从零开始构建微博爬虫与数据分析系统
引言
社交媒体平台蕴含着海量的信息和数据,通过对这些数据的收集和分析,我们可以挖掘出有价值的见解。本文将详细介绍如何构建一个完整的微博爬虫和数据分析系统,从数据爬取、清洗、到多维度分析与可视化。
系统架构
整个系统分为两个主要模块:
- 微博爬虫模块:负责通过API获取微博数据并保存
- 数据分析模块:对获取的数据进行清洗和多维度分析
一、微博爬虫实现
1.1 爬虫设计思路
微博的数据爬取主要基于其Ajax接口,通过模拟浏览器请求获取JSON格式数据。主要挑战在于:
- 需要登录凭证(Cookie)才能访问完整内容
- 接口限制和反爬措施
- 数据格式的解析与清洗
1.2 核心代码实现
WeiboCrawler类是爬虫的核心,主要包含以下功能:
class WeiboCrawler:
def __init__(self, cookie=None):
# 初始化请求头和会话
self.headers = {...}
if cookie:
self.headers['Cookie'] = cookie
self.session = requests.Session()
self.session.headers.update(self.headers)
def get_user_info(self, user_id):
# 获取用户基本信息
url = f'https://weibo.com/ajax/profile/info?uid={user_id}'
# 实现...
def get_user_weibos(self, user_id, page=1, count=20):
# 获取用户微博列表
url = f'https://weibo.com/ajax/statuses/mymblog?uid={user_id}&page={page}&feature=0'
# 实现...
def crawl_user_weibos(self, user_id, max_pages=None):
# 爬取所有微博并返回结果
# 实现...
1.3 数据清洗与存储
爬取的原始数据需要进行清洗,主要包括:
- 去除HTML标签和特殊字符
- 提取时间、内容、图片链接等信息
- 识别转发内容并单独处理
清洗后的数据以结构化文本形式存储,便于后续分析:
def format_weibo(self, weibo):
# 格式化微博内容为易读格式
created_at = datetime.strptime(weibo['created_at'], '%a %b %d %H:%M:%S %z %Y')
text = self.clean_text(weibo.get('text', ''))
formatted = f"[{created_at.strftime('%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S')}]\n{text}\n"
# 处理转发内容、图片链接等
# ...
return formatted
二、数据分析模块
2.1 数据加载与预处理
WeiboAnalyzer类负责从文本文件加载微博数据,并转换为结构化形式:
def load_data(self):
# 从文件加载微博数据
with open(self.file_path, 'r', encoding='utf-8') as f:
lines = f.readlines()
# 提取用户信息和微博内容
# ...
print(f"成功加载 {len(self.weibos)} 条微博")
2.2 时间分布分析
分析微博发布的时间规律,包括日期、小时和星期分布:
def time_distribution_analysis(self):
# 提取日期和时间
dates = [weibo['date'].date() for weibo in self.weibos]
hours = [weibo['date'].hour for weibo in self.weibos]
weekdays = [weibo['date'].weekday() for weibo in self.weibos]
# 使用pandas和matplotlib进行统计和可视化
# ...
通过这一分析,我们可以了解用户在什么时间段最活跃,是否有固定的发布模式。
2.3 内容分析与关键词提取
使用jieba分词和TF-IDF算法提取微博内容的关键词:
def content_analysis(self):
# 合并所有微博内容
all_content = ' '.join([weibo['content'] for weibo in self.weibos])
# 使用jieba进行分词
jieba.analyse.set_stop_words('stopwords.txt')
words = jieba.cut(all_content)
# 过滤单个字符和数字
filtered_words = [word for word in words if len(word) > 1 and not word.isdigit()]
# 统计词频
word_counts = Counter(filtered_words)
# 提取关键词
keywords = jieba.analyse.extract_tags(all_content, topK=50, withWeight=True)
# 生成词云和关键词图表
# ...
词云能直观地展示内容主题,关键词分析则揭示了用户最关注的话题。
2.4 引用人物分析
分析微博中引用的名人或专家:
def quote_analysis(self):
# 定义可能被引用的人物列表
famous_people = [
'曾国藩', '尼采', '荣格', '苏格拉底', '马云', '武志红',
'阿德勒', '王安石', '苏东坡', '海德格尔', '左宗棠', '宗萨'
]
# 统计每个人物被引用的次数
quotes = {person: 0 for person in famous_people}
for weibo in self.weibos:
content = weibo['content']
for person in famous_people:
if person in content:
quotes[person] += 1
# 绘制引用人物条形图
# ...
这一分析可以揭示用户的思想倾向和崇拜的对象。
2.5 图片使用分析
分析微博中的图片使用情况:
def image_analysis(self):
# 统计带图片的微博数量
weibos_with_images = [weibo for weibo in self.weibos if weibo['images']]
image_counts = [len(weibo['images']) for weibo in weibos_with_images]
# 计算统计数据
total_weibos = len(self.weibos)
weibos_with_images_count = len(weibos_with_images)
percentage = weibos_with_images_count / total_weibos * 100 if total_weibos > 0 else 0
# 绘制饼图和分布图
# ...
三、可视化报告生成
最终,将所有分析结果整合为一个HTML报告:
def generate_report(self):
# 执行所有分析
self.time_distribution_analysis()
self.content_analysis()
self.quote_analysis()
self.image_analysis()
# 生成HTML报告
html_content = f"""
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>微博数据分析报告</title>
<style>
body {{ font-family: Arial, sans-serif; margin: 20px; }}
h1, h2 {{ color: #1DA1F2; }}
.section {{ margin-bottom: 30px; }}
img {{ max-width: 100%; border: 1px solid #ddd; }}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1>微博数据分析报告</h1>
<!-- 各部分分析结果 -->
<!-- ... -->
</body>
</html>
"""
with open('weibo_analysis_report.html', 'w', encoding='utf-8') as f:
f.write(html_content)
四、实际应用案例
以用户"侯小强"(ID: 1004524612)为例,我爬取了其全部1069条微博并进行分析。以下是一些关键发现:
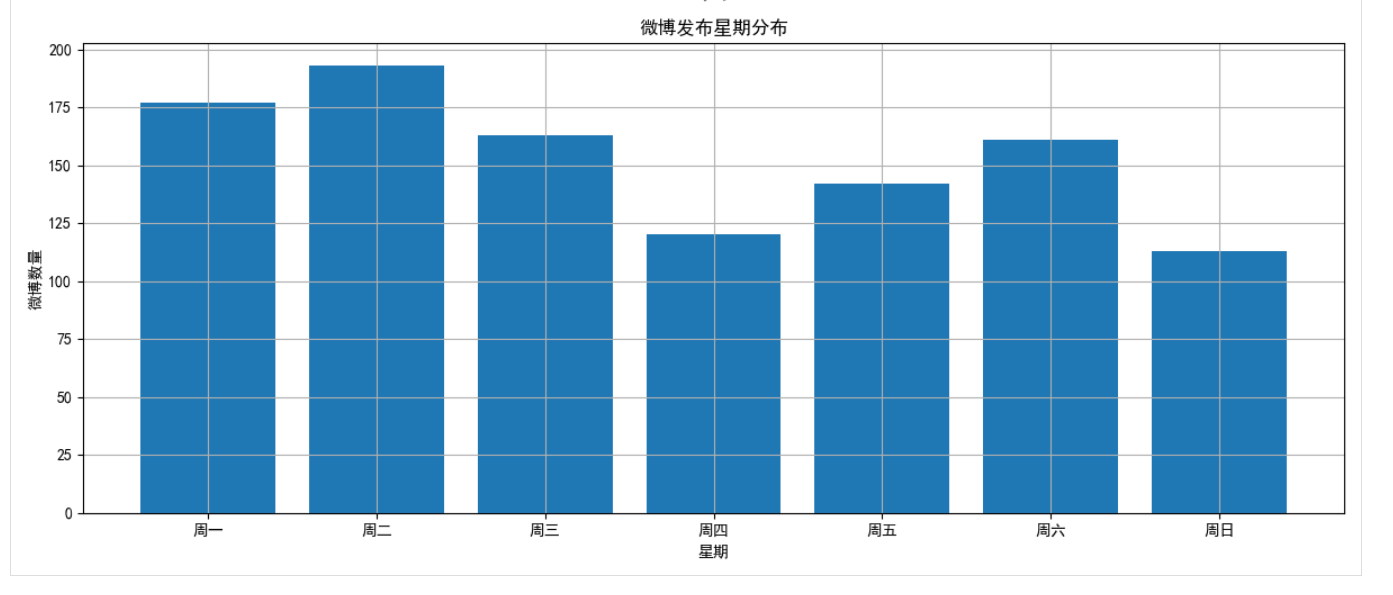
- 时间分布:该用户主要在晚上8点至10点发布微博,周六和周日活跃度明显高于工作日
- 关键词分析:心理、生活、思考是最常出现的关键词,表明用户关注心理学和个人成长话题
- 引用分析:尼采、荣格、苏格拉底是被最多引用的人物,表明用户对西方哲学有较深兴趣
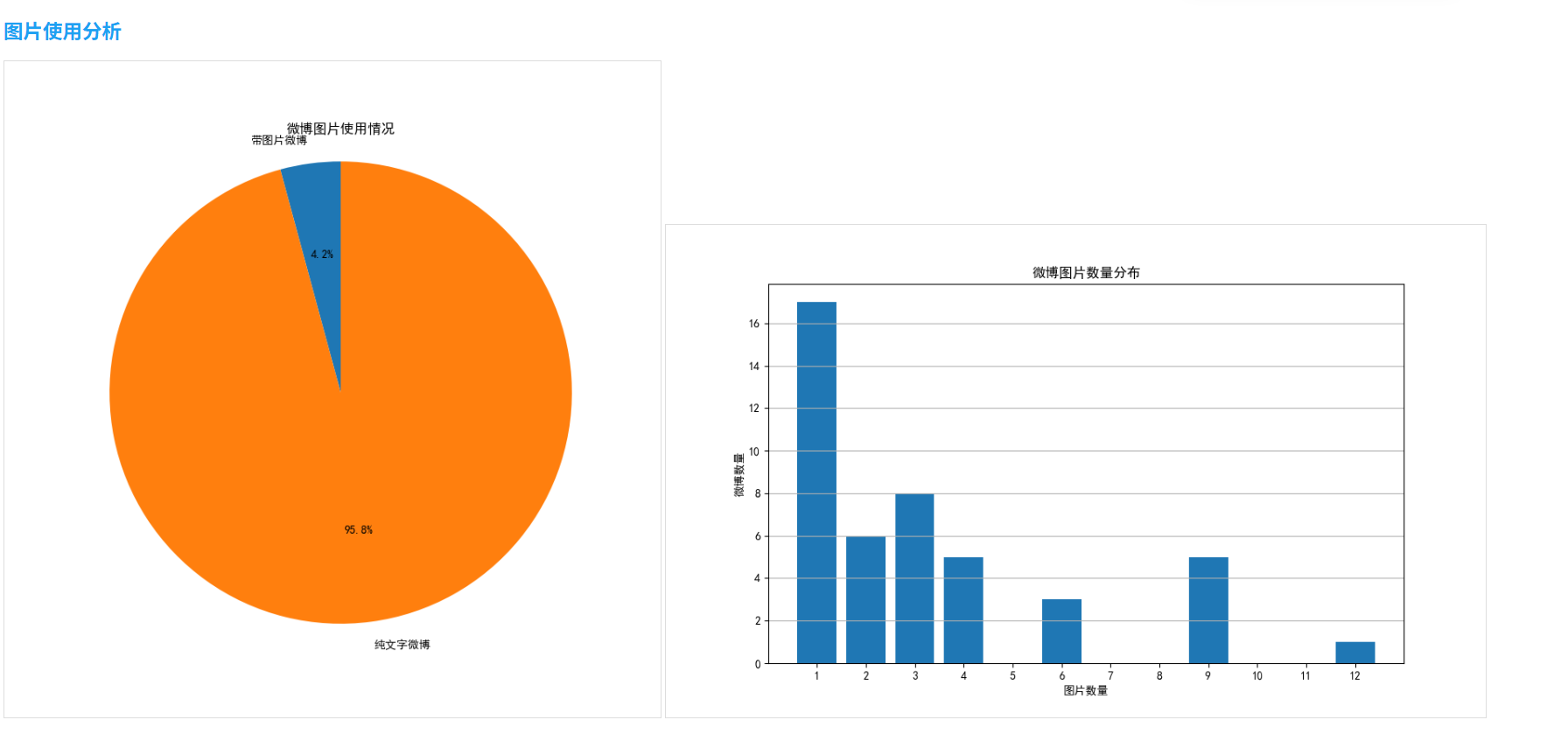
- 图片使用:约37%的微博包含图片,其中以单图发布为主
网页展示效果如下:






五、技术难点与解决方案
- 反爬虫机制:微博有严格的请求频率限制,我通过设置合理的请求间隔(1秒)和会话保持来解决
- 中文分词挑战:中文分词准确度对内容分析至关重要,使用jieba库并自定义停用词表提高分析质量
- 数据清洗:微博内容中包含大量HTML标签和特殊字符,需要精心设计正则表达式进行清洗
- 可视化定制:调整matplotlib的中文字体和样式设置,确保图表美观且信息丰富
六、总结与展望
本项目实现了一个完整的微博数据爬取和分析系统,可以帮助我们从用户的微博内容中挖掘出有价值的信息。未来的改进方向包括:
- 支持多用户批量爬取和对比分析
- 加入情感分析功能,评估微博的情感倾向
- 增加互动数据(点赞、评论、转发)的分析
- 开发时间序列分析,检测用户兴趣变化趋势
通过这个项目,我们不仅可以了解特定用户的发布规律和内容偏好,还能窥探社交媒体用户的思想动态和关注重点,为社会学和心理学研究提供数据支持。
完整代码:爬取数据代码-weibo_crawler.py
import requests
import json
import time
import os
import re
import argparse
from datetime import datetime
class WeiboCrawler:
def __init__(self, cookie=None):
"""
初始化微博爬虫
:param cookie: 用户登录的cookie字符串
"""
self.headers = {
'User-Agent': 'Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/91.0.4472.124 Safari/537.36',
'Accept': 'application/json, text/plain, */*',
'Accept-Language': 'zh-CN,zh;q=0.9',
'Referer': 'https://weibo.com/',
'Origin': 'https://weibo.com',
}
if cookie:
self.headers['Cookie'] = cookie
self.session = requests.Session()
self.session.headers.update(self.headers)
def get_user_info(self, user_id):
"""
获取用户基本信息
:param user_id: 用户ID
:return: 用户信息字典
"""
url = f'https://weibo.com/ajax/profile/info?uid={user_id}'
try:
response = self.session.get(url)
if response.status_code == 200:
data = response.json()
if data.get('ok') == 1 and 'data' in data:
return data['data']['user']
return None
except Exception as e:
print(f"获取用户信息失败: {e}")
return None
def get_user_weibos(self, user_id, page=1, count=20):
"""
获取用户的微博列表
:param user_id: 用户ID
:param page: 页码
:param count: 每页微博数量
:return: 微博列表
"""
url = f'https://weibo.com/ajax/statuses/mymblog?uid={user_id}&page={page}&feature=0'
try:
response = self.session.get(url)
if response.status_code == 200:
data = response.json()
if data.get('ok') == 1 and 'data' in data:
return data['data']['list'], data['data']['total']
return [], 0
except Exception as e:
print(f"获取微博列表失败: {e}")
return [], 0
def clean_text(self, text):
"""
清理文本内容,去除HTML标签等
:param text: 原始文本
:return: 清理后的文本
"""
if not text:
return ""
# 去除HTML标签
text = re.sub(r'<[^>]+>', '', text)
# 替换特殊字符
text = text.replace(' ', ' ')
text = text.replace('<', '<')
text = text.replace('>', '>')
text = text.replace('&', '&')
# 去除多余空格和换行
text = re.sub(r'\s+', ' ', text).strip()
return text
def format_weibo(self, weibo):
"""
格式化微博内容
:param weibo: 微博数据
:return: 格式化后的微博文本
"""
created_at = datetime.strptime(weibo['created_at'], '%a %b %d %H:%M:%S %z %Y').strftime('%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S')
text = self.clean_text(weibo.get('text', ''))
formatted = f"[{created_at}]\n"
formatted += f"{text}\n"
# 添加转发内容
if 'retweeted_status' in weibo and weibo['retweeted_status']:
retweeted = weibo['retweeted_status']
retweeted_user = retweeted.get('user', {}).get('screen_name', '未知用户')
retweeted_text = self.clean_text(retweeted.get('text', ''))
formatted += f"\n转发 @{retweeted_user}: {retweeted_text}\n"
# 添加图片链接
if 'pic_ids' in weibo and weibo['pic_ids']:
formatted += "\n图片链接:\n"
for pic_id in weibo['pic_ids']:
pic_url = f"https://wx1.sinaimg.cn/large/{pic_id}.jpg"
formatted += f"{pic_url}\n"
formatted += "-" * 50 + "\n"
return formatted
def crawl_user_weibos(self, user_id, max_pages=None):
"""
爬取用户的所有微博
:param user_id: 用户ID
:param max_pages: 最大爬取页数,None表示爬取全部
:return: 所有微博内容的列表
"""
user_info = self.get_user_info(user_id)
if not user_info:
print(f"未找到用户 {user_id} 的信息")
return []
screen_name = user_info.get('screen_name', user_id)
print(f"开始爬取用户 {screen_name} 的微博")
all_weibos = []
page = 1
total_pages = float('inf')
while (max_pages is None or page <= max_pages) and page <= total_pages:
print(f"正在爬取第 {page} 页...")
weibos, total = self.get_user_weibos(user_id, page)
if not weibos:
break
all_weibos.extend(weibos)
# 计算总页数
if total > 0:
total_pages = (total + 19) // 20 # 每页20条,向上取整
page += 1
# 防止请求过快
time.sleep(1)
print(f"共爬取到 {len(all_weibos)} 条微博")
return all_weibos, screen_name
def save_weibos_to_file(self, user_id, max_pages=None):
"""
爬取用户微博并保存到文件
:param user_id: 用户ID
:param max_pages: 最大爬取页数
:return: 保存的文件路径
"""
weibos, screen_name = self.crawl_user_weibos(user_id, max_pages)
if not weibos:
return None
# 创建文件名
filename = f"{user_id}_weibos.txt"
# 写入文件
with open(filename, 'w', encoding='utf-8') as f:
f.write(f"用户: {screen_name} (ID: {user_id})\n")
f.write(f"爬取时间: {datetime.now().strftime('%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S')}\n")
f.write(f"微博数量: {len(weibos)}\n")
f.write("=" * 50 + "\n\n")
for weibo in weibos:
formatted = self.format_weibo(weibo)
f.write(formatted)
print(f"微博内容已保存到文件: {filename}")
return filename
def main():
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description='微博爬虫 - 爬取指定用户的微博')
parser.add_argument('user_id', help='微博用户ID')
parser.add_argument('--cookie', help='登录cookie字符串', default=None)
parser.add_argument('--max-pages', type=int, help='最大爬取页数', default=None)
parser.add_argument('--cookie-file', help='包含cookie的文件路径', default=None)
args = parser.parse_args()
cookie = args.cookie
# 如果提供了cookie文件,从文件读取cookie
if args.cookie_file and not cookie:
try:
with open(args.cookie_file, 'r', encoding='utf-8') as f:
cookie = f.read().strip()
except Exception as e:
print(f"读取cookie文件失败: {e}")
crawler = WeiboCrawler(cookie=cookie)
crawler.save_weibos_to_file(args.user_id, args.max_pages)
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
数据分析代码:weibo_analsis.py
import re
import os
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from datetime import datetime
import jieba
import jieba.analyse
from collections import Counter
import numpy as np
from wordcloud import WordCloud
import matplotlib.font_manager as fm
from matplotlib.font_manager import FontProperties
import pandas as pd
from matplotlib.dates import DateFormatter
import seaborn as sns
# 设置中文字体
plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['SimHei'] # 用来正常显示中文标签
plt.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False # 用来正常显示负号
class WeiboAnalyzer:
def __init__(self, file_path):
"""
初始化微博分析器
:param file_path: 微博数据文件路径
"""
self.file_path = file_path
self.weibos = []
self.user_info = {}
self.load_data()
def load_data(self):
"""
加载微博数据
"""
with open(self.file_path, 'r', encoding='utf-8') as f:
lines = f.readlines()
# 提取用户信息
if lines and "用户:" in lines[0]:
user_info_match = re.match(r'用户: (.*) \(ID: (.*)\)', lines[0])
if user_info_match:
self.user_info['name'] = user_info_match.group(1)
self.user_info['id'] = user_info_match.group(2)
if len(lines) > 2 and "微博数量:" in lines[2]:
count_match = re.match(r'微博数量: (\d+)', lines[2])
if count_match:
self.user_info['count'] = int(count_match.group(1))
# 提取微博内容
current_weibo = None
for line in lines:
# 新微博的开始
if re.match(r'\[\d{4}-\d{2}-\d{2} \d{2}:\d{2}:\d{2}\]', line):
if current_weibo:
self.weibos.append(current_weibo)
date_match = re.match(r'\[(\d{4}-\d{2}-\d{2} \d{2}:\d{2}:\d{2})\]', line)
if date_match:
date_str = date_match.group(1)
content = line[len(date_str) + 3:].strip()
current_weibo = {
'date': datetime.strptime(date_str, '%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S'),
'content': content,
'images': [],
'is_retweet': False,
'retweet_content': '',
'retweet_user': ''
}
# 图片链接
elif line.strip().startswith('https://wx1.sinaimg.cn/'):
if current_weibo:
current_weibo['images'].append(line.strip())
# 转发内容
elif current_weibo and line.strip().startswith('转发 @'):
current_weibo['is_retweet'] = True
retweet_match = re.match(r'转发 @(.*): (.*)', line.strip())
if retweet_match:
current_weibo['retweet_user'] = retweet_match.group(1)
current_weibo['retweet_content'] = retweet_match.group(2)
# 继续添加内容
elif current_weibo and not line.strip() == '-' * 50 and not line.strip() == '=' * 50:
current_weibo['content'] += ' ' + line.strip()
# 添加最后一条微博
if current_weibo:
self.weibos.append(current_weibo)
print(f"成功加载 {len(self.weibos)} 条微博")
def time_distribution_analysis(self):
"""
分析微博发布时间分布
"""
if not self.weibos:
print("没有微博数据可分析")
return
# 提取日期和时间
dates = [weibo['date'].date() for weibo in self.weibos]
hours = [weibo['date'].hour for weibo in self.weibos]
weekdays = [weibo['date'].weekday() for weibo in self.weibos]
# 创建日期DataFrame
df = pd.DataFrame({
'date': dates,
'hour': hours,
'weekday': weekdays
})
# 按日期统计
date_counts = df['date'].value_counts().sort_index()
# 按小时统计
hour_counts = df['hour'].value_counts().sort_index()
# 按星期几统计
weekday_counts = df['weekday'].value_counts().sort_index()
weekday_names = ['周一', '周二', '周三', '周四', '周五', '周六', '周日']
# 创建图表
fig, axes = plt.subplots(3, 1, figsize=(12, 15))
# 日期分布图
axes[0].plot(date_counts.index, date_counts.values, marker='o')
axes[0].set_title('微博发布日期分布')
axes[0].set_xlabel('日期')
axes[0].set_ylabel('微博数量')
axes[0].grid(True)
# 小时分布图
axes[1].bar(hour_counts.index, hour_counts.values)
axes[1].set_title('微博发布时间段分布')
axes[1].set_xlabel('小时')
axes[1].set_ylabel('微博数量')
axes[1].set_xticks(range(0, 24))
axes[1].grid(True)
# 星期几分布图
axes[2].bar([weekday_names[i] for i in weekday_counts.index], weekday_counts.values)
axes[2].set_title('微博发布星期分布')
axes[2].set_xlabel('星期')
axes[2].set_ylabel('微博数量')
axes[2].grid(True)
plt.tight_layout()
plt.savefig('time_distribution.png')
plt.close()
print("时间分布分析完成,结果已保存为 time_distribution.png")
def content_analysis(self):
"""
分析微博内容
"""
if not self.weibos:
print("没有微博数据可分析")
return
# 合并所有微博内容
all_content = ' '.join([weibo['content'] for weibo in self.weibos])
# 使用jieba进行分词
jieba.analyse.set_stop_words('stopwords.txt') # 如果有停用词表
words = jieba.cut(all_content)
# 过滤掉单个字符和数字
filtered_words = [word for word in words if len(word) > 1 and not word.isdigit()]
# 统计词频
word_counts = Counter(filtered_words)
# 提取关键词
keywords = jieba.analyse.extract_tags(all_content, topK=50, withWeight=True)
# 创建词云
wordcloud = WordCloud(
font_path='simhei.ttf', # 设置中文字体
width=800,
height=400,
background_color='white'
).generate_from_frequencies(dict(word_counts))
# 绘制词云图
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 6))
plt.imshow(wordcloud, interpolation='bilinear')
plt.axis('off')
plt.title('微博内容词云')
plt.savefig('wordcloud.png')
plt.close()
# 绘制关键词条形图
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 8))
keywords_dict = dict(keywords[:20])
plt.barh(list(reversed(list(keywords_dict.keys()))),
list(reversed(list(keywords_dict.values()))))
plt.title('微博内容关键词TOP20')
plt.xlabel('权重')
plt.tight_layout()
plt.savefig('keywords.png')
plt.close()
print("内容分析完成,结果已保存为 wordcloud.png 和 keywords.png")
def quote_analysis(self):
"""
分析微博中引用的人物
"""
if not self.weibos:
print("没有微博数据可分析")
return
# 定义可能被引用的人物列表
famous_people = [
'曾国藩', '尼采', '荣格', '苏格拉底', '马云', '武志红',
'阿德勒', '王安石', '苏东坡', '海德格尔', '左宗棠', '宗萨'
]
# 统计每个人物被引用的次数
quotes = {person: 0 for person in famous_people}
for weibo in self.weibos:
content = weibo['content']
for person in famous_people:
if person in content:
quotes[person] += 1
# 过滤掉未被引用的人物
quotes = {k: v for k, v in quotes.items() if v > 0}
# 按引用次数排序
sorted_quotes = dict(sorted(quotes.items(), key=lambda item: item[1], reverse=True))
# 绘制引用人物条形图
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 6))
plt.bar(sorted_quotes.keys(), sorted_quotes.values())
plt.title('微博中引用人物统计')
plt.xlabel('人物')
plt.ylabel('引用次数')
plt.xticks(rotation=45)
plt.tight_layout()
plt.savefig('quotes.png')
plt.close()
print("引用人物分析完成,结果已保存为 quotes.png")
def image_analysis(self):
"""
分析微博中的图片使用情况
"""
if not self.weibos:
print("没有微博数据可分析")
return
# 统计带图片的微博数量
weibos_with_images = [weibo for weibo in self.weibos if weibo['images']]
image_counts = [len(weibo['images']) for weibo in weibos_with_images]
# 计算统计数据
total_weibos = len(self.weibos)
weibos_with_images_count = len(weibos_with_images)
percentage = weibos_with_images_count / total_weibos * 100 if total_weibos > 0 else 0
# 绘制饼图
plt.figure(figsize=(8, 8))
plt.pie([weibos_with_images_count, total_weibos - weibos_with_images_count],
labels=['带图片微博', '纯文字微博'],
autopct='%1.1f%%',
startangle=90)
plt.title('微博图片使用情况')
plt.axis('equal')
plt.savefig('image_usage.png')
plt.close()
# 绘制图片数量分布
if image_counts:
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 6))
counter = Counter(image_counts)
plt.bar(counter.keys(), counter.values())
plt.title('微博图片数量分布')
plt.xlabel('图片数量')
plt.ylabel('微博数量')
plt.xticks(range(1, max(image_counts) + 1))
plt.grid(axis='y')
plt.savefig('image_count.png')
plt.close()
print("图片使用分析完成,结果已保存为 image_usage.png 和 image_count.png")
def generate_report(self):
"""
生成分析报告
"""
# 执行所有分析
self.time_distribution_analysis()
self.content_analysis()
self.quote_analysis()
self.image_analysis()
# 生成HTML报告
html_content = f"""
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>微博数据分析报告</title>
<style>
body {{ font-family: Arial, sans-serif; margin: 20px; }}
h1, h2 {{ color: #1DA1F2; }}
.section {{ margin-bottom: 30px; }}
img {{ max-width: 100%; border: 1px solid #ddd; }}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1>微博数据分析报告</h1>
<div class="section">
<h2>用户信息</h2>
<p>用户名: {self.user_info.get('name', '未知')}</p>
<p>用户ID: {self.user_info.get('id', '未知')}</p>
<p>微博总数: {self.user_info.get('count', len(self.weibos))}</p>
<p>分析微博数: {len(self.weibos)}</p>
</div>
<div class="section">
<h2>时间分布分析</h2>
<img src="time_distribution.png" alt="时间分布分析">
</div>
<div class="section">
<h2>内容分析</h2>
<h3>词云</h3>
<img src="wordcloud.png" alt="词云">
<h3>关键词</h3>
<img src="keywords.png" alt="关键词">
</div>
<div class="section">
<h2>引用人物分析</h2>
<img src="quotes.png" alt="引用人物分析">
</div>
<div class="section">
<h2>图片使用分析</h2>
<img src="image_usage.png" alt="图片使用情况">
<img src="image_count.png" alt="图片数量分布">
</div>
</body>
</html>
"""
with open('weibo_analysis_report.html', 'w', encoding='utf-8') as f:
f.write(html_content)
print("分析报告已生成: weibo_analysis_report.html")
def main():
# 创建停用词文件(如果需要)
stopwords = [
'的', '了', '在', '是', '我', '有', '和', '就', '不', '人', '都',
'一', '一个', '上', '也', '很', '到', '说', '要', '去', '你', '会',
'着', '没有', '看', '好', '自己', '这', '那', '啊', '吧', '把', '给',
'但是', '但', '还', '可以', '这个', '这样', '这些', '因为', '所以',
'如果', '就是', '么', '什么', '只是', '只有', '这种', '那个', '他们'
]
with open('stopwords.txt', 'w', encoding='utf-8') as f:
f.write('\n'.join(stopwords))
# 分析微博数据
analyzer = WeiboAnalyzer('1004524612_weibos.txt')
analyzer.generate_report()
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
所有数据以及代码也放在下面的仓库里了:源码链接
参考资料
- Python爬虫实战指南
- 《数据可视化之美》
- 自然语言处理与文本挖掘技术
- jieba中文分词官方文档























 2331
2331

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








