Lecture 1
资源:https://web.mit.edu/dimitrib/www/RLbook.html
在未来的自动控制方向研究中,强化学习与控制系统决策将通过互补的形式推导该领域技术的发展。强化学习与最优控制系统的核心是决策A technological “miracle” couched in sequential decision making methodology
人工智能(特别是强化学习)与动态规划是该研究方向的两个重要的理论基础:
- AI/RL = artificial intelligence / reinforcement learning: Learning through data/experience, simulation, model-free methods, feature-based representations
- Decision/Control/DP = Dynamic programming: Principle of Optimality; Markov decision problem; POMDP; policy iteration/value iteration
该领域的发展历史:Historical highlights
- Optimal control (Bellman, Shannon, and other 1950s)
- Al/Rl and decision/control/ DP ideas meet (late 80s-early 90s)
- First success, backgammon program (Tesauro, 1992, 1996)
- Algorithmic progress, analysis, applications (mid 90s)
- Machine learning, big data, robotics, deep neural networks (mid 00s)
- AlphaGo and Alphazero (Deep mind, google)
准确模型的动态规划(extra DP)问题是基础问题:
- 确定性: Deterministic - stochastic
- 最优化目的: Combinatorial optimization – optimal control/ infinite state control spaces
- 决策者数量:One decision maker – multi agent
近似DP/RL可以解决exact DP中存在的技术挑战:Approximate DP/RL overcomes the difficulties of exact DP by:
- Approximation (use neural nets and other architectures to reduce dimension)
- Simulation (use computer model in place of a math model)
该领域前沿:State of the art
- Broadly applicable methodology可高效率实施的方法学
- There are no methods that are guaranteed to work for all or even most problems 通用性
- There are enough methods to try with a reasonable chance of success for most types of optimization problems
- Role of the theory: guide the art, delineate the sound ideas.
关键点:时序决策/价值空间近似
Exact DP:最优决策(确定的状态转移过程中的最优决策)
Exact DP: making optimal decision in stages (deterministic state transitions)
当前状态下采用的决策,是能够将代价最小化的决策(或奖励最高的决策)
At current state, apply decision that minimizes
Min: Current stage cost + J*(next state)
Where J* (next state) is the optimal future cost, staring from the next state.
This defines an optimal policy (最优策略,an optimal control to apply at each state and stage)
Approximate DP: use approximiate cost J~ instead of J*
At current state, apply decision that minimizes
Min: Current stage csot + J~ (next state)
This defines a suboptimal policy (次优策略, an suboptimal control to apply)
计算近似代价函数的主要方法:
- (简化问题)Problem approximate: use as the optimal cost function of a related problem (computed by exact DP)
- (模型与测控)Rollout and model predictive control:Use as the cost function of some policy (computed by some optimization, simulation, and approximation)
- (神经网络和基于特征的体系框架):作为函数逼近器They serve as function approximator
- (采用仿真训练框架):Use of simulation to train the architectures. Approximation architecture involve parameters that are optimized using data
- (策略迭代/自学习/政策反复变化)Policy iteration/self-learning ,repeated policy changes. Multiple policies are sequentially generated, each is used to provide the data to train the next
目的 Purpose
- 研究生水平的近似DP/RL To explore the state of the art of approximate DP/RL at a graduate level
- AI与最优控制的共同边界 To explore the common boundary between ai and optimal control
- 跨界学习 To provide a bridge that workers with background in either field find it accessible
参考文献
l Exact DP: Dynamic p
- Programming and optimal control, Vol. 1 (2017), Vol. 2 (2012)
l Approximate DP/RL:
- Neuro-dynamic programming, 1996
- Reinforcement learning (new edition 2018, on-line)
- Approximate dynamic programming, 2011
RL/AL 与 DP/Control 中的名词对比
RL use Max/Value, DP uses Min/Cost
Reward of stage = opposite of cost of a stage
State value = opposite of state cost
Value (or state-value) function = opposite of cost funciotn
控制系统名词 Control system terminology
Agent = decision maker or controller
Action = decision or control
Environment = dynamic system
方法名词 Methods terminology
Learning = Solving a DP-related problem using simulation
Self-learning (or self-play in the context of games) = Solving a DP problem simulation-based policy iteration
Planning vs learning distinction = solving a DP problem with
model-based vs model-based simulation
有限层确定问题
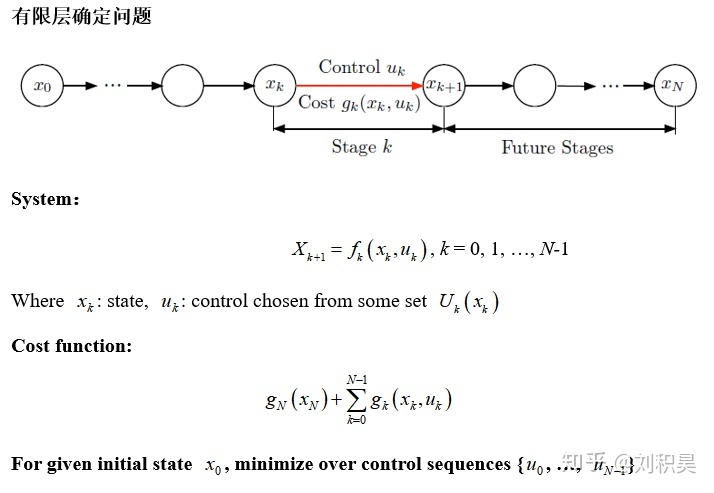
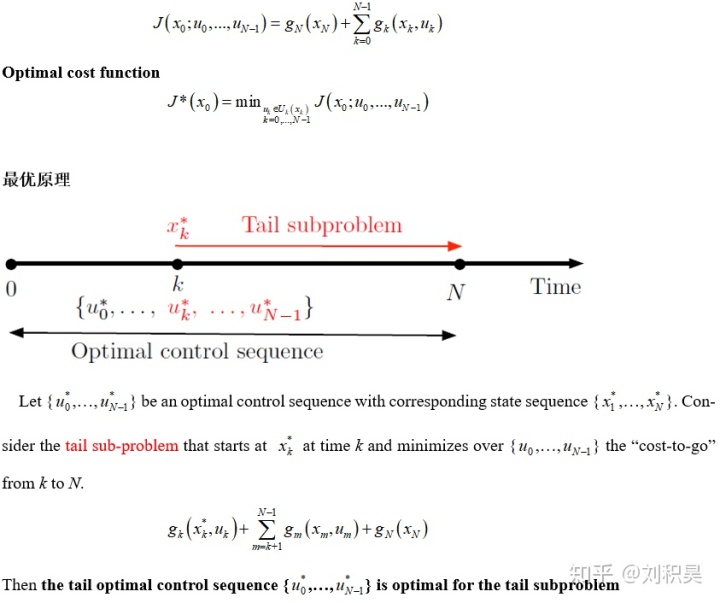










 本文探讨了强化学习与最优控制的关系,强调它们在自动控制领域的互补作用。文章介绍了动态规划的基础,包括确定性和随机性问题,以及单决策者和多决策者的情况。近似动态规划/强化学习通过神经网络和模拟来解决问题,提供了一种广泛适用但不保证通用的方法。文章旨在探索研究生级别的近似DP/RL,并为AI和控制领域的交叉学习建立桥梁。
本文探讨了强化学习与最优控制的关系,强调它们在自动控制领域的互补作用。文章介绍了动态规划的基础,包括确定性和随机性问题,以及单决策者和多决策者的情况。近似动态规划/强化学习通过神经网络和模拟来解决问题,提供了一种广泛适用但不保证通用的方法。文章旨在探索研究生级别的近似DP/RL,并为AI和控制领域的交叉学习建立桥梁。
















 1356
1356

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








