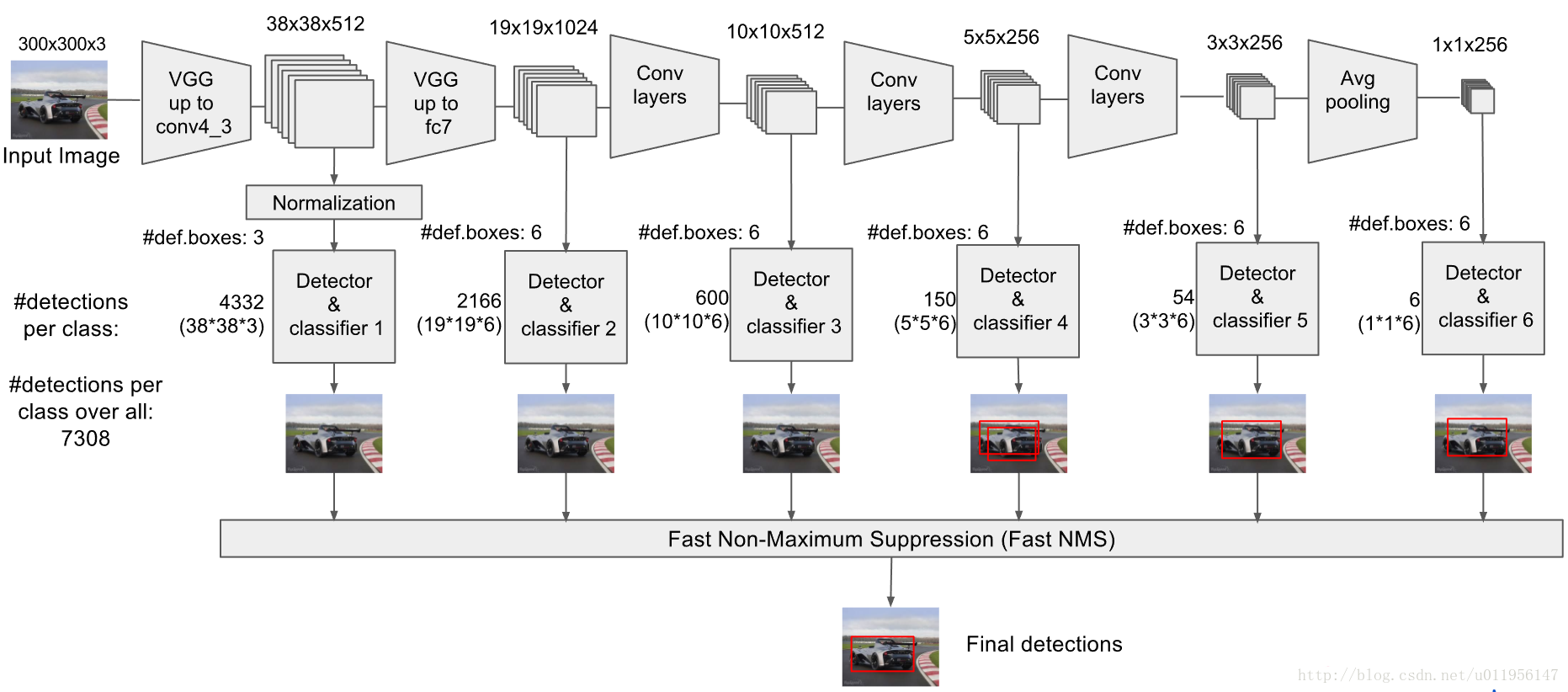
1:SSD更具体的框架如下:
2: Prior Box
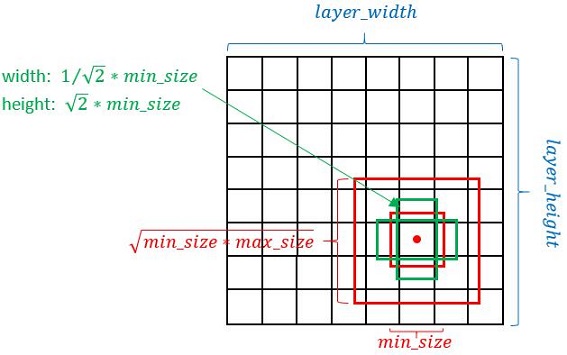
缩进在SSD中引入了Prior Box,实际上与anchor非常类似,就是一些目标的预选框,后续通过softmax分类+bounding box regression获得真实目标的位置。SSD按照如下规则生成prior box:
- 以feature map上每个点的中点为中心(offset=0.5),生成一些列同心的prior box(然后中心点的坐标会乘以step,相当于从feature map位置映射回原图位置)
- 正方形prior box最小边长为
,最大边长为:
- 每在prototxt设置一个aspect ratio,会生成2个长方形,长宽为:
和
图4 prior box
- 而每个feature map对应prior box的min_size和max_size由以下公式决定,公式中m是使用feature map的数量(SSD 300中m=6):
第一层feature map对应的min_size=S1,max_size=S2;第二层min_size=S2,max_size=S3;其他类推。在原文中,Smin=0.2,Smax=0.9,但是在SSD 300中prior box设置并不能和paper中上述公式对应:
| min_size | max_size | |
|---|---|---|
| conv4_3 |
30
|
60
|
| fc7 |
60
|
111
|
| conv6_2 |
111
|
162
|
| conv7_2 |
162
|
213
|
| conv8_2 |
213
|
264
|
| conv9_2 |
264
|
315
|
不过依然可以看出,SSD使用低层feature map检测小目标,使用高层feature map检测大目标,这也应该是SSD的突出贡献了。其中SSD 300在conv4_3生成prior box的conv4_3_norm_priorbox层prototxt定义如下:
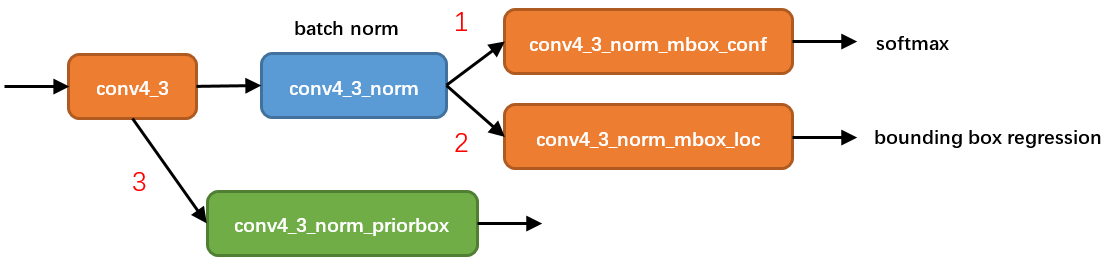
知道了priorbox如何产生,接下来分析prior box如何使用。这里以conv4_3为例进行分析。
图5
从图5可以看到,在conv4_3 feature map网络pipeline分为了3条线路:
- 经过一次batch norm+一次卷积后,生成了[1, num_class*num_priorbox, layer_height, layer_width]大小的feature用于softmax分类目标和非目标(其中num_class是目标类别,SSD 300中num_class = 21)
- 经过一次batch norm+一次卷积后,生成了[1, 4*num_priorbox, layer_height, layer_width]大小的feature用于bounding box regression(即每个点一组[dxmin,dymin,dxmax,dymax],参考Faster RCNN 2.5节)
- 生成了[1, 2, 4*num_priorbox]大小的prior box blob,其中2个channel分别存储prior box的4个点坐标和对应的4个variance
缩进后续通过softmax分类+bounding box regression即可从priox box中预测到目标,熟悉Faster RCNN的读者应该对上述过程应该并不陌生。其实pribox box的与Faster RCNN中的anchor非常类似,都是目标的预设框,没有本质的差异。区别是每个位置的prior box一般是4~6个,少于Faster RCNN默认的9个anchor;同时prior box是设置在不同尺度的feature maps上的,而且大小不同。
缩进还有一个细节就是上面prototxt中的4个variance,这实际上是一种bounding regression中的权重。在图4线路(2)中,网络输出[dxmin,dymin,dxmax,dymax],即对应下面代码中bbox;然后利用如下方法进行针对prior box的位置回归:
上述代码可以在SSD box_utils.cpp的void DecodeBBox()函数见到。












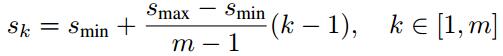














 5798
5798

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








