代码参考
- https://github.com/honeyandme/RAGQnASystem
- https://github.com/LongxingTan/open-retrievals
- https://github.com/WangRongsheng/MedQA-ChatGLM
TLDR
if '疾病症状' in entities and '疾病' not in entities:
sql_q = "match (a:疾病)-[r:疾病的症状]->(b:疾病症状 {名称:'%s'}) return a.名称" % (entities['疾病症状'])
res = list(client.run(sql_q).data()[0].values())
# print('res=',res)
if len(res)>0:
entities['疾病'] = random.choice(res)
all_en = "、".join(res)
prompt+=f"<提示>用户有{entities['疾病症状']}的情况,知识库推测其可能是得了{all_en}。请注意这只是一个推测,你需要明确告知用户这一点。</提示>"
根据实体确定图数据库查询语句,从中查询得到结果。疾病症状和知识库查询结果一起组成prompt,输入大模型中
系统设计
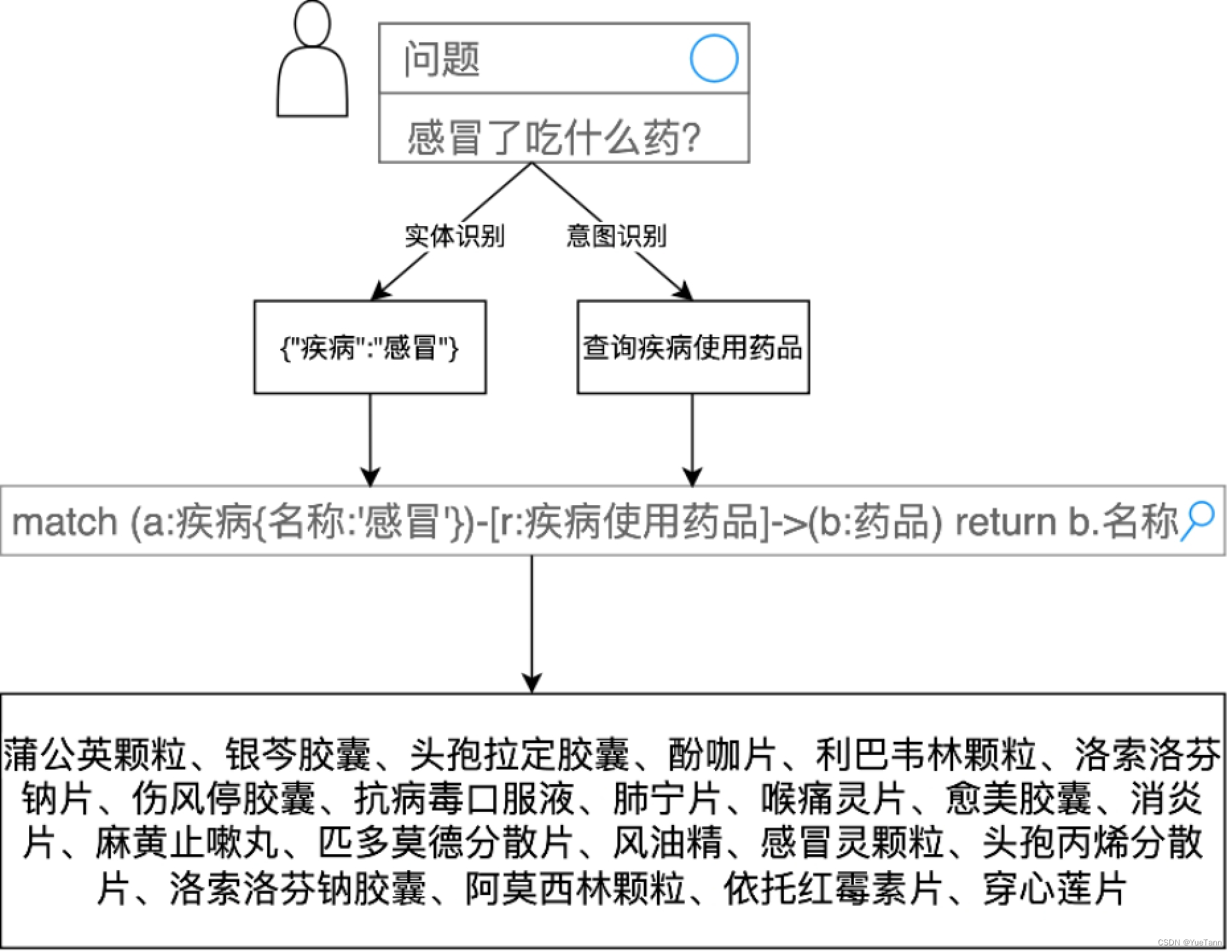
实体识别
- token classification
意图识别
- sequence classification
知识图谱
- graph
对话
搭建知识图谱
实体识别
LLM做的特点
优势
- they can handle a broad spectrum of entity types;
- they are highly adaptable to various domains and languages;
- their performance often surpasses that of traditional rule-based (e.g. regular expressions) or feature-based NER system;
- they can capture contextual information and context dependencies more effectively (e.g. sentiment analysis or intent detection);
- LLMs are capable of transfer learning, meaning they can be pre-trained on a general language corpus and fine-tuned for specific NER tasks, thus requiring fewer annotated data points for training.
con
- LLMs may raise concerns about model bias, model interpretability and ethical considerations, which require careful attention;
- LLM responses may contain “hallucinations” that can lead to the spread of misinformation;
- Fine-tuning requires designing appropriate training data, carefully selecting hyper-parameters, and often involves substantial computational resources.
prompt
intent
intent_name_field = ResponseSchema(name=“intent”, description=f"Based on the latest user message, extract the user message intent. Here are some possible labels: ‘greetings’, ‘booking’, ‘complaint’ or ‘other’")
user need
user_need_field = ResponseSchema(name=“user_need”, description=“Rephrase the latest user request and make it a meaningful question without missing any details. Use ‘’ if it is not available”)
user sentiment
sentiment_field = ResponseSchema(name=“sentiment”, description=“Based on the latest user message, extract the user sentiment. Here are some possible labels: ‘positive’, ‘neutral’, ‘negative’, ‘mixed’ or ‘other’”)
number of pizzas to be ordered
n_pizzas_field = ResponseSchema(name=“n_pizzas”, description=“Based on the user need, extract the number of pizzas to be made. Use ‘’ if it is not available”)






















 908
908











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










