环境:OpenCV3.2.0 + VS2017
61、轮廓集合重排序(按轮廓面积从小到大)
//对轮廓集合面积从大到小排序
bool compareValue_bs(const std::vector<cv::Point> & c1, const std::vector<cv::Point> & c2)
{
int area1 = cv::contourArea(c1);
int area2 = cv::contourArea(c2);
return area1 > area2;
} std::vector<std::vector<cv::Point>> ENDcontour;
std::vector<std::vector<cv::Point>> contours;
std::vector<cv::Vec4i> hierarchy;
std::vector<std::vector<cv::Point>>::iterator k; //迭代器,访问容器数据
cv::findContours(thresholdMat, contours, hierarchy, cv::RETR_EXTERNAL, CV_RETR_LIST); //查找外轮廓,压缩存储轮廓点
std::sort(contours.begin(), contours.end(), compareValue_bs);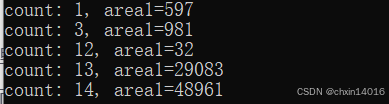
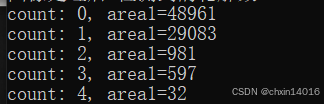
62、只删除过小轮廓及挨边轮廓
bool deleteSmallMat(cv::Mat thresholdMat, cv::Mat &resMat, int minSize = 30, bool debug = false);bool PlaneRec::deleteSmallMat(cv::Mat thresholdMat, cv::Mat &resMat, int minSize, bool debug)
{
thresholdMat.copyTo(resMat);
std::vector<cv::Rect> boundRect;
std::vector<cv::RotatedRect> minRect;
cv::Mat visual_bR;
if (debug) thresholdMat.copyTo(visual_bR);
if (visual_bR.type() != CV_8UC3) cv::cvtColor(visual_bR, visual_bR, cv::COLOR_GRAY2BGR);
std::vector<std::vector<cv::Point>> ENDcontour;
std::vector<std::vector<cv::Point>> contours;
std::vector<cv::Vec4i> hierarchy;
std::vector<std::vector<cv::Point>>::iterator k; //迭代器,访问容器数据
cv::findContours(thresholdMat, contours, hierarchy, cv::RETR_EXTERNAL, CV_RETR_LIST); //查找外轮廓,压缩存储轮廓点
std::sort(contours.begin(), contours.end(), compareValue_bs);
if (debug) printf("\n\n\n\n\n");
if (contours.size() <= 0)//图为全黑时
{
std::cout << __FUNCTION__ << "cons.size() <= 0";
//return false;
}
if (debug) printf("图像处理后 检测到的轮廓数 cons.size() = %d \n", contours.size());
int remainNum = 0;//剩余的轮廓数(有重画出来的轮廓数)
cv::Mat tmpMat = cv::Mat(thresholdMat.rows, thresholdMat.cols, CV_8UC1, cv::Scalar(0, 0, 0));
//画出轮廓;
int count = 0;
for (k = contours.begin(); k != contours.end(); ++k, count++) //删除小连通域的
{
std::vector<cv::Point> curContours = *k;
if (curContours.size() < minSize) {
cv::drawContours(resMat, contours, count, cv::Scalar(0, 0, 0), -1, CV_AA, hierarchy);
cv::drawContours(resMat, contours, count, cv::Scalar(0, 0, 0), 2, CV_AA, hierarchy);
continue;
}
remainNum++;
if (1) {
int area1 = cv::contourArea(curContours);
if (debug) cout << __FUNCTION__ << " count: " << count << ", area1=" << area1 << endl;
}
minRect.push_back(cv::minAreaRect(curContours));
boundRect.push_back(cv::boundingRect(curContours));
if (debug) cv::rectangle(visual_bR, boundRect[boundRect.size() - 1].tl(), boundRect[boundRect.size() - 1].br(), cv::Scalar(0, 255, 0), 1);
if (debug) cv::putText(visual_bR, std::to_string(boundRect.size() - 1), boundRect[boundRect.size() - 1].tl(), cv::FONT_HERSHEY_COMPLEX, 0.45, cv::Scalar(255, 135, 160), 1);
if (debug) cv::putText(visual_bR, std::to_string(boundRect.size() - 1), boundRect[boundRect.size() - 1].br(), cv::FONT_HERSHEY_COMPLEX, 0.45, cv::Scalar(255, 135, 160), 1);
if (debug) cv::drawContours(visual_bR, contours, count, cv::Scalar(255, 135, 160), -1, CV_AA, hierarchy);
if (debug) {
cv::circle(visual_bR, minRect.at(minRect.size() - 1).center, 3, cv::Scalar(0, 0, 255), -1, 8); //绘制最小外接矩形的中心点
cv::Point2f rect[4];
minRect.at(minRect.size() - 1).points(rect); //把最小外接矩形四个端点复制给rect数组
for (int j = 0; j < 4; j++) {
cv::line(visual_bR, rect[j], rect[(j + 1) % 4], cv::Scalar(0, 0, 255), 1, 8); //绘制最小外接矩形每条边
}
}
//if (boundRect.at(boundRect.size() - 1).height < src.rows / 5) continue;//轮廓是长度比图像的1/5短则直接过掉
if (boundRect.size() > 0) {
cv::Rect curBR = boundRect.at(boundRect.size() - 1);
cv::RotatedRect curMR = minRect.at(minRect.size() - 1);
double whRatio = curBR.width*1.0 / curBR.height;//宽高比
double longMR = curMR.size.width;
double shortMR = curMR.size.height;
longMR = curMR.size.width > curMR.size.height ? curMR.size.width : curMR.size.height;
shortMR = curMR.size.width < curMR.size.height ? curMR.size.width : curMR.size.height;
double wh_MR_Ratio = longMR * 1.0 / shortMR;//非垂直的外接矩形框的长边短边比
int area = cv::contourArea(curContours);
double curS_tect = longMR * shortMR;//非垂直最小外接矩形面积
double aRetio = area / curS_tect;//轮廓本身与非垂直最小外接矩形的面积比值
if (shortMR <= 10) {
cv::drawContours(resMat, contours, count, cv::Scalar(0, 0, 0), -1, CV_AA, hierarchy);
cv::drawContours(resMat, contours, count, cv::Scalar(0, 0, 0), 2, CV_AA, hierarchy);
continue;
}
if (curBR.x == 0 ||
curBR.y == 0 ||
curBR.x + curBR.width >= thresholdMat.cols ||
curBR.y + curBR.height >= thresholdMat.rows) {
cv::drawContours(resMat, contours, count, cv::Scalar(0, 0, 0), -1, CV_AA, hierarchy);
cv::drawContours(resMat, contours, count, cv::Scalar(0, 0, 0), 2, CV_AA, hierarchy);
continue;//挨边的删掉
}
if (debug) printf("area = %d, curS_rect=%lf, aRetio=%lf \n", area, curS_tect, aRetio);
if (aRetio >= 0.9) {
//continue;
}
if (debug) cout << "--- curBR_" << boundRect.size() - 1 << curBR << whRatio << "\t";
if (debug) cout << " \tMR.angle=" << curMR.angle << " \t, MR.center=" << curMR.center << " \t, MR.points=" << curMR.size << ", wh_MR_Ratio" << wh_MR_Ratio << endl;
//if (whRatio > 1) continue;//宽高比不满足要求的直接 continue
}
ENDcontour.push_back(curContours);
cv::drawContours(tmpMat, contours, count, cv::Scalar(255, 255, 255), -1, CV_AA, hierarchy);
}
if (debug) cv::namedWindow("visual_bR222", cv::NORMCONV_FILTER);
if (debug) cv::imshow("visual_bR222", visual_bR);
if (debug) cv::imshow("tmpMat222", tmpMat);
//tmpMat.copyTo(resMat);
return true;
} deleteSmallMat(thresholdMat, thresholdMat, 30, debug);63、获取轮廓点集
初始版:
std::vector<cv::Point> curContours = *k;
cv::Mat curMat = cv::Mat(thresholdMat.rows, thresholdMat.cols, CV_8UC1, cv::Scalar(0, 0, 0));
float peri = cv::arcLength(curContours, true);
cv::approxPolyDP(curContours, conPoly[count], 0.02 * peri, true);
cv::drawContours(curMat, contours, count, cv::Scalar(255, 255, 255), -1,cv::LINE_8, hierarchy);
if (debug)cv::namedWindow("curMat", cv::NORMCONV_FILTER);
if (debug) cv::imshow("curMat", curMat);
if (1) {
//找白的,白占比大于 才认为是小圆角
cv::Mat imgReadOriPv;//原图上轮廓的对应位置
imgGray.copyTo(imgReadOriPv, curMat);
if (debug) cv::imshow("imgReadOriPv", imgReadOriPv);
cv::threshold(imgMark, imgMark, 105, 255, cv::THRESH_BINARY);
cv::Mat open;
int tempk = 3;
cv::Mat imgDil;
cv::dilate(curMat, imgDil, cv::getStructuringElement(cv::MORPH_CROSS, cv::Size(tempk, tempk)));
if (debug)cv::namedWindow("dilate-WriteMat2", cv::NORMCONV_FILTER);
if (debug) cv::imshow("dilate-WriteMat2", imgDil);
//cv::erode(dil, open, cv::getStructuringElement(cv::MORPH_CROSS, cv::Size(tempk, tempk)));
imgDil.copyTo(open);
open = open ^ curMat;
//if (debug)cv::namedWindow("open-WriteMat2", cv::NORMCONV_FILTER);
//if (debug) cv::imshow("open-WriteMat2", open);
cv::threshold(open, open, 254, 255, cv::THRESH_BINARY);
if (debug)cv::namedWindow("imgConEdge-WriteMat3", cv::NORMCONV_FILTER);
if (debug) cv::imshow("imgConEdge-WriteMat3", open);//膨胀后减原轮廓只余下轮廓外圈,以获取边缘点集
cv::Point startPnt = curContours[0];//第一个点
for (int row = 0; row < open.rows; row++) {
for (int col = 0; col < open.cols; col++) {
cv::Point curp = cv::Point(col, row);
if (open.at<uchar>(curp) >= 205) {
startPnt = curp;
break;
}
}
}
//if (debug) cout << "----------------- open.size()=" << open.size() << ", startPnt" << startPnt << endl;
//if (debug) circle(open, startPnt, 2, cv::Scalar(0, 0, 0), cv::FILLED);
if (1) {//轮廓完整点集 //为了测试轮廓形态对比 先原图像素值判定0914cxl
vector<cv::Point> conPntLst;
cv::Mat imgFindPnt;
curMat.copyTo(imgFindPnt);
cv::Mat imgFound = cv::Mat::zeros(imgFindPnt.size(), CV_8UC1);
getPntLst_dfs_clockwise(imgFindPnt, imgFound, conPntLst, startPnt, 140);//以顺时针沿外边缘的顺序存入
//if (debug) cout << "-----------------conPntLst.size()=" << conPntLst.size() << endl;
if (debug) cv::imshow("imgFound", imgFound);
if (0) {//可视化
cv::Mat imgF111ound = cv::Mat::zeros(imgFindPnt.size(), CV_8UC1);
if (debug) circle(imgF111ound, startPnt, 2, cv::Scalar(255, 255, 255), cv::FILLED);
for (cv::Point curp : conPntLst) {
if (debug) cout << "*** startPnt=" << curp << endl;
imgFindPnt.at<uchar>(curp) = 0;
if (debug) cv::imshow("visual_conPntLst", imgFindPnt);
imgF111ound.at<uchar>(curp) = 255;
if (debug) cv::imshow("img--------------ound", imgF111ound);
//if (debug) cv::waitKey(51);
}
}
double avgPv = 0;
for (cv::Point curp : conPntLst) {
int pv = imgReadOriPv.at<uchar>(curp);
avgPv += pv;
}
avgPv /= conPntLst.size();
if (debug) cout << "-----------------avgPv=" << avgPv << endl;
if (avgPv <= 200) {//轮廓对应原图上不够白的小轮廓,认为不是小圆角
cv::drawContours(thresholdMat, contours, count, cv::Scalar(0, 0, 0), -1, CV_AA, hierarchy);
cv::drawContours(thresholdMat, contours, count, cv::Scalar(0, 0, 0), 3, CV_AA, hierarchy);
continue;
//不要了
}
}
if (0) {//轮廓外边缘点集
//cv::Mat newMat = cv::Mat(thresholdMat.rows, thresholdMat.cols, CV_8UC1, cv::Scalar(0, 0, 0));
//drawContours(newMat, conPoly, count, cv::Scalar(255, 255, 255), 1);
//drawContours(open, conPoly, count, cv::Scalar(255, 255, 255), 1);
vector<cv::Point> conPntLst;
cv::Mat imgFindPnt;
open.copyTo(imgFindPnt);
//newMat.copyTo(imgFindPnt);
cv::Mat imgFound = cv::Mat::zeros(imgFindPnt.size(), CV_8UC1);
getPntLst_dfs_clockwise(imgFindPnt, imgFound, conPntLst, startPnt, 140);//以顺时针沿外边缘的顺序存入
if (debug) cout << "-----------------conPntAllLst.size()=" << conPntLst.size() << endl;
if (debug) cv::imshow("imgFound", imgFound);
if (1) {//可视化
cv::Mat imgF111ound = cv::Mat::zeros(imgFindPnt.size(), CV_8UC1);
if (debug) circle(imgF111ound, startPnt, 1, cv::Scalar(255, 255, 255), cv::FILLED);
for (cv::Point curp : conPntLst) {
if (debug) cout << "*** startPnt=" << curp << endl;
imgFindPnt.at<uchar>(curp) = 0;
if (debug) cv::imshow("visual_conPntLst", imgFindPnt);
imgF111ound.at<uchar>(curp) = 255;
if (debug) cv::imshow("img--------------ound", imgF111ound);
if (debug) cv::waitKey(51);
}
}
if (1) {
std::vector<double> resList;
int res = getAngleChange(conPntLst, resList);
for (int i = 0; i < resList.size(); ++i) {
if (debug) std::cout << resList[i] / (2.0*PI) * 360 << " -> ";
}
std::vector<double> trend;
trend = get_trendList(resList, 1, debug);
resList = trend;
if (1) {
int smoothCnt = 2;
std::vector<double> newWLst = resList;
int curCnt = smoothCnt;
while (curCnt--) {
linearSmooth3(newWLst, newWLst, 1);
}
resList = newWLst;
}
if (1) {
if (debug) printf("disList.size()= %d \n", resList.size());
float mean, variance, standard_deviation;
get_meanCorrelationTest(resList, mean, variance, standard_deviation);
if (debug) printf("disList 均值: %f \n", mean); // 均值
if (debug) printf("disList 方差: %f \n", variance); // 方差
if (debug) printf("disList 标准差: %f \n\n", standard_deviation); // 标准差
}
if (debug) showLine(resList);
}
}//轮廓外边缘点集
}64、获取满足阈值的连通域点集(顺时针搜索存入)
64.1 【深搜版本】获取满足阈值的连通域点集(深搜,顺时针搜索存入)
/*
//以深搜的方式,顺时针方向获取轮廓外边缘点集
#include <stack>
cv::Mat& src, cv::Mat& matDst, 搜索结果可视化标识
vector<cv::Point> &conPntLst, 获取到的轮廓边缘点集
cv::Point2i startPnt, 起始种子点
int th,像素值大于该值才被认为是轮廓部分
*/
void getPntLst_dfs_clockwise(cv::Mat& src, cv::Mat& matDst, vector<cv::Point> &conPntLst, cv::Point2i startPnt, int th)
{
//cout << __FUNCTION__ << " conPntLst.size()=" << conPntLst.size() << ", startPnt" << startPnt << endl;
stack<cv::Point> ptStack;//种子点队列
//搜索方向顺序数据
int DIR[8][2] = { { 0, -1 }, { 1, -1 }, { 1, 0 }, { 1, 1 }, { 0, 1 }, { -1, 1 }, { -1, 0 }, { -1, -1 } };//从上往右顺时针搜
ptStack.push(startPnt);//起始种子点入栈
conPntLst.clear();
while (!ptStack.empty()) {
cv::Point curp = ptStack.top();
ptStack.pop();
conPntLst.push_back(curp);
//分别对八个方向上的点进行生长
for (int i = 0; i < 8; ++i) {
cv::Point tmpp;
tmpp.x = curp.x + DIR[i][0];
tmpp.y = curp.y + DIR[i][1];
//检查是否是边缘点
if (tmpp.x < 0 ||
tmpp.y < 0 ||
tmpp.x > (src.cols - 1) ||
tmpp.y > (src.rows - 1)) {
continue;
}
int nGrowLable = matDst.at<uchar>(tmpp.y, tmpp.x); //是否已搜过
if (nGrowLable == 0) {//未搜过
int nCurValue = src.at<uchar>(tmpp.y, tmpp.x);//是否属于轮廓
if (nCurValue >= th) {//属于轮廓
matDst.at<uchar>(tmpp.y, tmpp.x) = 255; //标记为已搜过
ptStack.push(tmpp);
}
}
}
}
}调用示例:
cv::Point startPnt = curContours[0];//起始第一个点
for (int row = 0; row < open.rows; row++) {
for (int col = 0; col < open.cols; col++) {
cv::Point curp = cv::Point(col, row);
if (open.at<uchar>(curp) >= 205) {
startPnt = curp;
break;
}
}
}
vector<cv::Point> conPntLst;
cv::Mat imgFindPnt;
open.copyTo(imgFindPnt);
//newMat.copyTo(imgFindPnt);
cv::Mat imgFound = cv::Mat::zeros(imgFindPnt.size(), CV_8UC1);
getPntLst_dfs_clockwise(imgFindPnt, imgFound, conPntLst, startPnt, 140);//以顺时针沿外边缘的顺序存入
if (debug) cout << "-----------------conPntAllLst.size()=" << conPntLst.size() << endl;
if (debug) cv::imshow("imgFound", imgFound);
if (1) {//可视化(点集及其存入顺序)
cv::Mat imgF111ound = cv::Mat::zeros(imgFindPnt.size(), CV_8UC1);
if (debug) circle(imgF111ound, startPnt, 2, cv::Scalar(255, 255, 255), cv::FILLED);
for (cv::Point curp : conPntLst) {
if (debug) cout << "*** startPnt=" << curp << endl;
imgFindPnt.at<uchar>(curp) = 0;
if (debug) cv::imshow("visual_conPntLst", imgFindPnt);
imgF111ound.at<uchar>(curp) = 255;
if (debug) cv::imshow("img--------------ound", imgF111ound);
if (debug) cv::waitKey(51);
}
}64.2 【广搜版本】获取满足阈值的连通域点集(广搜,顺时针搜索存入)
/*
//以广搜的方式,顺时针方向获取轮廓外边缘点集
#include <stack>
cv::Mat& src, cv::Mat& matDst, 搜索结果可视化标识
vector<cv::Point> &conPntLst, 获取到的轮廓边缘点集
cv::Point2i startPnt, 起始种子点
int th,像素值大于该值才被认为是轮廓部分
*/
void getPntLst_bfs_clockwise(cv::Mat& src, cv::Mat& matDst, vector<cv::Point> &conPntLst, cv::Point2i startPnt, int th)
{
//cout << __FUNCTION__ << " conPntLst.size()=" << conPntLst.size() << ", startPnt" << startPnt << endl;
queue<cv::Point> ptQueue;//种子点队列
//搜索方向顺序数据
int DIR[8][2] = { { 0, -1 }, { 1, -1 }, { 1, 0 }, { 1, 1 }, { 0, 1 }, { -1, 1 }, { -1, 0 }, { -1, -1 } };//从上往右顺时针搜
ptQueue.push(startPnt);//起始种子点入栈
conPntLst.clear();
while (!ptQueue.empty()) {
cv::Point curp = ptQueue.front();
ptQueue.pop();
conPntLst.push_back(curp);
//分别对八个方向上的点进行生长
for (int i = 0; i < 8; ++i) {
cv::Point tmpp;
tmpp.x = curp.x + DIR[i][0];
tmpp.y = curp.y + DIR[i][1];
//检查是否是边缘点
if (tmpp.x < 0 ||
tmpp.y < 0 ||
tmpp.x >(src.cols - 1) ||
tmpp.y >(src.rows - 1)) {
continue;
}
int nGrowLable = matDst.at<uchar>(tmpp.y, tmpp.x); //是否已搜过
if (nGrowLable == 0) {//未搜过
int nCurValue = src.at<uchar>(tmpp.y, tmpp.x);//是否属于轮廓
if (nCurValue >= th) {//属于轮廓
matDst.at<uchar>(tmpp.y, tmpp.x) = 255; //标记为已搜过
ptQueue.push(tmpp);
}
}
}
}
}调用示例:同深搜版本。
65、从轮廓中获取所需点集(轮廓外边缘点集/轮廓完整点集)
/*
//从轮廓中获取所需点集(轮廓外边缘点集/轮廓完整点集)
cv::Mat imgOriginal, 提供图像尺寸大小
std::vector<cv::Point> curContour, 依据轮廓
cv::Mat& matDst, 搜索结果可视化标识
vector<cv::Point> &conPntLst, 获取到的轮廓边缘点集(第一个点是图像最上的轮廓白点)
int mode, 模式:0为获取轮廓外边缘点集(以顺时针沿外边缘的顺序存入),1为获取轮廓完整点集
*/
void getPntLst_fromContour(cv::Mat imgOriginal, std::vector<cv::Point> curContour, cv::Mat& imgFound, vector<cv::Point> &conPntLst, int mode = 1, bool debug = false);/*
//从轮廓中获取所需点集(轮廓外边缘点集/轮廓完整点集)
cv::Mat imgOriginal, 提供图像尺寸大小
std::vector<cv::Point> curContour, 依据轮廓
cv::Mat& matDst, 搜索结果可视化标识
vector<cv::Point> &conPntLst, 获取到的轮廓边缘点集(第一个点是图像最上的轮廓白点)
int mode, 模式:0为获取轮廓外边缘点集(以顺时针沿外边缘的顺序存入),1为获取轮廓完整点集
*/
void getPntLst_fromContour(cv::Mat imgOriginal, std::vector<cv::Point> curContour, cv::Mat& imgFound, vector<cv::Point> &conPntLst, int mode, bool debug)
{
if (curContour.empty()) return;
imgFound = cv::Mat::zeros(imgOriginal.size(), CV_8UC1);
std::vector<cv::Point> curContours = curContour;
cv::Mat curMat = cv::Mat(imgOriginal.rows, imgOriginal.cols, CV_8UC1, cv::Scalar(0, 0, 0));//当前轮廓
std::vector<std::vector<cv::Point>> contours;
contours.push_back(curContours);
cv::drawContours(curMat, contours, 0, cv::Scalar(255, 255, 255), -1, cv::LINE_8);
if (debug)cv::namedWindow("curMat", cv::NORMCONV_FILTER);
if (debug) cv::imshow("curMat", curMat);
cv::Mat imgFindPnt;
curMat.copyTo(imgFindPnt);
if (mode == 0) {
cv::Mat imgConEdge;//轮廓外边缘
if (0) {
//实验证明用形态学梯度回导致轮廓边缘有两层点集
cv::morphologyEx(curMat, imgConEdge, cv::MORPH_GRADIENT, cv::getStructuringElement(cv::MORPH_CROSS, cv::Size(3, 3)));
}
else {
//为了使轮廓边缘只余一层点集,选择用膨胀后与原图取异或
cv::Mat imgDil;
int tempk = 3;
cv::dilate(curMat, imgDil, cv::getStructuringElement(cv::MORPH_CROSS, cv::Size(tempk, tempk)));
if (debug)cv::namedWindow("dilate-ConEdge", cv::NORMCONV_FILTER);
if (debug) cv::imshow("dilate-ConEdge", imgDil);
imgDil.copyTo(imgConEdge);
imgConEdge = imgConEdge ^ curMat;
cv::threshold(imgConEdge, imgConEdge, 254, 255, cv::THRESH_BINARY);
}
if (debug)cv::namedWindow("imgConEdge", cv::NORMCONV_FILTER);
if (debug) cv::imshow("imgConEdge", imgConEdge);//膨胀后减原轮廓只余下轮廓外圈,以获取边缘点集
imgConEdge.copyTo(imgFindPnt);
}
else if (mode == 1) {
curMat.copyTo(imgFindPnt);
}
cv::Point startPnt = curContours[0];//第一个点
for (int row = 0; row < imgFindPnt.rows; row++) {
for (int col = 0; col < imgFindPnt.cols; col++) {
cv::Point curp = cv::Point(col, row);
if (imgFindPnt.at<uchar>(curp) >= 205) {
startPnt = curp;
break;
}
}
}
//if (debug) cout << "----------------- imgFindPnt.size()=" << imgFindPnt.size() << ", startPnt" << startPnt << endl;
//if (debug) circle(open, startPnt, 2, cv::Scalar(0, 0, 0), cv::FILLED);
getPntLst_dfs_clockwise(imgFindPnt, imgFound, conPntLst, startPnt, 140);//以顺时针沿外边缘的顺序存入
//if (debug) cout << "-----------------conPntLst.size()=" << conPntLst.size() << endl;
if (debug) cv::imshow("imgFound", imgFound);
if (0) {//可视化(点集及其存入顺序)
cv::Mat imgF111ound = cv::Mat::zeros(imgFindPnt.size(), CV_8UC1);
if (debug) circle(imgF111ound, startPnt, 1, cv::Scalar(255, 255, 255), cv::FILLED);
for (cv::Point curp : conPntLst) {
if (debug) cout << "*** startPnt=" << curp << endl;
imgFindPnt.at<uchar>(curp) = 0;
if (debug) cv::imshow("visual_conPntLst", imgFindPnt);
imgF111ound.at<uchar>(curp) = 255;
if (debug) cv::imshow("img--------------ound", imgF111ound);
if (debug) cv::waitKey(51);
}
}
}调用示例:
//轮廓完整点集
vector<cv::Point> conPntLst;
cv::Mat imgFound;
getPntLst_fromContour(imgOriginal, curContours, imgFound, conPntLst, 1, debug);
//找白的,白占比大于 才认为是小圆角
cv::Mat imgReadOriPv;//原图上轮廓的对应位置
imgGray.copyTo(imgReadOriPv, curMat);
if (debug) cv::imshow("imgReadOriPv", imgReadOriPv);
double avgPv = 0;
for (cv::Point curp : conPntLst) {
int pv = imgReadOriPv.at<uchar>(curp);
avgPv += pv;
}
avgPv /= conPntLst.size();
if (debug) cout << "-----------------avgPv=" << avgPv << endl;
if (avgPv <= 200) {//轮廓对应原图上不够白的小轮廓,认为不是小圆角
cv::drawContours(thresholdMat, contours, count, cv::Scalar(0, 0, 0), -1, CV_AA, hierarchy);
cv::drawContours(thresholdMat, contours, count, cv::Scalar(0, 0, 0), 3, CV_AA, hierarchy);
continue;
//不要了
} //轮廓外边缘点集
vector<cv::Point> conPntLst;
cv::Mat imgFound;
getPntLst_fromContour(imgOriginal, curContours, imgFound, conPntLst, 0, debug);
if (1) {
std::vector<double> resList;
int res = getAngleChange(conPntLst, resList);
for (int i = 0; i < resList.size(); ++i) {
if (debug) std::cout << resList[i] / (2.0*PI) * 360 << " -> ";
}
std::vector<double> trend;
trend = get_trendList(resList, 1, debug);
resList = trend;
if (1) {
int smoothCnt = 2;
std::vector<double> newWLst = resList;
int curCnt = smoothCnt;
while (curCnt--) {
linearSmooth3(newWLst, newWLst, 1);
}
resList = newWLst;
}
if (1) {
if (debug) printf("disList.size()= %d \n", resList.size());
float mean, variance, standard_deviation;
get_meanCorrelationTest(resList, mean, variance, standard_deviation);
if (debug) printf("disList 均值: %f \n", mean); // 均值
if (debug) printf("disList 方差: %f \n", variance); // 方差
if (debug) printf("disList 标准差: %f \n\n", standard_deviation); // 标准差
}
if (debug) showLine(resList); static void showLine(std::vector<double>posList, bool debug = false);
void PlaneRec::showLine(std::vector<double> posList, bool debug)
{
if (posList.size() < 2) {
return;
}
int maxVar = 360 + 1;
int minVar = -360 - 1;
cv::Mat canva = cv::Mat::zeros(cv::Size(posList.size()*10 + 1, maxVar - minVar), CV_8UC3);
cv::Point startPos(0,(int)posList[0] / (2.0*PI) * 360 + maxVar);
for (int i = 1; i < posList.size(); ++i) {
double tmp = posList[i] / (2.0*PI) * 360 + maxVar;
cv::Point posEnd(i*10, (int)tmp);
//canva.at<cv::Vec3b>(posEnd) = cv::Vec3b(255, 255, 255);
cv::line(canva, startPos, posEnd, cv::Scalar(255,255,255), 3, 8);
startPos = posEnd;
}
if (debug) cv::namedWindow("showLine", cv::NORMCONV_FILTER);
if (debug) cv::imshow("showLine", canva);
}65【拓展】、从已画好的轮廓图中获取轮廓点集(完整点集/外圈边缘点集)
/*
//从已画好的轮廓图中获取轮廓点集
cv::Mat imgOriginal, 提供图像尺寸大小
cv::Mat imgContour, 已画好的轮廓图
vector<cv::Point> &conPntLst, 获取到的轮廓边缘点集(第一个点是图像最上的轮廓白点)
int mode, 模式:0为获取轮廓外边缘点集(以顺时针沿外边缘的顺序存入),1为获取轮廓完整点集
*/
void getPntLst_fromContourImg(cv::Mat imgOriginal, cv::Mat imgContour, vector<cv::Point> &conPntLst, int mode = 1, bool debug = false);void ImageProcessing::getPntLst_fromContourImg(cv::Mat imgOriginal, cv::Mat imgContour, vector<cv::Point>& conPntLst, int mode, bool debug)
{
if (imgContour.empty()) return;
cv::Mat curMat;
imgContour.copyTo(curMat);
if (debug)cv::namedWindow("imgContour", cv::NORMCONV_FILTER);
if (debug) cv::imshow("imgContour", curMat);
cv::Mat imgFindPnt;
curMat.copyTo(imgFindPnt);
if (mode == 0) {
cv::Mat imgConEdge;//轮廓外边缘
//为了使轮廓边缘只余一层点集,选择用原图减去腐蚀图
cv::Mat imgErode;
int tempk = 3;
cv::erode(curMat, imgErode, cv::getStructuringElement(cv::MORPH_CROSS, cv::Size(tempk, tempk)));
if (debug)cv::namedWindow("erode-ConEdge", cv::NORMCONV_FILTER);
if (debug) cv::imshow("erode-ConEdge", imgErode);
imgErode.copyTo(imgConEdge);
imgConEdge = curMat - imgConEdge;
cv::threshold(imgConEdge, imgConEdge, 254, 255, cv::THRESH_BINARY);//确保轮廓边缘图的边缘处是凝实的而不是虚的
if (debug)cv::namedWindow("imgConEdge", cv::NORMCONV_FILTER);
if (debug) cv::imshow("imgConEdge", imgConEdge);//膨胀后减原轮廓只余下轮廓外圈,以获取边缘点集
imgConEdge.copyTo(imgFindPnt);
}
else if (mode == 1) {
curMat.copyTo(imgFindPnt);
}
cv::Point startPnt = cv::Point(-1, -1);//第一个点
for (int row = 0; row < imgFindPnt.rows; row++) {
for (int col = 0; col < imgFindPnt.cols; col++) {
cv::Point curp = cv::Point(col, row);
if (imgFindPnt.at<uchar>(curp) >= 205) {
startPnt = curp;
break;
}
}
}
//if (debug) cout << "----------------- imgFindPnt.size()=" << imgFindPnt.size() << ", startPnt" << startPnt << endl;
if (startPnt == cv::Point(-1, -1)) return;
//if (debug) circle(open, startPnt, 2, cv::Scalar(0, 0, 0), cv::FILLED);
cv::Mat imgFound = cv::Mat::zeros(imgOriginal.size(), CV_8UC1);
getPntLst_dfs_clockwise(imgFindPnt, imgFound, conPntLst, startPnt, 140);//以顺时针沿外边缘的顺序存入
//if (debug) cout << "-----------------conPntLst.size()=" << conPntLst.size() << endl;
if (debug) cv::imshow("imgFound", imgFound);
if (0) {//可视化(点集及其存入顺序)
cv::Mat imgF111ound = cv::Mat::zeros(imgFindPnt.size(), CV_8UC1);
if (debug) circle(imgF111ound, startPnt, 1, cv::Scalar(255, 255, 255), cv::FILLED);
for (cv::Point curp : conPntLst) {
if (debug) cout << "*** startPnt=" << curp << endl;
imgFindPnt.at<uchar>(curp) = 0;
if (debug) cv::imshow("visual_conPntLst", imgFindPnt);
imgF111ound.at<uchar>(curp) = 255;
if (debug) cv::imshow("img--------------ound", imgF111ound);
if (debug) cv::waitKey(51);
}
}
}调用示例:
vector<cv::Point> conPntLst;
cv::Mat imgFound;
//getPntLst_fromContour(imgOriginal, curContours, imgFound, conPntLst, 1, debug);
cv::Mat imgContour = cv::Mat(imgOriginal.rows, imgOriginal.cols, CV_8UC1, cv::Scalar(0, 0, 0));//当前轮廓
cv::drawContours(imgContour, contours, count, cv::Scalar(255, 255, 255), -1, cv::LINE_8);
if (debug)cv::namedWindow("imgContour", cv::NORMCONV_FILTER);
if (debug) cv::imshow("imgContour", imgContour);
getPntLst_fromContourImg(imgOriginal, imgContour, conPntLst, 1, debug);
if (debug) std::cout << " conPntLst.size()=" << conPntLst.size() /*<< std::endl*/;
double avgPv = 0;
for (cv::Point curp : conPntLst) {
int pv = imgReadOriPv.at<uchar>(curp);
avgPv += pv;
}
avgPv /= conPntLst.size();
if (debug) cout << "-----------------avgPv=" << avgPv << endl;
if (avgPv < minContourPv) continue;66、删除轮廓(不再会误删被包围在中间的内圈小轮廓)
前提:
直接轮廓查找后,利用cv::drawContours()涂黑。
//cv::drawContours(resMat, contours, count, cv::Scalar(0, 0, 0), -1, CV_AA, hierarchy); //cv::drawContours(resMat, contours, count, cv::Scalar(0, 0, 0), 2, CV_AA, hierarchy);一旦出现:需要删除的轮廓中 完整包含着 不需要删除的小轮廓 在其内圈,
则会在删除的同时将小轮廓也一起误删。
为避免这种情况,则需按连通域来进行删除。操作如下:
1)获取待删除轮廓对应的连通域,即其完整轮廓点集。
2)然后一个点一个点地去进行涂黑删除。
即可。
如此则不会误删其包含在内部的小轮廓。
for (k = contours.begin(); k != contours.end(); ++k, count++) //删除小连通域的
{
std::vector<cv::Point> curContours = *k;
cv::Mat curMat = cv::Mat(imgOriginal.rows, imgOriginal.cols, CV_8UC1, cv::Scalar(0, 0, 0));//当前轮廓
cv::drawContours(curMat, contours, count, cv::Scalar(255, 255, 255), -1, cv::LINE_8);
vector<cv::Point> conPntAllLst;//轮廓完整点集
if (1) {//以便将连通域位置删除而不会误删大轮廓包含在内的小轮廓
cv::Mat imgFindPnt;
curMat.copyTo(imgFindPnt);
cv::Mat imgFound = cv::Mat::zeros(imgFindPnt.size(), CV_8UC1);
cv::Point startPnt = curContours[0];//第一个点
getPntLst_dfs_clockwise(imgFindPnt, imgFound, conPntAllLst, startPnt, 140);//以顺时针沿外边缘的顺序存入
//if (debug) cout << "-----------------conPntLst.size()=" << conPntLst.size() << endl;
if (debug) cv::imshow("imgFound", imgFound);
if (0) {//可视化
cv::Mat imgF111ound = cv::Mat::zeros(thresholdMat.size(), CV_8UC1);
for (cv::Point curp : conPntAllLst) {
if (debug) cout << "*** startPnt=" << curp << endl;
thresholdMat.at<uchar>(curp) = 0;
if (debug) cv::imshow("visual_conPntLst", thresholdMat);
imgF111ound.at<uchar>(curp) = 255;
if (debug) circle(imgF111ound, startPnt, 2, cv::Scalar(255, 255, 255), cv::FILLED);
if (debug) cv::imshow("img--------------ound", imgF111ound);
//if (debug) cv::waitKey(51);
}
}
}
//需要删除的轮廓,则轮廓对应位置涂黑
for (cv::Point curp : conPntAllLst) {
resMat.at<uchar>(curp) = 0;//轮廓对应位置涂黑
}
}拓展:改一下画轮廓的方式
if (0) {
cv::drawContours(tmpMat, contours, i, cv::Scalar(255, 255, 255), -1, CV_AA, hierarchy);
}
else {
//改一下画轮廓的方式
vector<cv::Point> conPntAllLst;//轮廓完整点集
if (1) {//以便将连通域位置删除而不会误删大轮廓包含在内的小轮廓
cv::Mat imgFindPnt;
thresholdMat.copyTo(imgFindPnt);
cv::Mat imgFound = cv::Mat::zeros(imgFindPnt.size(), CV_8UC1);
cv::Point startPnt = curContours[0];//第一个点
getPntLst_dfs_clockwise(imgFindPnt, imgFound, conPntAllLst, startPnt, 140);//以顺时针沿外边缘的顺序存入
//if (debug) cout << "-----------------conPntLst.size()=" << conPntLst.size() << endl;
if (debug) cv::imshow("imgFound", imgFound);
if (0) {//可视化
cv::Mat imgF111ound = cv::Mat::zeros(thresholdMat.size(), CV_8UC1);
for (cv::Point curp : conPntAllLst) {
if (debug) cout << "*** startPnt=" << curp << endl;
thresholdMat.at<uchar>(curp) = 0;
if (debug) cv::imshow("visual_conPntLst", thresholdMat);
imgF111ound.at<uchar>(curp) = 255;
if (debug) circle(imgF111ound, startPnt, 2, cv::Scalar(255, 255, 255), cv::FILLED);
if (debug) cv::imshow("img--------------ound", imgF111ound);
//if (debug) cv::waitKey(51);
}
}
}
for (cv::Point curp : conPntAllLst) tmpMat.at<uchar>(curp) = 255;//轮廓对应位置涂白
}67、图像或轮廓的Hu矩
什么叫图像或轮廓的空间矩、中心矩、归一化中心矩?并利用OpenCV的类Moments计算轮廓的这几个矩和质心位置-CSDN博客
图像或轮廓的Hu矩的定义、优缺点、适用范围,并利用OpenCV的函数HuMoments()和matchShapes()实现Hu矩的计算和轮廓匹配-CSDN博客
68、cv::grabCut()图像分割
原理讲解:16. 如何通过缝隙抠出前景 - GraphCut 和 GrabCut - 知乎 (zhihu.com)
代码示例:
OpenCV - C++实战(06) — Grabcut图像分割_opencv c++ grabcut对图片进行处理-CSDN博客
【从零学习OpenCV 4】分割图像——Grabcut图像分割 - 知乎 (zhihu.com)
GrabCut是Graph Cut的改进版,是迭代的Graph Cut。
OpenCV中的GrabCut算法是依据《"GrabCut" - Interactive Foreground Extraction using Iterated Graph Cuts》这篇文章来实现的。
该算法利用了图像中的纹理(颜色)信息和边界(反差)信息,只要少量的用户交互操作即可得到比较好的分割结果。
与Graph cut指定两个顶点不同,grabcut只需指定一个粗略的能将目标框住的边框就可以完成良好的分割。
其特点和创新点是:
- 迭代式的采用GraphCut算法进行前景背景的分离
- 用户只需要用方框或套索标出背景就可以对很多图像进行初步分割
- 对边缘采用Matting方法进行精细化的软分割
- 在用户交互上运行进行迭代式的修补
void grabCut( InputArray img, // 待分割图像,8bit,3通道 // 输入输出参数,保存处理后的结果,8bit单通道掩码(与img同rows cols),mask元素值只能为 GC_BGD, GC_FGD, GC_PR_BGD, GC_PR_FGD 之一 InputOutputArray mask, // 如果没有手动标记 GC_BGD或GC_FGD ,那么结果只会有 GC_PR_BGD或GC_PR_FGD Rect rect, // 当 mode=GC_INIT_WITH_RECT时使用,rect外部的为GC_BGD,rect内部的为GC_FGD InputOutputArray bgdModel, // 背景模型(内部使用) InputOutputArray fgdModel, //前景模型(内部使用) int iterCount, // 迭代次数,必须大于0 int mode = GC_EVAL // GC_INIT_WITH_RECT表示用矩形框初始化Grabcut,GC_INIT_WITH_MASK表示用掩码图像初始化Grabcut, GC_EVAL表示执行分割 );
- img:输入图像(CV_8U的三通道彩色图像)
- mask:得到掩码矩阵(既用于输入又用于输出),其值为以下四种
cv::GC_BGD == 0//表示明显是背景
cv::GC_FGD == 1//表示明显是前景或者对象的像素
cv::GC_PR_BGD == 2//表示可能是背景
cv::GC_PR_FGD == 3//表示可能是前景或者对象的像素
- rect:指定的包含目标对象的矩阵,即包含对象的ROI区域
(该参数仅在mode == GC_INIT_WITH_RECT时使用)
在ROI区域的外部会被标记为“明显的背景”区域
- bdgModel:背景模型的临时数组
如果为null,函数内部会自动创建一个bgdModel;
bgdModel必须是单通道浮点型(CV_32FC1)图像,且行数只能为1,列数只能为13*5
- fgdModel:前景模型的临时数组
如果为null,函数内部会自动创建一个fgdModel;
fgdModel必须是单通道浮点型(CV_32FC1)图像,且行数只能为1,列数只能为13*5;
(bgdModel , fgdModel可以在 cv::GC_INIT_WITH_MASK下使用,可以在以往迭代的基础上用它们保存的信息继续迭代)
- iterCount:指定迭代次数
- mode:分割模式标志,有三个值可用
cv::GC_INIT_WITH_RECT//用矩阵初始化grabCut(状态和掩码)
cv::GC_INIT_WITH_MASK//用掩码初始化grabCut
cv::GC_EVAL//执行分割
cv::Mat imgGrabCut;// 定义分割结果
cv::Mat bgModel = cv::Mat::zeros(1, 65, CV_64FC1);//前景
cv::Mat fgModel = cv::Mat::zeros(1, 65, CV_64FC1);//背景
cv::Mat mask = cv::Mat::zeros(imgOriginal.size(), CV_8UC1);
int tmpRange = 30;
cv::Rect gcRect(tmpRange, tmpRange, imgOriginal.cols - tmpRange, imgOriginal.rows - tmpRange); // 定义边框矩形
cv::grabCut(imgOriginal, mask, gcRect, bgModel, fgModel, 5, cv::GC_INIT_WITH_RECT);
//将分割出的前景绘制回来
for (int row = 0; row < mask.rows; row++) {
for (int col = 0; col < mask.cols; col++) {
int n = mask.at<uchar>(row, col);
//将明显是前景和可能是前景的区域都保留
if (n == 1 || n == 3) {
mask.at<uchar>(row, col) = 255;
}
//将明显是背景和可能是背景的区域都删除
else {
mask.at<uchar>(row, col) = 0;
}
}
}
bitwise_and(imgOriginal, imgOriginal, imgGrabCut, mask);
if (debug) cv::imshow("分割结果", imgGrabCut);69、cv::compare()图像比较
cv::compare() 主要用于两个图像之间进行逐像素的比较,并输出比较的结果。具体用法如下:
bool cv::compare(cv::InputArray src1, // 输入数组1
cv::InputArray src2, // 输入数组2
cv::OutputArray dst, // 输出数组
int cmpop // 比较操作子,见注释
- cmpop:比较操作子
cv::CMP_EQ src == src1
cv::CMP_GT src > src1cv::CMP_GE src >= src1
cv::CMP_LT src < src1
cv::CMP_LE src <= src1
cv::CMP_NE src != src1
70、sort 排序相关 拓展
70.1 二维/三维点集重排(按x坐标或y坐标)
工业视觉笔记 6
70.2 轮廓集合(按轮廓面积从小到大)
openCV笔记 61
70.3 直线集合重排序(按线段长度从长到短)
double distanced(cv::Point p1, cv::Point p2)
{
return sqrt((p1.x - p2.x)*(p1.x - p2.x) + (p1.y - p2.y)*(p1.y - p2.y));
}
//对直线集合长度从长到短排序
bool compareValue_lenOfLine(const cv::Vec4i & l1, const cv::Vec4i & l2)
{
cv::Vec4i ln = l1;
int len1 = distanced(cv::Point(ln[0], ln[1]), cv::Point(ln[2], ln[3]));
ln = l2;
int len2 = distanced(cv::Point(ln[0], ln[1]), cv::Point(ln[2], ln[3]));
return len1 > len2;
} std::vector<cv::Vec4i> lines;
//直线集合按长度排序
std::sort(lines.begin(), lines.end(), compareValue_lenOfLine);70.4 按vector中下标为3的元素值从小到大(vector[3]从小到大)
bool compare_vecVal3Idx(const vector<int>& a, const vector<int>& b) {
return a[3] < b[3];
} vector<vector<int>> rowData;
sort(rowData.begin(), rowData.end(), compare_vecVal3Idx);
for (int i = 0; i < rowData.size(); i++) {
vector<int> curColData = rowData[i];
if (debug) for (int curData : curColData) cout << curData << ", ";
if (debug) cout << endl;
}

71、图像旋转
void Image::rotate_img(const cv::Mat& srcImage, cv::Mat& destImage, double angle)
{
//cv::Point2f center(0, 0);//中心
//cv::Point2f center(srcImage.cols / 2, srcImage.rows / 2);
cv::Point2f center(srcImage.cols, srcImage.rows);
cv::Mat M = getRotationMatrix2D(center, angle, 1);//计算旋转的仿射变换矩阵
warpAffine(srcImage, destImage, M, cv::Size(srcImage.cols, srcImage.rows));//仿射变换
}调用示例:
cv::Mat rotated;
//根据斜率用原图旋转,旋转后激光是垂直的状态
image.rotate_img(denoising, rotated, angle);
if (debug) cv::imshow("denoising", denoising);//要做旋转的原图
if (debug) cv::imshow("rotated", rotated);
//cv::Mat erased;
//擦除后的图片转回来
image.rotate_img(rotated_with_erased, erased, -angle);
cv::threshold(rotated_with_erased, rotated_with_erased, 100, 255, CV_THRESH_BINARY);
if (debug) cv::imshow("erased", rotated_with_erased);




















 3499
3499

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








