一、简介
AutoResetEvent 是 .NET 中一个重要的线程同步原语,用于线程间的信号通知。下面我将从多个方面详细讲解 AutoResetEvent。
AutoResetEvent 是 System.Threading 命名空间下的一个类,它表示一个线程同步事件,在等待线程被释放后会自动重置。
核心特点
-
自动重置:当事件被设置(Set)后,它会自动释放一个等待线程,然后立即重置为非信号状态
-
线程同步:用于协调多个线程的执行顺序
-
内核模式:基于操作系统内核对象实现,会有一定的性能开销
二、工作原理
AutoResetEvent 有两种状态:
-
有信号状态(Set):允许一个等待线程继续执行
-
无信号状态(Reset):使后续线程等待
当调用 Set() 方法时:
-
如果有线程正在等待,则释放其中一个线程,然后自动重置为无信号状态
-
如果没有线程等待,则保持有信号状态,直到第一个线程调用 WaitOne()
AutoResetEvent 方法
public class AutoResetEvent : EventWaitHandle
{
// 构造函数,initialState参数指定初始状态
public AutoResetEvent(bool initialState);
// 将事件设置为有信号状态,释放一个等待线程
public bool Set();
// 将事件设置为无信号状态
public bool Reset();
// 阻塞当前线程,直到事件变为有信号状态
public bool WaitOne();
public bool WaitOne(int millisecondsTimeout);
public bool WaitOne(TimeSpan timeout);
}三、基本使用
案例一
C# NetworkStream、ConcurrentDictionary、Socket、SerialPort、广域IP、AutoResetEvent-CSDN博客
public class test
{
public AutoResetEvent autoResetEvent = new AutoResetEvent(false); // 初始状态为无信号状态
public void workerThread()
{
Console.WriteLine("worker thread start ,waiting for signal ....... "+ DateTime.Now.ToLongTimeString().ToString());
autoResetEvent.WaitOne(); // 等待信号
Console.WriteLine("worker thread received signal , continuing work------ " + DateTime.Now.ToLongTimeString().ToString());
}
}
// 调用:
static void Main()
{
Application.EnableVisualStyles();
Application.SetCompatibleTextRenderingDefault(false);
// Application.Run(new Form1());
test t=new test();
Thread workder = new Thread(t.workerThread);
workder.Start();
Thread.Sleep(3000); //休息3s
Console.WriteLine("Main thread signals worker thread ........ " + DateTime.Now.ToLongTimeString().ToString());
t.autoResetEvent.Set(); // 唤醒worker 信号
Console.ReadLine();
}
案例二-两个线程
static AutoResetEvent itemAvailable = new AutoResetEvent(false);
static Queue<int> queue = new Queue<int>();
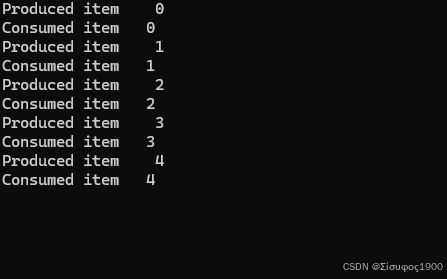
static void Producer()
{
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
Thread.Sleep(5000); // 模拟生产时间
lock (queue)
{
queue.Enqueue(i);
Console.WriteLine($"Produced item {i}");
}
itemAvailable.Set(); // 通知消费者有新项
}
}
static void Consumer()
{
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
itemAvailable.WaitOne(); // 等待新项
lock (queue)
{
int item = queue.Dequeue();
Console.WriteLine($"Consumed item {item}");
}
}
}
调用:
Thread producer = new Thread(Producer);
Thread consumer = new Thread(Consumer);
producer.Start();
consumer.Start();
Console.ReadLine(); 案例三3个线程
static AutoResetEvent autoEvent = new AutoResetEvent(false);
static void Worker(int id)
{
Console.WriteLine($"Worker {id} waiting..." + DateTime.Now.ToLongTimeString().ToString());
autoEvent.WaitOne();
Console.WriteLine($"Worker {id} released!" + DateTime.Now.ToLongTimeString().ToString());
}
调用:
// 启动3个工作线程
for (int i = 1; i <= 3; i++)
{
int id = i;
new Thread(() => Worker(id)).Start();
}
Thread.Sleep(2000);
Console.WriteLine("Releasing 1 worker..." + DateTime.Now.ToLongTimeString().ToString());
autoEvent.Set(); // 只会释放一个线程
Thread.Sleep(3000);
Console.WriteLine("Releasing 2 worker..." + DateTime.Now.ToLongTimeString().ToString());
autoEvent.Set(); // 释放第二个线程
Thread.Sleep(3000);
Console.WriteLine("Releasing 3 worker..." + DateTime.Now.ToLongTimeString().ToString());
autoEvent.Set(); // 释放第三个线程
Console.ReadLine(); 四、多线程使用
说明:
当启动多个线程后,如果需要使用 AutoResetEvent 来精确控制其中某个特定线程的执行,可以采用以下几种方法:
方法一:为每个线程创建单独的 AutoResetEvent
// 为三个线程分别创建 AutoResetEvent
static AutoResetEvent event1 = new AutoResetEvent(false);
static AutoResetEvent event2 = new AutoResetEvent(false);
static AutoResetEvent event3 = new AutoResetEvent(false);
static void Main()
{
Application.EnableVisualStyles();
Application.SetCompatibleTextRenderingDefault(false);
// 启动三个线程,每个线程使用自己的 AutoResetEvent
Thread thread1 = new Thread(() => WorkerTest(1, event1));
Thread thread2 = new Thread(() => WorkerTest(2, event2));
Thread thread3 = new Thread(() => WorkerTest(3, event3));
thread1.Start();
thread2.Start();
thread3.Start();
// 只让第二个线程继续
Thread.Sleep(3000);
Console.WriteLine("只唤醒第二个线程" + DateTime.Now.ToLongTimeString().ToString());
event2.Set(); // 只设置第二个线程的事件
Console.ReadLine();
}
static void WorkerTest(int id, AutoResetEvent signal)
{
Console.WriteLine($"Worker {id} 开始等待..." + DateTime.Now.ToLongTimeString().ToString());
signal.WaitOne();
Console.WriteLine($"Worker {id} 收到信号继续执行!" + DateTime.Now.ToLongTimeString().ToString());
}

方法二:使用共享 AutoResetEvent 结合标识变量
一个AutoResetEvent 控制3个线程
// 为三个线程分别创建 AutoResetEvent
static AutoResetEvent eventtest = new AutoResetEvent(false);
static int AutoResetEventId = 0;
static object lockobj=new object();
/// <summary>
/// 应用程序的主入口点。
/// </summary>
[STAThread]
static void Main()
{
Application.EnableVisualStyles();
Application.SetCompatibleTextRenderingDefault(false);
// 启动三个线程
Thread thread1 = new Thread(() => WorkPlace(1));
Thread thread2 = new Thread(() => WorkPlace(2));
Thread thread3 = new Thread(() => WorkPlace(3));
thread1.Start();
thread2.Start();
thread3.Start();
// 只让第二个线程继续
Thread.Sleep(2000);
Console.WriteLine("准备唤醒第二个线程" + DateTime.Now.ToLongTimeString().ToString());
lock (lockobj)
{
AutoResetEventId = 2; // 设置允许线程2通过
eventtest.Set(); // 发送信号
}
Console.ReadLine();
}
static void WorkPlace(int id)
{
Console.WriteLine($"WorkPlace {id} "+DateTime.Now.ToLongTimeString().ToString());
// 循环等待直到本线程的信号拿到
while (true)
{
eventtest.WaitOne();
lock (lockobj)
{
if (AutoResetEventId==id)
{
Console.WriteLine($"WorkPlace {id} 收到启动信号 " + DateTime.Now.ToLongTimeString().ToString());
AutoResetEventId = 0;
break;
}
else
{
// 如果不是本线程的信号,怎不需要处理
eventtest.Set();
}
}
}
}

方法三:使用 Dictionary 管理线程和事件
// 为三个线程分别创建 AutoResetEvent
static Dictionary<int, AutoResetEvent> threadEvents = new Dictionary<int, AutoResetEvent>();
static object dictLock = new object();
/// <summary>
/// 应用程序的主入口点。
/// </summary>
[STAThread]
static void Main()
{
Application.EnableVisualStyles();
Application.SetCompatibleTextRenderingDefault(false);
// 启动三个线程
new Thread(() => Worker2(1)).Start();
new Thread(() => Worker2(2)).Start();
new Thread(() => Worker2(3)).Start();
// 等待所有线程注册完成
Thread.Sleep(1000);
// 只唤醒第二个线程
lock (dictLock)
{
if (threadEvents.TryGetValue(2, out var eventToSet))
{
Console.WriteLine("唤醒第二个线程" + DateTime.Now.ToLongTimeString().ToString());
eventToSet.Set();
}
}
Console.ReadLine();
}
static void Worker2(int id)
{
AutoResetEvent myEvent;
lock (dictLock)
{
myEvent = new AutoResetEvent(false);
threadEvents[id] = myEvent;
}
Console.WriteLine($"Worker2 {id} 开始等待..." + DateTime.Now.ToLongTimeString().ToString());
myEvent.WaitOne();
Console.WriteLine($"Worker2 {id} 收到信号继续执行!" + DateTime.Now.ToLongTimeString().ToString());
}

方法四:使用 ManualResetEvent 和条件判断
如果需要更灵活的控制,可以结合 ManualResetEvent 和条件判断。
static ManualResetEvent manualEvent = new ManualResetEvent(false);
static int targetThreadId = 0;
static void Worker3(int id)
{
Console.WriteLine($"Worker {id} 开始等待..." + DateTime.Now.ToLongTimeString().ToString());
while (true)
{
manualEvent.WaitOne();
if (targetThreadId == id)
{
Console.WriteLine($"Worker {id} 收到信号继续执行!" + DateTime.Now.ToLongTimeString().ToString());
manualEvent.Reset(); // 重置事件
break;
}
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 应用程序的主入口点。
/// </summary>
[STAThread]
static void Main()
{
Application.EnableVisualStyles();
Application.SetCompatibleTextRenderingDefault(false);
// 启动三个线程
new Thread(() => Worker3(1)).Start();
new Thread(() => Worker3(2)).Start();
new Thread(() => Worker3(3)).Start();
// 只让第二个线程继续
Thread.Sleep(1000);
Console.WriteLine("准备唤醒第二个线程");
targetThreadId = 2;
manualEvent.Set(); // 设置事件为有信号状态
Console.ReadLine();
}

最佳实践建议
-
优先使用方法一:为每个线程分配单独的 AutoResetEvent 是最清晰、最可靠的方式
-
避免共享事件:共享 AutoResetEvent 会增加复杂性,容易引入竞态条件
-
考虑使用更高级同步原语:如 Barrier、Semaphore 或 Monitor 可能更适合复杂场景
-
确保资源释放:记得在使用完毕后调用 Dispose() 释放 AutoResetEvent 资源
性能考虑
-
每个 AutoResetEvent 都是一个内核对象,创建过多会影响性能
-
对于高频同步场景,考虑使用用户模式的同步机制如 SpinWait
-
在 .NET 4.0+ 中,Task 和 async/await 模式可能是更好的选择
五、 与 ManualResetEvent 的区别

























 336
336

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








