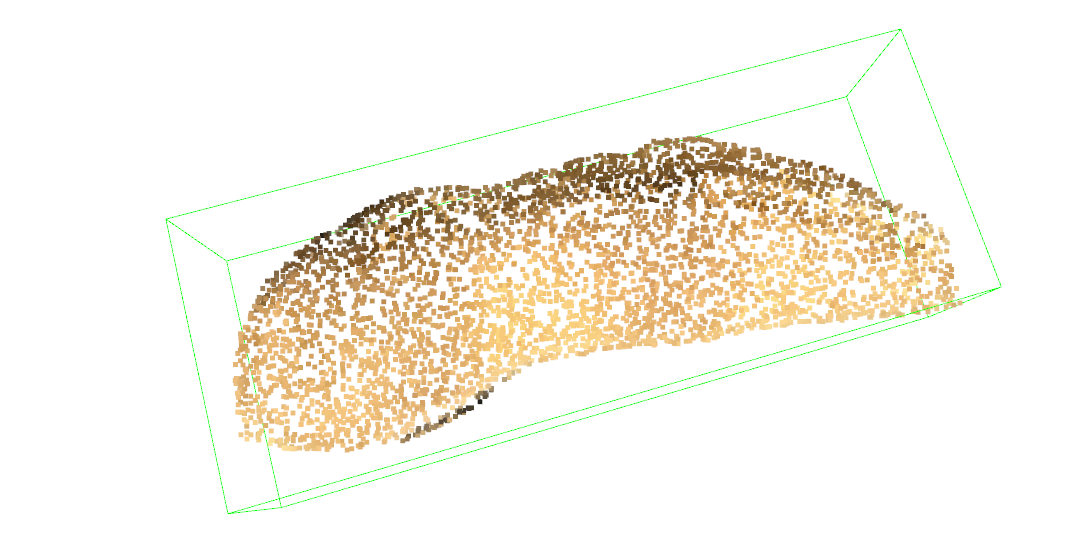
利用Open3D使用OBB算法
import open3d as o3d
import numpy as np
# 读取点云 txt 文件,假设文件名为 'point_cloud.txt'
file_path = './data/5.txt'
# 使用 numpy 读取数据
point_cloud_data = np.loadtxt(file_path)
# 提取点的坐标 (x, y, z) 和颜色 (r, g, b)
points = point_cloud_data[:, :3]
colors = point_cloud_data[:, 3:] / 255.0 # Open3D expects colors in [0, 1] range
# 创建 Open3D 点云对象
pcd = o3d.geometry.PointCloud()
pcd.points = o3d.utility.Vector3dVector(points)
pcd.colors = o3d.utility.Vector3dVector(colors)
# 计算AABB(轴对齐包围盒)
obb = pcd.get_oriented_bounding_box()
axis = o3d.geometry.TriangleMesh.create_coordinate_frame()
# 可视化点云和AABB
obb.color = (0, 1, 0)
o3d.visualization.draw_geometries([pcd,obb])
可视化结果:
























 536
536

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








