深入浅出ros2时间同步
多传感器时间同步中提到,
ROS2提供了message_filters来进行时间同步,message_filters类似一个消息缓存,分别订阅不同的需要融合的传感器的topic,当消息到达message_filters的时候,可能并不会立即输出,而是在稍后的时间点里满足一定条件下输出,message_filters并不会修改各个topic传过来的数据(也就是缓冲区中的数据),而是将各个缓冲区建立时间线,然后根据时间线上的各个时间点来判断是否需要输出。
理论部分
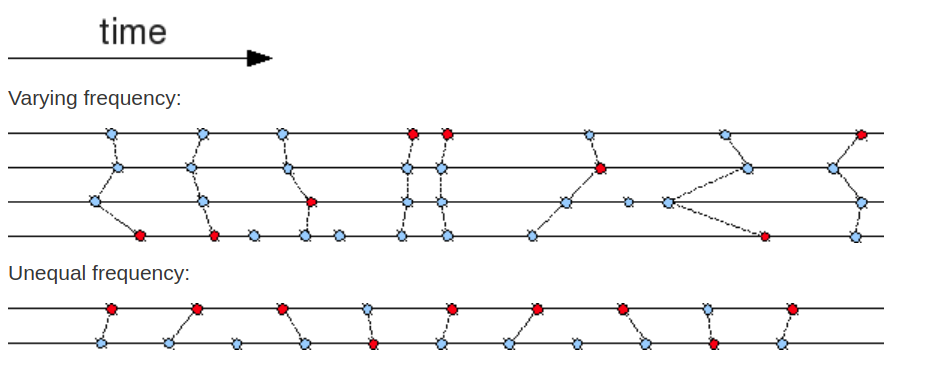
ros2时间同步有两种策略,ExactTime Policy和ApproximateTime Policy,前者需要严格的时间匹配,而ApproximateTime Policy则提供了时间窗口的匹配逻辑。WIKI上描述如下:
令 S 为最后发布的集合,T 为下一个正在创建的集合。其工作原理如下
- 发布集合S
当一个集合S被发布时,对于每一个topic,时间戳小于 m a x t { S } max_{t}\{S\} maxt{S}的数据都将被丢弃 - 更新消息队列
每一个topic生成一个指定长度的queue, 新的消息按照到达的顺序插入到各自topic的队列中。 - 寻找pivot消息
一旦每个topic的队列中至少有一个消息,就会找到队首消息中最新的那个,称为pivot消息。pivot消息是创建集合T的基石,时间匹配机制都依赖于pivot消息,记pivot消息对应的时间戳为 t p i v o t t_{pivot} tpivot - 构建集合Tm
对于所有topic中每比 t p i v o t t_{pivot} tpivot要大的消息m,找到一个最小的集合Tm,按时间顺序检查消息m,如果下一个消息还不能确定,就等待直到队列达到指定大小。 - 发布最小集合Tm
一旦到达pivot消息,就意味着所有的Tm都已经被枚举出来,或者当可以使用各种界限证明已经找到了最小的Tm时,就发布最小的Tm。
代码部分
说实话,WIKI的描述有点云里雾里,不结合代码的话很难理解,Talk is cheap, show me the code
ApproximateTimeSynchronizer集成自TimeSynchronizer和SimpleFilter
SimpleFilter <- TimeSynchronizer <- ApproximateTimeSynchronizer
初始化
通过TimeSynchronizer.connectInput初始化队列,每个ros topic初始化一个队列,注册add回调函数, 添加到input_connections列表。队列实际上是字典的形式。消息的毫秒时间戳作为key,消息体为value,消息先进先出
def __init__(self, fs, queue_size):
SimpleFilter.__init__(self)
self.connectInput(fs)
self.queue_size = queue_size
self.lock = threading.Lock()
def connectInput(self, fs):
self.queues = [{} for f in fs]
self.input_connections = [
f.registerCallback(self.add, q, i_q)
for i_q, (f, q) in enumerate(zip(fs, self.queues))]
add回调函数负责筛选数据并发布,不同的Synchronizer有不同的逻辑。TimeSynchronizer每次添加新的消息时,获取所有队列具有相同时间戳的数据,发布上述具有相同时间戳的数据并从队列中删除。而ApproximateTimeSynchronizer根据pivot和时间窗口,筛选并发布具有近似时间戳的数据
ApproximateTimeSynchronizer
相对TimeSynchronizer严格的时间同步,多了个slop参数,单位为秒。对应的回调函数add的逻辑也不一样。slop是时间同步的阈值窗口,说人话就是对于每一条需要进行同步的数据,其他队列的数据,与其时间戳差值超过slop的,就被pass掉了,不进入候选项。其关键步骤如下
-
基于pivot计算stamps列表
对每个队列中的每条数据s_ego,即pivot消息。遍历其他队列search_queues,找到时间阈值窗口内的数据,并按与数据s_ego的时间差从小到大排序,添加到stamps中,stamps是一个列表,保存当前队列之外的其他队列的数据时间戳,及其与s_ego数据的时间差## 一般需要在消息体里加上带有时间戳的header if not hasattr(msg, 'header') or not hasattr(msg.header, 'stamp'): if not self.allow_headerless: msg_filters_logger = rclpy.logging.get_logger('message_filters_approx') msg_filters_logger.set_level(LoggingSeverity.INFO) msg_filters_logger.warn("can not use message filters for " "messages without timestamp infomation when " "'allow_headerless' is disabled. auto assign " "ROSTIME to headerless messages once enabling " "constructor option of 'allow_headerless'.") return stamp = ROSClock().now() else: stamp = msg.header.stamp if not hasattr(stamp, 'nanoseconds'): stamp = Time.from_msg(stamp) # print(stamp) self.lock.acquire() my_queue[stamp.nanoseconds] = msg while len(my_queue) > self.queue_size: del my_queue[min(my_queue)] # self.queues = [topic_0 {stamp: msg}, topic_1 {stamp: msg}, ...] if my_queue_index is None: search_queues = self.queues else: search_queues = self.queues[:my_queue_index] + \ self.queues[my_queue_index+1:] # sort and leave only reasonable stamps for synchronization stamps = [] for queue in search_queues: topic_stamps = [] for s in queue: stamp_delta = Duration(nanoseconds=abs(s - stamp.nanoseconds)) if stamp_delta > self.slop: continue # far over the slop topic_stamps.append(((Time(nanoseconds=s, clock_type=stamp.clock_type)), stamp_delta)) if not topic_stamps: self.lock.release() return topic_stamps = sorted(topic_stamps, key=lambda x: x[1]) stamps.append(topic_stamps) -
获取所有stamps中时间戳的笛卡尔积,即每一个时间戳对
如stamp中包含三个队列的时间戳,分别如下
[('t11','t12'),('t21','t22','t23'),('t31','t32')],则笛卡尔积为('t11', 't21', 't31') ('t11', 't21', 't32') ('t11', 't22', 't31') ('t11', 't22', 't32') ('t11', 't23', 't31') ('t11', 't23', 't32') ('t12', 't21', 't31') ('t12', 't21', 't32') ('t12', 't22', 't31') ('t12', 't22', 't32') ('t12', 't23', 't31') ('t12', 't23', 't32') -
根据条件筛选和发布时间近似匹配的数据
循环每个时间戳对,条件有两个:- 如果最小时间戳和最大时间戳的差值在时间窗口阈值内
- 且该时间戳对里的所有数据(如(‘t12’, ‘t23’, ‘t31’))还在各自的队列里(没有被发布出去,也没有被删掉)
就将此时间戳对,及对应的数据作为近似同步的数据对,发布给下游,同时从各自队列里删除此数据对
for vv in itertools.product(*[list(zip(*s))[0] for s in stamps]): # vv表示每一个时间戳对 vv = list(vv) # insert the new message if my_queue_index is not None: vv.insert(my_queue_index, stamp) qt = list(zip(self.queues, vv)) if ( ((max(vv) - min(vv)) < self.slop) and (len([1 for q,t in qt if t.nanoseconds not in q]) == 0) ): msgs = [q[t.nanoseconds] for q,t in qt] self.signalMessage(*msgs) for q,t in qt: del q[t.nanoseconds] break # fast finish after the synchronizatio
总结
代码部分主要的逻辑在于构建笛卡尔积、根据条件筛选和发布时间近似匹配的数据,这部分和WIKI的描述有点区别,不知道是我理解有误还是我理解有误?官网肯定不会错的吧。。。
ROS2 TimeSynchronizer In Action
时间戳替换
通过ros2 bag record命令录取的ros bag,其时间戳对应着ros bag的记录时间,也就是消息记录时间,部分场景下,而每个消息一般带有消息的产生时间,记录在std_msgs/msg/Header接口中
# Standard metadata for higher-level stamped data types.
# This is generally used to communicate timestamped data
# in a particular coordinate frame.
# Two-integer timestamp that is expressed as seconds and nanoseconds.
builtin_interfaces/Time stamp
int32 sec
uint32 nanosec
# Transform frame with which this data is associated.
string frame_id
为了能够在在基于消息产生时间的时间轴来可视化分析不同ros topic消息,需要替换离线录制的ros2 bag中的时间戳。 ros1提供了此类样例和api:http://wiki.ros.org/rosbag/Cookbook
包含了如下功能:
- Rewrite bag with header timestamps
- Add metadata to a bag
- Get summary information about a bag
- Get lists of topics and types from a bag
- Create a cropped bagfile
- Reorder a Bag File Based on Header Timestamps
- Export message contents to CSV
但是目前还没发现类似的ros2官方文档。ros2 humble版本中,ros2 bag只提供了如下功能
usage: ros2 bag [-h] Call `ros2 bag <command> -h` for more detailed usage. ...
Various rosbag related sub-commands
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
Commands:
convert Given an input bag, write out a new bag with different settings
info Print information about a bag to the screen
list Print information about available plugins to the screen
play Play back ROS data from a bag
record Record ROS data to a bag
reindex Reconstruct metadata file for a bag
Call `ros2 bag <command> -h` for more detailed usage.
但是可以通过第三方库ros2bag_tools来扩展ros2 bag的功能, 经过扩展后的功能如下表,其中restamp就是进行时间戳替换的模块,既可以将消息记录时间戳替换为header stamp,也能反向替换。
| command | description |
|---|---|
| add | add new topic, with messages aligned to existing topic |
| cut | cut time slice by wall time or duration offset |
| drop | drop X out of every Y messages of a topic |
| export | export data to other formats, see export |
| extract | extract topics by name |
| plot | plot message data to a new window, see plot |
| process | chain multiple filters, see chaining |
| prune | remove topics without messages |
| reframe | change frame_id on messages with headers |
| rename | change name of a topic |
| replace | replace messages of a specific topic with message data specified in a yaml file |
| restamp | for all messages with headers, change the bag timestamp to their header stamp |
| summary | print summary on data to stdout |
| sync | output synchronized bundles of messages using the ApproximateTimeSynchronizer |
| video | show or write video of image data |
安装及使用
- 创建ros2_ws目录,并在ros2_ws/src路径下clone以下github repo
- https://github.com/ros2/rosbag2
- https://github.com/AIT-Assistive-Autonomous-Systems/ros2bag_tools
- 在ros2_ws下执行colcon build,正常情况下等待一会即可构建成功
- Source install/setup.bash or setup.zsh,激活环境变量
- 验证是否安装成功(可以忽略和时间戳替换无关的错误提示)
Failed to load entry point 'plot': cannot import name 'get_reader_options' from 'ros2bag.verb' (/home/daili/my_ros2_humble_ws/install/ros2bag/lib/python3.8/site-packages/ros2bag/verb/__init__.py)
usage: ros2 bag [-h]
Call `ros2 bag <command> -h` for more detailed usage. ...
Various rosbag related sub-commands
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
Commands:
add Add new topic, with messages aligned to existing topic
convert Given an input bag, write out a new bag with different settings
cut Cut timespan from a bag and write to new bag
drop Drop X out of every Y messages
echo Print message data as yaml
export Export bag data to other formats
extract Extract specific topics from a bag and write to new bag
info Print information about a bag to the screen
list Print information about available plugins to the screen
play Play back ROS data from a bag
process Run a set of filters on input bags and write to new bag
prune Remove empty topics and write rest to new bag
record Record ROS data to a bag
reframe Change header.frame_id of some messages, and write to a new bag
reindex Reconstruct metadata file for a bag
rename Rename specific topics in a bag, and write to new bag
replace Replace content of messages in a bag with a constant, and write to new bag
restamp Set bag timestamps to message header timestamps and write to new bag
summary Print a summary of the contents of a bag
sync Synchronize topics dropping unsynchronized messages
video Display or write a video of image data in a bag
Call `ros2 bag <command> -h` for more detailed usage.
执行以下命令,转换成功的ros2 bag文件夹名默认以时间戳结尾
ros2 bag restamp <your ros2 bag path> -s sqlite3 --out-storage sqlite3
时间同步测试
除了在代码中调试时间同步之外,也可以利用上述ros2bag_tools工具基于录制好的ros bag来分析和测试时间同步效果
ros2 bag sync <rosbag-path> -s sqlite3 --out-storage sqlite3 --slop 0.05 --progress -o <rosbag-path>-sync -t /multi_stream_detections_0 /multi_stream_detections_1 /multi_stream_detections_2 /multi_stream_detections_3
同时对四路ros topic数据进行时间同步,上下图分别表示同步前后的数据。对50ms(slop=0.05)内的topic数据,近似认为是时间同步的数据,并输出,可以看到,超过时间窗口的数据,并没有被推送出来,也就是说,对于n路ros topic,要么输出近似同步的n路数据,要么都不输出,不存在只输出小于n路数据的情况。
部分场景下,这显然不是一个合理的做法,比如部分传感器失效的情况下,经过ros TimeSynchronizer之后,所有结果都不会被发布出来,即使有正常工作的传感器。一种可能的解决方案是,部分传感器失效的情况下,按既定频率往所属的ros topic发送空的消息,防止所有的topic数据都被过滤掉
-
整体

-
局部

参考
- https://wiki.ros.org/message_filters/ApproximateTime
- https://github.com/AIT-Assistive-Autonomous-Systems/ros2bag_tools


























 320
320

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








