Chapter 3 Mixed, Correlated, and Evolutionary Equilibrium
3.1 Mixed Strategy Nash Equilibrium
3.1.1 Definitions
The notion of mixed strategy Nash equilibrium is designed to model a steady state of a game in which the participants’ choices are not deterministic but are regulated by probabilistic rules.

mixed strategy Nash equilibrium
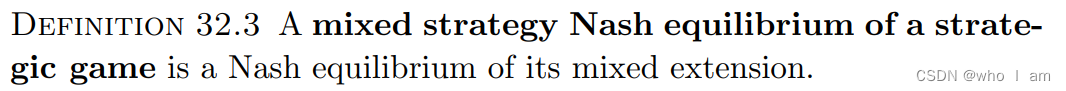
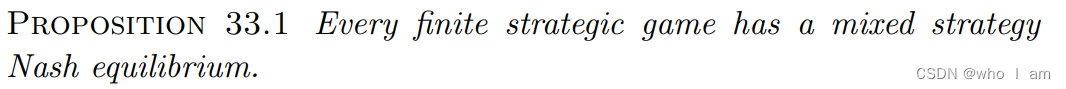
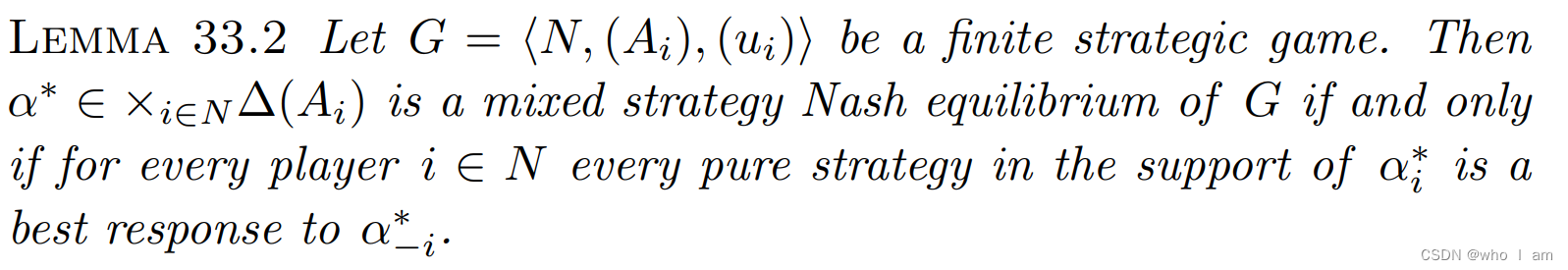
First,if an action ai in the support of a* is not a best response to α*−i,player i can increase his payoff by transferring probability from ai to an action that is a best response
Second, if there is a mixed strategy α'i that gives a higher expected payoff than does α*i in response to α*−i,at least one action in the support of α'i must give a higher payoff than some action in the support of α*i,so that not all actions in the support of α*i are best responses to α*−i .
every action in the support of any player’s equilibrium mixed strategy yields that player the same payoff
If the set of actions of some player is not finite:
α*is a mixed strategy Nash equilibrium of G if and only if (i) for every player i no action in Ai yields, given α*−i , a payoff to player i that exceeds his equilibrium payoff, and (ii) the set of actions that yield, given α*−i , a payoff less than his equilibrium payoff has α*i -measure zero.
3.1.2 Examples
BoS P34
3.2 Interpretations of Mixed Strategy Nash Equilibrium
3.2.1 Mixed Strategies as Objects of Choice
A mixed strategy entails a deliberate decision by a player to introduce randomness into his behavior.
The players’ motivation to introduce randomness into their behavior.:usually a player deliberately randomizes in order to influence the other players’ behavior.
The main problem with interpreting a player’s equilibrium mixed strategy as a deliberate choice is the fact that in a mixed strategy equilibrium each player is indifferent between all mixed strategies whose supports are subsets of her equilibrium strategy: her equilibrium strategy is only one of many strategies that yield her the same expected payoff, given the other players’ equilibrium behavior.
The mixed strategy equilibrium provides a good description of the steady state behavior of players who play the game repeatedly against randomly selected opponents, and it is reasonable for her to adopt the strategy that maximizes the payoff that she can guarantee.
3.2.2 Mixed Strategy Nash Equilibrium as a Steady State
Each player uses the frequencies with which actions were taken in the past to form his belief about the future behavior of the other players, and hence formulate his action.
A variant of this interpretation is based on an interpretation of an nplayer game as a model of the interaction of n large populations.
3.2.3 Mixed Strategies as Pure Strategies in an Extended Game
A mixed strategy Nash equilibrium, viewed in this way, is a description of a steady state of the system that reflects elements missing from the original description of the game.
There are three criticisms of this interpretation:
1.It is hard to accept that the deliberate behavior of a player depends on factors that have no effect on his payoff.
In a mixed strategy equilibrium each player is indifferent between all the actions in the support of her equilibrium strategy.
2.The behavior predicted by an equilibrium under this interpretation is very fragile.
For each structure of the random events there is a pattern of behavior that leads to the same equilibrium.
3.One needs to indicate the “real life” exogenous variables on which the players base their behavior.
To interpret mixed strategies as pure strategies in a larger game nicely captures the idea that the action chosen by a player may depend on factors outside the model.
3.2.4 Mixed Strategies as Pure Strategies in a Perturbed Game
Even if no player makes any effort to use his pure strategies with the required probabilities, the random variations in the payoff functions induce each player to choose his pure strategies with the right frequencies.
The equilibrium behavior of the other players is such that a player who chooses the uniquely optimal pure strategy for each realization of his payoff function chooses his actions with the frequencies required by his equilibrium mixed strategy.
3.2.5 Mixed Strategies as Beliefs
A mixed strategy Nash equilibrium is a profile β of beliefs, in which βi is the common belief of all the other players about player i’s actions.
An equilibrium is a steady state of the players’ beliefs, not their actions.These beliefs are required to satisfy two properties: they are common among all players and are consistent with the assumption that every player is an expected utility maximizer.
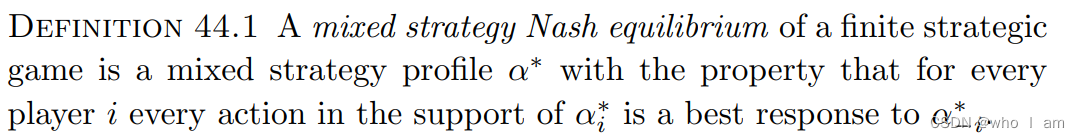
3.3 Correlated Equilibrium
The signals are not private and independent.
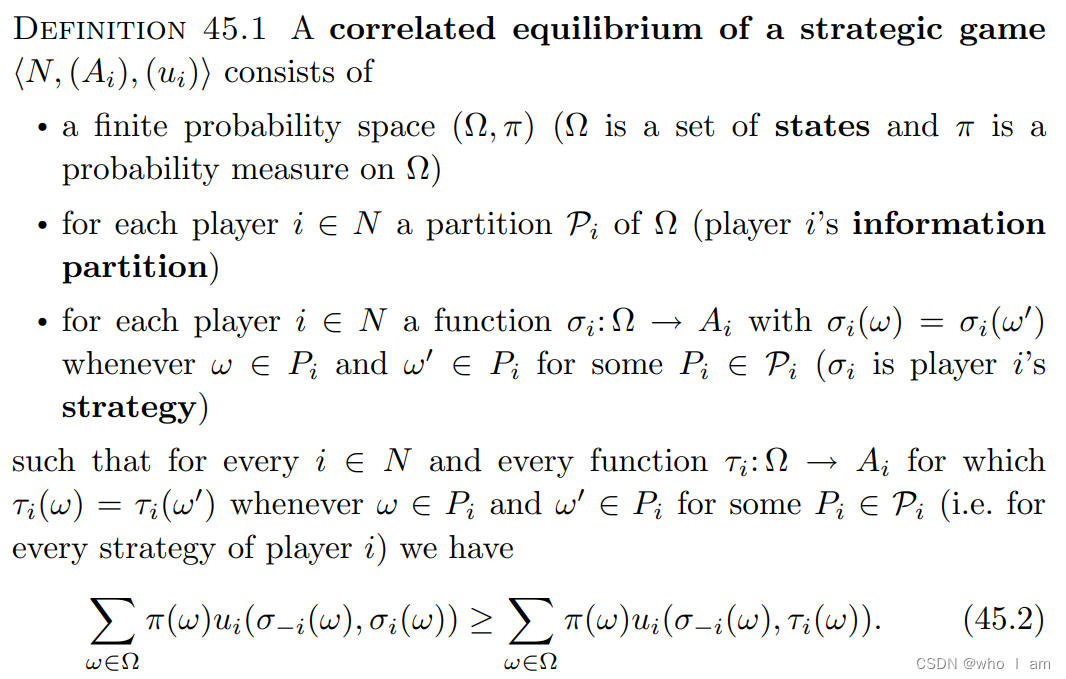 for every state ω that occurs with positive probability the action σi(ω) is optimal given the other players’ strategies and player i’s knowledge about ω.
for every state ω that occurs with positive probability the action σi(ω) is optimal given the other players’ strategies and player i’s knowledge about ω.
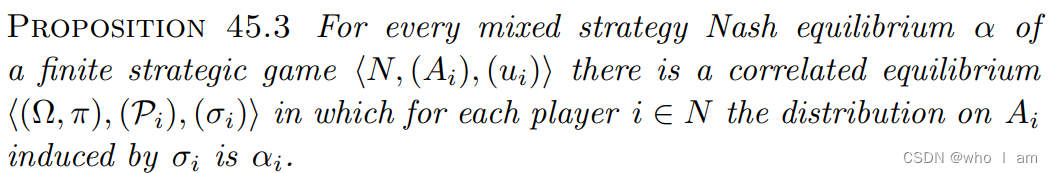
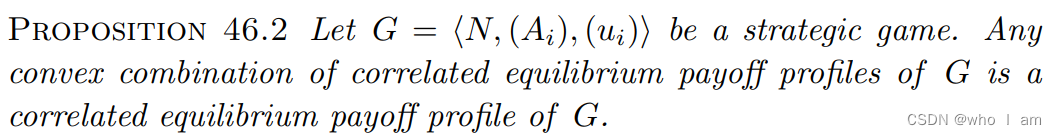

3.4 Evolutionary Equilibrium
The players’ actions are determined by the forces of evolution.
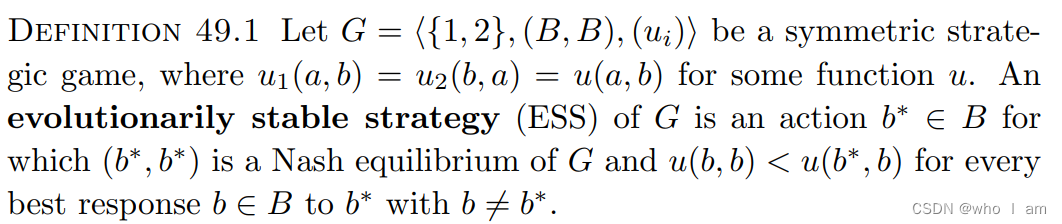






















 798
798

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








