一、VGG网络
VGG模型是2014年ILSVRC竞赛的第二名,第一名是GoogLeNet。但是VGG模型在多个迁移学习任务中的表现要优于googLeNet。VGG是在从Alexnet发展而来的网络,VGG共有十九层(16+3),一共有五段卷积每段卷积之后紧接着最大池化层(整个网络都使用了同样大小的3*3卷积核尺寸和2*2最大池化尺寸,网络结果简洁),三层全连接层最后接一个softmax,所有隐层的激活单元都采用ReLU函数。
VGG最大的贡献就是证明了卷积神经网络的深度增加和小卷积核的使用对网络的最终分类识别效果有很大的作用。
二、创新
因为VGG是在Alexnet网络基础上为了增加网络深度而进行改进,接下来介绍一下VGG与Alexnet区别:
1、整个网络采用小卷积核(3*3)取代Alexnet网络中的5*5甚至11*11的大卷积核。使用多个较小卷积核的卷积层代替一个卷积核较大的卷积层,一方面可以减少参数,另一方面作者认为相当于进行了更多的非线性映射,增加了网络的拟合表达能力。
【两个3x3的卷积堆叠获得的感受野大小,相当一个5x5的卷积;而3个3x3卷积的堆叠获取到的感受野相当于一个7x7的卷积。】
2、池化核也变小了,在VGG中的池化核是2x2stride为2,Alexnet池化核是3x3stride为2。
3、在VGG中去掉了LRN层,因为在训练中发现不能提高网络性能,增加了内存消耗和计算时间。
三、结构分析
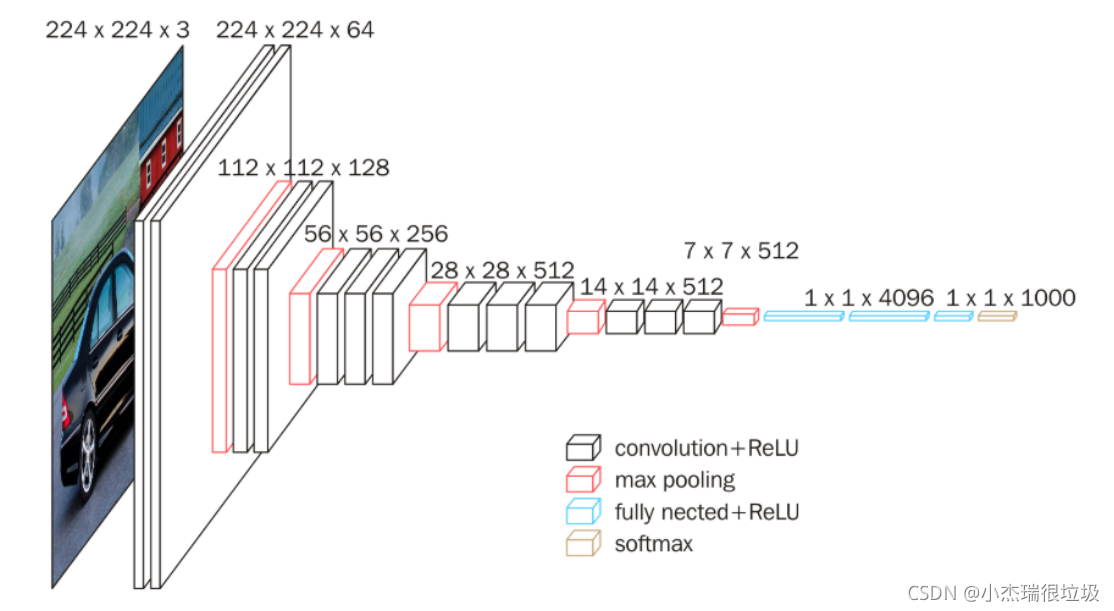
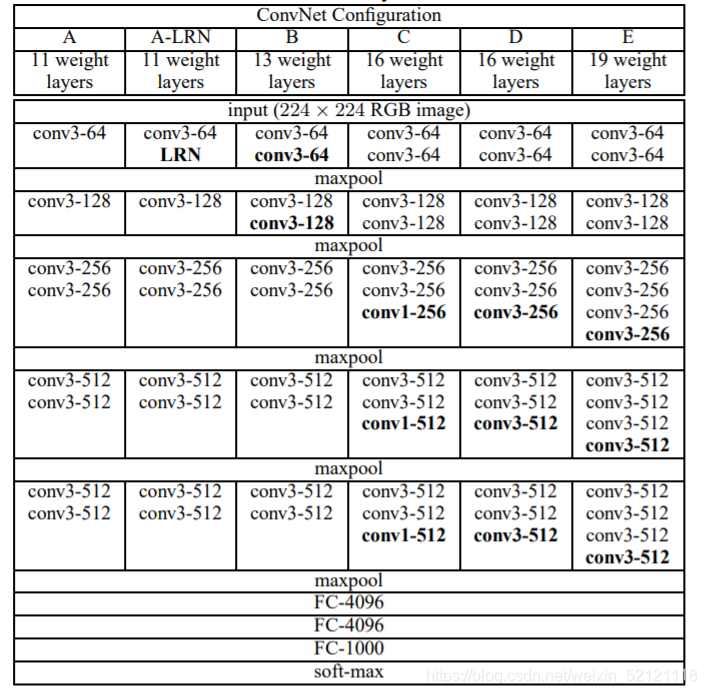
如图作者试验了六种网络结构,区别在于每个卷积层的子层数量不同,网络结构D就是著名的VGG16,网络结构E就是著名的VGG19。(conv3-64代表3*3的卷积核有64个通道)
接下来以VGG16网络结构为例:

(每进行3*3卷积时都先进行1个像素的padding)
四、代码实现
from torch import nn
class Vgg16Net(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(Vgg16Net, self).__init__()
# 第一层,2个卷积层和一个最大池化层
self.layer1 = nn.Sequential(
# 输入3通道,卷积核3*3,输出64通道(如32*32*3的样本图片,(32+2*1-3)/1+1=32,输出32*32*64)
nn.Conv2d(3, 64, 3, padding=1),
nn.BatchNorm2d(64),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
# 输入64通道,卷积核3*3,输出64通道(输入32*32*64,卷积3*3*64*64,输出32*32*64)
nn.Conv2d(64, 64, 3, padding=1),
nn.BatchNorm2d(64),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
# 输入32*32*64,输出16*16*64
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2)
)
# 第二层,2个卷积层和一个最大池化层
self.layer2 = nn.Sequential(
# 输入64通道,卷积核3*3,输出128通道(输入16*16*64,卷积3*3*64*128,输出16*16*128)
nn.Conv2d(64, 128, 3, padding=1),
nn.BatchNorm2d(128),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
# 输入128通道,卷积核3*3,输出128通道(输入16*16*128,卷积3*3*128*128,输出16*16*128)
nn.Conv2d(128, 128, 3, padding=1),
nn.BatchNorm2d(128),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
# 输入16*16*128,输出8*8*128
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2)
)
# 第三层,3个卷积层和一个最大池化层
self.layer3 = nn.Sequential(
# 输入128通道,卷积核3*3,输出256通道(输入8*8*128,卷积3*3*128*256,输出8*8*256)
nn.Conv2d(128, 256, 3, padding=1),
nn.BatchNorm2d(256),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
# 输入256通道,卷积核3*3,输出256通道(输入8*8*256,卷积3*3*256*256,输出8*8*256)
nn.Conv2d(256, 256, 3, padding=1),
nn.BatchNorm2d(256),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
# 输入256通道,卷积核3*3,输出256通道(输入8*8*256,卷积3*3*256*256,输出8*8*256)
nn.Conv2d(256, 256, 3, padding=1),
nn.BatchNorm2d(256),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
# 输入8*8*256,输出4*4*256
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2)
)
# 第四层,3个卷积层和1个最大池化层
self.layer4 = nn.Sequential(
# 输入256通道,卷积3*3,输出512通道(输入4*4*256,卷积3*3*256*512,输出4*4*512)
nn.Conv2d(256, 512, 3, padding=1),
nn.BatchNorm2d(512),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
# 输入512通道,卷积3*3,输出512通道(输入4*4*512,卷积3*3*512*512,输出4*4*512)
nn.Conv2d(512, 512, 3, padding=1),
nn.BatchNorm2d(512),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
# 输入512通道,卷积3*3,输出512通道(输入4*4*512,卷积3*3*512*512,输出4*4*512)
nn.Conv2d(512, 512, 3, padding=1),
nn.BatchNorm2d(512),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
# 输入4*4*512,输出2*2*512
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2)
)
# 第五层,3个卷积层和1个最大池化层
self.layer5 = nn.Sequential(
# 输入512通道,卷积3*3,输出512通道(输入2*2*512,卷积3*3*512*512,输出2*2*512)
nn.Conv2d(512, 512, 3, padding=1),
nn.BatchNorm2d(512),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
# 输入512通道,卷积3*3,输出512通道(输入2*2*512,卷积3*3*512*512,输出2*2*512)
nn.Conv2d(512, 512, 3, padding=1),
nn.BatchNorm2d(512),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
# 输入512通道,卷积3*3,输出512通道(输入2*2*512,卷积3*3*512*512,输出2*2*512)
nn.Conv2d(512, 512, 3, padding=1),
nn.BatchNorm2d(512),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
# 输入2*2*512,输出1*1*512
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2)
)
self.conv_layer = nn.Sequential(
self.layer1,
self.layer2,
self.layer3,
self.layer4,
self.layer5
)
self.fc = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(512, 4096),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Dropout(),
nn.Linear(4096, 4096),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Dropout(),
nn.Linear(4096, 1000)
)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.conv_layer(x)
x = x.view(-1, 512)
x = self.fc(x)
return x
参考:
https://blog.csdn.net/daydayup_668819/article/details/79932324
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_25737169
https://blog.csdn.net/dcrmg/article/details/79254654







 本文深入介绍了VGG网络,它是2014年ILSVRC竞赛的亚军,但其在迁移学习上的表现超过GoogLeNet。VGG通过使用小卷积核和深度增加来提升网络性能。与Alexnet相比,VGG网络使用3*3卷积核替代大卷积核,减少了参数数量并增强了非线性表达能力。文章还提供了VGG16的PyTorch代码实现,展示了一个典型的深度卷积网络结构。
本文深入介绍了VGG网络,它是2014年ILSVRC竞赛的亚军,但其在迁移学习上的表现超过GoogLeNet。VGG通过使用小卷积核和深度增加来提升网络性能。与Alexnet相比,VGG网络使用3*3卷积核替代大卷积核,减少了参数数量并增强了非线性表达能力。文章还提供了VGG16的PyTorch代码实现,展示了一个典型的深度卷积网络结构。
















 508
508

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








