高斯随机数发生器(verilog实现)
文章目录
一、理论部分
经查阅网络资料与文献,首先通过细胞自动机(cellular automata)获得均匀分布的随机变量,然后通过Box-Muller变换将均匀分布的随机变量变换为服从高斯分布的随机变量。
(一)细胞自动机
细胞自动机是一个细说起来十分复杂的概念,但是可以在我们的应用场景中可以得到简化。先放表达式
s
i
t
+
1
=
f
i
(
s
i
−
1
t
,
s
i
t
,
s
i
+
1
t
)
s_i^{t+1}=f_i(s_{i-1}^{t},s_{i}^{t},s_{i+1}^{t})
sit+1=fi(si−1t,sit,si+1t)
式中
s
i
t
+
1
s_i^{t+1}
sit+1表示在t+1时刻第i个细胞的状态,它取决于t时刻第i-1个、第i个、第i+1个细胞的状态为自变量的某一种函数映射关系(
f
i
f_i
fi)。
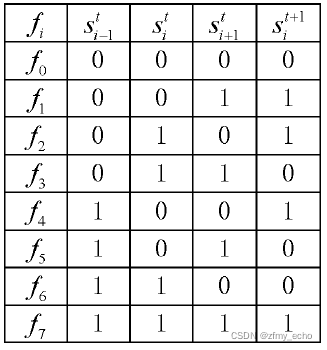
为了方便起见,将基本细胞自动机的邻域状态配置{ s i t − 1 s_i^{t-1} sit−1, s i t s_i^{t} sit, s i t + 1 s_i^{t+1} sit+1}的映射 { f 7 f_7 f7=(111), f 6 f_6 f6=(110),… f 1 f_1 f1=(001), f 0 f_0 f0=(000)} 的组合 I f I_f If= ∑ i = 0 7 f i 2 i \sum_{i=0}^{7}f_i2^i ∑i=07fi2i 称为基本细胞自动机的规则号。
例如{
f
7
f
6
f
5
f
4
f
3
f
2
f
1
f
0
=
10010110
f_7f_6f_5f_4f_3f_2f_1f_0=10010110
f7f6f5f4f3f2f1f0=10010110} 即
150
=
2
1
+
2
2
+
2
4
+
2
7
150=2^1+2^2+2^4+2^7
150=21+22+24+27 对应的规则号是150。对于规则150,上述表达式可以写为
s
i
t
+
1
=
s
i
−
1
t
+
s
i
t
+
s
i
+
1
t
s_i^{t+1}=s_{i-1}^{t}+s_{i}^{t}+s_{i+1}^{t}
sit+1=si−1t+sit+si+1t
如下图
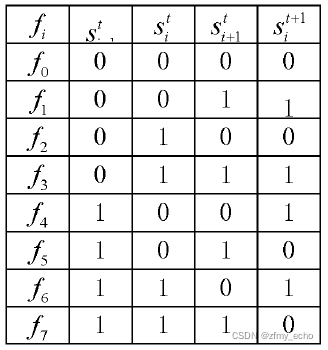
再如{
f
7
f
6
f
5
f
4
f
3
f
2
f
1
f
0
=
01011010
f_7f_6f_5f_4f_3f_2f_1f_0=01011010
f7f6f5f4f3f2f1f0=01011010} 即
90
=
2
1
+
2
3
+
2
4
+
2
6
90=2^1+2^3+2^4+2^6
90=21+23+24+26 对应的规则号是90。对于规则90,上述表达式可以写为
s
i
t
+
1
=
s
i
−
1
t
+
s
i
+
1
t
s_i^{t+1}=s_{i-1}^{t}+s_{i+1}^{t}
sit+1=si−1t+si+1t
如下图
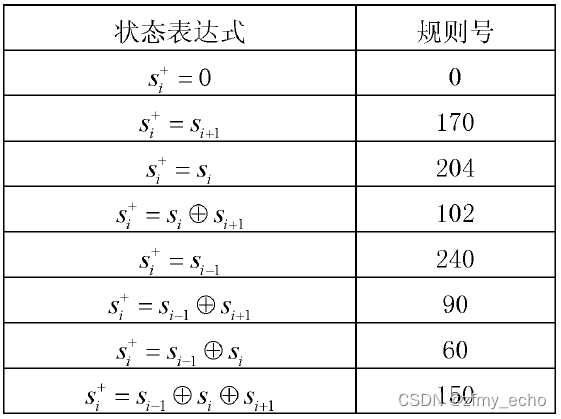
在这里贴上一些规则号与状态表达式的映射关系
(二)Box-Muller变换
Box-Muller变换是通过服从均匀分布 的随机变量,来构建服从高斯分布 的随机变量的一种方法。设 U1、U2为服从[0,1]上均匀分布的随机变量,若 X、**Y **满足
X
=
c
o
s
(
2
π
U
1
)
−
2
l
n
U
2
Y
=
s
i
n
(
2
π
U
1
)
−
2
l
n
U
2
X=cos(2\pi U_1 )\sqrt{-2lnU_2}\\ Y=sin(2\pi U_1 )\sqrt{-2lnU_2}
X=cos(2πU1)−2lnU2Y=sin(2πU1)−2lnU2
则 X、Y 服从均值为0,方差为1的高斯分布。
以下是数学推导,若以实现功能为目的可自行跳过。
假定 X、Y 服从均值为0,方差为1的高斯分布,且相互独立。令p(X)和p(Y)分别为其密度函数,则
p
(
X
)
=
1
2
π
e
−
X
2
2
p
(
Y
)
=
1
2
π
e
−
Y
2
2
p(X)= \frac{1}{\sqrt{2\pi}}e^{-\frac{X^2}{2}}\\ p(Y)= \frac{1}{\sqrt{2\pi}}e^{-\frac{Y^2}{2}}
p(X)=2π1e−2X2p(Y)=2π1e−2Y2
由于X、Y相互独立,因此它们的联合概率密度满足
p
(
X
,
Y
)
=
1
2
π
e
−
X
2
+
Y
2
2
p(X,Y)=\frac{1}{\sqrt{2\pi}}e^{-\frac{X^2+Y^2}{2}}
p(X,Y)=2π1e−2X2+Y2
将X、Y作坐标变换,使
X
=
R
cos
θ
Y
=
R
sin
θ
X=R\cos{\theta}\\ Y=R\sin{\theta}
X=RcosθY=Rsinθ
则
∫
−
∞
∞
∫
−
∞
∞
1
2
π
e
−
X
2
+
Y
2
2
d
X
d
Y
=
∫
−
∞
∞
∫
−
∞
∞
1
2
π
e
−
R
2
2
R
d
θ
d
R
=
1
\int_{-\infty}^{\infty}\int_{-\infty}^{\infty}\frac{1}{2\pi}e^{-\frac{X^2+Y^2}{2}}dXdY=\int_{-\infty}^{\infty}\int_{-\infty}^{\infty}\frac{1}{2\pi}e^{-\frac{R^2}{2}}Rd\theta dR=1
∫−∞∞∫−∞∞2π1e−2X2+Y2dXdY=∫−∞∞∫−∞∞2π1e−2R2RdθdR=1
由此可得R与θ的分布函数
P
R
(
R
≤
r
)
=
∫
0
2
π
∫
0
r
1
2
π
e
−
R
2
2
R
d
θ
d
R
=
1
−
e
−
r
2
2
P
θ
(
θ
≤
ϕ
)
=
∫
0
ϕ
∫
0
∞
1
2
π
e
−
R
2
2
R
d
θ
d
R
=
ϕ
2
π
P_R(R\leq r)=\int_{0}^{2\pi}\int_0^{r}\frac{1}{2\pi}e^{-\frac{R^2}{2}}Rd\theta dR=1-e^{-\frac{r^2}{2}}\\ P_\theta(\theta\leq \phi)=\int_{0}^{\phi}\int_0^{\infty}\frac{1}{2\pi}e^{-\frac{R^2}{2}}Rd\theta dR=\frac{\phi}{2\pi}
PR(R≤r)=∫02π∫0r2π1e−2R2RdθdR=1−e−2r2Pθ(θ≤ϕ)=∫0ϕ∫0∞2π1e−2R2RdθdR=2πϕ
显然,θ服从[0,2π]上的均匀分布。令
F
R
(
r
)
=
1
−
e
r
2
2
F_R(r)=1-e^{\frac{r^2}{2}}
FR(r)=1−e2r2
则其反函数
R
=
F
R
−
1
=
−
2
l
n
(
1
−
z
)
R=F^{-1}_{R}=\sqrt{-2ln(1-z)}
R=FR−1=−2ln(1−z)
当z服从[0,1]上均匀分布时,R的分布函数为
F
R
(
r
)
F_R(r)
FR(r) 。因此可以选择两个服从[0,1]上均匀分布的随机变量U1、U2,使得
U
1
=
θ
2
π
,
U
2
=
1
−
z
U_1 = \frac{\theta}{2\pi}, U_2 = 1-z
U1=2πθ,U2=1−z
即
θ
=
2
π
U
1
,
R
=
−
2
l
n
U
2
\theta = 2\pi U_1,R=\sqrt{-2lnU_2}
θ=2πU1,R=−2lnU2
将其带入
X
=
R
cos
θ
,
Y
=
R
sin
θ
X=R\cos{\theta}, Y=R\sin{\theta}
X=Rcosθ,Y=Rsinθ
得到最终表达式
X
=
c
o
s
(
2
π
U
1
)
−
2
l
n
U
2
Y
=
s
i
n
(
2
π
U
1
)
−
2
l
n
U
2
X=cos(2\pi U_1 )\sqrt{-2lnU_2}\\ Y=sin(2\pi U_1 )\sqrt{-2lnU_2}
X=cos(2πU1)−2lnU2Y=sin(2πU1)−2lnU2
二、实践部分
(一)一维细胞自动机的实现
对于单个细胞
always @(*)
begin
case({head,tail})
2'b10:self_next = ctrl ? self^right:right;
2'b01:self_next = ctrl ? left^self : left;
2'b00:self_next = ctrl ? left^self^right:left^right;
default:self_next=ctrl ? left^self^right:left^right;
endcase
end
head,tail用于判断该细胞是否处于队头或队尾。对头则无左侧细胞,队尾则无右侧细胞。
self_next 是该细胞下一时刻的值。
self、left、right 为本细胞、左侧细胞、右侧细胞的当前值。
ctrl用于判断规则号,这里只用到了规则150和规则90,分别以1和0表示。
当ctrl==1时,self_next =left ^ self ^ right,即规则150。
当ctrl==0时,self_next =left ^ right,即规则90。
对于N位的一维细胞自动机,只需要将上述单个细胞例化N次,并给出细胞的初始值和不同位置的规则号。
例如,对于32位自动细胞机,可以给出
parameter INIT_VEC = 32'b0100_1000_0001_0010_0100_1000_0001_0010,//初始值
parameter RULE_VEC = 32'b0000_1100_0100_0111_0000_1100_0000_0110,//规则号ctrl
通过使用generate语句简化例化过程。
generate
genvar i;
for(i=0; i<N; i=i+1) begin
if (i==0) begin
SingleCell#(.init(INIT_VEC[i]),.head(1'b0),.tail(1'b0))
inst_SingleCell(
.clk_i (clk_i),
.ctrl (RULE_VEC[i]),
.left (1'b0),
.right (uni_r[1]),
.self (uni_r[i]),
.out (uni_next[i])
);
end
......//省略部分内容减少篇幅
endgenerate
一般的语法流程不再赘述,只展示关键部分。
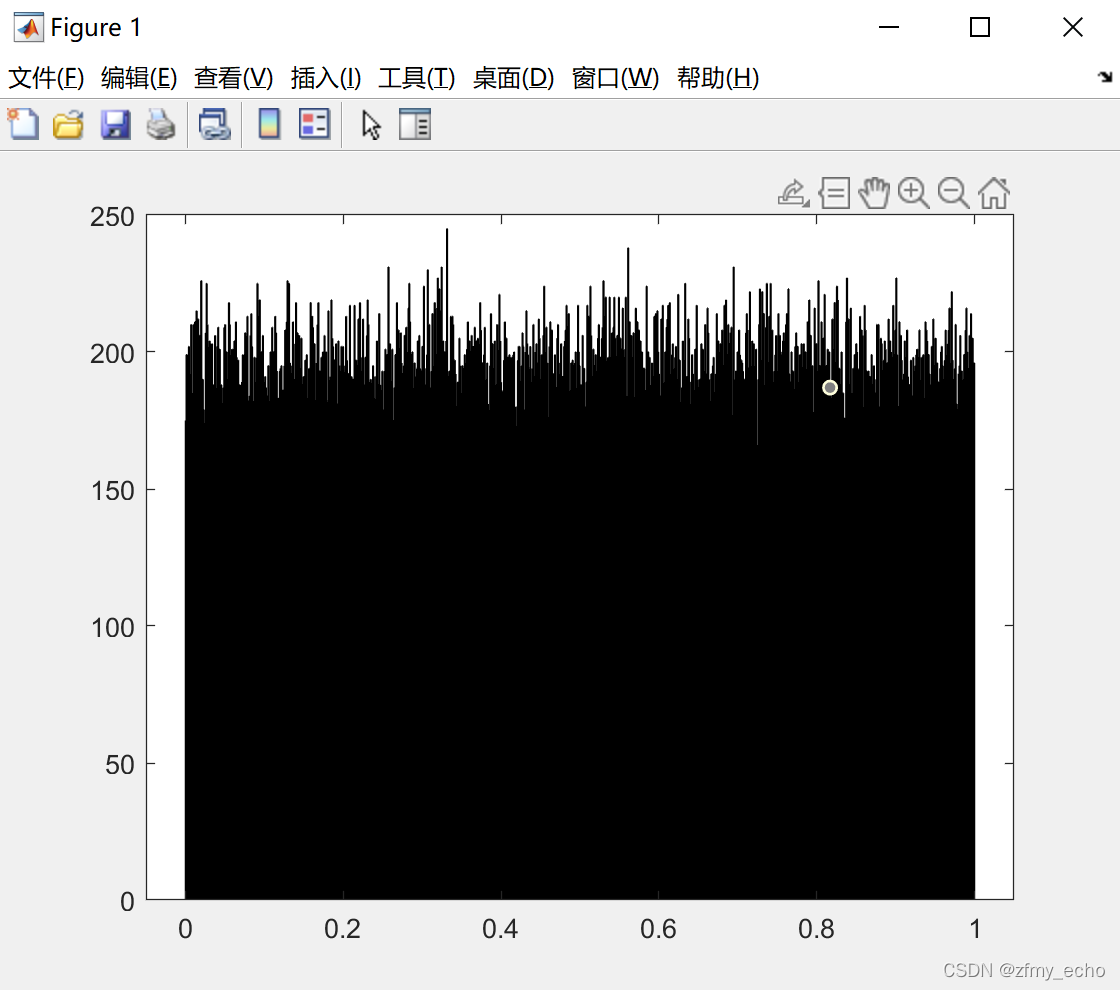
为了检验生成的数据是否为服从均匀分布的随机变量,我们在对本模块仿真时导出数据为txt文本,并在matlab上展示出来。
仿真代码
`timescale 1ns / 1ps
module tb_CellAutomata();
localparam INIT_VEC = 32'b0100_1000_0001_0010_0100_1000_0001_0010;
localparam RULE_VEC = 32'b0000_1100_0100_0111_0000_1100_0000_0110;
localparam N = 32;
localparam period = 10;
reg clk_i = 0;
reg rst_n_i = 1;
wire [N-1:0] uni_out;
CellularAutomata
#(
.INIT_VEC(INIT_VEC ),
.RULE_VEC(RULE_VEC ),
.N (N )
)
CellularAutomata_dut (
.clk_i (clk_i ),
.rst_n_i (rst_n_i ),
.uni_out (uni_out )
);
initial begin
begin
#(period*2) rst_n_i = 1'b0;
#(period*10) rst_n_i = 1'b1;
#(period*201_000);
$writememb("new_data.txt",mem);
$finish;
end
end
parameter M = 200_000;
reg [N-1:0] mem [M:1];
integer index = 1;
initial begin//采集数据
begin
#(period*100);
forever begin
#(period);
mem[index] = uni_out;
index = (index >= M) ? 1 : index + 1;
end
end
end
always
#(period/2) clk_i = !clk_i ;
endmodule
matlab部分
clear all;
clc;
fid = fopen("D:\MatlabProject\MatlabData\new_data.txt");
data = textscan(fid,"%b");
fclose(fid);
data = cell2mat(data);
data = double(data)/double(max(data));
h = histogram(data,1024,"Binlimits",[0,1]);
可以看出虽然有些参差,但大致符合[0,1]上的服从均匀分布的随机变量。
(二)Box-Muller变换的实现
X = c o s ( 2 π U 1 ) − 2 l n U 2 Y = s i n ( 2 π U 1 ) − 2 l n U 2 X=cos(2\pi U_1 )\sqrt{-2lnU_2}\\ Y=sin(2\pi U_1 )\sqrt{-2lnU_2} X=cos(2πU1)−2lnU2Y=sin(2πU1)−2lnU2
本次选择了简易的方法近似实现函数。大致思路是,首先用matlab生成 s i n x sinx sinx、 c o s x cosx cosx、 − 2 l n x \sqrt{-2lnx} −2lnx 函数自变量和因变量的映射,然后使IP核生成ROM并将其映射关系存放在ROM中,最后通过IP核生成乘法器将两部分相乘。
以 s i n sin sin函数为例,给出matlab代码
clc;clear; %储存单元地址线
depth=2^10; %存储单元;
widths=10; %数据宽度;
index = linspace(0,pi*2,depth);
sin_value = sin(index);
y1 = sin_value/max(sin_value);
sin_value = round(y1 * (depth/2 -1)); %扩大正弦幅度值
plot(sin_value);
number = [0:depth];
fid=fopen('fsin.coe','w+');
fprintf(fid,'memory_initialization_radix=10;\n');
fprintf(fid,'memory_initialization_vector=\n');
for i = 1 : depth - 1
fprintf(fid, '%d,\n', sin_value(i));
end
fprintf(fid, '%d;', sin_value(depth));
fclose(fid);
然后是IP核的使用。以Vivado2017.4为例。
第一步,点击IP Catalog,找到Block Memory Generator
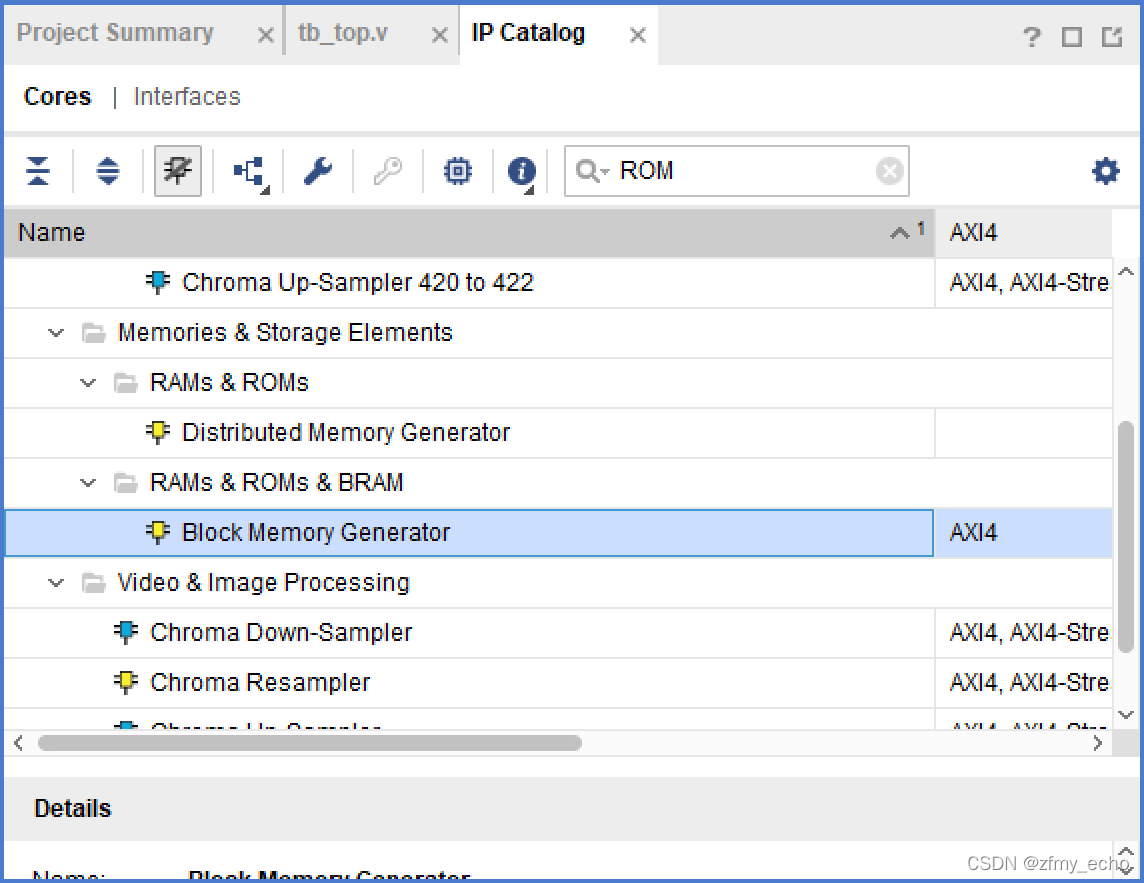
第二步,点击Block Memory Generator后进入Customize IP界面进行配置。
Basic界面中Memory Type使用 Single Port ROM即可。
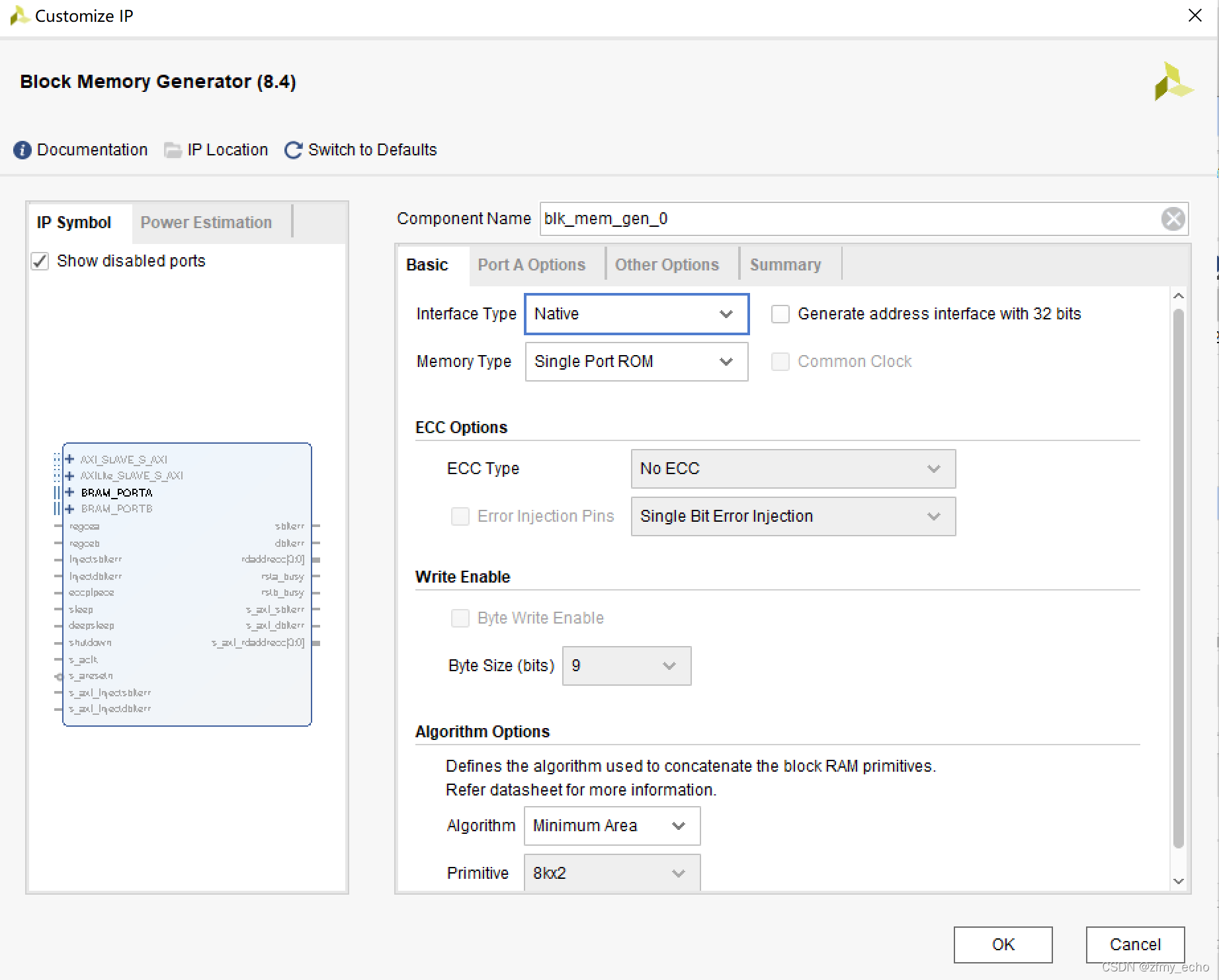
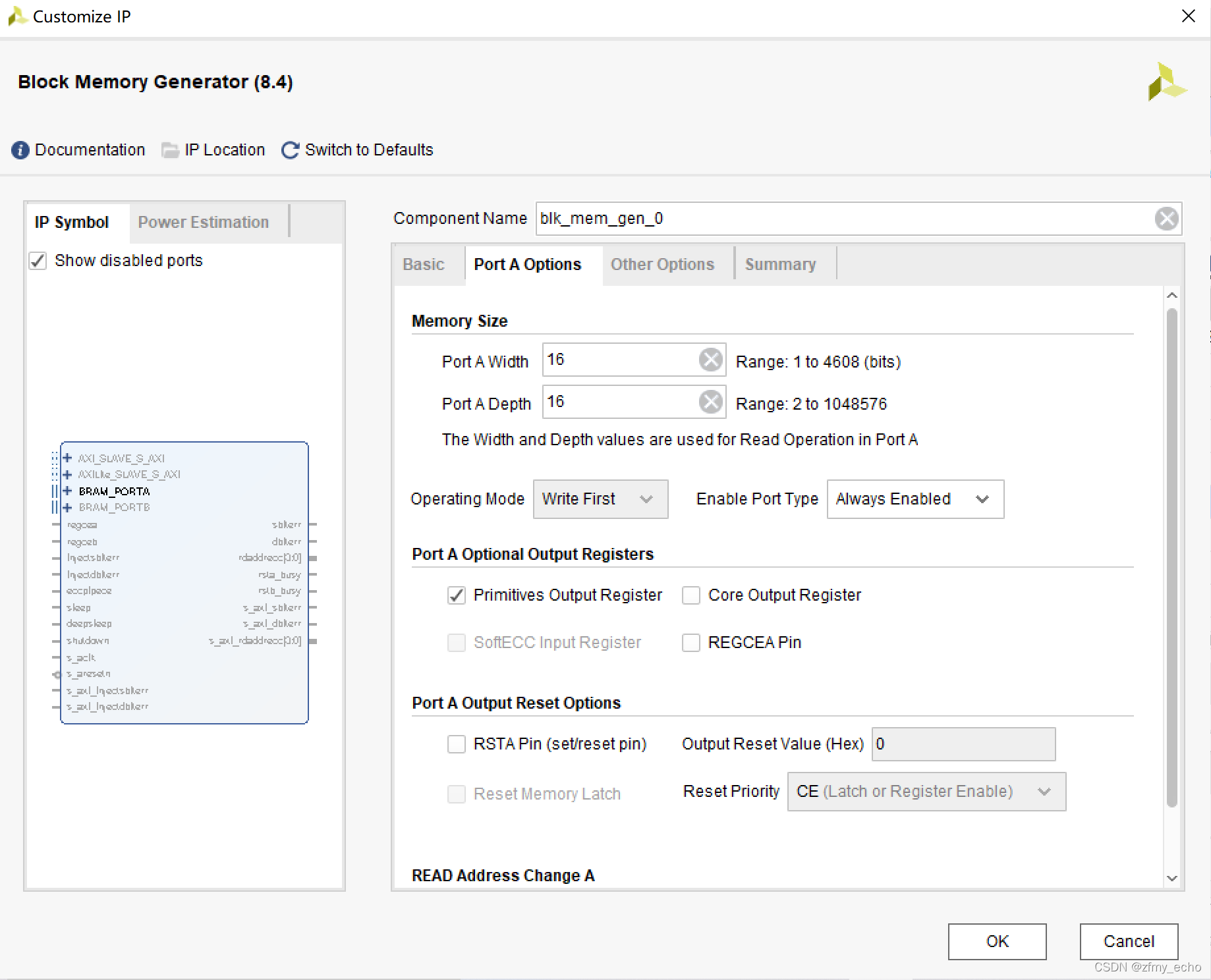
Port A Options中Port A Width决定了输出位宽,Port A Depth决定了输入地址的宽度。Enable Port Type 可以改成 Always Enabled,图个方便。
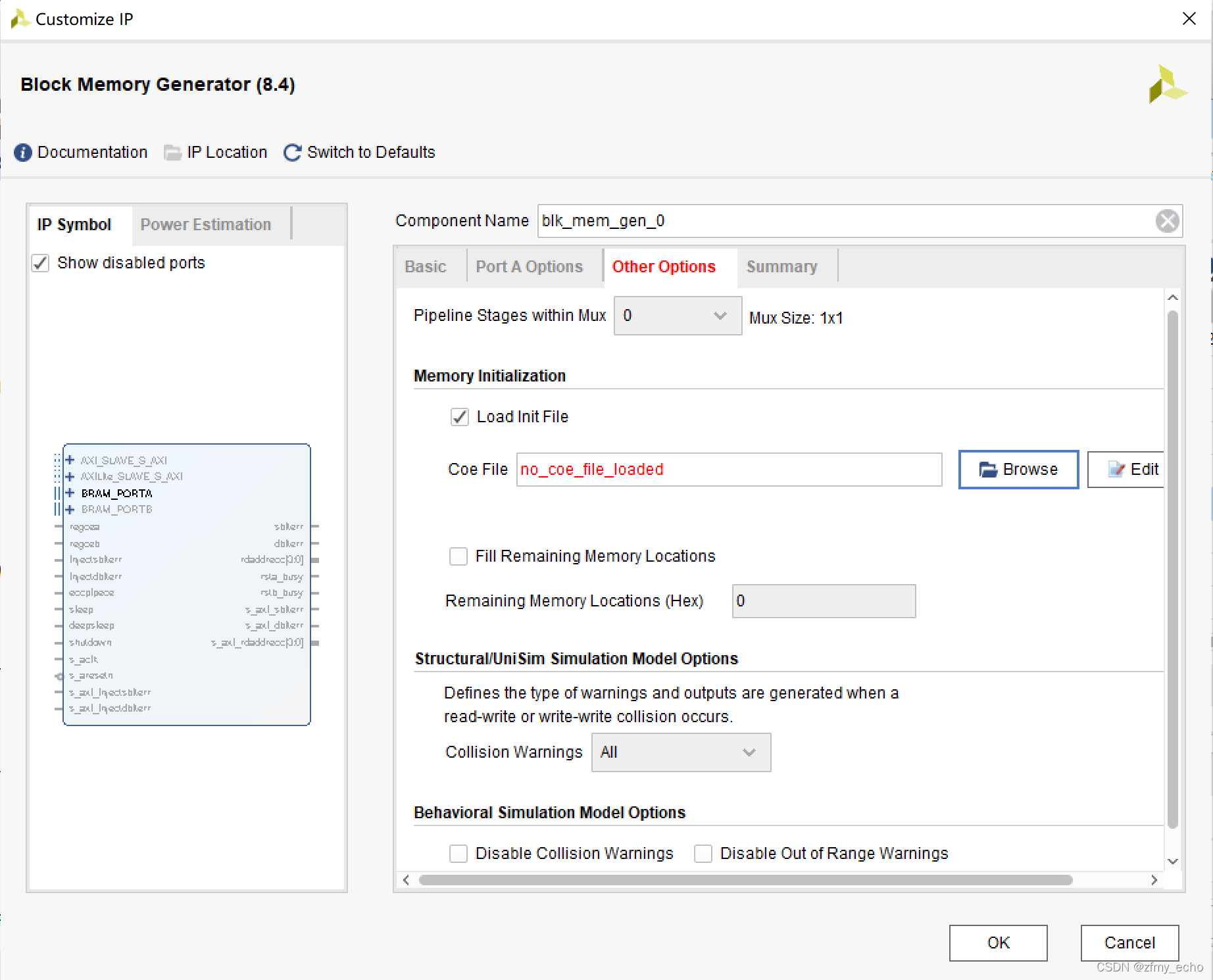
Other Options 界面中需要勾选 Load Init File 以将Matlab生成的.coe
文件导入。当文件格式、文件位置、文件中数据宽度不符合配置要求时都会标红。
Summary界面中可以看到一些相关信息,不再赘述。注意,当文件需要的IP核较多时,应当将IP核更改为条例清晰的命名以方便后续工作。生成完IP核后,使用时直接例化就ok了。乘法器IP核只需要找到 Multilplier核并配置即可,没有太大难度,不再演示。
按照有效果即可的原则(其实是电脑跑不动分析),我将原本计划的32位改为了20位输出。
module top_module(
input clk_i,
input reset,
output wire [19:0]gaus1,
output wire [19:0]gaus2
);
wire [31:0]uni_out;
wire [9:0]addr1 = uni_out[9:0];
wire [9:0]addr2 = uni_out[19:10];
wire [9:0]value_sin;
wire [9:0]value_cos;
wire [9:0]value_y;
CellularAutomata #(
.INIT_VEC(32'b0100_1000_0001_0010_0100_1000_0001_0010 ),
.RULE_VEC(32'b0000_1100_0100_0111_0000_1100_0000_0110 ),
.N (32 ))
CellularAutomata_dut (
.clk_i (clk_i ),
.reset (reset ),
.uni_out ( uni_out)
);
new
new_dut (
.clk_i (clk_i ),
.reset (reset ),
.addr1 (addr1 ),
.addr2 (addr2 ),
.value_sin (value_sin ),
.value_cos (value_cos ),
.value_y ( value_y)
);
Mult_Box_Muller inst1 (
.CLK(clk_i), // input wire CLK
.A(value_sin), // input wire [9 : 0] A
.B(value_y), // input wire [9 : 0] B
.P(gaus1) // output wire [19 : 0] P
);
Mult_Box_Muller inst2 (
.CLK(clk_i), // input wire CLK
.A(value_cos), // input wire [9 : 0] A
.B(value_y), // input wire [9 : 0] B
.P(gaus2) // output wire [19 : 0] P
);
endmodule
(三)结果的仿真与检验
第一次仿真我得到了20位的输出,想要用Matlab读入数据时,发现我只会用Matlab读入16、32位这种整位的有符号数据,没有读入20位有符号数据的方法(没详细学过Matlab,别骂了别骂了),然后本着能用就用的原则,我把20位数据后加了12个0,凑到了32位。
仿真文件
`timescale 1ns / 1ps
module tb_top();
localparam period = 10;
reg clk_i = 0;
reg reset = 0;
wire [19:0] gaus1;
wire [19:0] gaus2;
reg [31:0]buffer1;
reg [31:0]buffer2;
always@(*)begin
buffer1={gaus1,{12{1'b0}}};
buffer2={gaus2,{12{1'b0}}};
end
parameter M = 65536;
reg [31:0] mem1 [M:1];
reg [31:0] mem2 [M:1];
integer index = 1;
top_module top_module_dut (
.clk_i (clk_i ),
.reset (reset ),
.gaus1 (gaus1 ),
.gaus2 (gaus2 )
);
integer k;
initial begin
for(k=1;k<(M+1);k=k+1) begin mem1[k] = 31'd0;mem2[k] = 31'd0; end
end
initial begin
begin
#(period*2) reset = 1'b1;
#(period*10) reset = 1'b0;
#(period*(M+1000));
$writememb("gaus1.txt",mem1);
$writememb("gaus2.txt",mem2);
#(period*300);
$finish;
end
end
initial begin//采集数据
begin
#(period*12);
forever begin
#(period);
mem1 [index] = buffer1;
mem2 [index] = buffer2;
index = (index >= M) ? 1 : index + 1;
end
end
end
always
#(period/2) clk_i = ! clk_i ;
endmodule
写的比较稍微有亿点点乱。将生成的数据用Matlab展示一下。
clear all;
clc;
fid = fopen("D:\MatlabProject\MatlabData\gaus1.txt");
data = textscan(fid,"%bs32");
fclose(fid);
data = cell2mat(data);
disp(data);
data = double(data)/pow2(32);
h = histogram(data, 1024,'BinLimits',[-1,1]);
%[h,p]=lillietest(data);
%normplot(data);
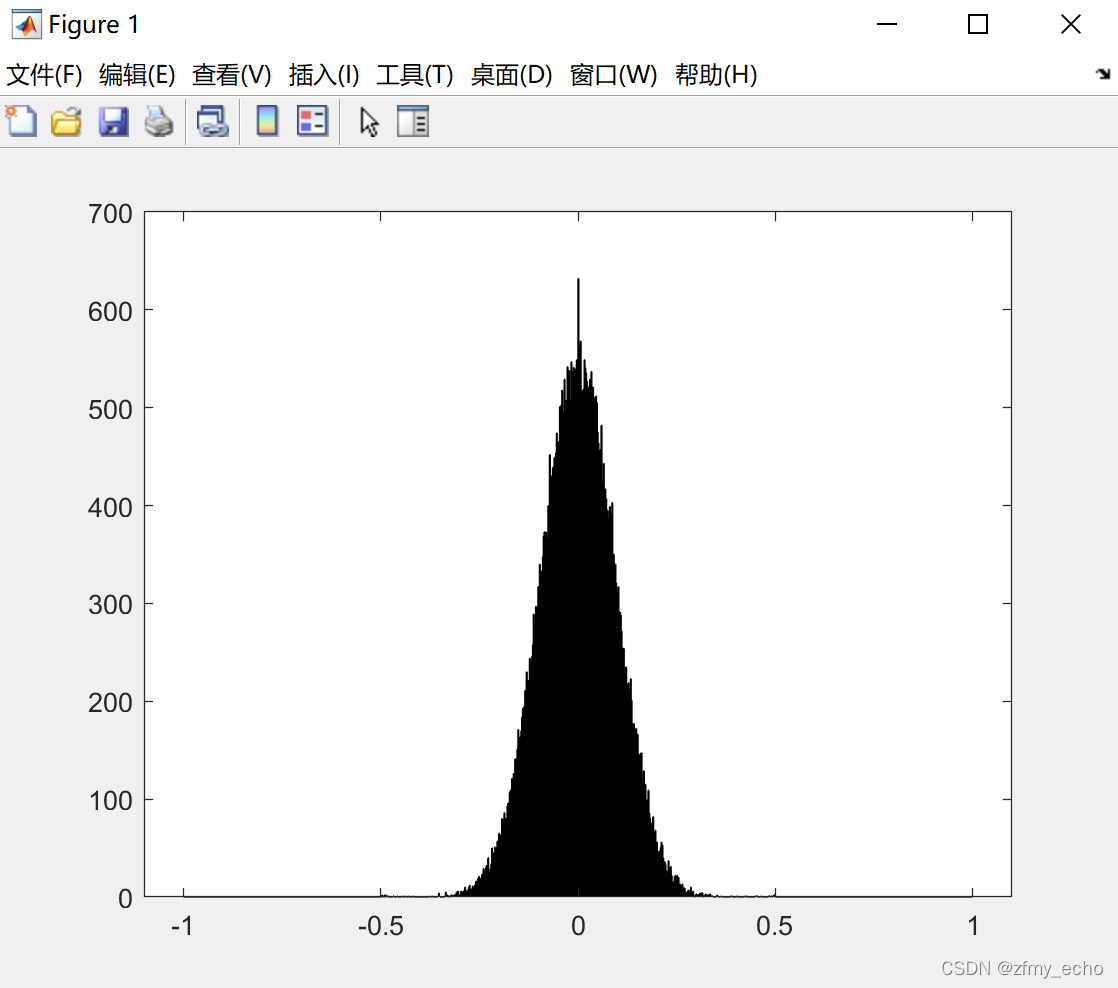
好像有点像高斯分布,为了验证,我查到了两种检测方法。没错,就是我注释了的那两句。
[h,p]=lillietest(data);

normplot(data);
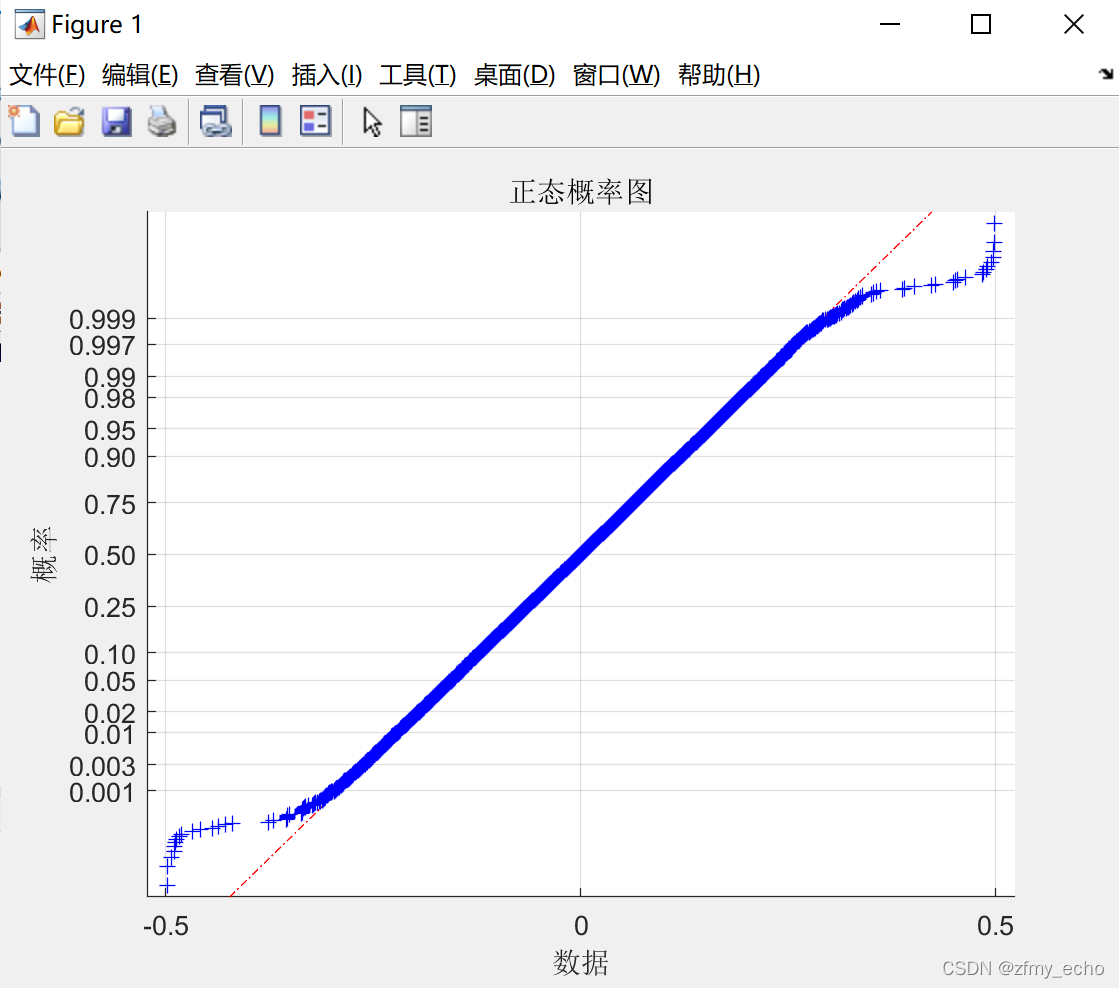
头尾较为稀疏且偏离较大,大概是因为原本数据只有20位数,强行加的12个0导致边缘稀疏。
三、一些感想
现在是2022年大年初四,立春,北京冬奥会开幕式。本来想写一下总结的,但是快到凌晨,所以不想了。新年快乐呀!





















 601
601











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








