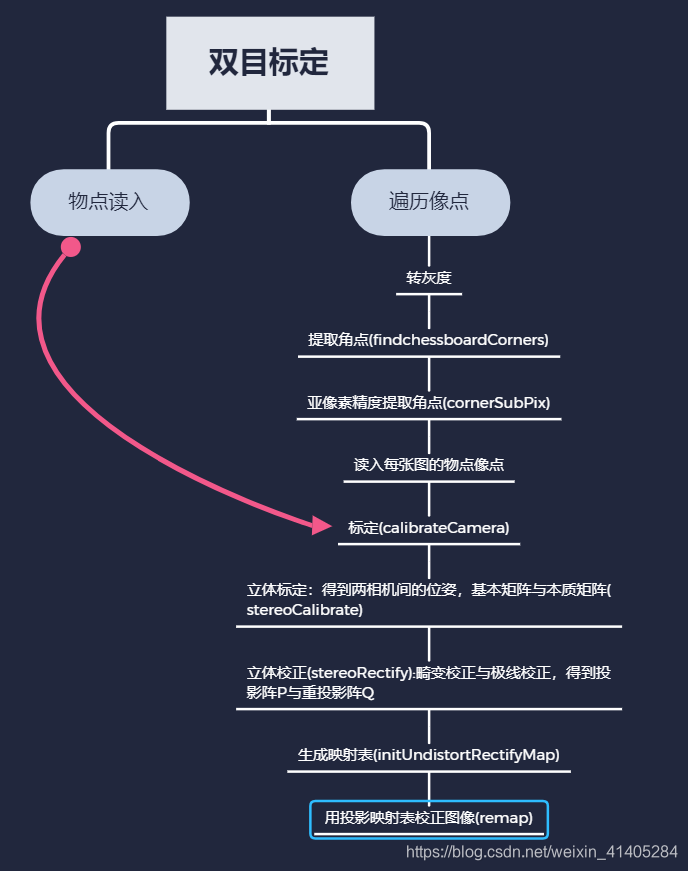
//双目标定无非就是重复两次单目标定的流程,单目标定参考我上一篇博客。
//在学习双目视觉之前,建议大家补充下,双目视觉模型,对极几何的知识,今天只讲源码的流程,以后出一篇对极几何的讲解。
//老规矩先来一段源码
#include "opencv2/core.hpp"
#include <opencv2/core/utility.hpp>
#include <opencv2/imgproc.hpp>
#include "opencv2/calib3d.hpp"
#include "opencv2/imgcodecs.hpp"
#include "opencv2/videoio.hpp"
#include "opencv2/highgui.hpp"
#include <cctype>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <time.h>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
using namespace cv;
static double computeReprojectionErrors(
const vector<vector<Point3f> >& objectPoints,
const vector<vector<Point2f> >& imagePoints,
const vector<Mat>& rvecs, const vector<Mat>& tvecs,
const Mat& cameraMatrix, const Mat& distCoeffs
)
{
vector<Point2f> imagePoints2;
int i, totalPoints = 0;
double totalErr = 0, err;
for (i = 0; i < (int)objectPoints.size(); i++)
{
projectPoints(Mat(objectPoints[i]), rvecs[i], tvecs[i],
cameraMatrix, distCoeffs, imagePoints2);
err = norm(Mat(imagePoints[i]), Mat(imagePoints2), NORM_L2);
int n = (int)objectPoints[i].size();
totalErr += err*err;
totalPoints += n;
}
return std::sqrt(totalErr / totalPoints);
}
int main(int argc, char** argv)
{
vector<string> files_left;
vector<string> files_right;
glob("E:\\mul_cam_images\\left1", files_left);
glob("E:\\mul_cam_images\\right1", files_right);
// 定义变量
vector<vector<Point2f>> image_leftPoints,image_rightPoints;//像点
vector<vector<Point3f>> objectPoints;//物点
TermCriteria criteria = TermCriteria(TermCriteria::EPS + TermCriteria::MAX_ITER, 30, 0.001);//进行亚像素精度的调整,获得亚像素级别的角点坐标
int numCornersHor = 8;//heigh
int numCornersVer = 11;//width
int numSquares = 15;//单位mm
Mat gray_l, gray_r;
Mat image_l, image_r;
vector<Point3f> obj;
for (int i = 0; i < numCornersHor; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < numCornersVer; j++)
obj.push_back(Point3f((float)j * numSquares, (float)i * numSquares, 0));
//存放每张图的角点坐标,并存入obj中(物点)
Size s1,s2;
//像点
for (int i = 0; i < 16; i++) {
printf("image file : %s \n", files_left[i].







 本文介绍OpenCV双目标定的过程,强调了物点与像点匹配的重要性,并给出了常见错误及其解决方案。通过标定、计算映射表和进行图像校正,实现了双目视觉的立体匹配。
本文介绍OpenCV双目标定的过程,强调了物点与像点匹配的重要性,并给出了常见错误及其解决方案。通过标定、计算映射表和进行图像校正,实现了双目视觉的立体匹配。
 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章

















 2493
2493

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








