需求
threejs学习-3D 地球
实现:
1、使用粒子效果模拟宇宙星空
2、贴图、模型等资源的加载
3、加载资源的监听
4、效果合成器 EffectComposer 的初级使用
5、在地球上设置坐标以及坐标涟漪动画
6、标点间建立飞线
7、简单动画
建议先浏览一遍git地址上代码,并运行启动一下在进行学习理解
基础准备
场景创建
let scene: THREE.Scene = new THREE.Scene();
相机
透视相机:PerspectiveCamera( fov : Number, aspect : Number, near : Number, far : Number )
fov — 摄像机视锥体垂直视野角度
aspect — 摄像机视锥体长宽比
near — 摄像机视锥体近端面
far — 摄像机视锥体远端面
const initCamera = (width: number, height: number): void => {
camera = new THREE.PerspectiveCamera(75, width / height, 0.1, 40);
// 设置相机位置
camera.position.set(0, 0, 40);
// 将相机添加到场景中
scene.add(camera);
};
坐标辅助器
const initAxesHelper = (): void => {
const axesHelper: THREE.AxesHelper = new THREE.AxesHelper(50);
scene.add(axesHelper);
};
状态检测器
import Stats from "stats.js"
const initStats = (): void => {
stats = new Stats();
canvas.value.appendChild(stats.dom);
};
渲染器
使用 WebGLRenderer 还是 WebGL1Renderer的区别:
如果看过 WebGL 的同学应该知道 WebGL 有 1 和 2 两个版本,从 r118 起,WebGLRenderer 会自动使用 WebGL2 来做渲染 那么这两个版本有何区别,简单说就是多了更多纹理格式、内置函数、3D 纹理贴图,同时还支持了非 2 的整数次方大小的图片。
同时,WebGL2 与 WebGL1 在对浏览器的兼容性上有很大的差异,这两者对浏览器兼容产生的巨大差异会导致陈旧的 WebGL1 的系统崩溃,所以 threejs 给我们提供了 WebGL1Renderer 来进行适配兼容
const initRenderer = (width: number, height: number): void => {
renderer = new THREE.WebGLRenderer();
renderer.setSize(width, height);
canvas.value.appendChild(renderer.domElement);
renderer.render(scene, camera);
};
轨道控制器
const initControls = (): void => {
controls = new OrbitControls(camera, renderer.domElement);
// 使动画循环使用时阻尼或自转 意思是否有惯性
controls.enableDamping = true;
//是否可以缩放
controls.enableZoom = true;
//是否自动旋转
controls.autoRotate = false;
//是否开启右键拖拽
controls.enablePan = true;
};
实现3D 地球
粒子星空
const createStar = (): void => {
// BufferGeometry 根据左边构建图形(面片、线或点)
let geometry: THREE.BufferGeometry = new THREE.BufferGeometry();
// 顶点集合 starCount星星数量
let vertices: Float32Array = new Float32Array(starCount * 3);
// 随机颜色集合
let colors: Float32Array = new Float32Array(starCount * 3);
for (let i = 0; i < starCount; i++) {
// -500 ~ 500
let x = (Math.random() - 0.5) * 1000;
let y = (Math.random() - 0.5) * 1000;
let z = (Math.random() - 0.5) * 1000;
// 解释下这个算法
// [
// x1,y1,z1,
// x2,y2,z2,
// x3,y3,z3
// ]
// 因为每个顶点都是一个三元组,所以[1 * 3 + 0]则是第一组的x轴,[2 * 3 + 0]则是第二组的x轴,以此类推,其他也是一样的算法
vertices[i * 3 + 0] = x;
vertices[i * 3 + 1] = y;
vertices[i * 3 + 2] = z;
// 随机颜色
let color: THREE.Color = new THREE.Color();
// setHSL(‘色调', '亮度', ‘饱和‘) 三个参数皆在[0, 1]之间
color.setHSL(Math.random() * 0.2 + 0.5, 0.55, Math.random() * 0.25 + 0.55);
colors[i * 3 + 0] = color.r;
colors[i * 3 + 1] = color.g;
colors[i * 3 + 2] = color.b;
}
geometry.setAttribute("position", new THREE.BufferAttribute(vertices, 3));
geometry.setAttribute("color", new THREE.BufferAttribute(colors, 3));
let starTexture: THREE.Texture = textureLoader.load(getAssetsFile("star.png"));
let starMaterial = new THREE.PointsMaterial({
map: starTexture,
size: 1, // 点大小
transparent: true, // 材质透明
opacity: 1, // 透明度
vertexColors: true, // 顶点着色
depthTest: true, // 是否在渲染此材质时启用深度测试
depthWrite: false, // 渲染此材质是否对深度缓冲区有任何影响
blending: THREE.AdditiveBlending, // 材质混合
sizeAttenuation: true, // 点的大小是否因相机深度而衰减
});
stars = new THREE.Points(geometry, starMaterial);
scene.add(stars);
};
地球和大气层创建
1、球型加贴图 DoubleSide双面渲染
const createEarth = () => {
// 地球
// 创建球形几何体
const earthGeo: THREE.SphereGeometry = new THREE.SphereGeometry(5, 32, 32);
// 贴图加载
const earthTexture: THREE.Texture = textureLoader.load(getAssetsFile("earth/earth.png"));
const earthBumpTexture: THREE.Texture = textureLoader.load(getAssetsFile("earth/earth_bump.png"));
const earthSpecTexture: THREE.Texture = textureLoader.load(getAssetsFile("earth/earth_spec.png"));
// 高光材质
const earthMaterial: THREE.MeshPhongMaterial = new THREE.MeshPhongMaterial({
map: earthTexture, // 贴图
bumpMap: earthBumpTexture, // 凹凸贴图纹理
bumpScale: 0.15, // 凹凸贴图会对材质产生多大影响 0~1
specularMap: earthSpecTexture, // 镜面反射贴图
specular: new THREE.Color("#909090"), // 材质的高光颜色
shininess: 5, // 高亮的程度,越高越亮
transparent: true, // 材质透明
side: THREE.DoubleSide // 定义将要渲染哪一面,THREE.DoubleSide是两面
});
const earth: THREE.Mesh = new THREE.Mesh(earthGeo, earthMaterial)
earthGroup.add(earth)
// 大气层
const cloudGeo: THREE.SphereGeometry = new THREE.SphereGeometry(5.1, 40, 40)
const cloudTexture: THREE.Texture = textureLoader.load(getAssetsFile("earth/earth_cloud.png"));
const cloudMaterial: THREE.MeshPhongMaterial = new THREE.MeshPhongMaterial({
map: cloudTexture,
transparent: true, // 材质透明
opacity: 1,
blending: THREE.AdditiveBlending,
side: THREE.DoubleSide
})
const cloud: THREE.Mesh = new THREE.Mesh(cloudGeo, cloudMaterial)
earthGroup.add(cloud)
// 设置地球组转向
earthGroup.rotation.set( 0.5, 0, -0.4 );
meshGroup.add(earthGroup)
scene.add(meshGroup)
};
创建星轨环
有关效果合成器通道的使用在 R149 版本中文档并无介绍,所以选择直接查看代码
后期处理:简单的说就是先渲染一张图存起来,在这张图上面"添油加醋",处理完后再渲染到屏幕上。这一过程three进行了封装,使用现成的可以更快实现需求
RenderPass: https://github.com/mrdoob/three.js/blob/r149/examples/jsm/postprocessing/RenderPass.js
OutlinePass: https://github.com/mrdoob/three.js/blob/r149/examples/jsm/postprocessing/OutlinePass.js
其他一些通道: https://github.com/mrdoob/three.js/tree/r149/examples/jsm/postprocessing
const createStarOrbit = (): void => {
// 创建环形几何体
const torusGeo: THREE.TorusGeometry = new THREE.TorusGeometry(8.0, 0.2, 2, 200)
const torusMaterial: THREE.MeshBasicMaterial = new THREE.MeshBasicMaterial({
color: new THREE.Color("rgb(147, 181, 207)"),
transparent: true,
opacity: 0.4
});
torus = new THREE.Mesh(torusGeo, torusMaterial);
torus.rotation.set( 1.7, 0.5, 1 );
torus.updateMatrix();
// 效果合成器,是Three.js中的一个后期处理效果库。EffectComposer允许您将多个RenderPass组合在一起,以创建复杂的后期处理效果
composer = new EffectComposer( renderer )
// 通用的渲染器通道,用于将场景渲染到纹理或屏幕上
const renderPass: RenderPass = new RenderPass( scene, camera );
composer.addPass( renderPass );
// 后期处理通道,可以在场景中的对象周围创建一个轮廓线
const outlinePass: OutlinePass = new OutlinePass( new THREE.Vector2( canvas.value.clientWidth, canvas.value.clientHeight ), scene, camera );
composer.addPass( outlinePass );
outlinePass.pulsePeriod = 0; // 数值越大,律动越慢
outlinePass.visibleEdgeColor.set( new THREE.Color("rgb(147, 181, 207)") ); // 高光颜色
outlinePass.usePatternTexture = false; // 使用纹理覆盖
outlinePass.edgeStrength = 2; // 高光边缘强度
outlinePass.edgeGlow = 1; // 边缘微光强度
outlinePass.edgeThickness = 1; // 高光厚度
outlinePass.selectedObjects = [torus]; // 需要后期的Mesh
meshGroup.add(torus)
}
创建卫星移动轨迹
该方法主要是创建圆环所需要的顶点以及圆环旋转后顶点的更新
如何得到圆上每个点的坐标???
根据三角函数正弦、余弦求得,假设圆心 P(0, 0, 0),半径 r(9),一共 length 300 个点,循环长度的到坐标位置 i
x = r * Math.sin(Math.PI * 2 * i / length) + p.x
y = r * Math.cos(Math.PI * 2 * i / length) + p.y
const createMoveTrack = (): void => {
// number 轨迹环总长度 radius 轨迹环半径 centerPoint 圆心 pointsArr 向量组合
const length: number = 300,
radius: number = 9,
centerPoint = { x: 0, y: 0, z: 0 },
pointsArr: THREE.Vector3[] = [];
// 通过三角函数计算圆上点坐标
// 根据三角函数正弦、余弦求得,假设圆心P(0, 0, 0),半径r(9),一共length300个点,循环长度的到坐标位置i
// x = r * Math.sin(Math.PI * 2 * i / length) + p.x
// y = r * Math.cos(Math.PI * 2 * i / length) + p.y
for (let i = 0; i <= length; i++) {
pointsArr.push(
new THREE.Vector3(
radius * Math.sin(Math.PI * 2 * i / length) + centerPoint.x,
radius * Math.cos(Math.PI * 2 * i / length) + centerPoint.y,
centerPoint.z
)
)
}
// 3阶段贝塞尔曲线 贝塞尔曲线是描述曲线趋势的一种表达
curve = new THREE.CatmullRomCurve3(pointsArr, true, 'catmullrom', 0.5);
// 分成50个点
const points: THREE.Vector3[] = curve.getPoints(50);
// 建立轨迹线并设置完全透明隐藏起来
const lineGeo: THREE.BufferGeometry = new THREE.BufferGeometry().setFromPoints(points);
const lineMaterial: THREE.LineBasicMaterial = new THREE.LineBasicMaterial({ transparent: true, opacity: 0 })
const line = new THREE.Line(lineGeo, lineMaterial)
// 设置跟星轨一样的转向,这样到卫星看起来就会在轨迹环边运动
line.rotation.set( 1.7, 0.5, 1 );
// 物体旋转移动后顶点不更新
// 创建一个四维矩阵
// 然后将torus.rotation创建一个旋转矩阵并赋值给matrix
// 最后将旋转矩阵应用于curve的顶点
// 通过applyMatrix4(matrix)方法,curve.points[i]对象的坐标会根据旋转矩阵matrix进行变换,从而实现旋转效果
const matrix = new THREE.Matrix4();
matrix.makeRotationFromEuler(torus.rotation);
for (let i = 0; i < curve.points.length; i++) {
curve.points[i].applyMatrix4(matrix);
}
meshGroup.add(line)
}
创建卫星
const createSatellite = (): void => {
mTLLoader.load(getAssetsFile('satellite/Satellite.mtl'), (material) => {
// 预加载材质所需的所有纹理、贴图
material.preload()
objLoader.setMaterials(material).load(getAssetsFile('satellite/Satellite.obj'), (obj) => {
// 将轨迹路线的第一个坐标设置成卫星的初始位置
obj.position.copy(curve.points[0])
satellite = obj
meshGroup.add(satellite)
})
})
}
二维经纬度坐标转三维球坐标
const lglnToxyz = (lg: number, lt: number, radius: number): THREE.Vector3 => {
// theta是俯仰面(竖直面)内的角度,范围0~180度
const theta = (90 + lg) * (Math.PI / 180)
// phi是方位面(水平面)内的角度,范围0~360度
const phi = (90 - lt) * (Math.PI / 180)
// 球坐标
const spherical = new THREE.Spherical(radius, phi, theta)
// 三维向量
const xyz = new THREE.Vector3()
// 从球坐标中设置该向量
xyz.setFromSpherical(spherical)
return xyz
}
创建标点
const createEarthPoint = (localton: THREE.Vector3, color: string): THREE.Group => {
// 新建一个标点组合
const pointGroup: THREE.Group = new THREE.Group();
// 涟漪圈圈
const waveGeo: THREE.PlaneGeometry = new THREE.PlaneGeometry( 0.3, 0.3 );
const waveTexture: THREE.Texture = textureLoader.load(getAssetsFile("wave.png"));
const waveMaterial: THREE.MeshBasicMaterial = new THREE.MeshBasicMaterial({
map: waveTexture,
color: color,
transparent: true,
opacity: 1.0,
side: THREE.DoubleSide,
depthWrite: false,
})
let waveMesh: THREE.Mesh = new THREE.Mesh(waveGeo, waveMaterial);
// 设置后期控制涟漪动画的大小和透明度阀值
(waveMesh as any).size = 5.1 * 0.3;
(waveMesh as any)._s = Math.random() * 1.0 + 1.0;
wareArr.push(waveMesh)
// 标点光柱
// 使用CylinderGeometry创建一个圆锥形圆柱体
const lightGeo: THREE.CylinderGeometry = new THREE.CylinderGeometry(0, 0.05, 0.5, 32)
const lightTexture: THREE.Texture = textureLoader.load(getAssetsFile("lightray.png"))
const lightMaterial: THREE.MeshBasicMaterial = new THREE.MeshBasicMaterial({
map: lightTexture,
color: color,
side: THREE.DoubleSide,
transparent: true,
opacity: 1.0,
depthWrite: false,
})
const lightMesh: THREE.Mesh = new THREE.Mesh(lightGeo, lightMaterial)
// 设置光柱的旋转和位置,让他竖立在涟漪圈上边
lightMesh.rotateX(Math.PI / 2)
lightMesh.position.z = 0.25
pointGroup.add(waveMesh, lightMesh)
pointGroup.position.set(localton.x, localton.y, localton.z)
// 调用normalize方法归一化向量,好处是保留了原向量信息而长度为1,在计算中更方便
const coordVec3 = new THREE.Vector3( localton.x, localton.y, localton.z ).normalize();
const meshNormal = new THREE.Vector3( 0, 0, 1 );
// setFromUnitVectors方法根据这两个向量计算并设置旋转四元数,使pointGroup中的物体朝向目标点
pointGroup.quaternion.setFromUnitVectors( meshNormal, coordVec3 );
return pointGroup
}
绘制飞线
两点一线,所以最先打算用二阶贝塞尔曲线实现,去两点之间的中点为控制点,后面随机去点时发现当起始点和终止点分别在两极,也就是两点连线为直径时,控制点在无穷远,故这里使用三阶贝塞尔曲线
这里的难点是在于如何通过起始点和终止点算出其他两个控制点,在参考其他大佬的方案以及 chatgpt 的答疑,最终整理出如下方法,如下图所示
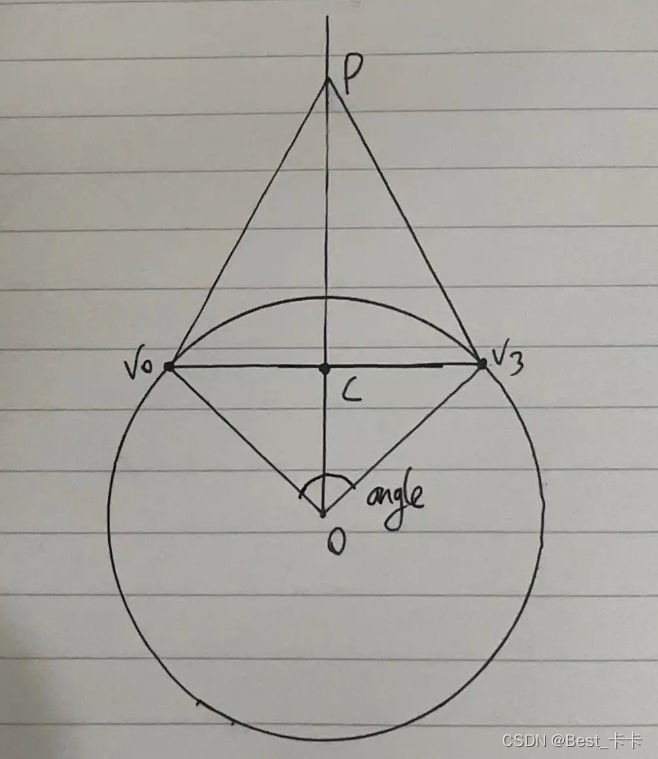
const createFlyLine = (v0: THREE.Vector3, v3: THREE.Vector3): THREE.Line => {
// v0.angleTo(v3)计算v0和v3之间的夹角,单位为弧度,(弧度 * 180) / Math.PI 将弧度转化为角度,单位为度
const angle: number = (v0.angleTo(v3) * 180) / Math.PI;
// 计算控制点的水平距离,将夹角 * 常数(这个常数是个经验值,根据实际情况调整,它的作用是控制曲线的弯曲程度)
const horizontal: number = angle * 0.04;
// 计算了控制点的垂直距离,将夹角的平方 * 常数(这个常数是个经验值,根据实际情况调整,它的作用是控制曲线的高度)
const vertical: number = angle * angle * 0.1;
// 法线向量,球心
const p0: THREE.Vector3 = new THREE.Vector3(0, 0, 0);
// 计算起始点到终止点两点间的中间点,即两向量的平均值
const centerPoint: THREE.Vector3 = v0.clone().add(v3.clone()).divideScalar(2);
// 从圆心到中间点形成无穷远的射线
const rayLine: THREE.Ray = new THREE.Ray(p0, centerPoint);
// rayLine.at需要传两个参数,所以这里创建一个临时变量
const temp = new THREE.Vector3();
// rayLine.at获取Ray对象起点与终点之间的向量并储存在temp中
// 从给定点p0开始,沿着给定方向(由Ray对象表示)上的一条射线上,到该射线与垂线所在平面的交点的计算
let vtop = rayLine.at( vertical / rayLine.at( 1, temp ).distanceTo( p0 ), temp );
// lerp方法v0到vtop和horizontal / v0.clone().distanceTo(vtop)之间进行插值
// v0.clone().distanceTo(vtop) 表示向量 v0 到向量 vtop 之间的距离,也就是线段 v0 和 vtop 的长度
// 将 horizontal 除以线段的长度,实际上是在计算一个在 v0 到 vtop 这条线段上的相对位置,这个相对位置是以 horizontal 所表示的距离来度量的
// 具体来说,horizontal 可以看作是线段长度的一个比例因子。当 horizontal 的值为 0 时
// 所得到的向量就是 v0,当 horizontal 的值为线段长度时,所得到的向量就是 vtop。当 horizontal 的值为线段长度的一半时
// 所得到的向量就是线段的中点。因此,horizontal / v0.clone().distanceTo(vtop) 表示在 v0 到 vtop 这条线段上的相对位置
// 这个位置是由 horizontal 和线段长度共同决定的
let v1 = v0.clone().lerp(vtop, horizontal / v0.clone().distanceTo(vtop));
let v2 = v3.clone().lerp(vtop, horizontal / v3.clone().distanceTo(vtop));
const curve: THREE.CubicBezierCurve3 = new THREE.CubicBezierCurve3( v0, v1, v2, v3 );
const points: THREE.Vector3[] = curve.getSpacedPoints( 100 );
const lineGeo: THREE.BufferGeometry = new THREE.BufferGeometry().setFromPoints(points)
const lineMaterial = new THREE.LineBasicMaterial( {
color: new THREE.Color('rgb(255, 255, 255)'),
linewidth: 1,
transparent: true,
opacity: 0
});
const line: THREE.Line = new THREE.Line(lineGeo, lineMaterial)
scene.add(line)
// 从0开始,每次取5个点的数量
const index = 0, num = 5
// 从曲线上取一段
let flyLinePoints = points.splice(index, index + num)
let flyLineGeo = new THREE.BufferGeometry().setFromPoints(flyLinePoints);
(flyLineGeo as any).points = points;
(flyLineGeo as any).num = num;
(flyLineGeo as any)._index = index;
var flyLineMaterial = new THREE.LineBasicMaterial({
linewidth: 1,
color: new THREE.Color('rgb(254, 215, 26)')
});
var flyLine = new THREE.Line(flyLineGeo, flyLineMaterial);
flyLineArr.push(flyLine);
return flyLine;
}
在地球上绘制标点和飞线
const drawPointOnEarth = (): void => {
// 标点集合
const localtionGroup: THREE.Group = new THREE.Group();
// 飞线集合
const flyLineGroup: THREE.Group = new THREE.Group()
for(let i = 0; i < lnglatData.length; i++) {
lnglatData[i].lnglat.forEach((lnglat: number[]) => {
const xyz = lglnToxyz(lnglat[0], lnglat[1], 5.1)
localtionGroup.add(createEarthPoint(xyz, lnglatData[i].color))
})
const from = lglnToxyz(lnglatData[i].lnglat[0][0], lnglatData[i].lnglat[0][1], 5.1)
const to = lglnToxyz(lnglatData[i].lnglat[1][0], lnglatData[i].lnglat[1][1], 5.1)
flyLineGroup.add(createFlyLine(from, to))
}
earthGroup.add(localtionGroup, flyLineGroup)
}
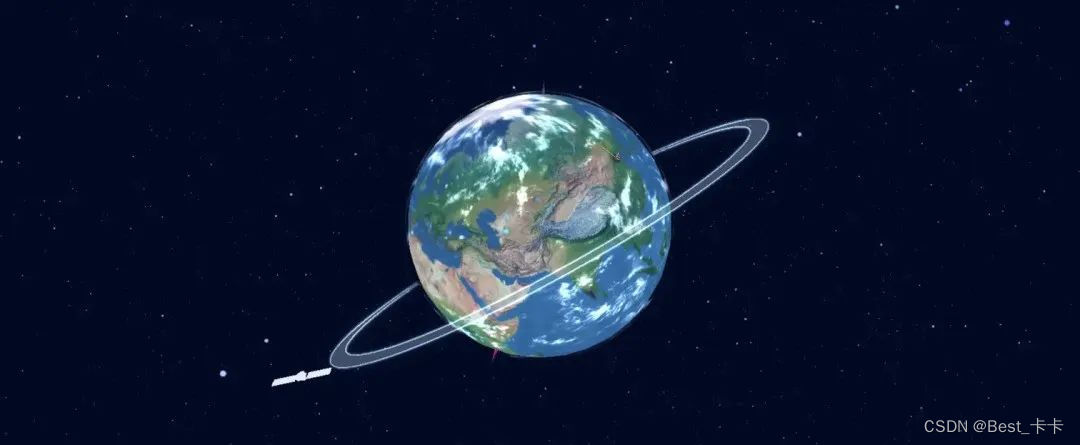
一般在执行完上述方法后能看到如下图的效果:
动画实现
const render = (): void => {
controls.update();
renderer.render(scene, camera);
if (stats) {
stats.update();
}
if(composer) {
composer.render();
}
if(stars){
stars.rotation.y += 0.0009;
stars.rotation.z -= 0.0003;
}
// 卫星公转
if(satellite) {
if (progress <= 1 - velocity) {
const satelliteMovePosition = curve.getPointAt(progress + velocity)
progress += velocity
satellite.position.copy(satelliteMovePosition)
} else {
progress = 0
}
}
// 飞线动画
if(flyLineArr.length) {
flyLineArr.forEach(flyLine => {
let flyLineGeo = flyLine.geometry
let points = (flyLineGeo as any).points
let p = JSON.parse(JSON.stringify(points))
let num = (flyLineGeo as any).num
let flyLinePoints = p.splice((flyLineGeo as any)._index, (flyLineGeo as any)._index + num)
flyLineGeo.setFromPoints(flyLinePoints)
if((flyLineGeo as any)._index < points.length) {
(flyLineGeo as any)._index += 1
} else {
(flyLineGeo as any)._index = 0
}
})
}
// 涟漪动画
if(wareArr.length) {
wareArr.forEach((ware: any) => {
ware._s += 0.01;
ware.scale.set( ware.size * ware._s, ware.size * ware._s, ware.size * ware._s );
if (ware._s <= 1.5) {
//mesh._s=1,透明度=0 mesh._s=1.5,透明度=1
ware.material.opacity = ( ware._s - 1 ) * 2;
} else if (ware._s > 1.5 && ware._s <= 2) {
//mesh._s=1.5,透明度=1 mesh._s=2,透明度=0
ware.material.opacity = 1 - ( ware._s - 1.5 ) * 2;
} else {
ware._s = 1.0;
}
})
}
requestAnimationFrame(render);
};
资源加载监听以及 loading 实现
const manager = new THREE.LoadingManager(); // 加载器管理器
manager.onProgress = function(item, loaded, total) {
// 百分比
let value = loaded / total * 100
process.value = Math.ceil(value)
// 加载完成1s后执行下列操作
if(value === 100) {
setTimeout(() => {
// 隐藏loading动画
loading.value = false
// 这边使用gsap实现一组动画
gsap.to(meshGroup.position, {
z: 0,
ease: "Power2.inOut",
duration: 1,
})
gsap.to(earthGroup.rotation, {
y: 10,
ease: "Power2.inOut",
duration: 2,
onComplete() {
if(flyLineArr.length === 0) {
drawPointOnEarth();
}
}
})
}, 1000)
}
};





















 1620
1620











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








