重建损失(MSE和MAE):
-
均方误差(Mean Squared Error, MSE):

其中, 是源图像的像素值,
是融合图像的像素值,N 是图像的像素总数
作用:用于衡量源图像和融合图像之间的平均平方差异,强调较大的误差。目标是使融合图像尽可能接近源图像。常见用于图像的强度损失函数
平均绝对误差(Mean Absolute Error, MAE):

在CDDfuse改进为
作用:用于衡量源图像和融合图像之间的平均绝对差异,对异常值不敏感,能平滑地反映误差。
在上面的基础上,引入a-Huber算子

进一步改进,引入Frobenius范数

相比于使用2范数

结构相似性损失(Structural Similarity Loss, SSIM):
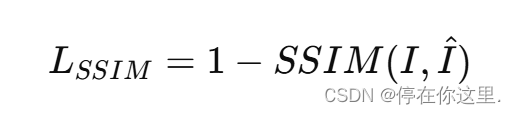
其中,𝑆𝑆𝐼𝑀(𝐼,𝐼^) 是源图像 和融合图像
之间的结构相似性指数。
作用:用于衡量两幅图像之间的结构相似性,比MSE和MAE更能反映图像的感知质量。它考虑了亮度、对比度和结构等因素,对人眼感知更友好。
全变分损失(Total Variation Loss, TV Loss):

其中, 是融合图像在位置 (𝑖,𝑗)的像素值。
作用:用于减少融合图像中的噪声和伪影,增强图像的平滑性。通过惩罚图像梯度的大变化,能够有效地减少图像中的不连续性和噪声。
边缘保持损失(Edge Preservation Loss):
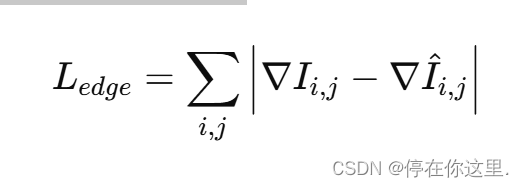
其中, 和
分别是源图像和融合图像在位置 (𝑖,𝑗) 处的梯度。
作用:用于保持源图像中的边缘信息,确保融合图像中的边缘与源图像相似。这有助于在融合过程中保留重要的细节和轮廓信息。
平滑损失函数:

𝑝是 或
中的像素位置索引,𝑅 表示 𝑝 的邻域集合,𝛼 是系数
作用:利用双边滤波器,以融合图像避免过度平滑
代码实现:未验证仅供参考,过段时间验证,哈哈
import torch
import torch.nn.functional as F
#在这个实现中:
#bilateral_filter 函数计算图像中每个像素与其邻域像素之间的双边滤波器权重。
#smoothness_loss 函数计算基于双边滤波器的平滑损失,通过遍历每个像素及其邻域像素的变化来实现。
def bilateral_filter(image, neighborhood_radius=1):
# image: Tensor of shape (B, C, H, W)
B, C, H, W = image.size()
smooth_loss = 0.0
for i in range(-neighborhood_radius, neighborhood_radius + 1):
for j in range(-neighborhood_radius, neighborhood_radius + 1):
if i == 0 and j == 0:
continue
shifted_image = torch.roll(image, shifts=(i, j), dims=(2, 3))
intensity_diff = torch.abs(image - shifted_image)
spatial_weight = torch.exp(-intensity_diff * alpha)
smooth_loss += torch.sum(spatial_weight * torch.abs(image - shifted_image))
return smooth_loss / (B * C * H * W)
def smoothness_loss(deformation_field, fused_image, alpha=0.5):
# deformation_field: Tensor of shape (B, 2, H, W) representing (dx, dy)
# fused_image: Tensor of shape (B, C, H, W)
B, C, H, W = fused_image.size()
# Compute the gradients of the deformation field
dx = deformation_field[:, 0, :, :]
dy = deformation_field[:, 1, :, :]
# Apply bilateral filter to the fused image
bf = bilateral_filter(fused_image, neighborhood_radius=1)
# Compute the smoothness loss
smooth_loss = 0.0
for p in range(H):
for q in range(W):
neighbors = [(p + dp, q + dq) for dp in range(-1, 2) for dq in range(-1, 2) if (dp, dq) != (0, 0)]
for (pn, qn) in neighbors:
if 0 <= pn < H and 0 <= qn < W:
smooth_loss += bf[p, q] * torch.abs(dx[p, q] - dx[pn, qn])
smooth_loss += bf[p, q] * torch.abs(dy[p, q] - dy[pn, qn])
return smooth_loss / (B * C * H * W)
# Example usage:
# fused_image: Tensor of shape (B, C, H, W)
# deformation_field: Tensor of shape (B, 2, H, W)
alpha = 0.5
loss = smoothness_loss(deformation_field, fused_image, alpha)
print("Smoothness loss:", loss.item())
分解损失函数:

公式解读:
分子部分:表示红外图像和可见光图像的高频成分之间的相关性。通过平方操作,强调了细节之间的强相关性,确保融合图像能够保留更多的细节信息。
分母部分:表示红外图像和可见光图像的低频成分之间的相关性。将基础成分的相关性置于分母,可以平衡细节与整体的相关性,确保在融合过程中不会过分丢失基础信息。
作用与意义
该损失函数用于优化图像的细节和基础成分之间的平衡。通过最大化细节成分的相关性并保持基础成分的相关性,模型可以在融合时保留细节特征,同时不丢失整体结构信息。这在红外和可见光图像融合中尤为重要,因为红外图像通常关注热信号(细节),而可见光图像则更注重视觉结构(基础)。



环境对比感知损失函数 :用来保留图像感知上的相似性,尤其适合图像重建和超分辨率任务。

import torch.nn.functional as F
def contextual_loss(pred, target, epsilon=1e-5):
pred_norm = F.normalize(pred, p=2, dim=1)
target_norm = F.normalize(target, p=2, dim=1)
sim_matrix = torch.matmul(pred_norm, target_norm.transpose(2, 3))
cx = torch.mean(torch.max(sim_matrix, dim=3).values)
return 1 - cx

























 2501
2501

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








